1. Project management
Over the course of this week, my primary focus was to crystallize the concept for my final project. I delved into the details, meticulously outlining the key components and goals to ensure a comprehensive and well-defined project scope. At the same time, I began to familiarize myself with the intricacies of the documentation process. This involved gaining the ability to articulate the project's purpose, methodology, and expected deliverables in a structured manner. Through this meticulous documentation, I aim to provide a clear roadmap for the project's development and evaluation. As I navigate through this initial phase, I am committed to refining and expanding my project idea and laying a solid foundation for its successful implementation in the weeks to come.
Research
The documentation of school projects through web pages is an essential practice in contemporary educational environments. It provides a significant dimension to the learning and collaboration process. This modality is important because it creates an accessible and structured record of the progress and results of each project. This allows students and educators to follow and evaluate the development over time.
The benefits of using web pages to document educational projects are their accessibility and multimedia capabilities. This approach enables participants to share their experiences and knowledge with a wider audience, promoting transparency and collaboration. Additionally, incorporating images, videos, and links enriches the presentation of information and provides a more holistic understanding of the project.
Web documentation promotes digital skills by teaching students how to structure and present their work professionally online. This approach facilitates feedback between peers and educators, contributes to the development of effective communication skills, and presents students with the opportunity to build an educational digital identity.
Web desing
The creation of web pages can be achieved through the utilisation of a multitude of tools and techniques. However, the most prevalent and pervasive approach within the technological community is the employment of HTML, coupled with the integration of CSS and JavaScript elements. This methodology will be the chosen avenue for the development of my future web pages.

Images taken from: https://www.cursosgis.com/como-integramos-los-lenguajes-html-css-y-javascript/#.
Hypertext Markup Language (HTML) is the markup language utilized to structure and present content on the World Wide Web. It is based on a series of tags that define different types of content, including headings, paragraphs, images, and links. Each web page is constituted by a hierarchical structure of elements, which are organized by opening and closing tags. These tags are essential for browsers to correctly interpret and display information to the user. Additionally, HTML allows the inclusion of attributes within tags, which provide additional information about the element. Since its creation, HTML has evolved, and more recent versions, such as HTML5, have introduced new tags and functionalities, improving the semantics and accessibility of the content.
Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) is a style language used to describe the presentation of Hypertext Markup Language (HTML) or Extensible Markup Language (XML) documents. CSS enables developers to define how elements should be displayed on screen, on paper, or on other media. Some key features of CSS include:
- Separation of Content and Presentation: One of the key benefits of CSS is that it allows HTML content to be separated from its visual presentation. This makes it easier to maintain and update websites, as the content and presentation can be managed separately.
- Cascading styles: Styles may be applied to elements in a variety of ways (e.g., inline, in the document header, or in external files), and are applied in a specific order, allowing for inheritance and specificity.
- Responsive design: CSS enables the creation of layouts that adapt to different screen sizes and devices, which is a crucial aspect of the modern web.
- Flexibility and Control: CSS affords the user the ability to control a multitude of design elements, including color, fonts, spacing, alignment, background images, and more.
- Animations and Transitions: Additionally, CSS enables the creation of animations and transitions, which can be employed to enhance the user experience.
In conclusion, it can be stated that CSS is a fundamental element in the design and presentation of websites, enabling developers to create visually appealing and coherent user experiences.
JavaScript (JS) is an interpreted programming language that is primarily utilized to create interactivity in web pages. It is an indispensable component of modern web development, along with HTML and CSS. While HTML is responsible for establishing the structure of a web page, CSS is tasked with styling and presentation. JavaScript, on the other hand, enables the incorporation of dynamic behavior, such as content manipulation, form validation, and animation creation.
The integration of JavaScript with HTML is accomplished through the use of <script> tags, which can be placed within the <head> or at the conclusion of the <body> in order to ensure that the Document Object Model (DOM) has been fully loaded prior to the execution of the code. Additionally, events, such as onclick or onload, can be utilized to trigger the execution of scripts in response to user actions.
The ability of JavaScript to manipulate styles in real time, allowing for the alteration of colors, sizes, and positions of elements, enhances the user experience. The integration of JavaScript with HTML and CSS forms the foundation of interactive and engaging web development.
Parts of a website
A web page can be divided into three principal sections: the header, the body, and the footer. To identify each part of the page, it is necessary to place their respective tags: <head>, <body> and <footer>. The <head> section contains meta information and links to styles and scripts. The <body> section contains the visible content, such as text and images, while the <footer> section includes additional information, such as copyright and contact links.
Most commonly used HTML tags
- The <html></html> tag is utilized to demarcate the commencement and conclusion of an HTML document, signifying that the content within these tags constitutes a web page. This tag serves as the primary container for all elements within a document, including the header and body. To utilize it, the <html> tag is placed at the beginning of the document and closed with </html> at the end. Within the <html> tag, metadata, links to style sheets, and the visible content of the page can be included, allowing for the structured presentation of information in a web browser.
- The <p></p> tag is utilized in HTML to delineate paragraphs of text, thus facilitating the organization of content into coherent units. Each paragraph is situated between these tags, which enhances accessibility and search engine optimization. Moreover, browsers apply default margins to visually distinguish paragraphs, and CSS styles can be applied to customize their appearance or directly to the tag attributes.
- The <ul></ul> tag in HTML is used to create unordered lists, i.e. lists in which the items are not ordered in a specific order and are represented by bullets. Each item in the list is defined within the <li> tag, which stands for “list item.” To use it, the <ul> tag is placed at the beginning and the list items are closed with </ul>, while each item is enclosed between <li> and </li>. This structure allows information to be organized in a clear and visually appealing way, improving the readability of the content on a web page.
- The <ol></ol> tag in HTML is used to create ordered lists, i.e. lists in which the items have a specific order and are represented by numbers or letters. Each item in the list is also defined within the <li> tagand ends with </li>. This structure is useful for presenting sequential or sorted information, improving the clarity and organization of content on a web page.
- The HTML <br> tag is employed to insert a line break into text, thereby creating a vertical space between lines without initiating a new paragraph. This tag is an empty element, meaning that it does not necessitate a closing tag. It is frequently utilized in scenarios where the objective is to separate lines of text within a single block, such as in poems, addresses, or lists of items.
- The <div> tag in HTML is used as a generic container for grouping elements and is primarily used to structure the content of a web page. It has no semantic meaning on its own, but it allows you to apply CSS styles and manipulate elements using JavaScript. To use it, you place the <div> tag at the beginning of the block you want to group and close it with </div>. This flexibility makes it a valuable tool for organizing the design and presentation of content, facilitating the creation of complex and responsive layouts.
- In HTML, the headings are defined by the use of the <h1> to <h6> tags. The <h1> tag represents the highest level of heading, while the <h6> tag represents the lowest. These tags are indispensable for the hierarchical organization of content on a web page, facilitating the clear and logical presentation of information. The h1 heading is typically utilized for the primary title of the page, while subsequent headings are employed for sections and subsections, thereby enhancing the readability and accessibility of the content. Furthermore, the appropriate utilisation of headings facilitates search engine optimisation, as they are regarded as pivotal components within the content hierarchy.
- The <a></a> tag in HTML is used to create hyperlinks that allow users to navigate from one page to another or to different sections within the same page. The most common attribute of this tag is href, which specifies the URL of the destination to which you want to link. To use it, you place the <a> tag with the href attribute followed by the desired address, and close it with </a>, including the text or content you want to display as a link between both tags. This functionality is essential for interactivity on the web, facilitating the connection between different resources and improving the user experience.
- The <img> tag in HTML is used to insert images into a web page. This tag is an empty element, meaning it does not need a closing tag, and is placed in the document where you want the image to appear. To use it, you include the src attribute, which specifies the URL of the image, and the alt attribute, which provides an alternative description of the image, useful for accessibility and in case the image fails to load. Other important attributes include width and height, which allow you to adjust the dimensions of the image. The <img> tag is essential for visually enriching content and improving the user experience on a web page.
- Table tags in HTML are used for the purpose of structuring and presenting data in tabular form. The <table> tag marks the beginning of the table, while the <tr> tag is employed to create rows within the table. Within each row, the <th> and <td> tags are used to define cells. The <th> tag is used for column headers and is displayed in bold and centered type, while the <td> tag is used for regular data cells. Additionally, attributes such as border can be included to define the border of the table and colspan or rowspan to merge cells.
- The <video></video> tag in HTML is utilized to embed video content into a web page, thereby enabling users to control the playback of video content directly within the browser. In order to utilize this functionality, it is necessary to include the <video> tag and specify the video source using either the <source> tag or the src attribute. The primary attributes of the video tag include the controls attribute, which adds playback controls such as play, pause, and volume; the autoplay attribute, which allows the video to play automatically when the page loads; the loop attribute, which causes the video to loop indefinitely; and the muted attribute, which starts the video without sound. Additionally, the dimensions of the video can be defined using the width and height attributes.
More information about HTML can be found at https://html.spec.whatwg.org/.
Git management
The initial step is to establish an SSH key for the management of Git, which is accomplished through the execution of the following command:
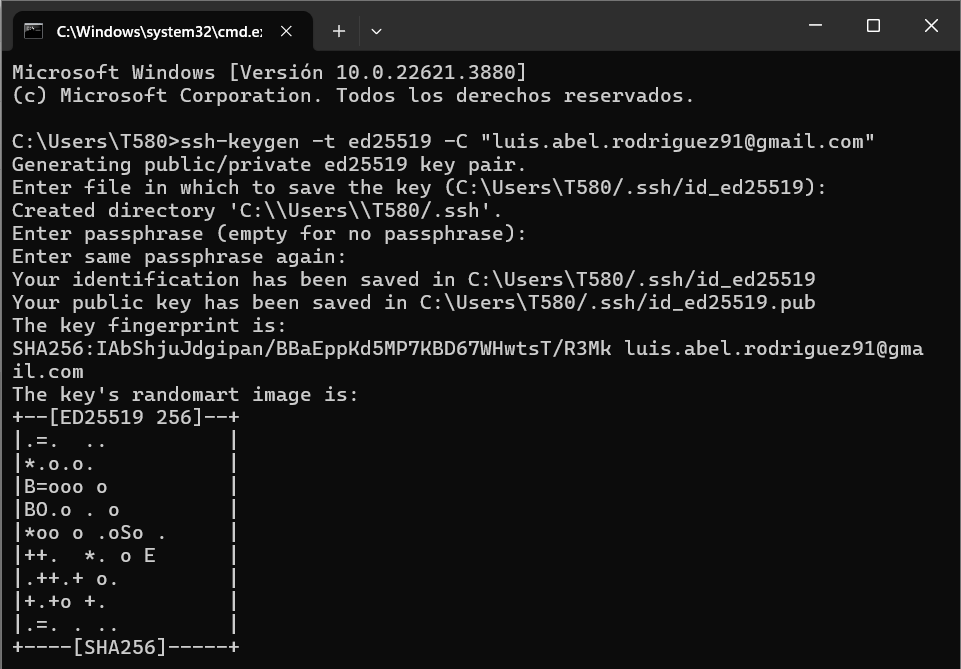
The process of creating an SSH key.
Subsequently, the successful generation of the SSH key is verified:

SSH key successfully created.
At this point, we proceed to clone our local repository in GitLab:
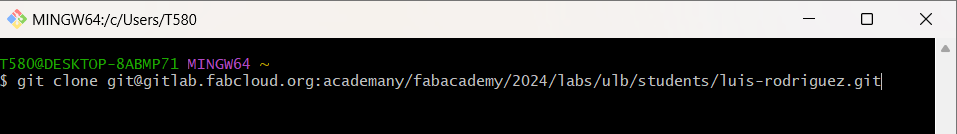
Cloning local repository into GitLab.
Once the modifications have been made to the repository, they can be pushed using the following commands:
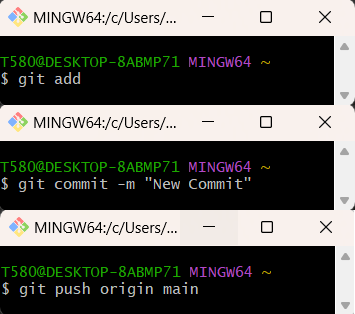
Git commands.
The pages
In regard to the weekly assignment page, a 4x5 matrix structure of images with their respective captions was utilized, wherein both elements direct the viewer to their respective weekly page. The images were generated through Bing, based on the descriptions I created for the AI of the weekly theme.

Images generated by Bing.
In the "About Me" section of my personal page, I have provided a concise overview of my educational and professional background.
At last, I completed the page design for my final project, which comprises a wave flume constructed from acrylic. This project draws upon my previous experience in the construction of a similar structure during my master's degree at the Faculty of Physicss of the University of Havana.
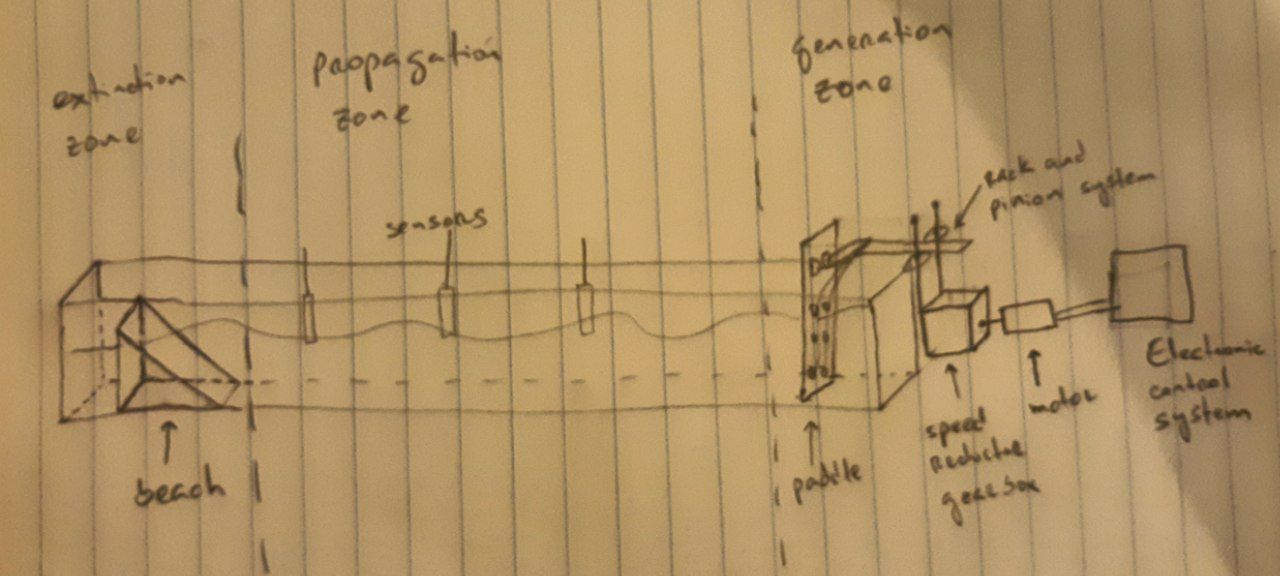
Sketch of my final project.