WEEK 2: Computer Aided Design
Create a raster, vector, 2D, and 3D representation of a possible final project, including rendering, animation, and simulation. Additionally, compress images and videos, and post a description along with your design files on your class page.
Raster
A raster is a type of digital image that is composed of a grid of pixels (tiny squares of color). Each pixel has a specific color and position, and together, these pixels form the complete image. Raster images are commonly used for photographs and detailed graphics where color and shading variations are essential. Popular types of raster files include JPEG, PNG and GIF images. However, because their pixel number is fixed, raster images can become distorted or blurry when resized to fill a bigger or smaller space. Raster files are also known as bitmap, raster files work best when you need to store and display high-quality photographs. Most photos come in the raster file format, whether they’re print or digital.
Vector Image
A vector image is a type of digital image that is created using mathematical equations to define lines, curves, shapes, and colors. Unlike raster images, which are made up of pixels, vector images are resolution-independent, meaning they can be scaled up or down infinitely without losing quality. Since vectors are based around formulas, a vector image can scale at high resolution to virtually unlimited sizes. If you have a business logo saved in a vector format, it can be resized to fit on a billboard with no problems or reduced to be printed on a ballpoint pen or business card. Many printing processes can only work with vector file input.
The most common type of editable vector file is the Adobe Illustrator (.ai) file. This file type can store an enormous amount of graphics information and is editable in Adobe Illustrator. Illustrator files can be easily converted to .pdf. Adobe Acrobat is the best tool for editing .pdf documents, which are designed for both printing and document transfer. Many printers utilise .pdf as a standard for printing. The work you do in an Illustrator file is non-destructive, so conversion to the .pdf format is usually a last step.

Comparison of 2D and 3D Software Tools
Here is a comparison of two different software tools used for 2D and 3D modeling:
1. AutoCAD
AutoCAD is a computer-aided design (CAD) software developed by Autodesk that enables users to create precise 2D and 3D drawings and models. It is widely used in architecture, engineering, construction, and manufacturing for designing buildings, mechanical parts, electrical schematics, and other technical drawings. AutoCAD offers powerful drafting tools, automation features, and customization options, making it a standard tool for professionals in design and engineering fields.
Features:
- 2D and 3D design capabilities
- Extensive library of templates and objects
- Advanced annotation and dimensioning tools
- Cloud storage integration
Advantages:
- Industry standard for drafting and design
- High precision and accuracy
- Supports a wide range of file formats
Applications: Used in architecture, mechanical engineering, electrical schematics, and urban planning.
2. SolidWorks
SolidWorks is a computer-aided design (CAD) and computer-aided engineering (CAE) software developed by Dassault Systèmes. It is widely used for 3D modeling, product design, and simulation in industries such as mechanical engineering, aerospace, and manufacturing. SolidWorks provides parametric and feature-based modeling, enabling users to create complex parts, assemblies, and detailed drawings efficiently. It also includes tools for finite element analysis (FEA), motion simulation, and rendering, making it a comprehensive solution for product development and prototyping.
Features:
- Parametric and direct modeling
- Assembly and simulation tools
- Motion analysis and rendering
Advantages:
- Intuitive user interface
- Efficient design validation and testing
- Excellent for mechanical design and manufacturing
Applications: Used in mechanical engineering, product design, and industrial manufacturing.
3. Fusion 360
Fusion 360 is a cloud-based 3D CAD, CAM, and CAE software developed by Autodesk. It integrates computer-aided design (CAD), manufacturing (CAM), and engineering (CAE) into a single platform, enabling product design, simulation, and machining in one workflow. Fusion 360 is widely used in mechanical engineering, industrial design, and product development due to its powerful modeling tools, collaboration features, and cloud-based accessibility. It supports parametric, direct, and freeform modeling, making it ideal for prototyping and manufacturing processes.
Features:
- Cloud-based collaboration
- Integrated CAD, CAM, and CAE tools
- Generative design and simulation
Advantages:
- Cost-effective compared to other high-end software
- Accessible from anywhere with cloud support
- Supports both professionals and hobbyists
Applications: Used in prototyping, CNC machining, and electronics design.
4. CATIA
CATIA (Computer-Aided Three-Dimensional Interactive Application) is a multi-platform CAD (Computer-Aided Design), CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing), CAE (Computer-Aided Engineering), and PLM (Product Lifecycle Management) software suite developed by Dassault Systèmes. It is widely used in aerospace, automotive, industrial machinery, and consumer goods industries for designing complex products, creating simulations, and managing product data. CATIA is known for its advanced surface modeling, parametric design capabilities, and seamless integration with engineering and manufacturing processes.
Features:
- Complex surface modeling
- Multidisciplinary design capabilities
- High-performance simulation tools
Advantages:
- Widely used in aerospace and automotive industries
- Highly scalable for large projects
- Advanced collaboration features
Applications: Used in aerospace, automotive, and industrial equipment design.
Video Tutorial
Video Compression and Screen Recording Tool
Tool Used : ScreenCapture.com
How this Tool Useful for Me?
2. This is an online tool that allows me to record my screen directly from the browser without the need for installing additional software.
3. I selected the recording area (entire screen of onshape window), disabled audio (enable if required), and then started the recording.
4. After finishing the recording, I downloaded the video. This platform automatically optimizes the video size for easier sharing without compromising too much on quality.
Benefits
ScreenCapture.com helped in creating professional-quality screen recordings without needing desktop software.
Image Compression
Tool Used : Optimizilla
How to Compress the image in Online Optimizilla software
2. I uploaded the required images to Optimizilla, a free online image compressor that supports both JPG and PNG formats.
3. The tool applied lossy compression to significantly reduce the file size.
4. After previewing the quality and comparing before and after sizes, I downloaded the compressed images for use in this document.
Benefits
Optimizilla ensured that image files were light and web-optimized, helping with faster loading and better performance.
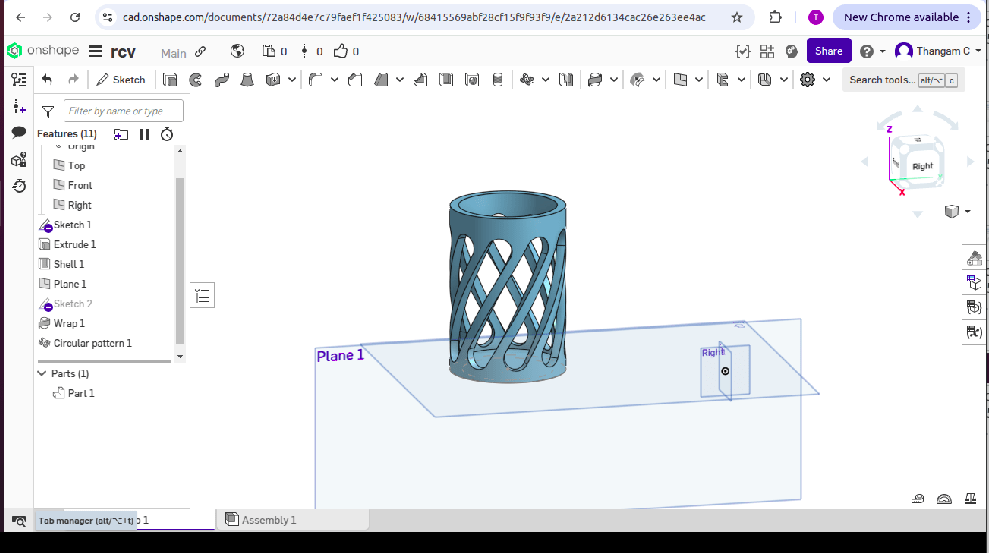
OnShape
Onshape’s CAD Drawings produce production-ready documentation for parts and assemblies which leverage industry standards for detailing and manufacturing. Only Onshape’s cloud-native platform provides the flexibility to share custom templates between users on any platform including iPad, iPhone and Android. Release manufacturing CAD blueprints using Onshape's built-in Release Management with automatic part numbering and customizable revision schemes.
Reference Link
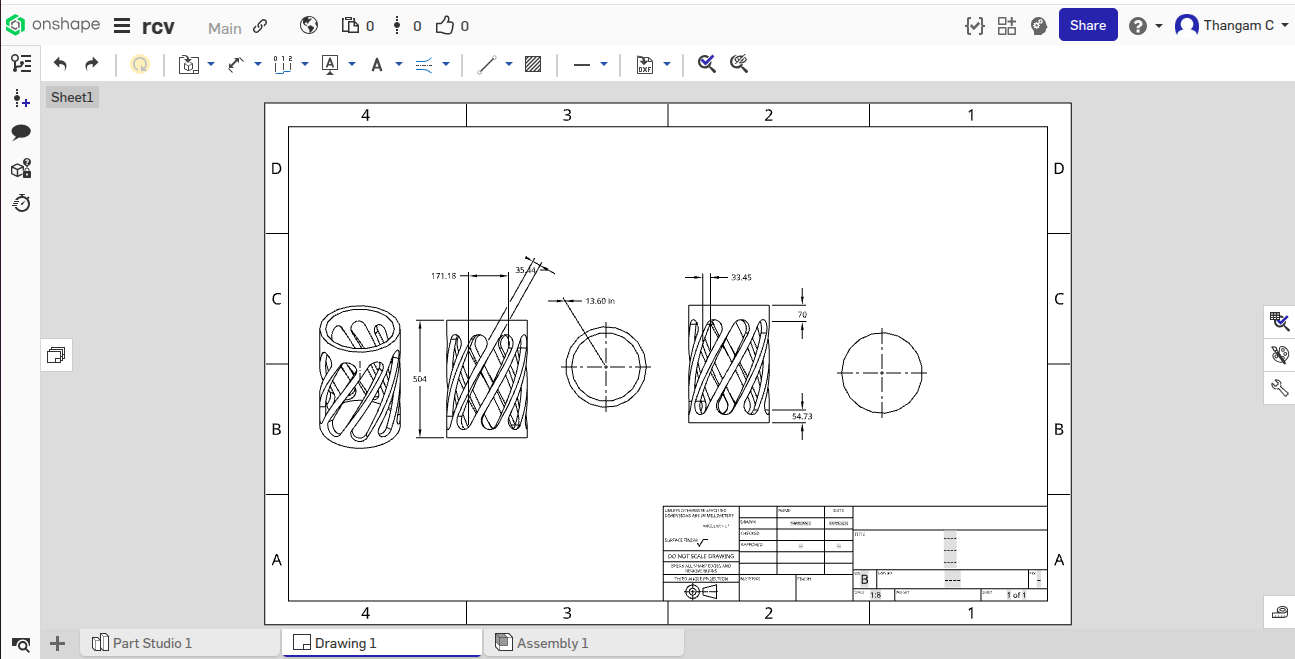
Onshape CAD DesignWith the help of R. Charanjit Vignesh, I have created the following image in Onshape. First, I would like to thank Charanjit Vignesh for helping me complete this assignment.

Creating 2D Sketch in oneshape software:
I have created 2D image using the following steps
2. Click on "Sketch" and select a plane (Top from Top, Right, Front).
3. Using tools like Circle, and line I have created a 2D image shape.
4. Exact measurements are set with ‘Dimension’ option and constraints to align elements.
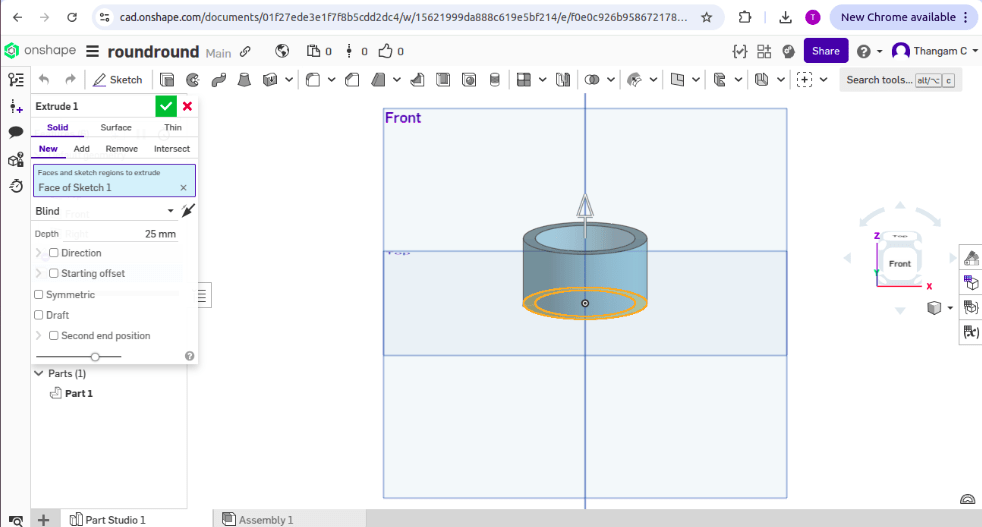
Creating 3D model
2. The sketch was rotated around an axis for cylindrical shape.
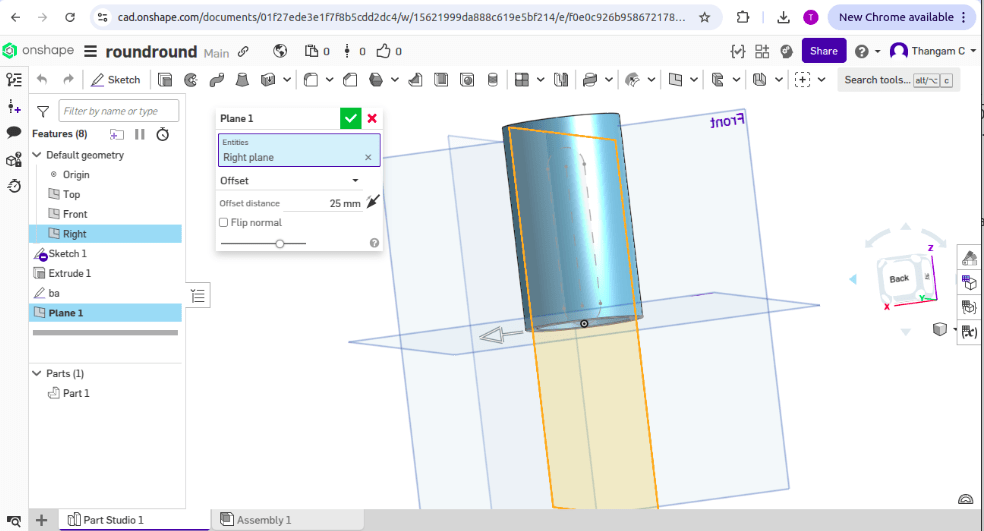
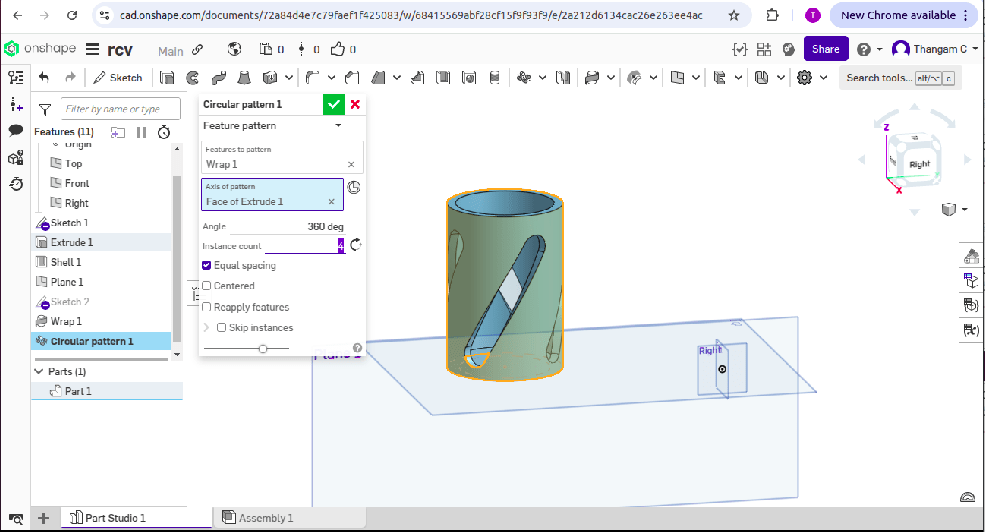
4. The Wrap tool is used for embossing and debossing on the sides of a cylinder.
Video
Download Original Design Files
Click on the links below to download the original design files: