Week 19 assignment: invention, intellectual property, and income
Summary
This week, I had to creat a dissemination plan for my final project answering some questions. Then, research the forms of intellectual property in my country that could fit with my project and uplode a summary slide and video.
Process
Dissemination plan
Target Audience
Homeowners: Individuals who own houses and are concerned about water leaks and potential damage.
Property Managers: Those managing multifamily buildings who need to maintain property value and ensure tenant satisfaction.
Real Estate Developers: Companies involved in constructing new residential buildings who could incorporate your detector into their real estate projects. Some of them are: Actual, Albamar, Aurora, Avenir, Bélgica, Besco, Casa Ideal, Cosapi whom I could go and offer the product.
Insurance Companies: Firms that could recommend or provide your detector to their clients to reduce claims related to water damage.
Maintenance Companies: Businesses that provide repair and maintenance services and could use or recommend your detector to their customers. There are many building management companies. The product would be oriented towards them as well, since they are in charge of controlling the consumption of common services of the building they manage.
Channels
Social Media: Platforms like Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter to reach a broad audience. I can use also LinkedIn for connecting with real estate developers and property managers.
Industry Events and Trade Shows: I would present my product at events related to home improvement, real estate, and technology like , like CASACOR or EXCON, which are massive fairs where everyone involved in the real estate sector attends.
Partnerships and Collaborations: I can also partner with real estate firms and maintenance companies to promote the detector.
Demo Videos: I could create and share videos demonstrating how the water leak detector works and its benefits.
Plan Development
Objectives: Raise awareness about having a the water leak detector at home and it´s benefits of having it.
Strategy: I will be making demonstration videos with influencers to position the product in houses. Likewise, I will contact building managers to offer them the benefits of this.
Monitor and Evaluate: I would have to track the performance of the videos I used using metrics like website traffic and social media. I will also be providing support to companies and companies that have purchased the product.
Key questions
-what tasks have been completed, and what tasks remain?
Until now, I am complying with the Gantt chart drawn at the beginning of the project. I am in the IoT connectivity part of my board with the cell phone app as well as in the total integration of all the components of the project.
-what's working? what's not?
I still need to make the OLED screen work so that it shows the alerts and consumption in case there is a leak, physically in the project module.
-what questions need to be resolved?
Seeing the possibilities that the Blync app offers for Wi-Fi connectivity, I must decide whether to use this app or use the RTC module with I2C connectivity that I designed on my board. For now, I'm leaning toward using the Blynk app.
-what will happen when?
In the next week, I will be connecting all the electronic components to test them at the same time.
-what have you learned?
I have learned more than I imagined at the beginning of the fab academy. I have manufactured and designed my own electronic board (after several mistakes and failures), as well as learned to solder SMD components. Additionally, I have become quite familiar with 3D printing and now understand how to better set the printing parameters. Finally, what I consider most important is what I learned in IoT connectivity that allowed me to develop my project. This tool is very useful since it eliminates the need for wiring and errors in it.
Intellectual property
A patent is a form of intellectual property that gives the patent holder exclusive rights to an invention. This means that the patent holder can prevent others from making, using, selling, or distributing the patented invention without permission. In exchange for these rights, the patent holder must publicly disclose detailed information about the invention.
In Peru, the regulatory body responsible for patents is the National Institute for the Defense of Competition and the Protection of Intellectual Property (INDECOPI). INDECOPI handles the registration, examination, and granting of patents, ensuring that the patents comply with Peruvian laws and regulations.

Aspects to Consider for Patents in Peru
Types of Patents:
Invention Patents: For new and useful inventions or discoveries. A patent for invention protects a new invention that involves an inventive step and is capable of industrial application.
Utility Models: For new technical improvements or enhancements to existing devices or processes. A utility model protects new inventions that provide a functional improvement to an existing product, giving it a new use or better functionality.
Industrial Designs: For the ornamental or aesthetic aspects of an object.
Patentability Requirements:
Novelty: The invention must be new, meaning it has not been publicly disclosed before the filing date.
Inventive Step (Non-obviousness): The invention must not be obvious to someone with ordinary skill in the relevant field.
Industrial Applicability: The invention must be capable of being used or manufactured in some kind of industry.
Application Process:
Preparation: Prepare a detailed description of the invention, including drawings, claims, and an abstract.
Filing: Submit the application to INDECOPI, including the required fees.
Examination: The application undergoes formal and substantive examination to ensure it meets all legal requirements.
Publication: The patent application is published to allow for public scrutiny and objections.
Granting: If the application passes all examinations and there are no valid objections, INDECOPI grants the patent.
Duration and Maintenance:
Invention Patents: Typically last for 20 years from the filing date, subject to payment of annual maintenance fees.
Utility Models: Usually last for 10 years from the filing date.
Industrial Designs: Generally last for 10 years, with the possibility of renewal.
Overview
A utility model patent could be highly suitable for my water leak detection project. This type of patent is ideal for inventions that involve improvements or incremental changes to existing technologies.
Given the technical nature of my project and the potential incremental innovations it brings to water leak detection and management systems, a utility model patent could provide the right level of protection without the stringent requirements of a standard invention patent. However, with this form that indecopi offers I would be restricting my design for other people to use, which would go against the entire FabAcademy program.
Creative Commons (CC)
I have found an organization that offers free licenses which I mention below:

Creative Commons (CC) is a nonprofit organization that provides free licenses for creators to share their works more flexibly while retaining their copyright. These licenses allow authors to specify how others can use their works, promoting a balance between copyright protection and the ability to share and legally reuse content easily.
Creative Commons licenses are divided into several categories, combining different permissions and restrictions. The most common combinations include:
Attribution (BY): Others can distribute, remix, adapt, and build upon the work, even commercially, as long as they credit the original creator.
NonCommercial (NC): Others can distribute, remix, adapt, and build upon the work, but not for commercial purposes.
NoDerivatives (ND): Others can redistribute the work in its original form, both commercially and non-commercially, but cannot create derivative works based on it.
ShareAlike (SA): Others can remix, adapt, and build upon the work for any purpose, even commercially, as long as they license their new creations under the same terms.
These licenses can be combined to form six main licenses:
CC BY: Attribution.
CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike.
CC BY-ND: Attribution-NoDerivatives.
CC BY-NC: Attribution-NonCommercial.
CC BY-NC-SA: Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike.
CC BY-NC-ND: Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives.
These licenses facilitate the legal distribution and use of creative, educational, and scientific works, promoting global access and collaboration.
The license I choose was: Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International. This license requires that reusers give credit to the creator. It allows reusers to distribute, remix, adapt, and build upon the material in any medium or format, for noncommercial purposes only.
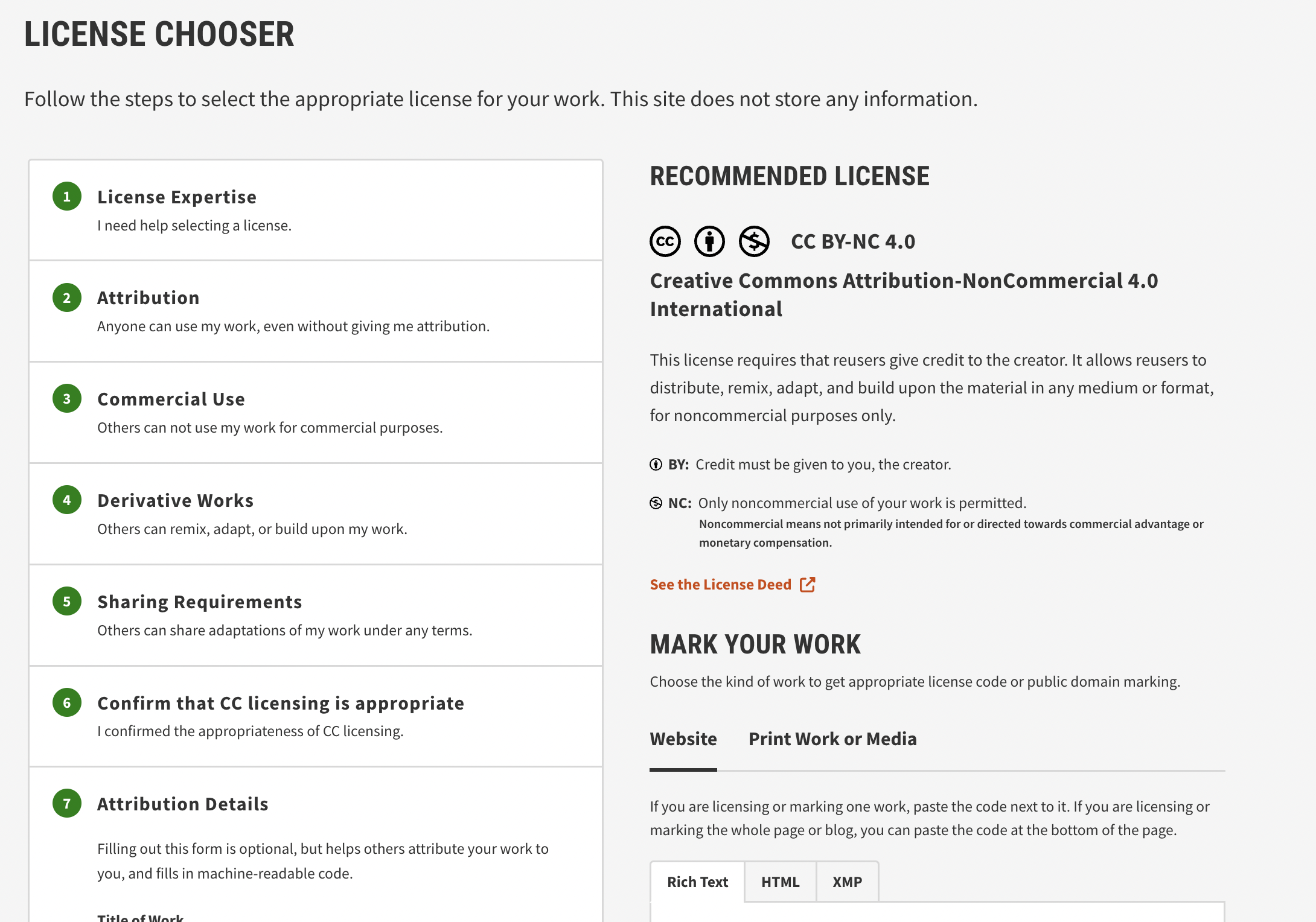

This is a link provided by the organization to see the license:
Aqua Alert by Ernesto Buendia Platas is licensed under CC BY-NC 4.0
Summary slide
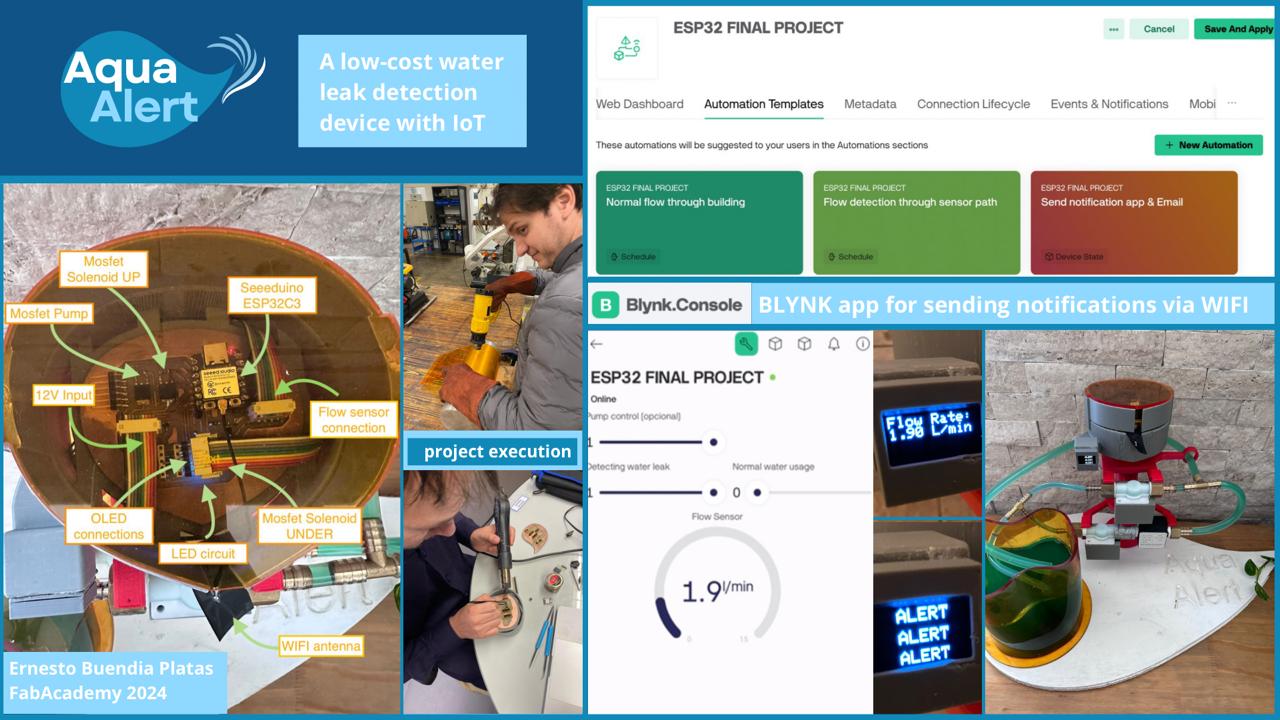
Video clip
Files:
Manual for patents in Peru - INDECOPI