1. Group assignment:
probe an input device's analog levels and digital signals.
2. Individual assignment:
measure something: add a sensor to a microcontroller board
that you have designed and read it.
an input device is a piece of equipment used to provide data and control signals to an information processing system, such as a computer or information appliance. Examples of input devices include keyboards, computer mice, scanners, cameras, joysticks, and microphones.
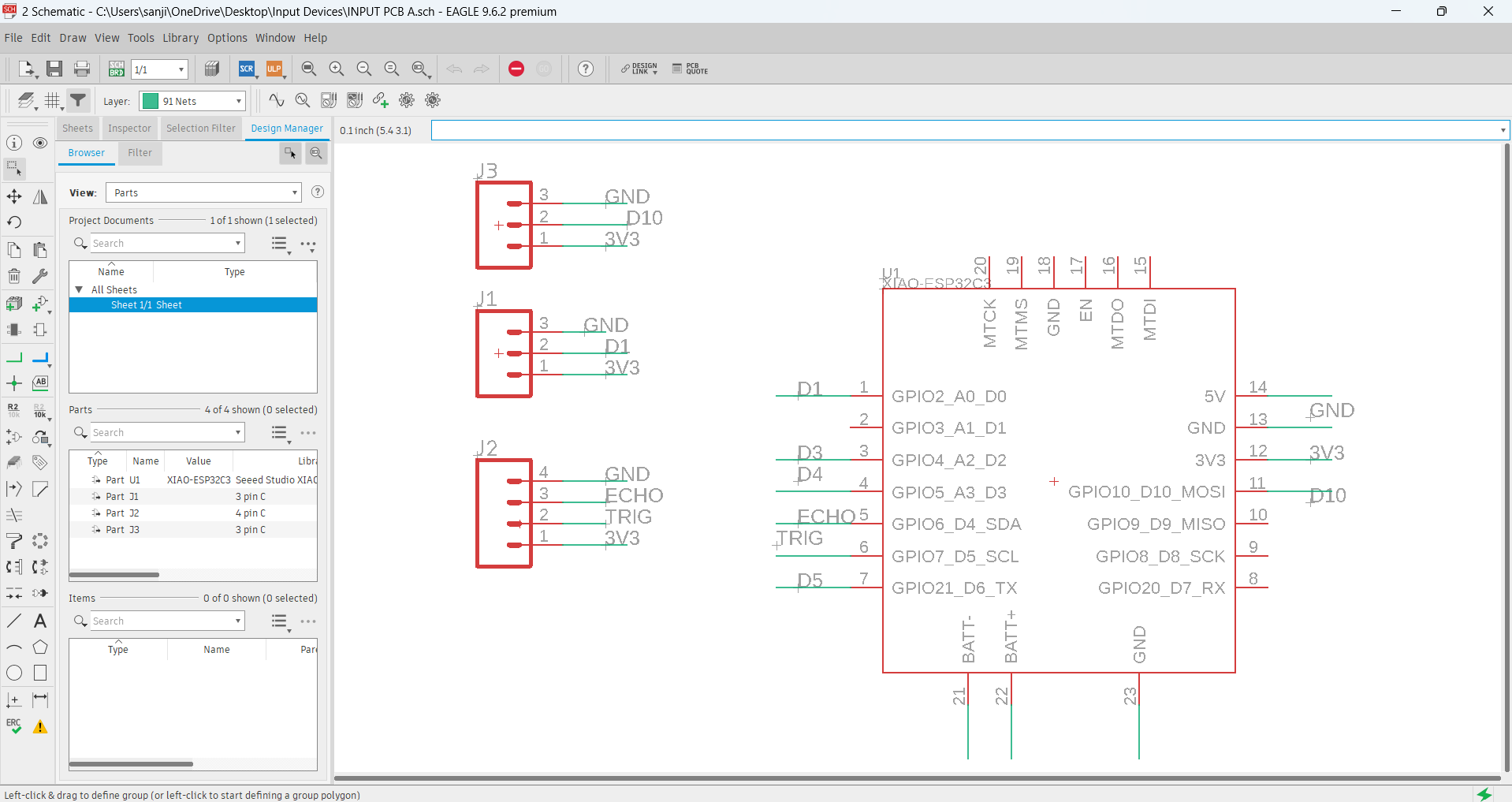
#_Schematic_Diagram_:)

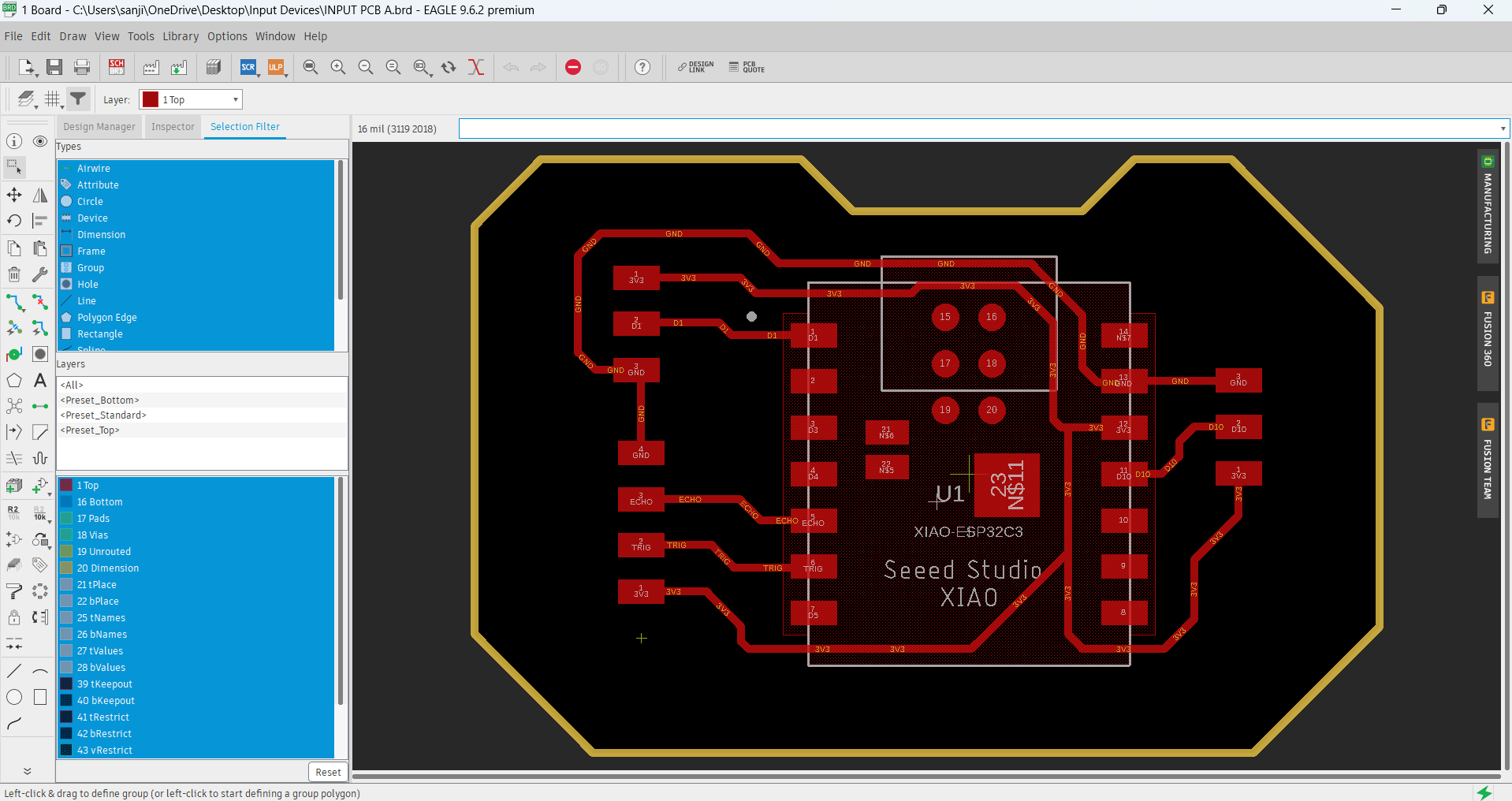
#_PCB_Board_:)
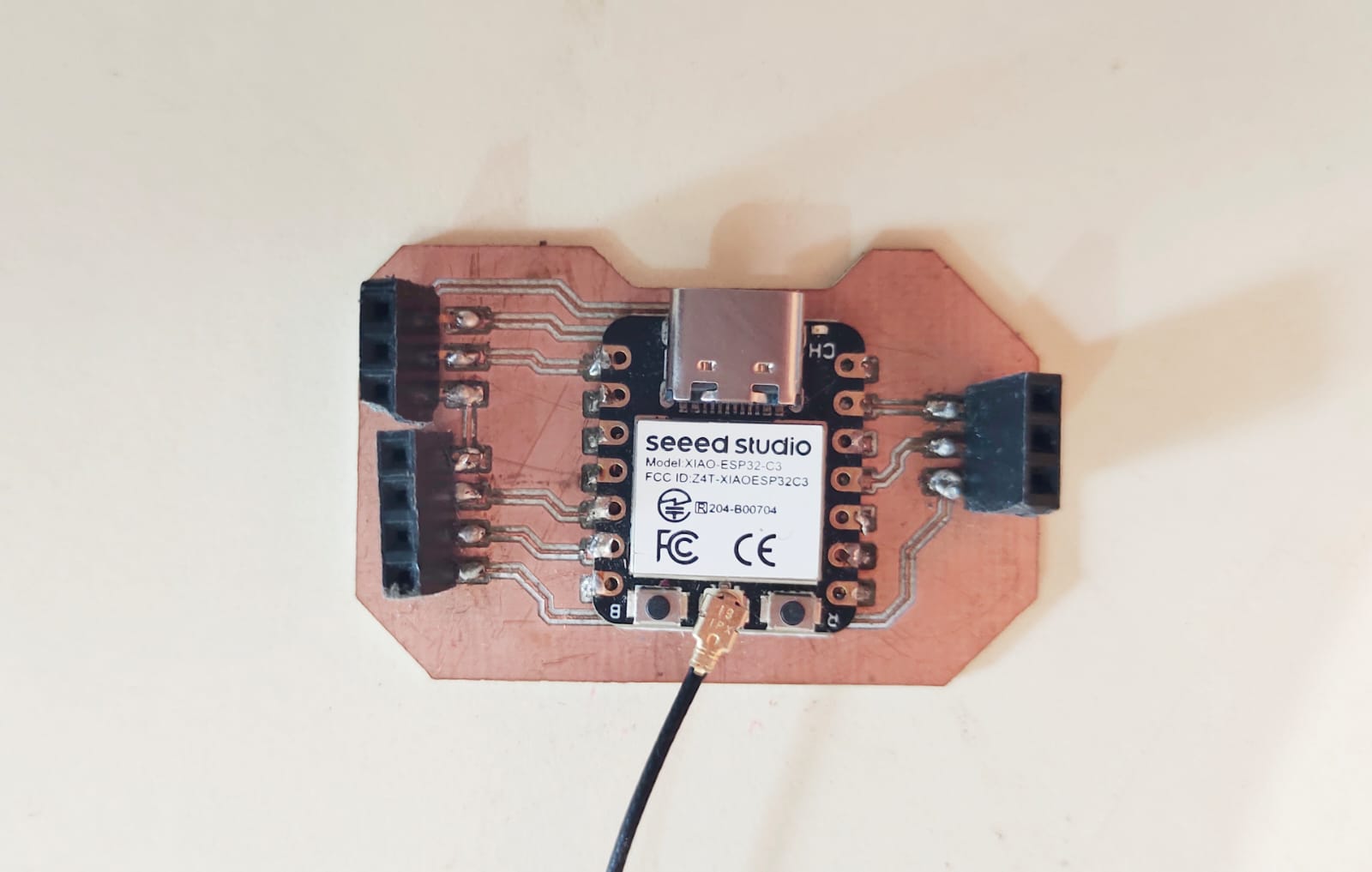
#_Final_Board_:)
DHT11 :- The DHT11 is a commonly used Temperature and humidity sensor that comes with a dedicated NTC to measure temperature and an 8-bit microcontroller to output the values of temperature and humidity as serial data.
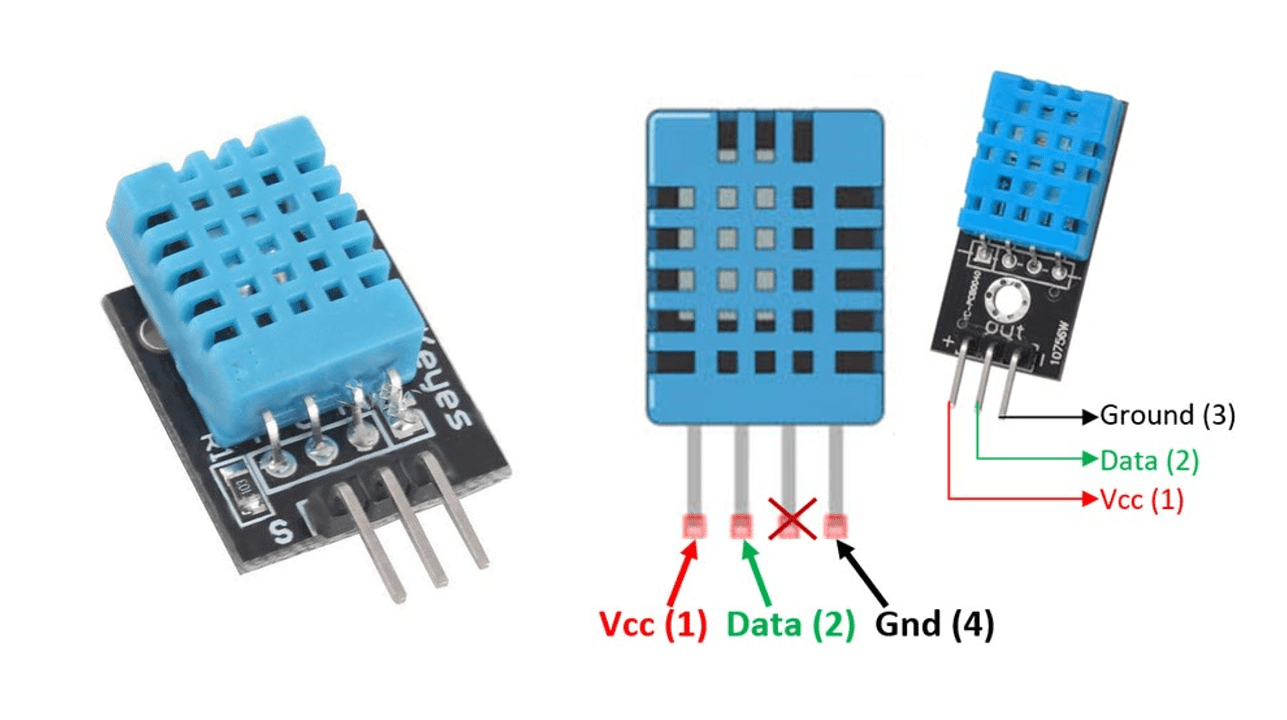
DHT11 Pinout Configuration
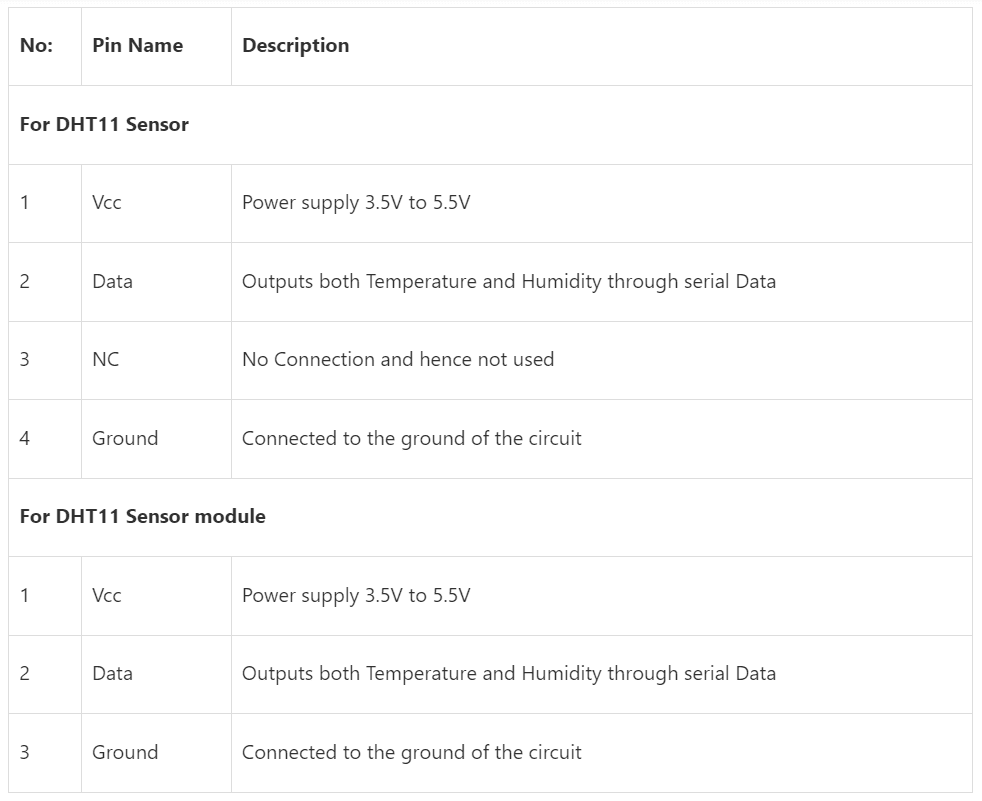
DHT11 Specifications :-
Operating Voltage: 3.5V to 5.5V
Operating current: 0.3mA (measuring) 60uA (standby)
Output: Serial data
Temperature Range: 0°C to 50°C
Humidity Range: 20% to 90%
Resolution: Temperature and Humidity both are 16-bit
Accuracy: ±1°C and ±1%
#_Connections_:)
XIAO ESP32C3 --> DHT11
3V3(VCC) --> VCC pin
D10 --> Data pin
GND --> Ground pin
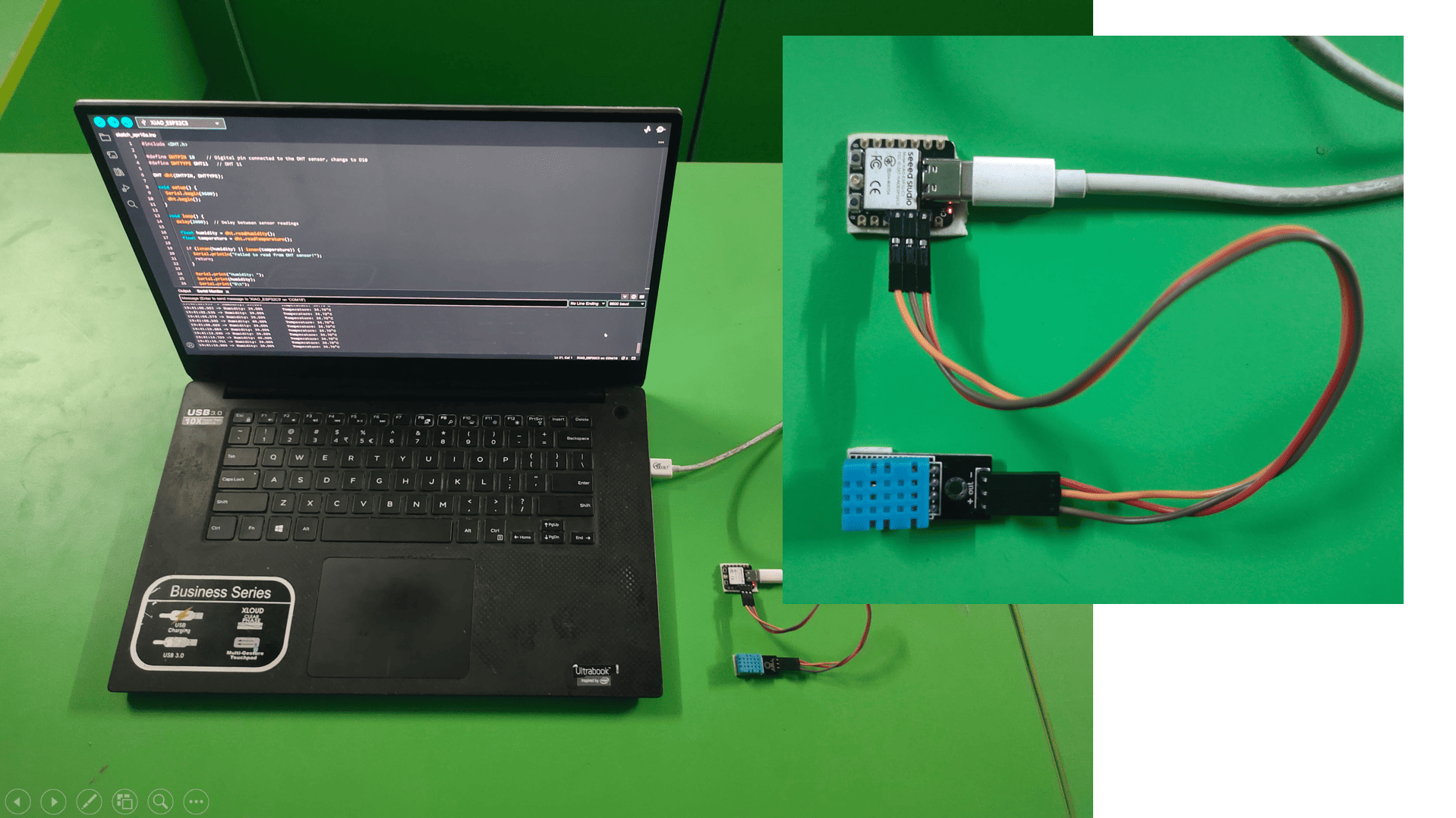
#_Program_:)
#include < DHT.h >
#define DHTPIN 10 // Digital pin connected to the DHT sensor, change to D10
#define DHTTYPE DHT11 // DHT 11
DHT dht(DHTPIN, DHTTYPE);
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
dht.begin();
}
void loop() {
delay(1000); // Delay between sensor readings
float humidity = dht.readHumidity();
float temperature = dht.readTemperature();
if (isnan(humidity) || isnan(temperature)) {
Serial.println("Failed to read from DHT sensor!");
return;
}
Serial.print("Humidity: ");
Serial.print(humidity);
Serial.print("%\t");
Serial.print("Temperature: ");
Serial.print(temperature);
Serial.println("°C");
}
#_Code_Explanation... :)
#include < DHT.h >
This line includes the DHT.h library, which provides functions for interacting with DHT sensors like the DHT11.
#define DHTPIN 10 // Digital pin connected to the DHT sensor.
#define DHTTYPE DHT11 // DHT 11 Sensor
These lines define constants:
DHTPIN: Sets the digital pin number where the DHT sensor is connected (pin 10 in this case, you can change it to match your actual pin).
DHTTYPE: Specifies the type of sensor being used (DHT11 in this case).
DHT dht(DHTPIN, DHTTYPE);
This line creates an object called dht of the DHT class. It provides the pin number and sensor type information defined earlier.
(setup function):
void setup() { ... }: This block defines the setup function which runs only once when the program starts.
Serial.begin(9600);: Initializes the serial communication at a baud rate of 9600. This allows the program to send data to the serial monitor on your computer for viewing.
dht.begin();: Starts the communication with the DHT sensor using the dht object.
(loop function):
void loop() { ... }: This block defines the loop function which runs repeatedly after the setup function finishes. This loop continuously reads and prints sensor data.
delay(1000); // Delay between sensor readings: This line pauses the program for 1 second (1000 milliseconds) between readings, preventing overwhelming the sensor with requests.
float humidity = dht.readHumidity();: Reads the humidity value from the sensor and stores it in the humidity variable (floating-point number).
float temperature = dht.readTemperature();: Reads the temperature value from the sensor and stores it in the temperature variable (floating-point number).
if (isnan(humidity) || isnan(temperature)) { ... }: This if statement checks if either the humidity or temperature reading resulted in "Not a Number" (NaN). This can happen due to sensor errors or communication issues.
Serial.println("Failed to read from DHT sensor!");: If a reading is NaN, this line prints an error message to the serial monitor.
return;: This statement exits the current loop iteration if there's an error, preventing further processing of potentially invalid data.
Serial.print("Humidity: ");: Prints the label "Humidity: " to the serial monitor.
Serial.print(humidity);: Prints the actual humidity value read from the sensor.
Serial.print("%\t");: Prints the percent symbol (%) and a tab character for formatting.
Serial.print("Temperature: ");: Prints the label "Temperature: " to the serial monitor.
Serial.print(temperature);: Prints the actual temperature value read from the sensor.
Serial.println("°C");: Prints the degree symbol (°) and "C" to indicate Celsius units, followed by a newline character.
#_Output_:)
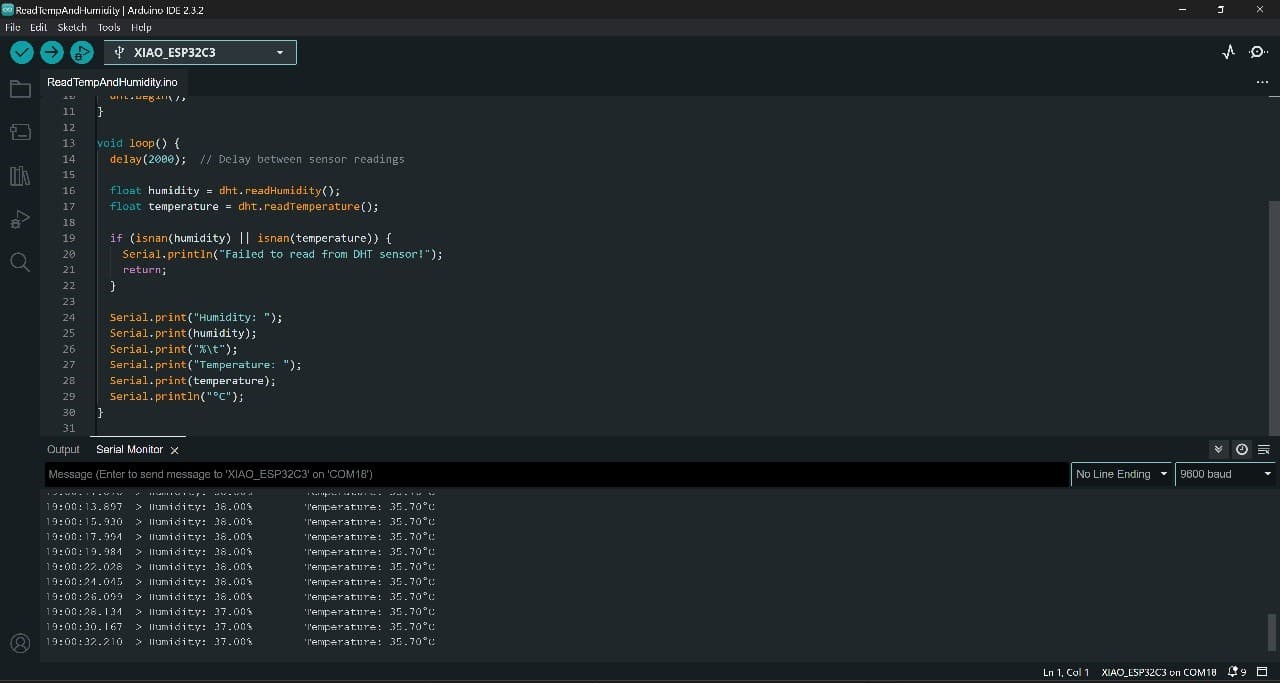
#_Output_on_PCB_:)