3D Printing and Scanning
Objectives for Week 5
- design and 3D print an object with,
- Small size(Few cm3)
- Limited by printer time
- Could not be made subtractively
- Test the design rules for your 3D printer(s)
Individual Assignment
Group Assignment:
Group Assignment
In our group assignment, we began by learning about essential safety precautions when working with 3D printers. We then explored key design rules for successful 3D printing and carried out various test prints, including support, overhang, bridging, wall thickness, and infill pattern evaluations. To further assess printer performance, we downloaded and printed a comprehensive test jig, which allowed us to examine multiple parameters such as bridging, support effectiveness, hole accuracy, stringing, dimensional scaling, diameter precision, overhangs, and clearances. The outcomes of these tests are documented on our group assignment page.
Group assignment link.
3D Printing
Additive manufacturing, also known as 3D printing, is a technology that builds objects by adding layers of material together. It's the opposite of traditional manufacturing, which involves cutting away material.
- Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM)
- Stereolithography (SLA)
- Digital Light Processing (DLP)
- Selective Laser Sintering (SLS)
- Material Jetting (MJ)
- Electron Beam Melting (EBM)
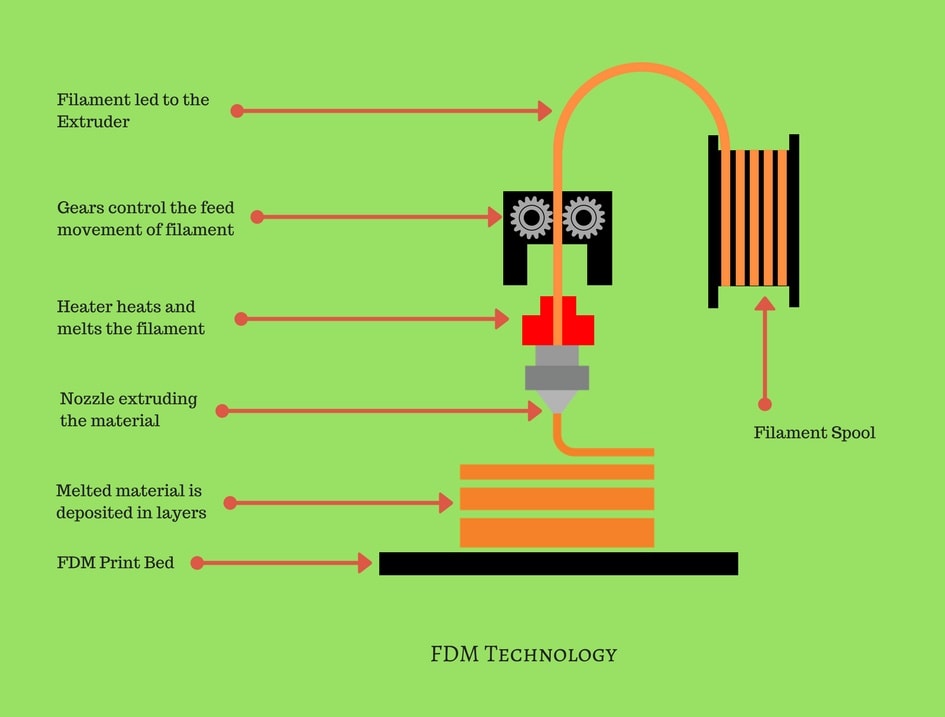
FDM is the most widely used 3D printing technology, where thermoplastic material is heated until it melts and then deposited layer by layer onto the build platform to create a three-dimensional object.
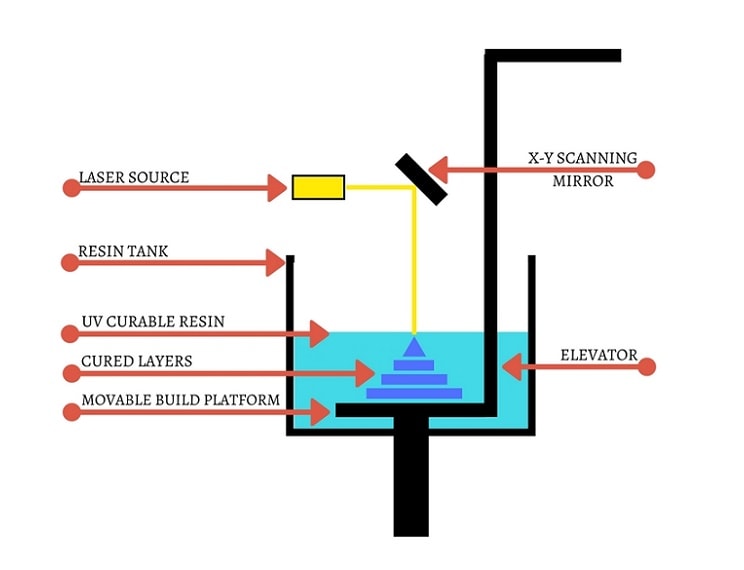
SLA is the first 3D printing technology ever developed. It operates using a process called Vat Polymerization, in which a photopolymer resin contained in a vat is selectively solidified by exposure to a light source.
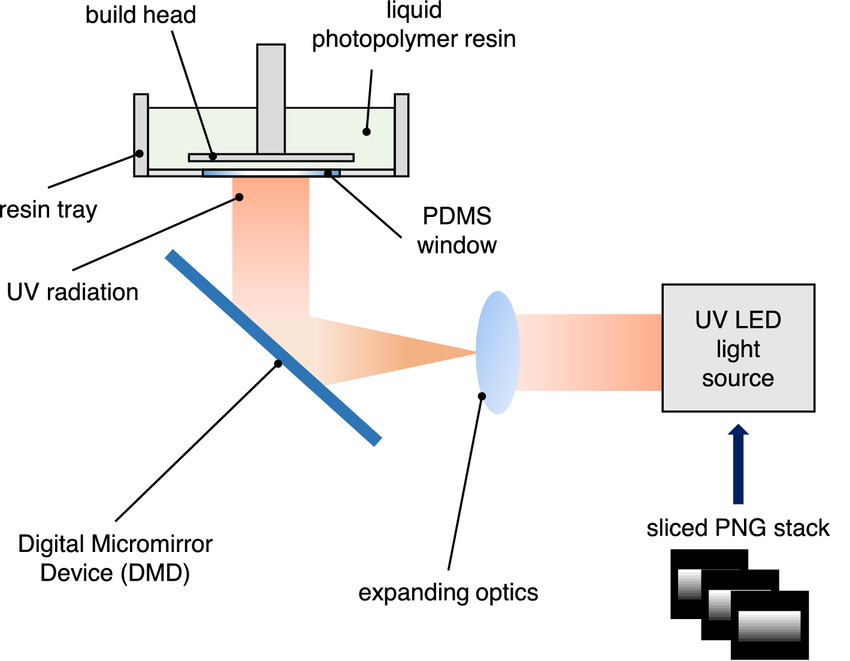
DLP (Digital Light Processing) is similar to SLA but differs in how it cures the resin. Instead of using a laser to trace each layer, DLP projects an entire layer at once using a digital light projector. The light, emitted by LED screens or a UV source, is directed onto the build surface through a digital micromirror device (DMD).
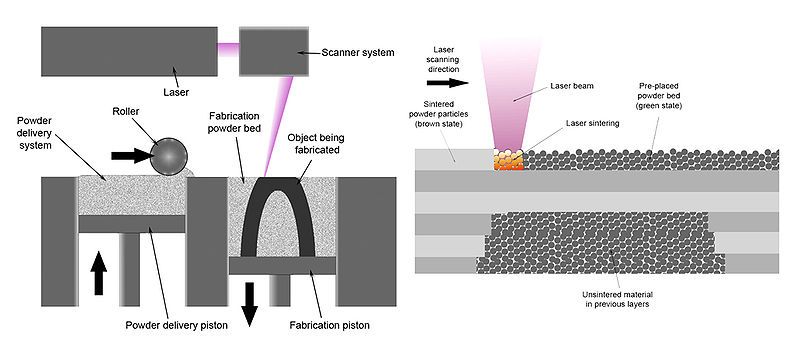
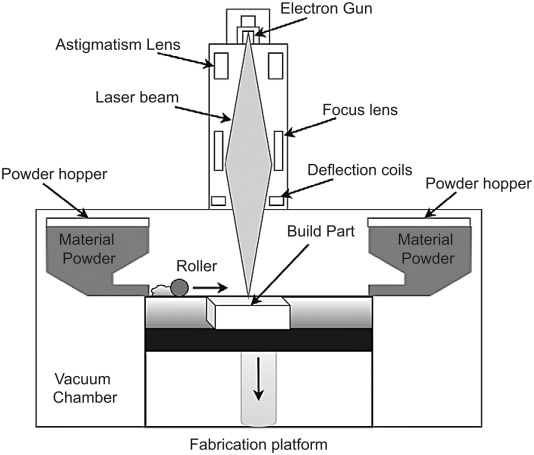
This 3D printing process, known as powder bed fusion, involves heating a bin of thermoplastic powder to just below its melting point. A wiper blade then spreads a thin layer of powder, typically around 0.1mm thick, onto the build platform. A laser then scans the surface, selectively sintering the material to form the desired shape.
Material Jetting (MJ) uses photopolymer resin and operates similarly to an inkjet printer. However, unlike inkjet printing, MJ builds objects layer by layer to create fully 3D structures. The process involves precise point-wise deposition of liquid resin droplets, which are then cured using UV light. One of MJ’s advantages is its ability to print in multiple materials and colors within a single print job.
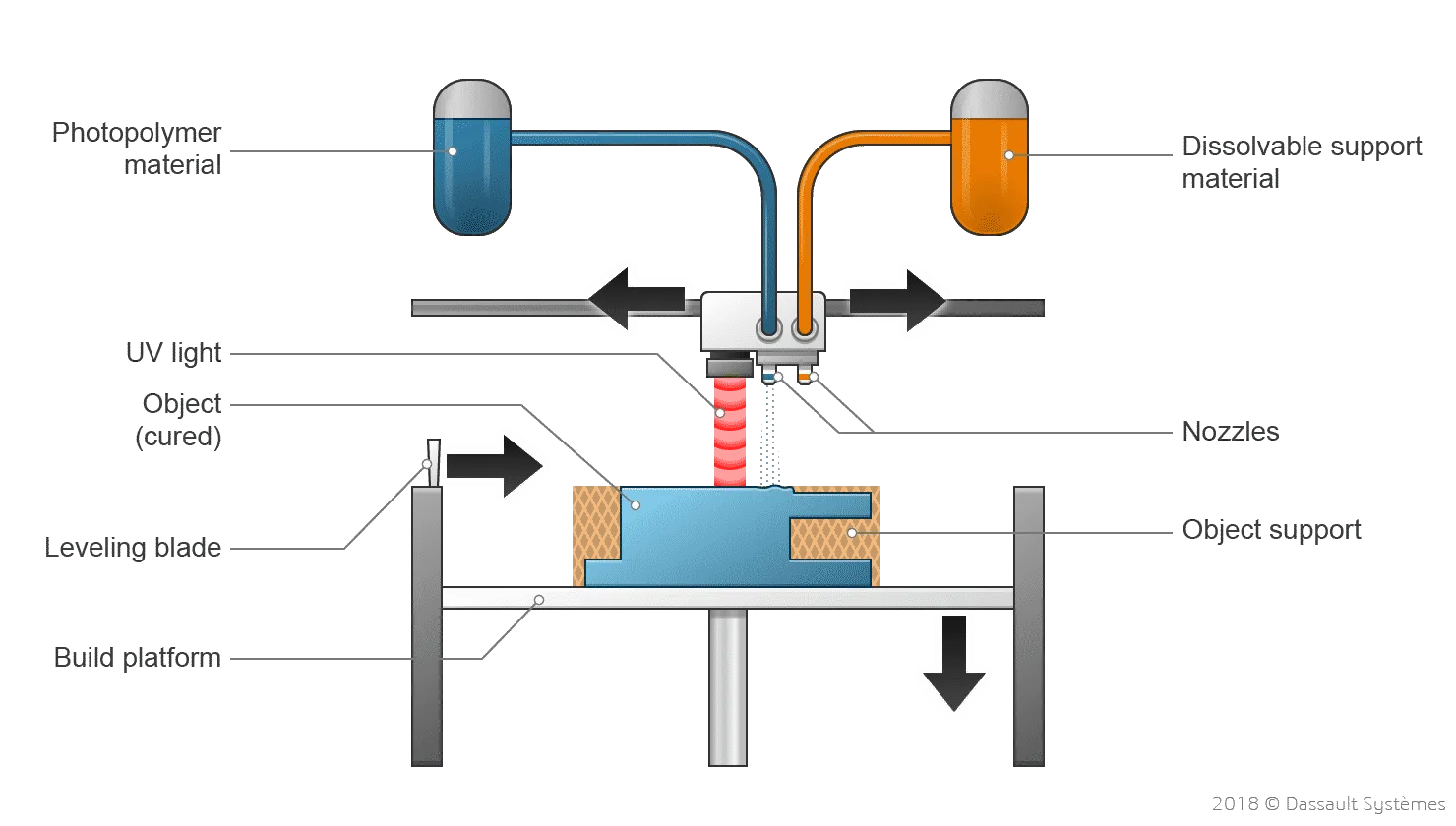
Electron Beam Melting (EBM) is a 3D printing technique where a high-energy electron beam melts metal powder to create objects layer by layer. The process occurs in a vacuum chamber to prevent oxidation, which is particularly important for highly reactive materials. EBM is similar to Selective Laser Melting (SLM) since both methods utilize a powder bed for printing. However, instead of a laser, EBM employs an electron beam to fuse the metal particles.
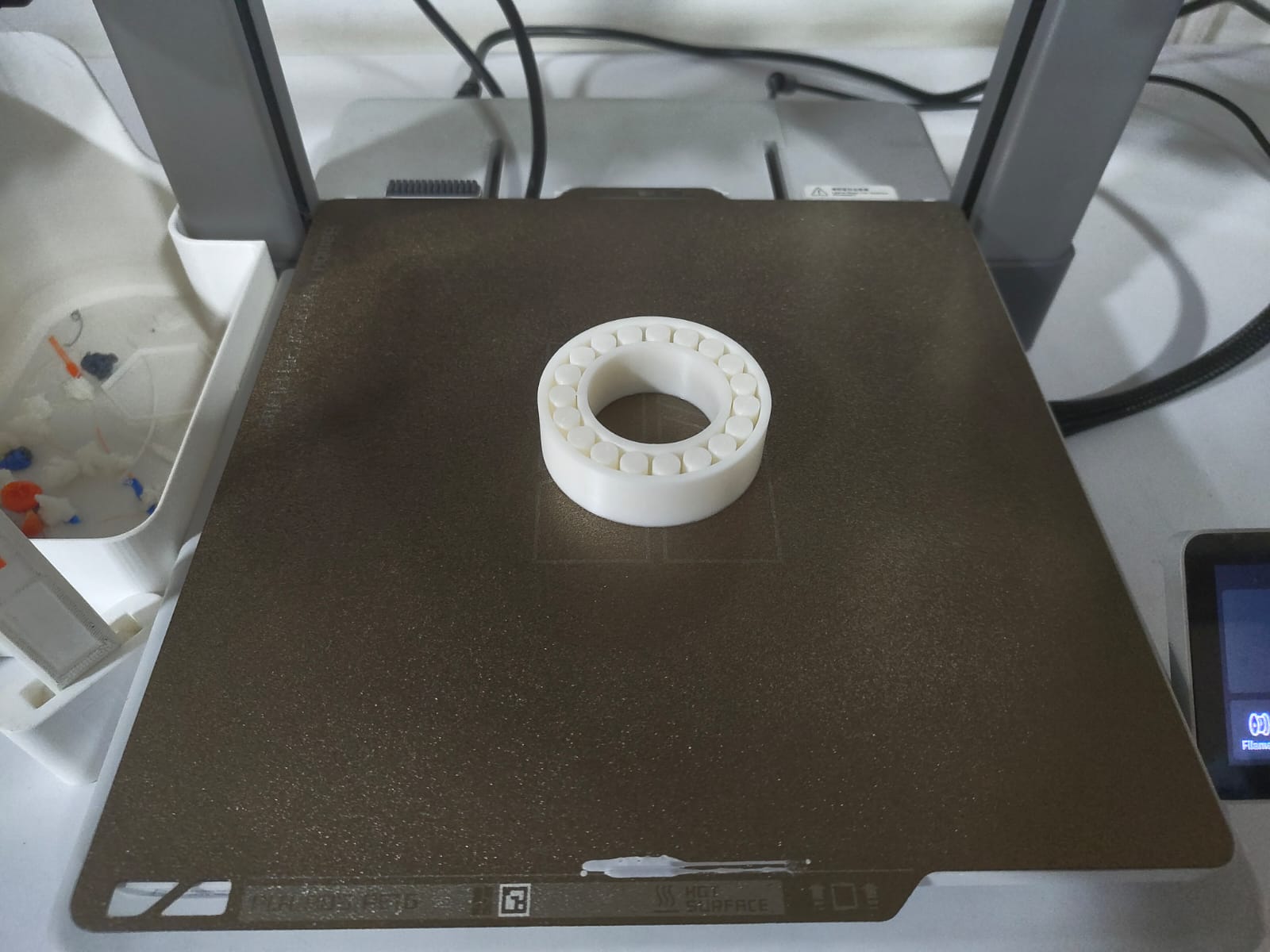
This week assignment is to design and print a model which can't be made using substratively. So I designed a bearing in Fusion 360, sliced it using the Bambu studio and printed it in the Bambu A1 printer which is available in our Lab. As the model have internal taper and have a clearance of 0.3mm the model can't me made using any substractive manufacturing techniques.
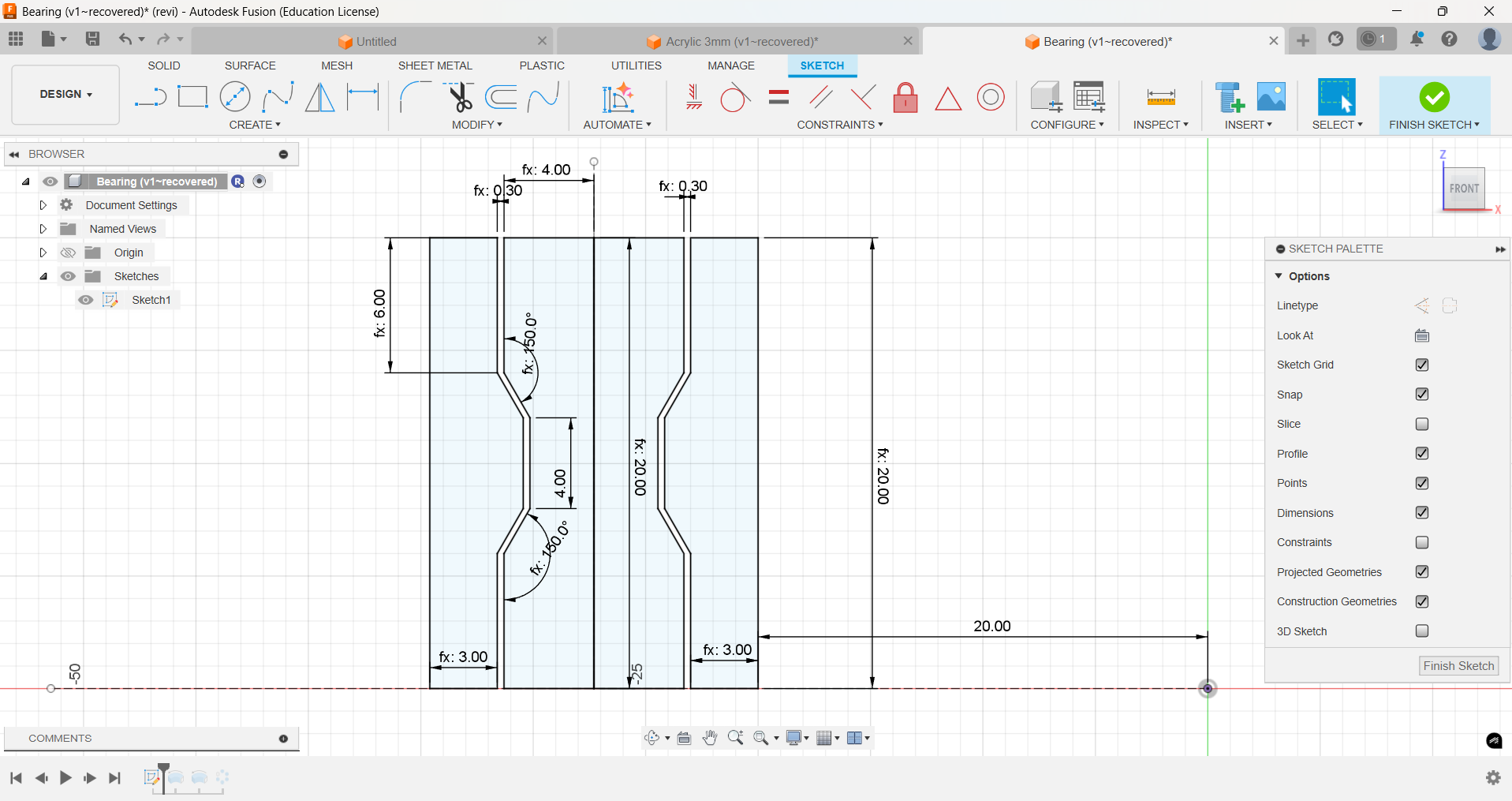
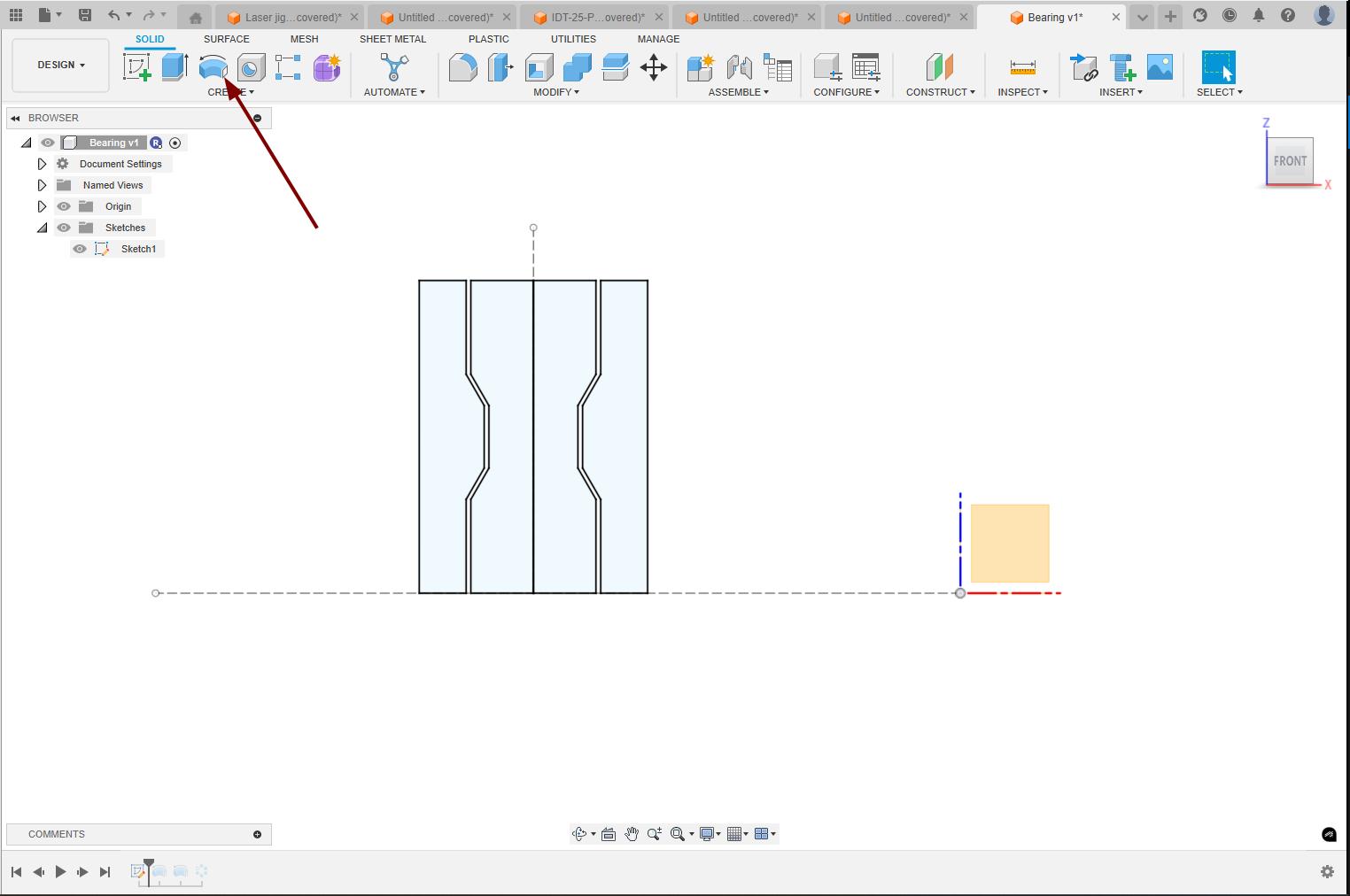
After completing the drawing, I used the revolve option to make the drawing as the outer part of the bearing.
 |
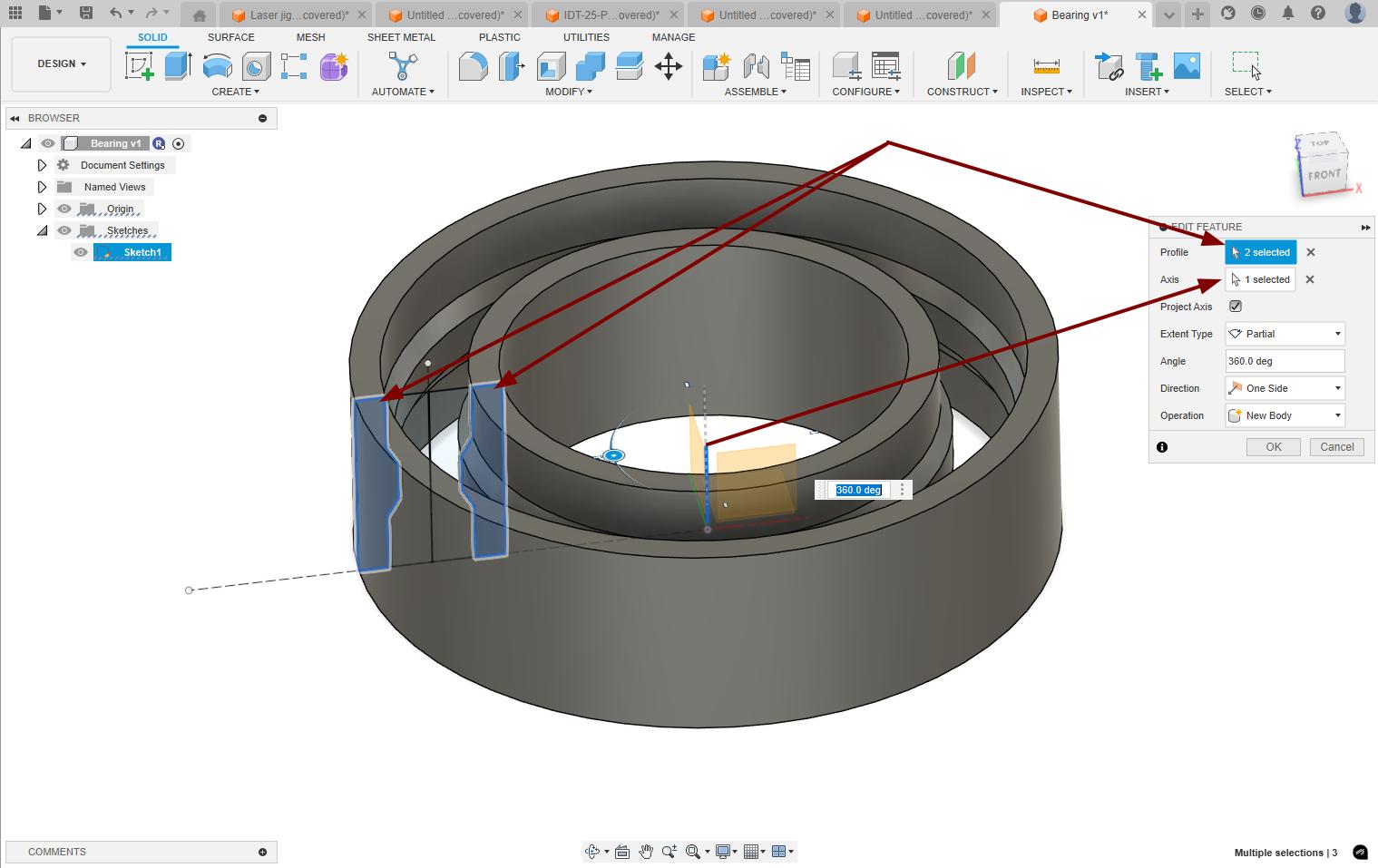 |
Again used the revolve option to make the internal rollers of the bearing.
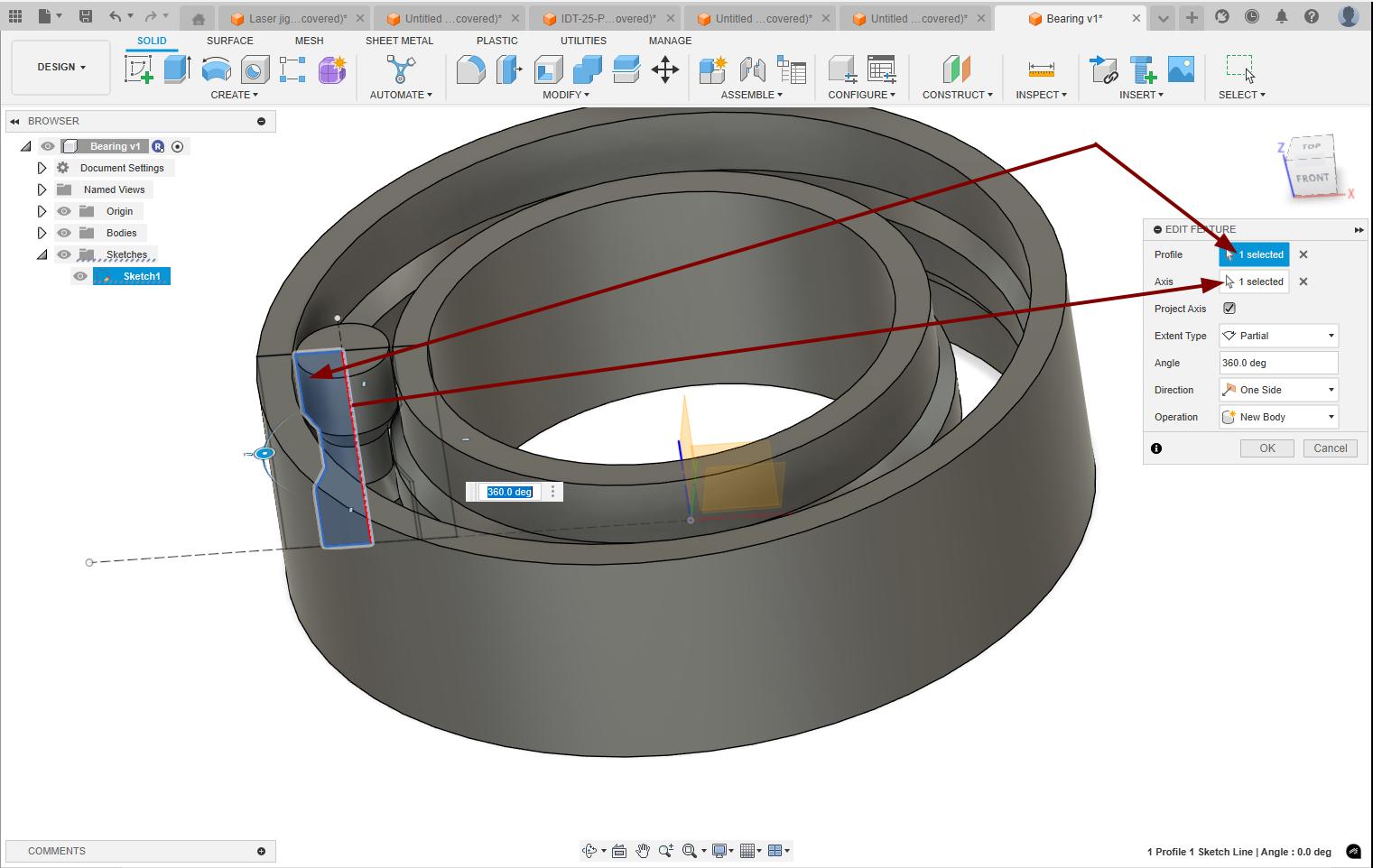
Used the circular pattern option to make the rollers around the bearing.
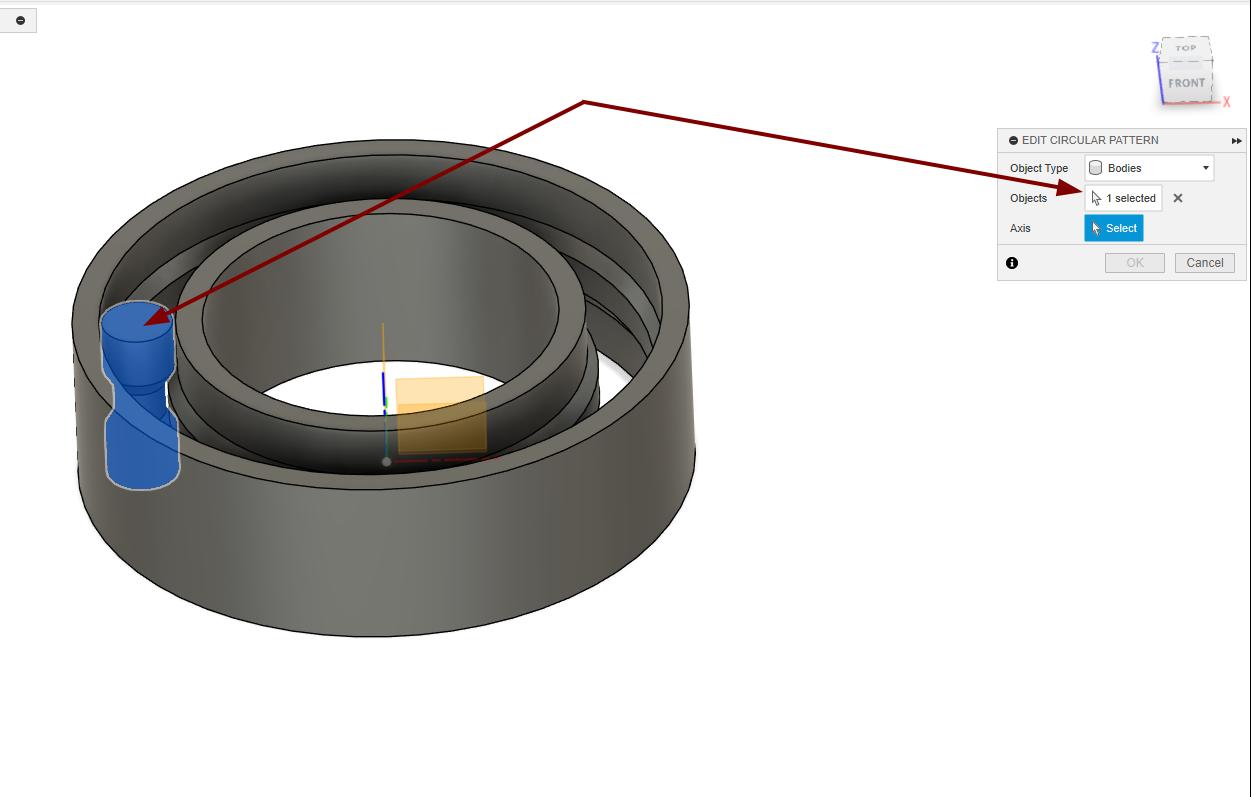 |
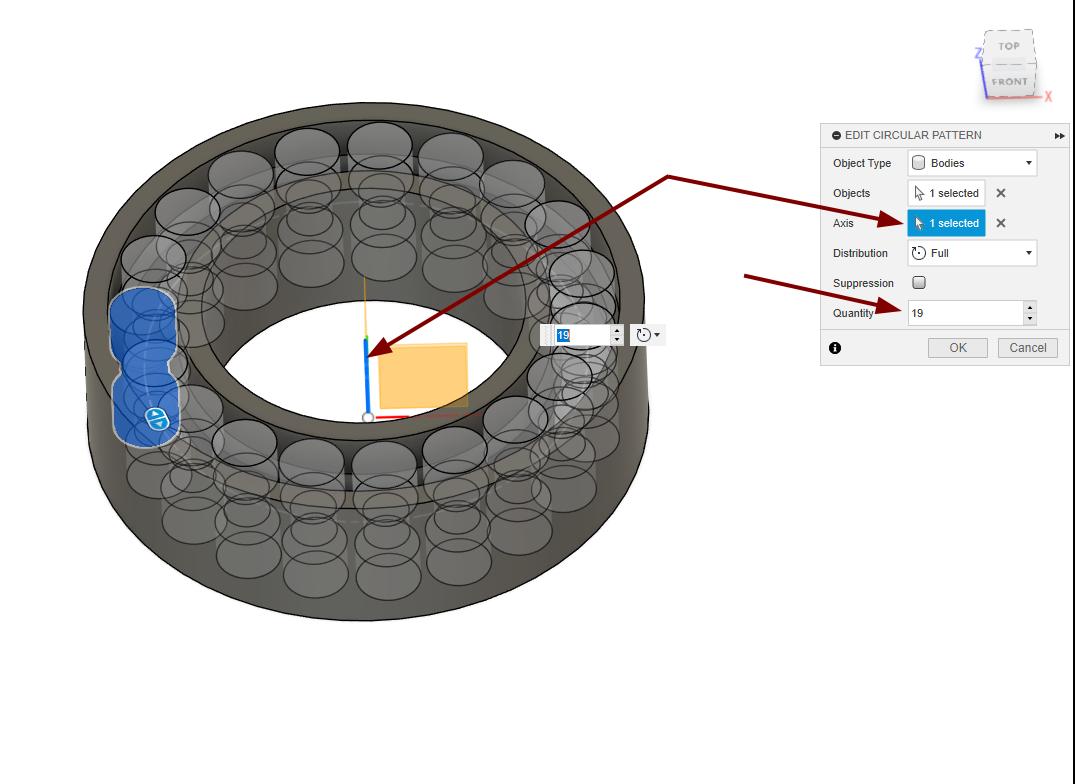 |
I exported the file as '.3mf' so that I can open it in the slicer software.
Slicing the Model
The .3mf file is opened in the Bambu Studio.
 |
|
In strength, changed the following and no support is needed for this design, so supports were disabled. The supports were disabled because during our group assignment we tested and foiund that maximum of 45 degrees can be print with out support in our printer.
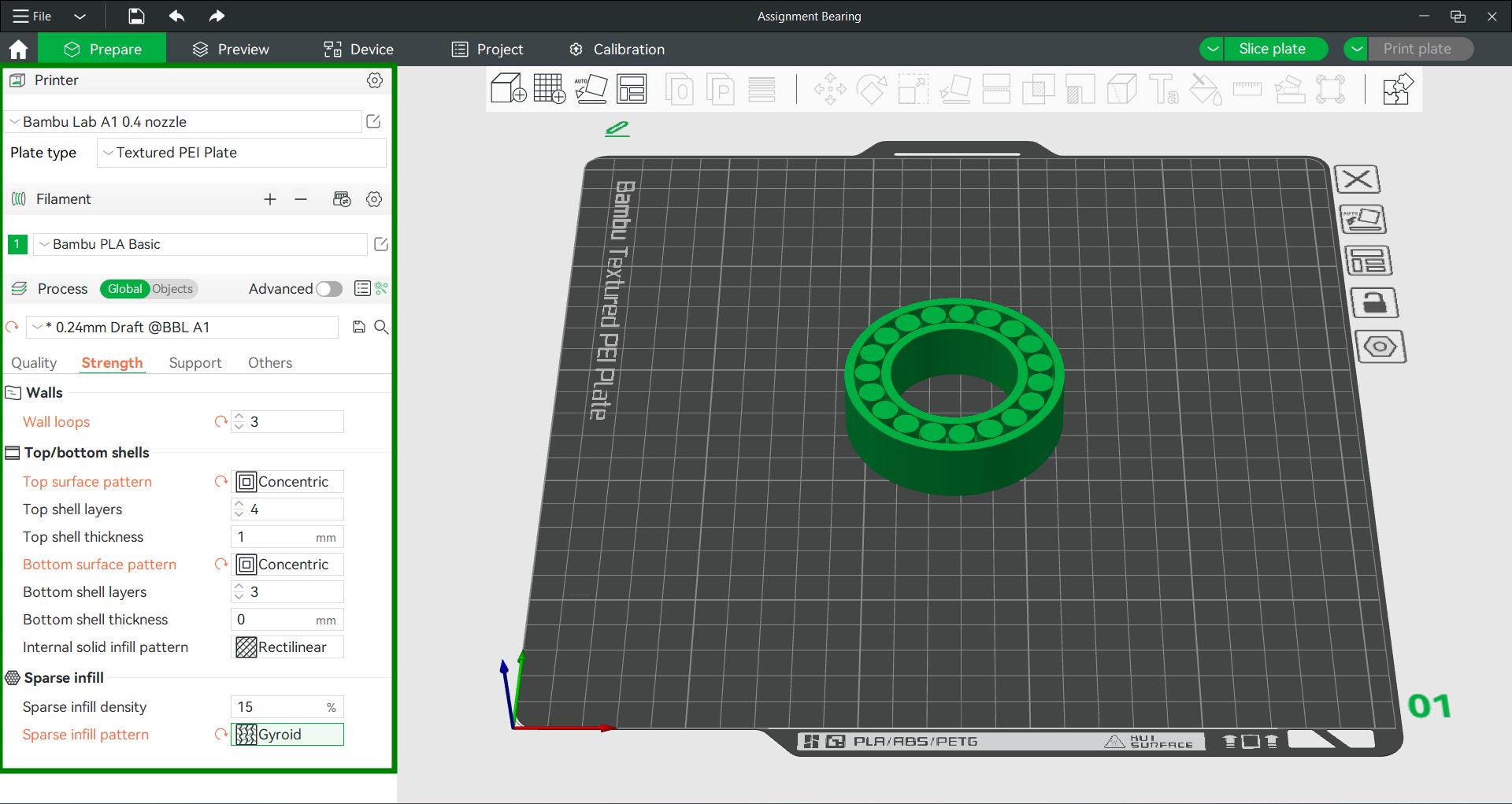
Sparse infill pattern= Gyroid |
 |
As the model is in cylindrical shape the Concentric Surface Pattern is ideal for its appearance. The Sparse infill pattern is given for attaining the strength of the material.
In others, disabled Brim and Prime tower.
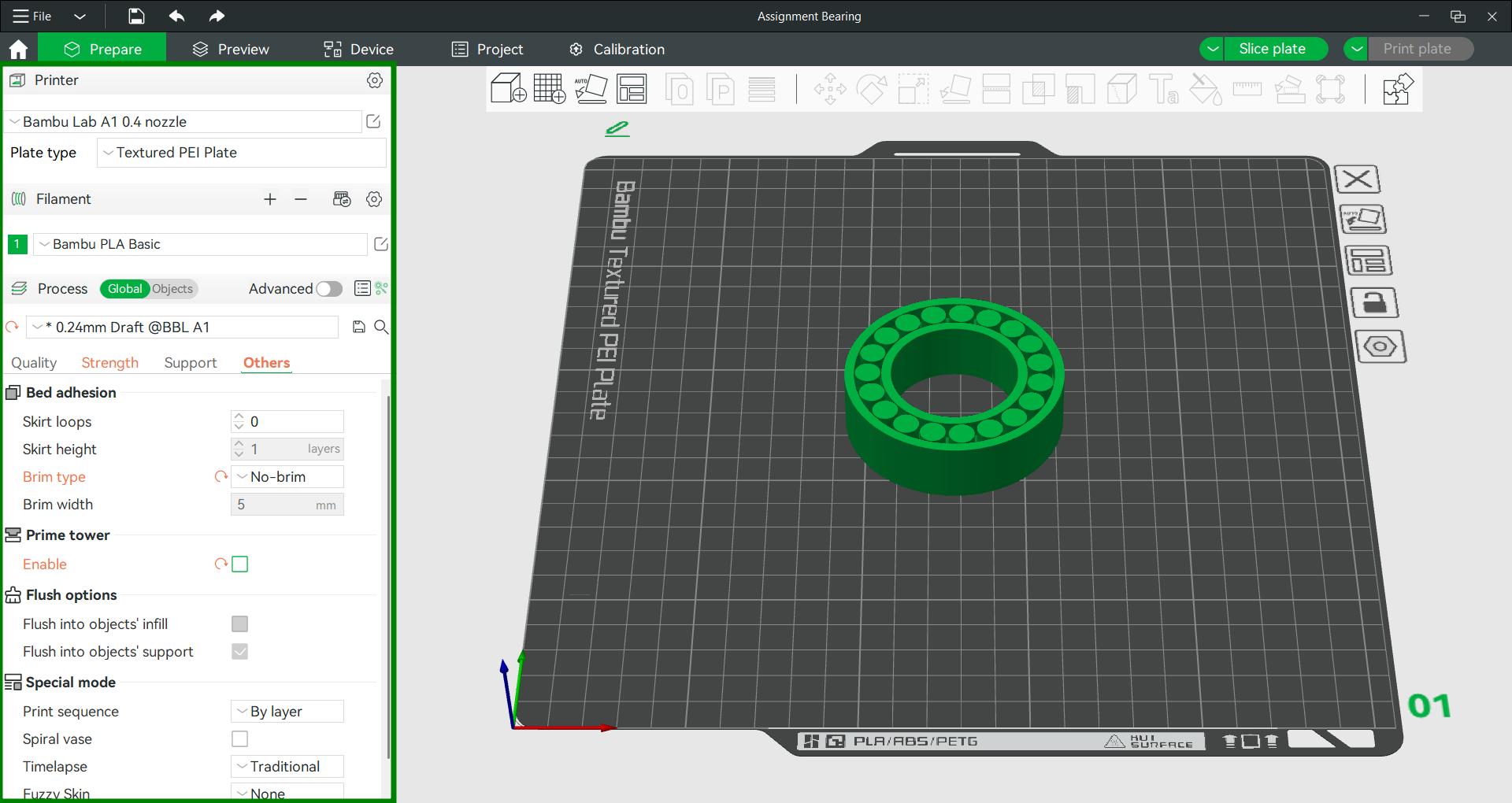
Sliced the model and shows it will take one hour and twelve minutes to print the model. Using print plate the G code is sent to the printer.
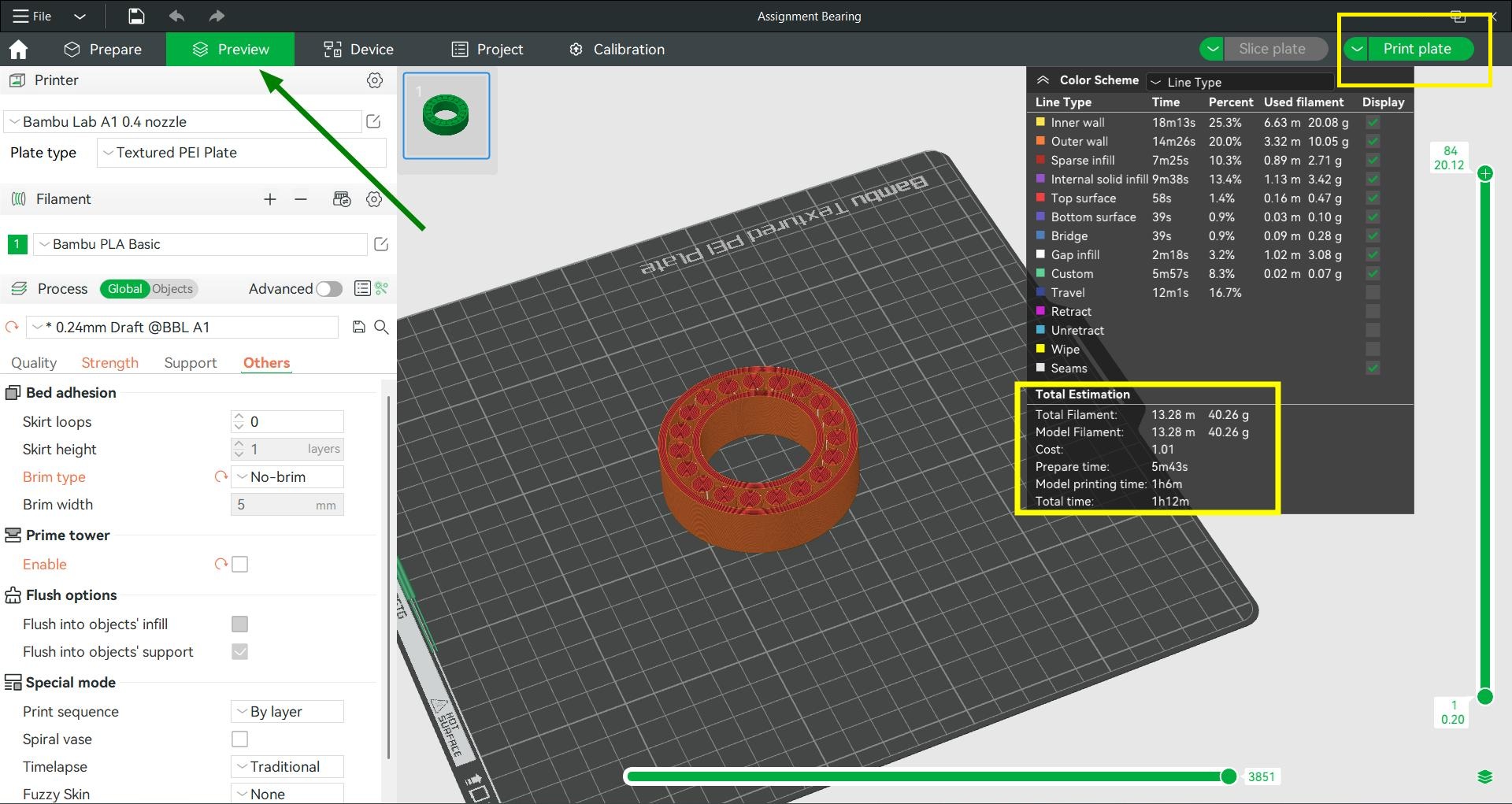
3D Printing
The printer I used was Bambu Lab A1.
Specification
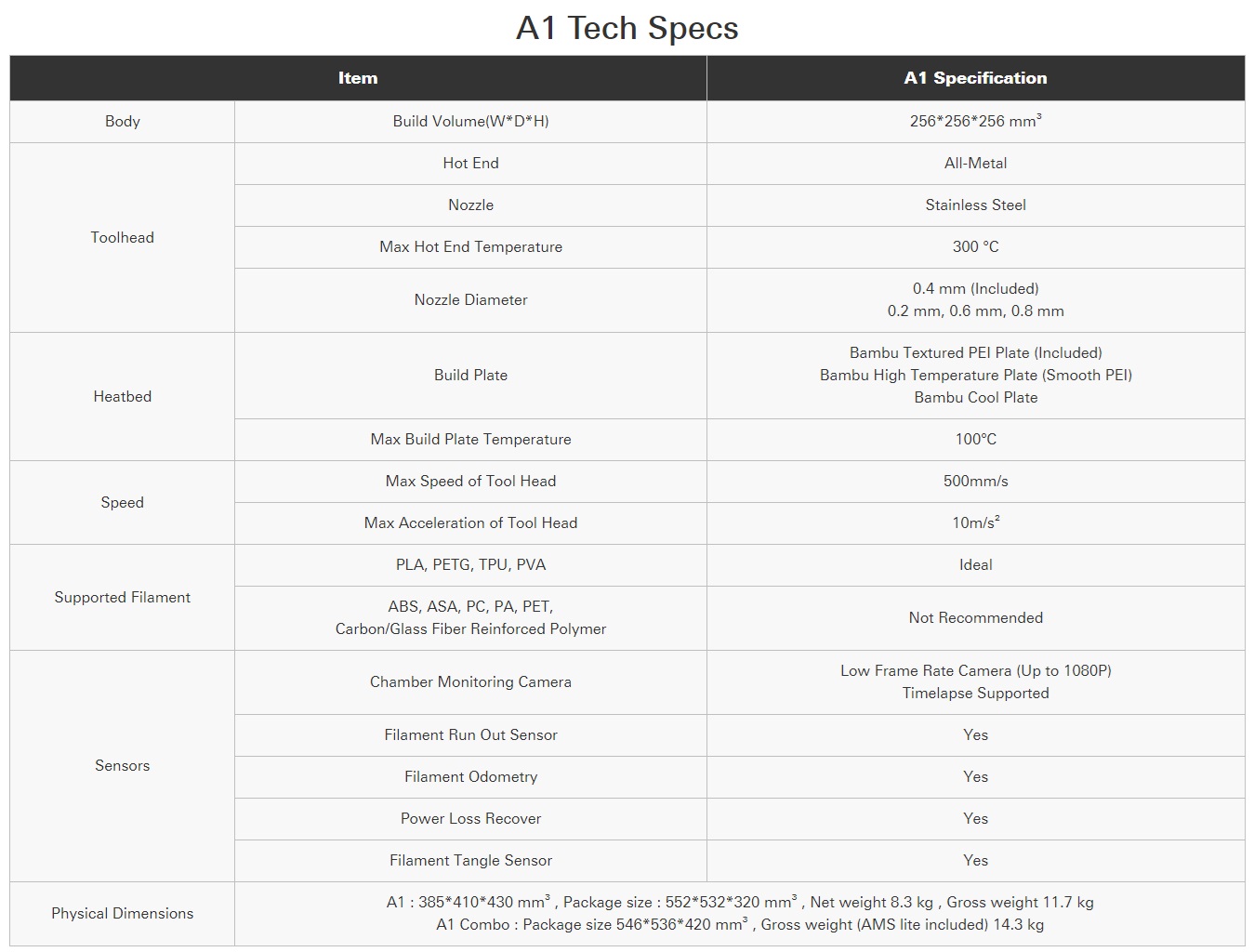
The bearing was printed, and it worked. A video of the printing process and its functionality is provided below.
3D Scanning
3D scanning refers to the process of capturing a physical subject to represent its geometry accurately in a digital environment. The subject can be any object, person, or even the surrounding environment. Just like a camera captures a flat, 2D image, a 3D scanner captures an object’s height, width, depth, and some also capture color.
We have Artec Leo wireless 3D scanner available in our lab.
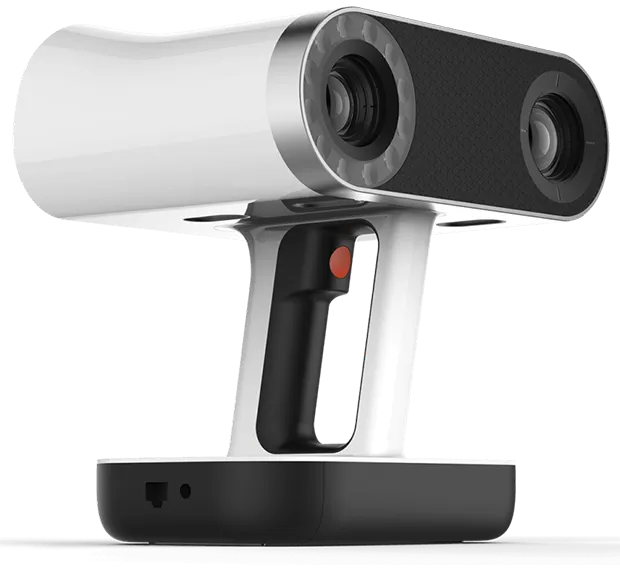

It is a portable 3D scanner with a built-in computer, eliminating the need for an external device for processing. It offers 0.1mm accuracy and real-time 3D visualization. Due to its portability, it is well-suited for scanning large areas efficiently.
Scanning
We recently created an art installation inspired by the book The Old Man and the Sea, made entirely from cardboard. For scanning, I chose the marlin, the fish featured in the story.
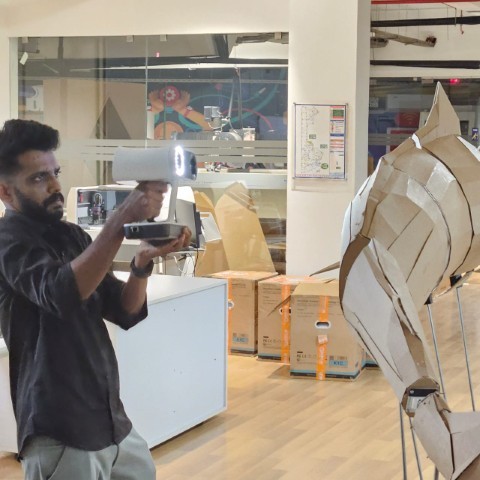 |
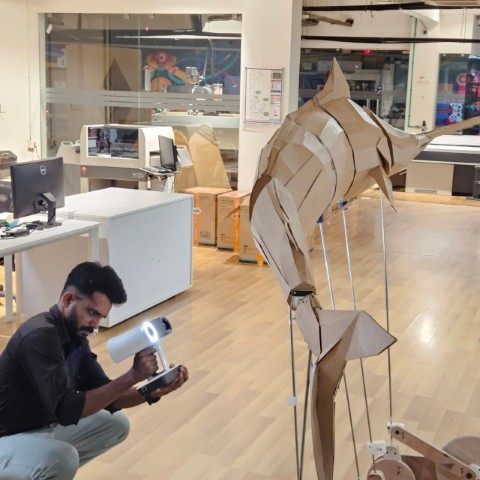 |
The final result looks like this,

Post Processing
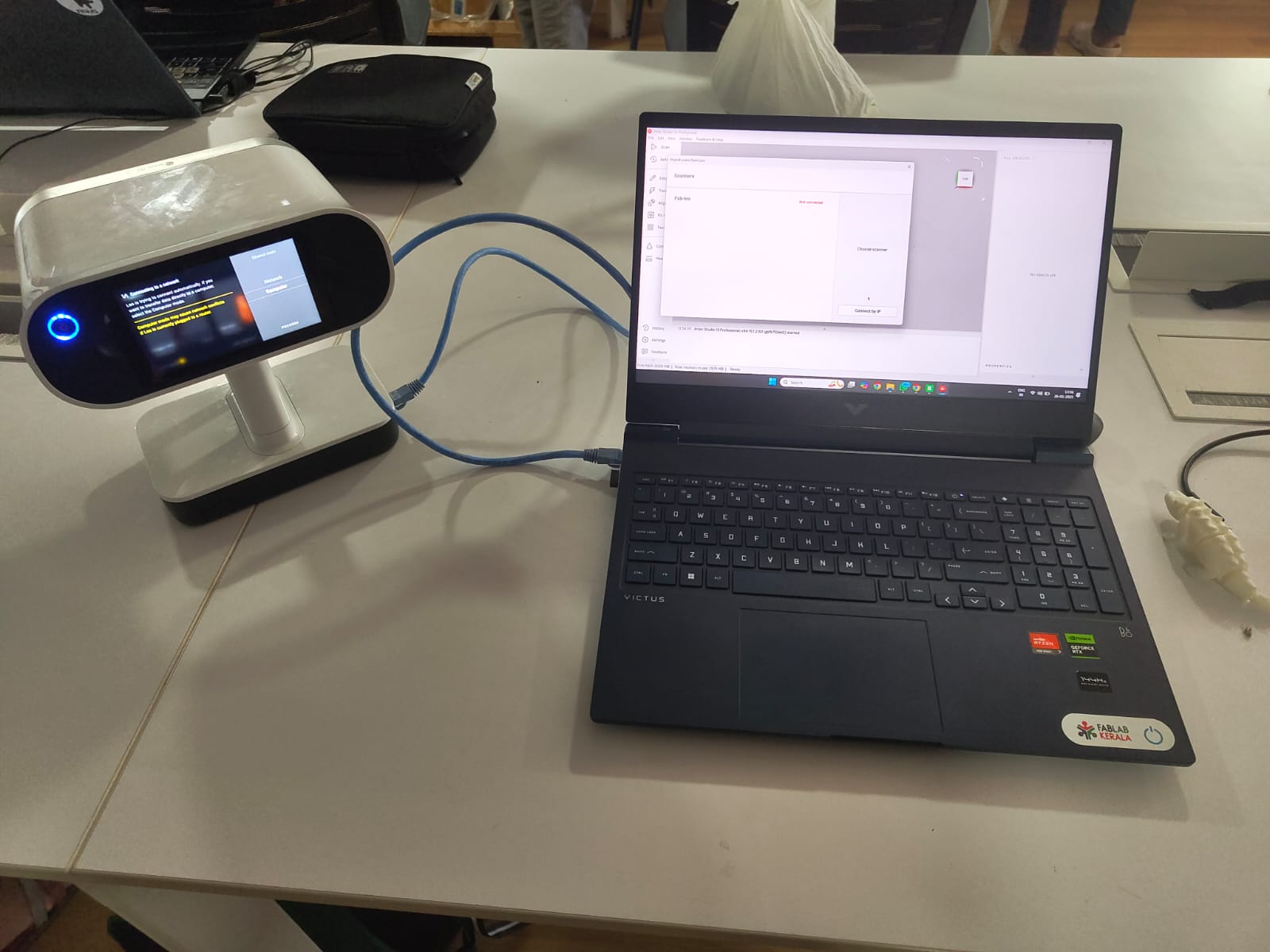
For post-processing the scanned model, I used Artec's proprietary software, Artec Studio 15 Professional. During scanning, some areas may be missed, so this software is used to fill in those gaps and enhance the texture.
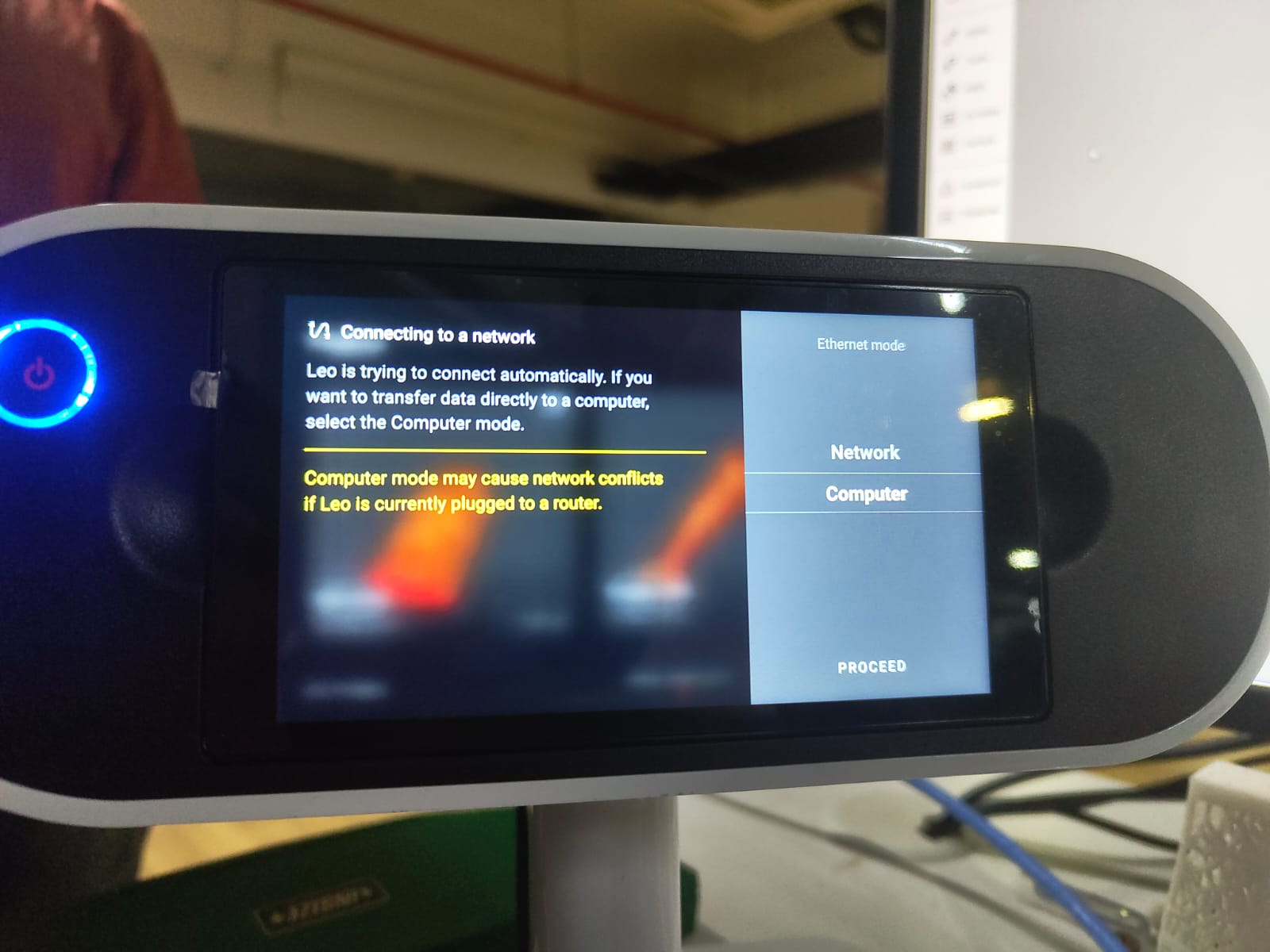
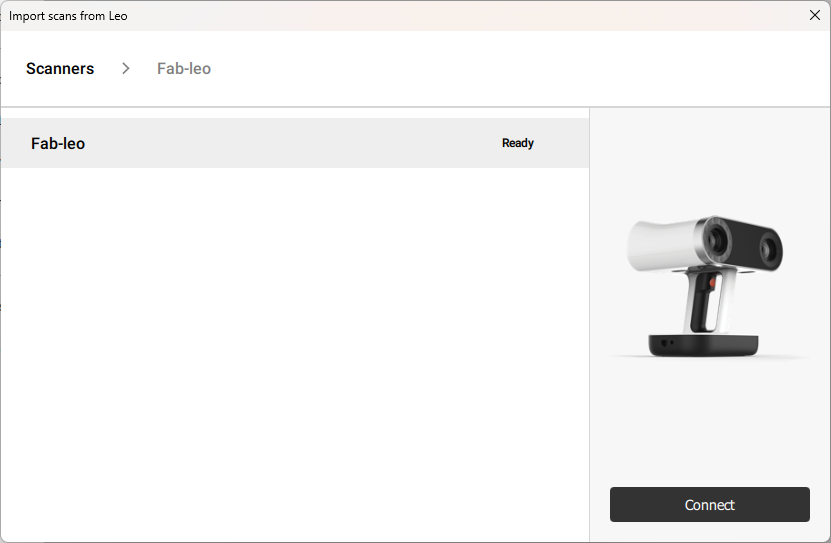
The 3D scanner is connected to PC via ethernet cable. In Artec Studio 15 select Import from Leo option. In scaner change the ethernet mode to computer and our scanner will be displayed in the software.

|
|
|
|
After connecting I imported the model from the scanner to the software.
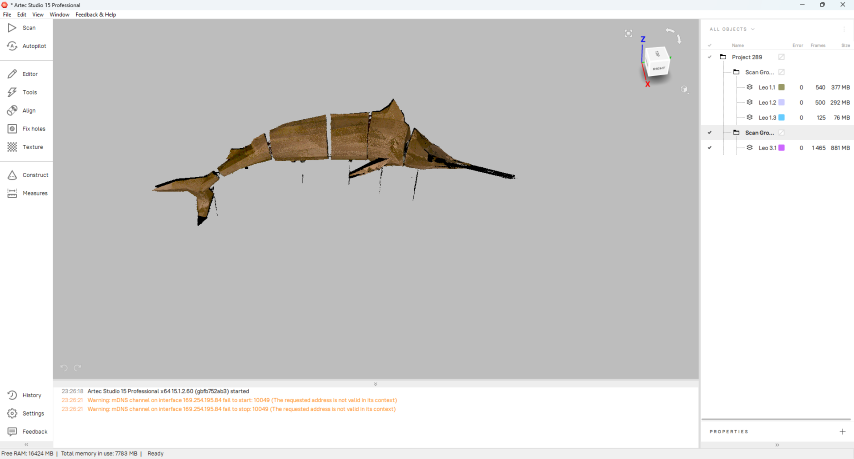
I used Autopilot option for post-processing my model. I followed the steps autopilot shown.
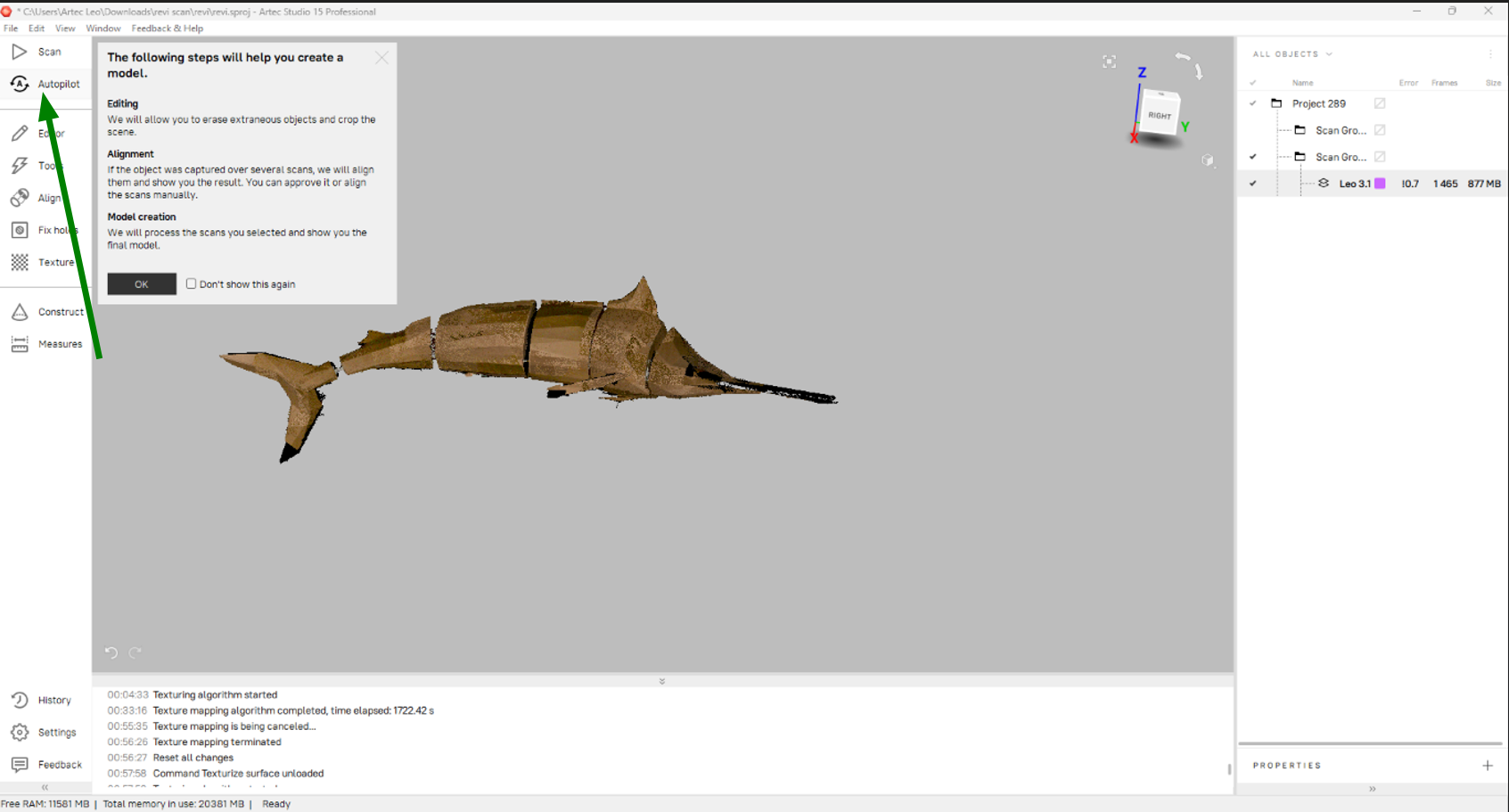
Then I selected the scaned model for post- processing.
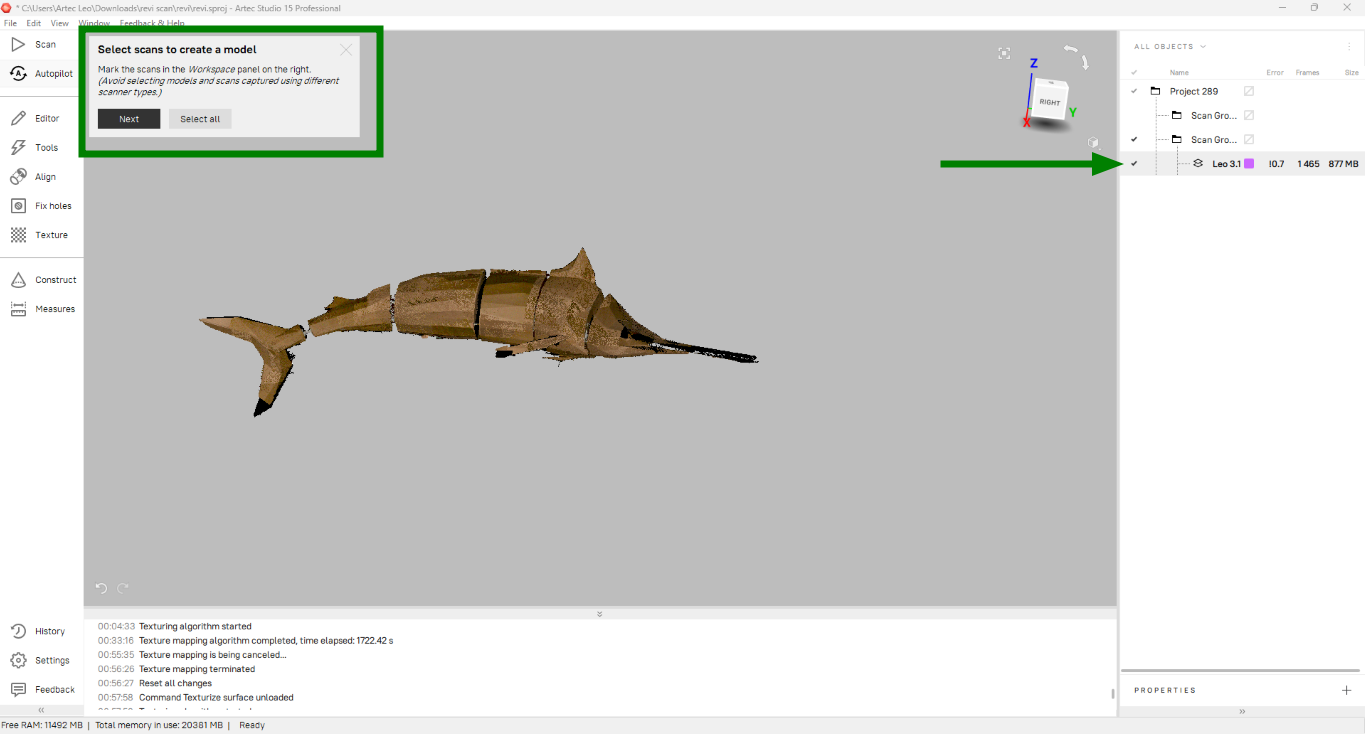
After selecting the model I followed these steps to get the final output.
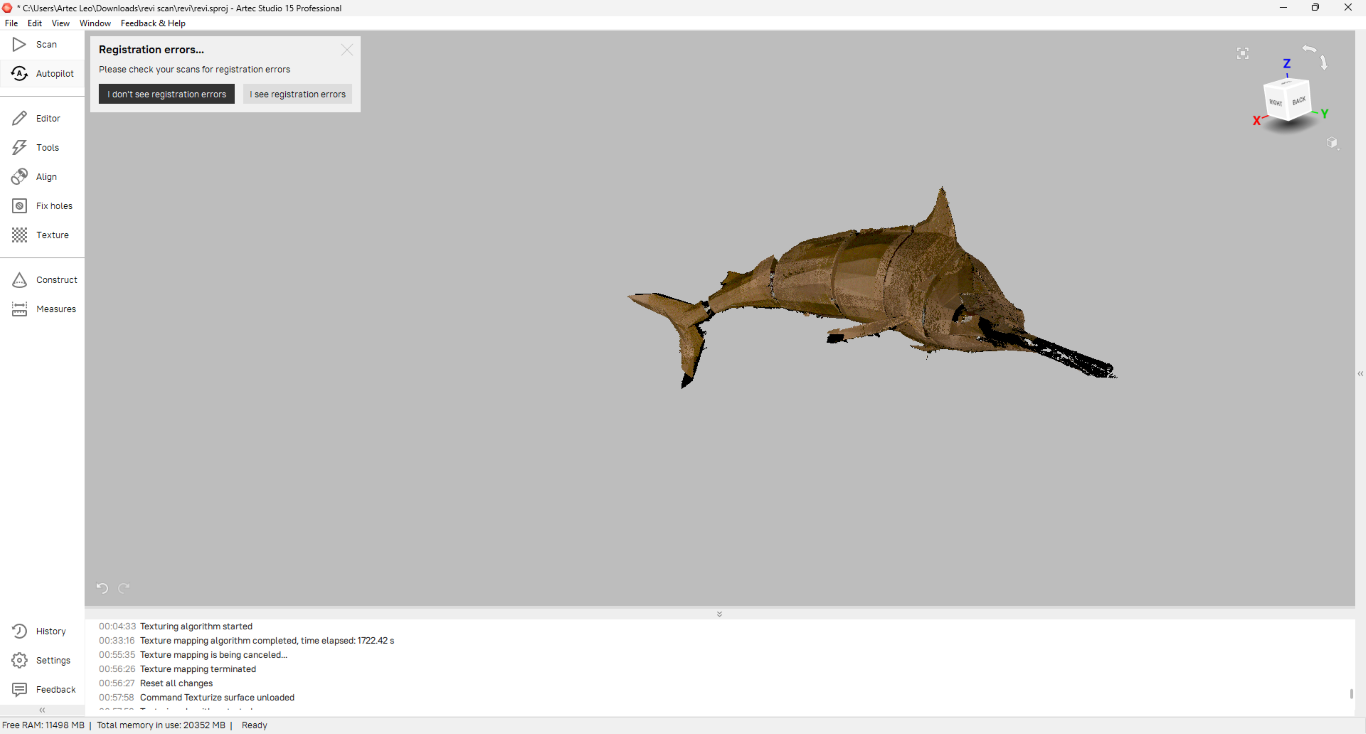
|
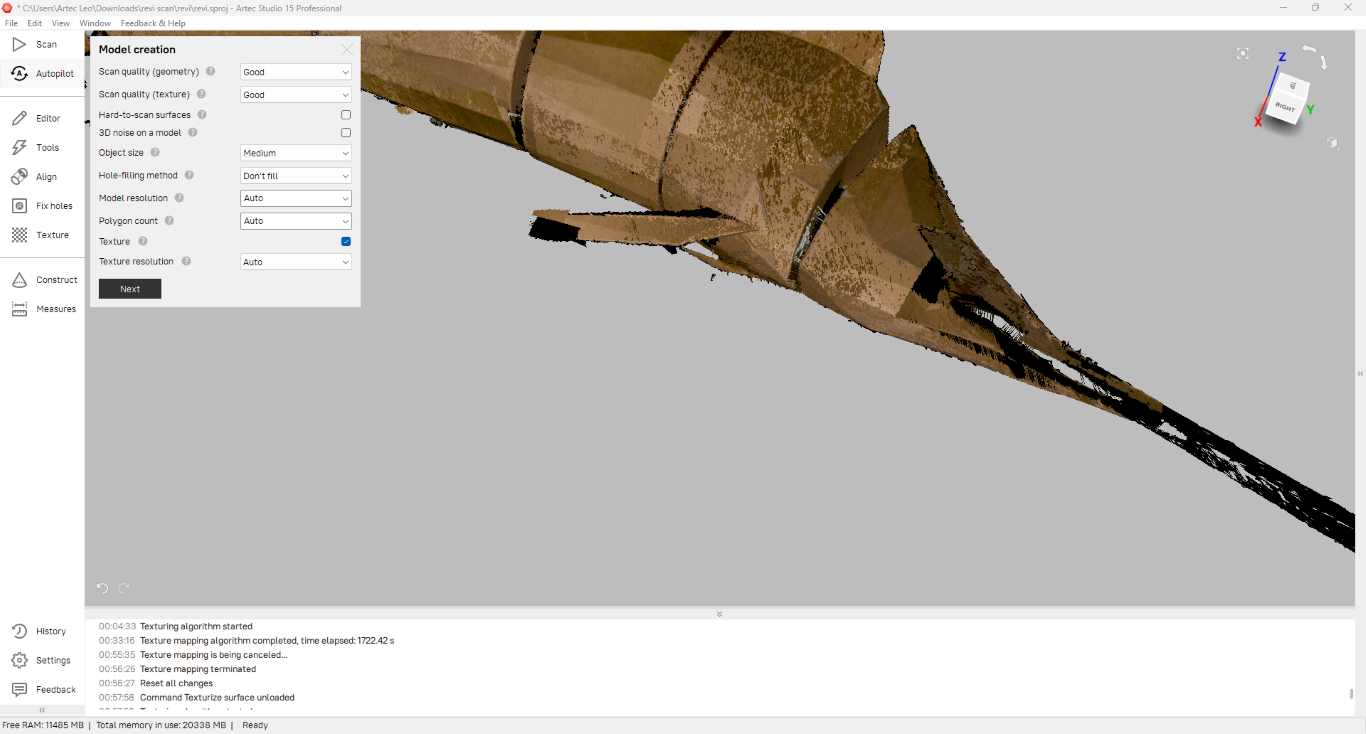
|
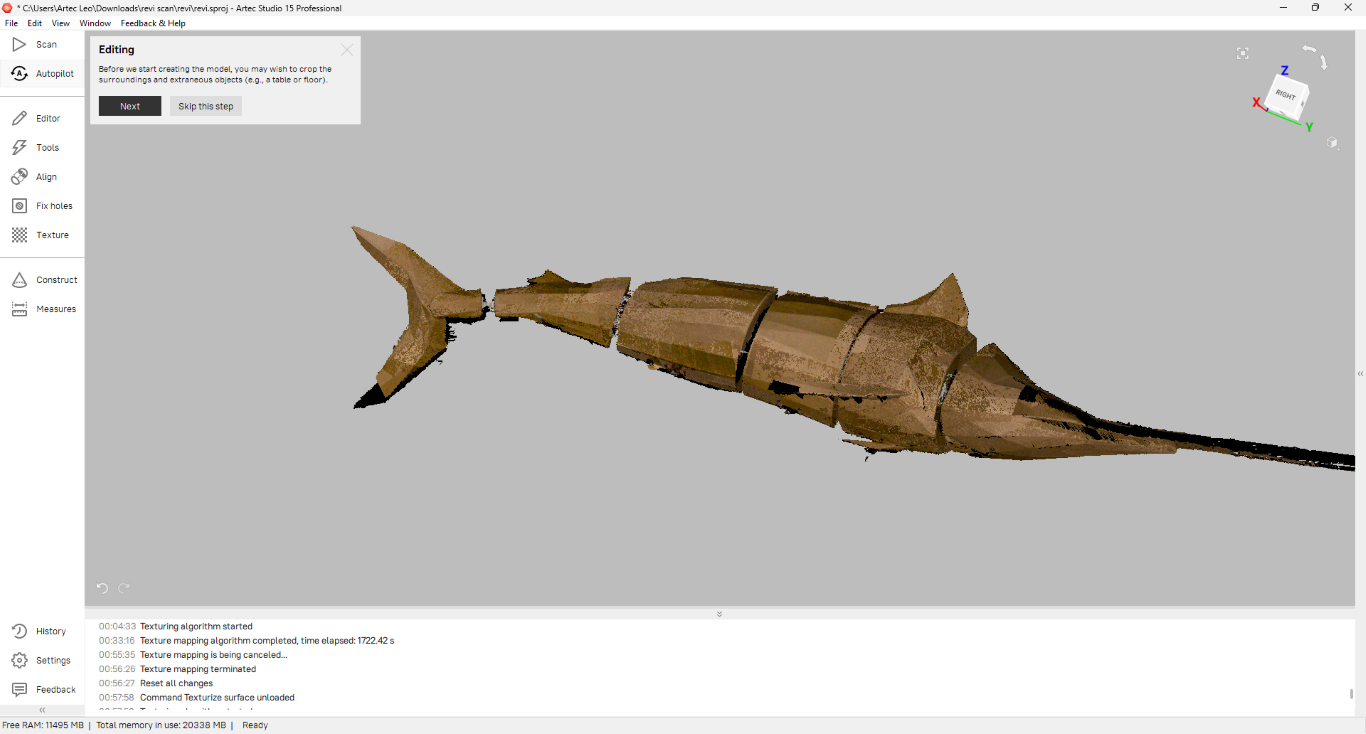
|
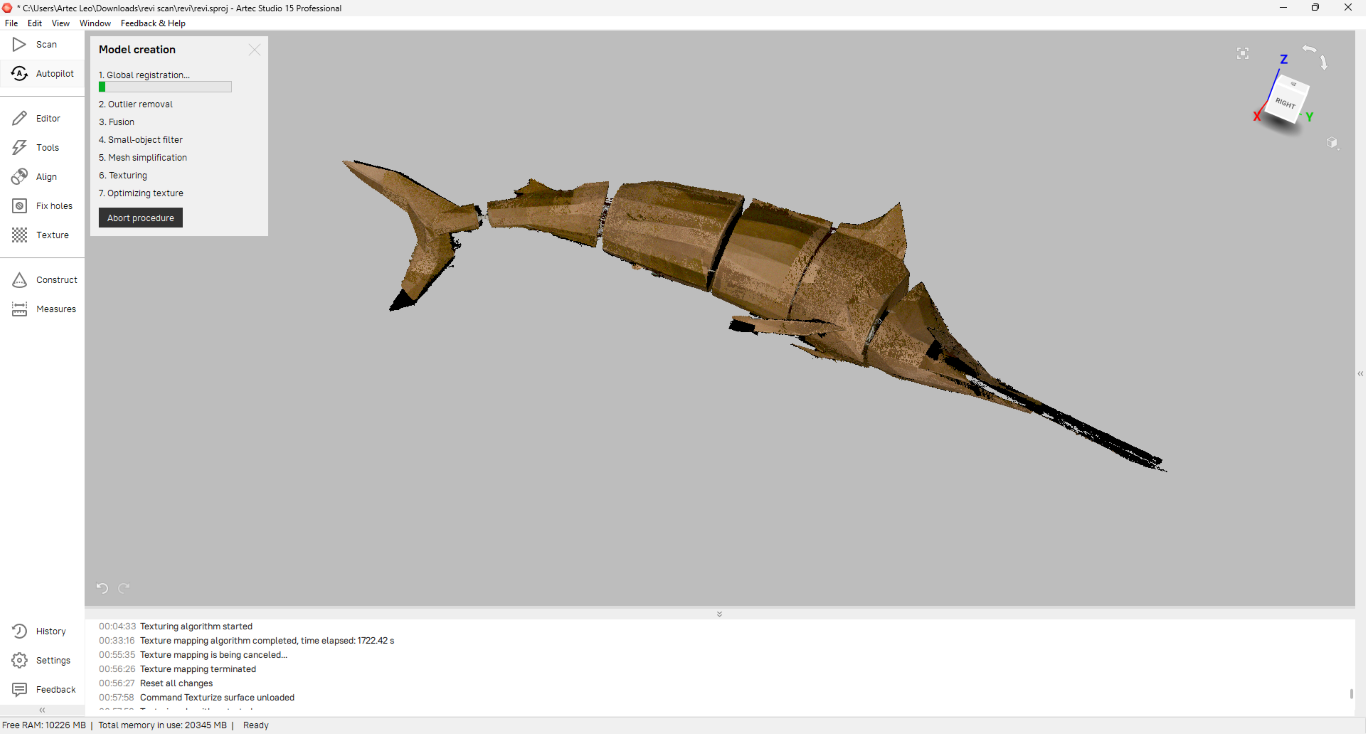
|
The output looks like this.
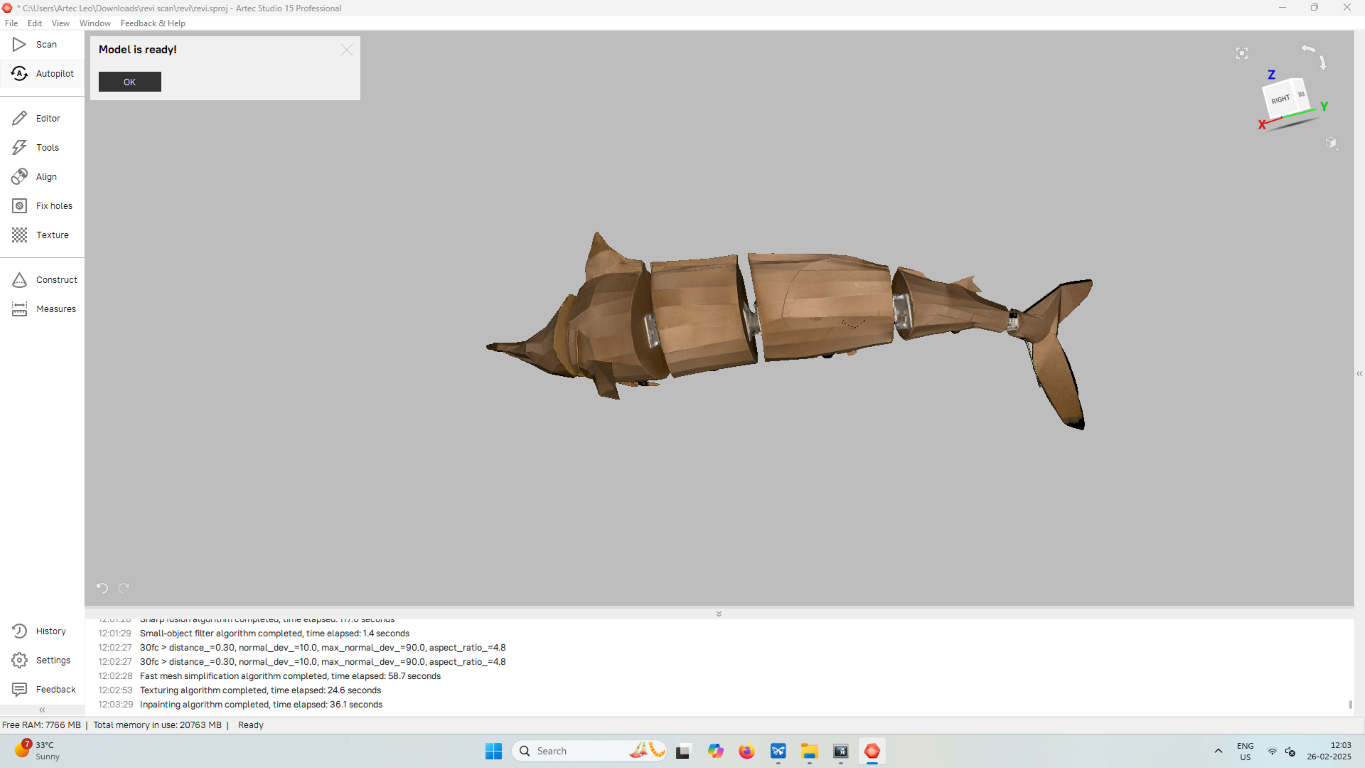
Conclusion
This week, I explored various 3D printing techniques and analyzed the necessary clearances for successful printing. Based on the values gathered from our group assignment, I designed a model that couldn't be manufactured using subtractive methods. After finalizing the design, I sliced and printed it. Additionally, I delved into 3D scanning and its post-processing techniques.