16. Aplications and Implications
What does it do?
My final project is divided into 2 different parts; a remote-control model aircraft with functional control systems moved by servos that respond to the user´s input and steers the plane accordingly. The other part is a cockpit´s controls simulator consisting of the center stick, throttle, flaps selector, and rudder pedals.
Who has done what beforehand?
Remote control drones have been created by individuals and companies for decades now, where there is an endless market and community behind them. Flight simulator cockpits are usually made for video games and simulators. One example of this product on the market is the “Flight Simulator Boeing Military Edition”, a semi realistic cockpit designed for simulators.
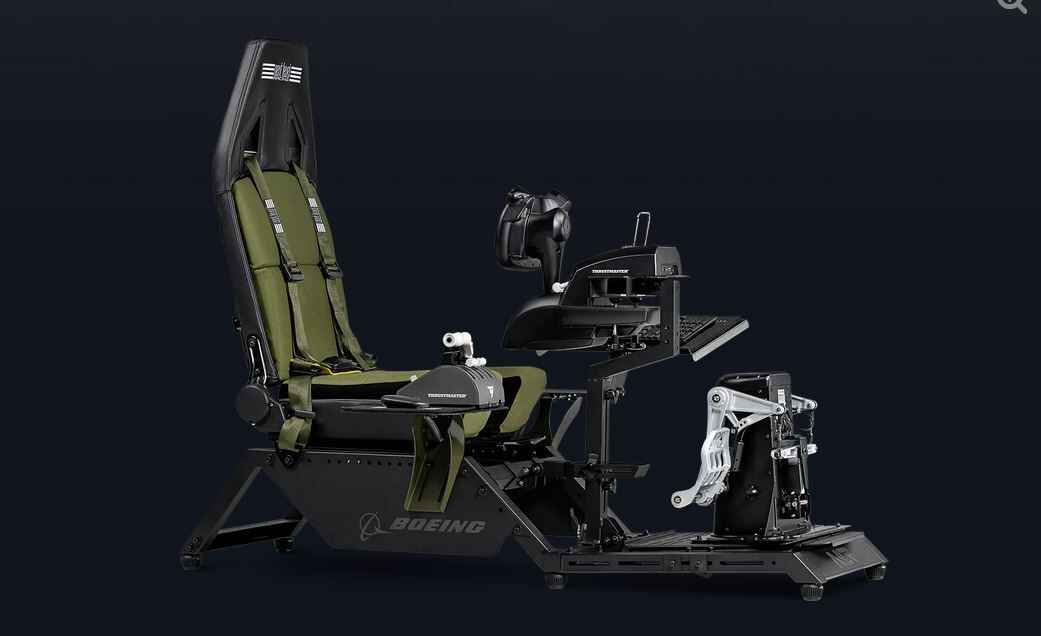

What will you design
I designed the overall build of the project in Solidworks, as well as all the subfiles needed to produce the project; laser cuts, CNC routing, individual 3D printed objects. Also designed the PCB to house the microcontroller that will control all the inputs and outputs.
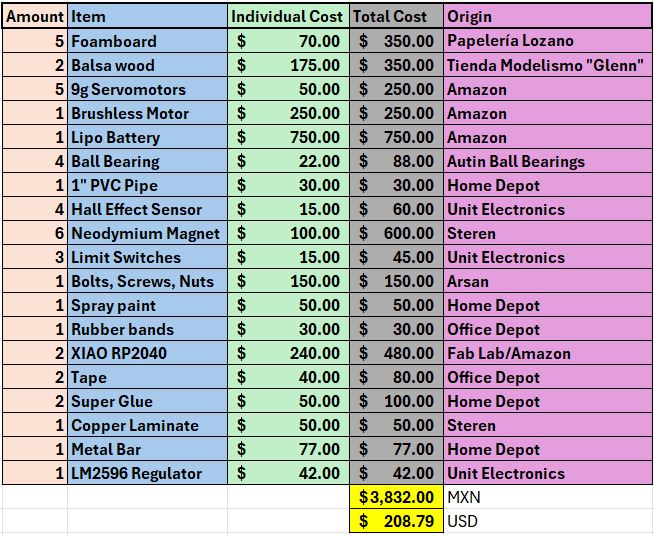
What materials and components will be used? Where will they come from? How much will they cost?
What parts and systems will be made? What processes will be used?
- 3D CAD design: Create a 1:1 scale of the design to have it as a reference to base the project on.
- Laser cutting: The foamboard which creates the overall structure of the plane, is cut with high speed parameters on the laser cutter.
- CNC Router cutting: The throttle/flaps assembly is made almost in it´s entirety with 12mm MDF.
- 3D printing: The control stick base, which controls the movement and distance of the joystick, is made with 3D printed parts taken directly from the 3D assembly on Solidworks.
- Electronics Design: A XIAO RP2040 that connects and controls both the inputs and the outputs of the system is wired on a PBC designed for this purpose.
- Metal cutting and drilling: Metal profiles and tubes were cut using a circular saw and a drill.
- How accurate and effective are the control systems in the airplane?
- Can they control the movement in flight?
- What range does the connection have?
- What is the battery duration during flight?
What questions need to be answered?
How will it be evaluated?
The main goal of this assembly is to move control surfaces of a scaled remote-control airplane, meaning the ailerons, rudder, elevator, motor speed amongst others, with inputs made from the controls. The controls should simulate to some degree, the inputs a real plane should have in the cockpit to control and aircraft by moving the control surfaces.

