WEEK 13: NETWORKING AND COMMUNICATIONS
Networking refers to the practice of connecting computers and other devices together to share resources and information. This can be done using wired or wireless connections and allows devices to communicate with each other.
Communications refers to the process of exchanging information between two or more entities. In the context of networking, communications often involve transmitting data between devices over a network.
Networking can be broadly classified into two main types based on the type of connection used: wired and wireless.
Wired involves the use of physical connections to connect devices.
Wireless enables devices to communicate without the need for physical connections
Group Assignment
For this group assignment, we successfully sent a message between two distinct projects. This exercise involved setting up communication protocols, ensuring data integrity, and verifying successful message delivery. Our team's collaboration and technical skills were essential in achieving this milestone.
Personal work to do
design, build, and connect wired or wireless node(s) with network or bus addresses and local input &/or output device(s).
For the assignment, I tried Wireless communication, ESPNOW.
ESPNOW is a communication protocol developed by Espressif Systems, the manufacturer of the popular ESP8266 and ESP32 series of microcontrollers. It is designed for low-power, peer-to-peer communication between ESP8266 and ESP32 devices, allowing them to exchange data without the need for a traditional Wi-Fi network or internet connection.
I worked on two devices of ESP8266 to test with ESPNOW.
ESP-NOW is a wireless communication protocol based on the data-link layer, which reduces the five layers of the OSI model to only one.
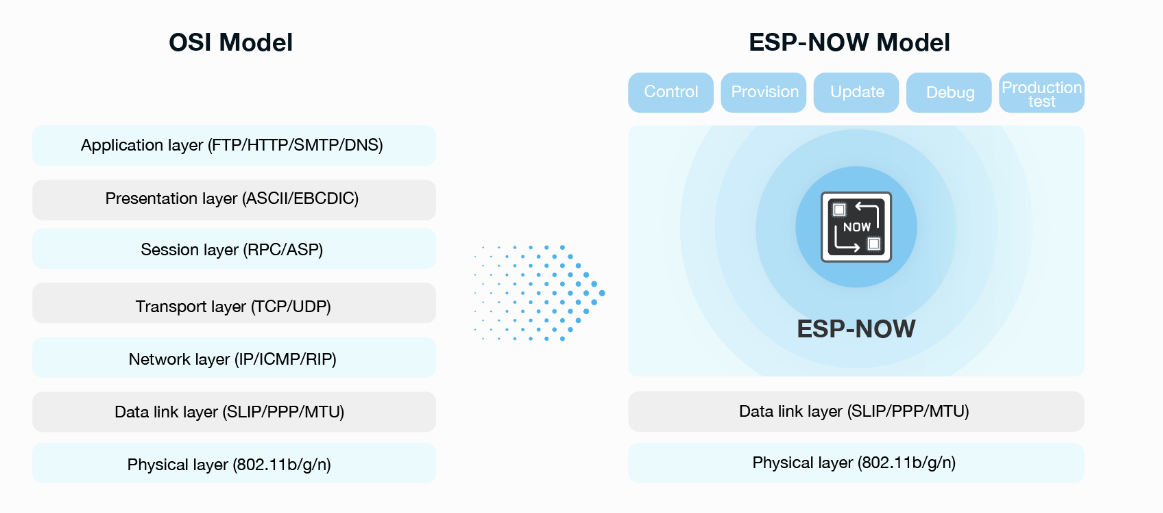
The above screenshot taken from web of espressif, if you are interested for details.
Code development for a Sender and Receiver devises.
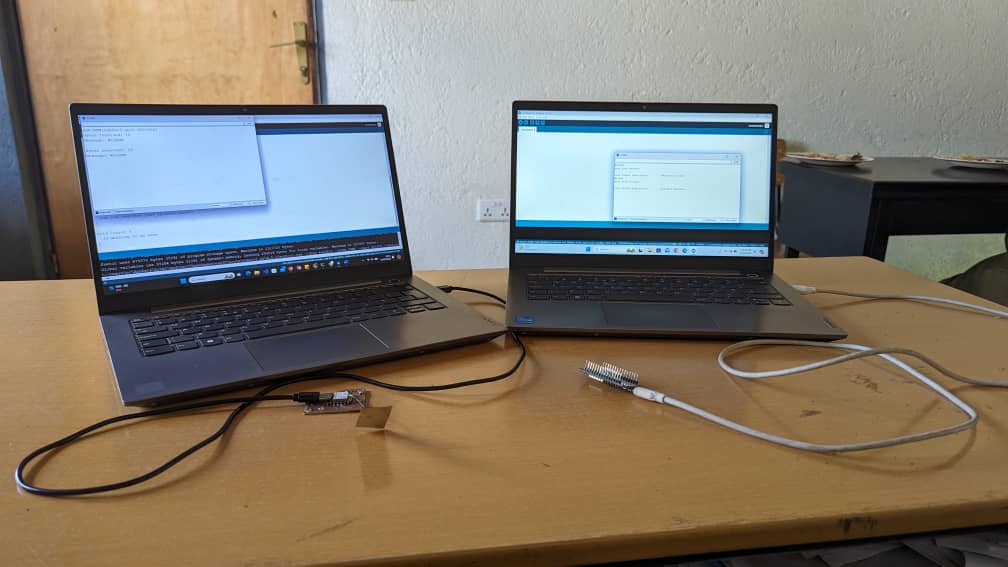
Setup of the receiver with my own desigend PCB with XIAO-ESP32-C3 and Sender With ESP8266 Module.
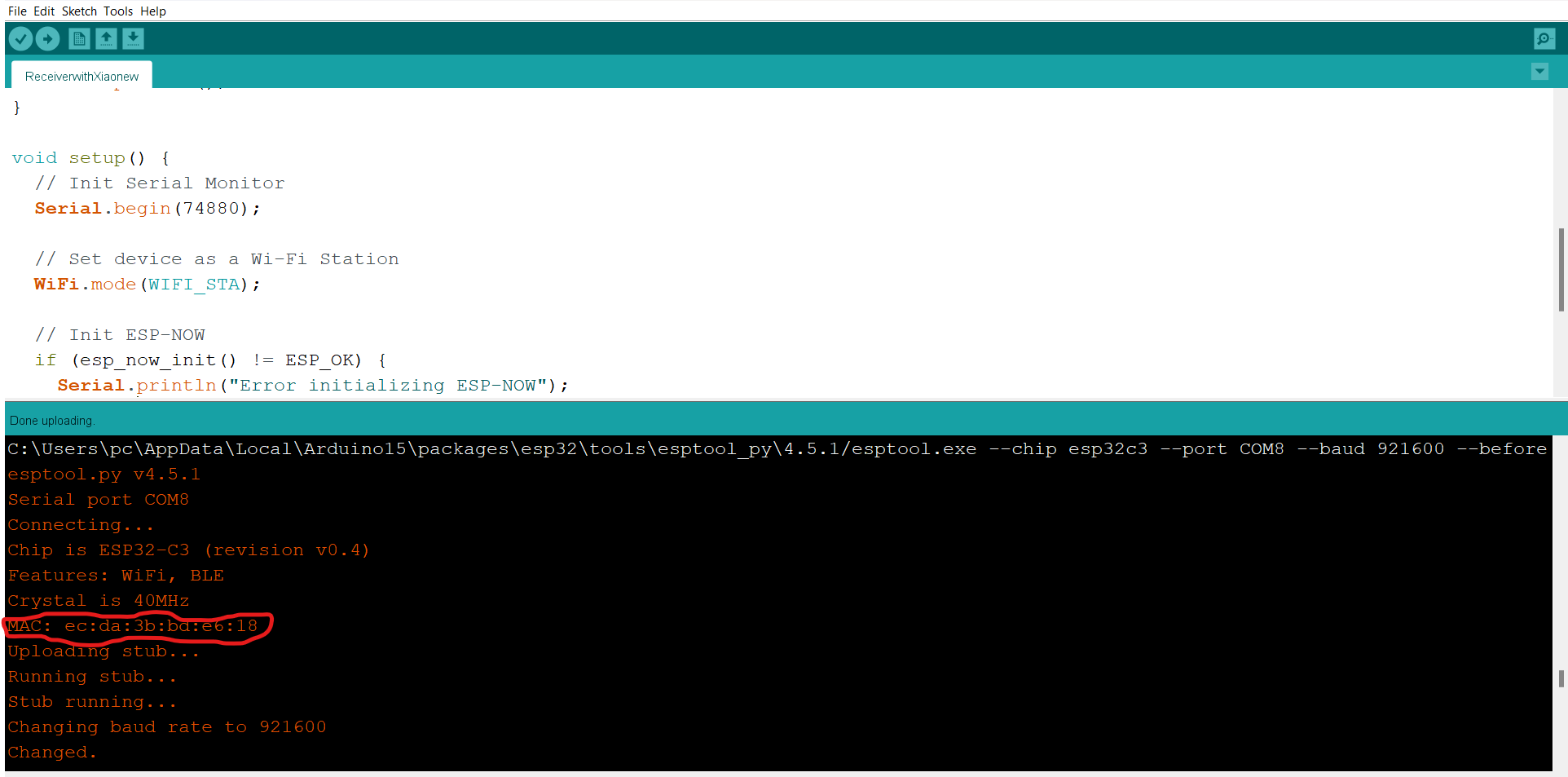
I. Code for Receiver device
Remember to copy the Mac Address of the receiver to put in the sender.
#include <WiFi.h>
#include <esp_now.h>
String myData = "Ready";
// Callback function that will be executed when data is received
void OnDataRecv(const uint8_t *mac, const uint8_t *incomingData, int len) {
Serial.print("Bytes received: ");
Serial.println(len);
Serial.print("Message: ");
char message[len + 1];
memcpy(message, incomingData, len);
message[len] = '\0'; // Null-terminate the string
myData = String(message);
Serial.println(myData);
Serial.println();
}
void setup() {
// Init Serial Monitor
Serial.begin(74880);
// Set device as a Wi-Fi Station
WiFi.mode(WIFI_STA);
// Init ESP-NOW
if (esp_now_init() != ESP_OK) {
Serial.println("Error initializing ESP-NOW");
return;
}
// Register callback function to be called when data is received
esp_now_register_recv_cb(OnDataRecv);
}
void loop() {
// Nothing to do here
}
The MAC is found here.
II. Code for Sender
In the code of sender, you have to remember to put Mac Address of Receiver copied from serial monitor after uploading the reciever code in ESP8266.
#include <ESP8266WiFi.h>
#include <espnow.h>
// REPLACE WITH YOUR RECEIVER MAC Address
uint8_t broadcastAddress[] = {0xec, 0xda, 0x3b, 0xbd, 0xe6, 0x18};
String myData = "Test";
// Callback function called when data is sent
void OnDataSent(uint8_t *mac_addr, uint8_t status) {
Serial.print("\r\nLast Packet Send Status:\t");
Serial.println(status == 0 ? "Delivery Success" : "Delivery Fail");
}
void setup() {
// Init Serial Monitor
Serial.begin(74880);
// Set device as a Wi-Fi Station
WiFi.mode(WIFI_STA);
// Initilize ESP-NOW
if (esp_now_init() != 0) {
Serial.println("Error initializing ESP-NOW");
return;
} else {
Serial.println("Initialized ESP-NOW");
}
// Once ESPNow is successfully Init, we will register for Send CB to
// get the status of Trasnmitted packet
esp_now_set_self_role(ESP_NOW_ROLE_CONTROLLER);
esp_now_register_send_cb(OnDataSent);
// Add peer
if (esp_now_add_peer(broadcastAddress, ESP_NOW_ROLE_SLAVE, 0, NULL, 0) != 0) {
Serial.println("Failed to add peer");
return;
} else {
Serial.println("Added peer");
}
if (esp_now_is_peer_exist(broadcastAddress)) {
Serial.println("Peer exists");
} else
Serial.println("No exists");
}
void loop() {
if (Serial.available() > 0) {
myData = Serial.readString(); //read until timeout
myData.trim(); // remove any \r \n whitespace at the end of the String
Serial.println(myData);
// Send message via ESP-NOW
int result = esp_now_send(broadcastAddress, (uint8_t *)&myData, sizeof(myData));
if (result == 0) {
Serial.println("Sent with success");
} else {
Serial.println("Error sending the data");
}
}
delay(1000);
}
The output can be seen in the video below.