1. Project management
Hello intriguing reader, welcome to the first week of this journey, in this week we have a busy agenda, that include creating our own webpage, learning the git and cloud based git software, think,sketch an idea for the final project, add the neccesary parts to the website and sign the student's Agreement, so lets start with the first block:
So, what is version control?
Version control is a system that manages and tracks changes to files, particularly source code, over time, It allows developers to revert to previous versions, compare changes, and allows simultaneous collaborative work, Git is the most widely used version control protocol, offering a decentralized approach where each contributor has a complete history of the project. Other version control protocols include Subversion (SVN), which uses a centralized model where a single server hosts the repository, and Mercurial, which is similar to Git in its distributed nature but emphasizes simplicity and performance.

Git
Git, a distributed version control system, revolutionizes collaborative software development with its powerful branching system. Branches in Git allow you to work on isolated features or fixes without impacting the main codebase. By creating a branch, you can experiment, test ideas, and make changes independently. Once a feature is complete or a bug fixed, the branch can be merged back into the main branch (often called master or main). it runs locally with previous installation and you can upgrade the experience with cloud computing appliances like Github or GitLab improving colaboration across devices and developers, it has many commands in order to create, merge, clone, upload and check the status of a repository, that's why I got this cheat sheet (credits: Danny Adams).
 (1)-min.jpg)
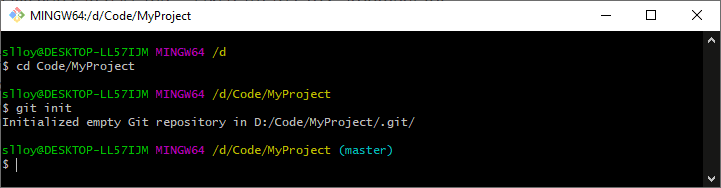
To start using git we need to run it locally so go to the Download links and choose the one for your PC, when you install it and choose to have git in the root of your computer you will gain access to two new options git GUI it's a visual interface to know the status of your branch and the new terminal git bash.

When you open this new terminal you can use the command git innit to create a new git file and then git remote add origin "GitLab repository URL" to log with your credentials.
Let's suppose you have added and edited a bunch of files and now you feel ready too upload your changes too the cloud, use the commands in the next order: git status(to see what've changed) / git add . (to upload al the changes to) / git commit -m 'a message'(wraps the changes) / git push (send them too the cloud), if you see an error related to credentials login, just check if your email and name are well written and you have logged in your gitlab account.

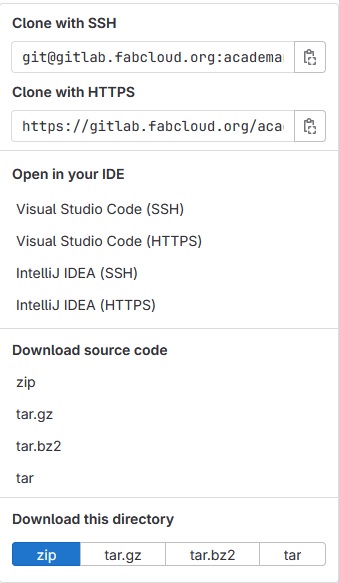
Steps to clone a repository
In the cloud servers like github or gitlab, on the top right of a repository is a button called code, there you will find options to extract the code and all documents of the repository, the easiest method to clone something in your pc is using the https clone tool, with the (git clone {https key}) command in your git terminal you can clone easily any project even if you dont own the credentials, using the ssh method requires you to create keys in every computer you clone, then those keys will be need to be added in your profile, thats why in this case because we are working with gitlabs and the login doesnt take many time I've used the https method.
web development tools
Selecting an IDE
One of the most impactfull things in web development and programming is the application where you write the code, you can do it in the default text editor but choosing a powerfull tool improves the way you code with formatting and highlighting, the most popular ones are: sublime text, visual studio code and jetbrains stuff; i choosed vscode as i like the community and the power it has.
What i recommend you is to allways have a lot of folders to keep track of your items, as you can see the file manager inside VS code is really easy to navigate and every time you need to work in just open it form the main folder and have all your files at handle.
Other usefull part of vs code is the addons and themes manager, you can get the one that makes you understand your code easier and powerfull addons like this live server addon wich is really helpfull.
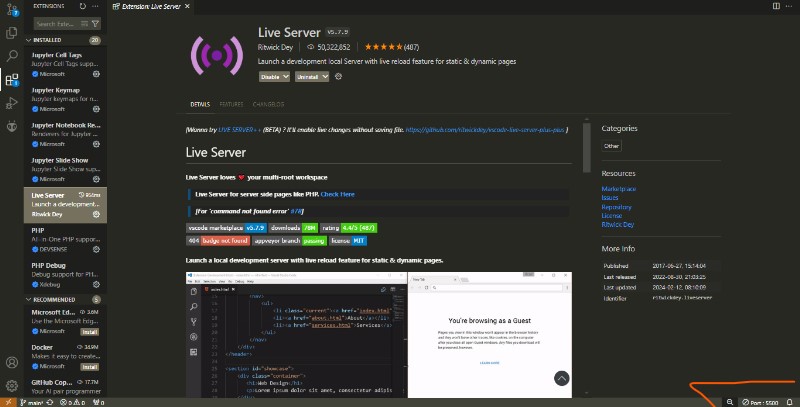
Usefull websites and libraries
I'm not a big fan of the bootstrap library, i feel is a little bit discontinued, and when talking about style and design that's a very bad signal, so i recommend other sites like: freefrontend.com, you can use the examples from this site for inspiration or take the designs give credit and change them to make them yours.
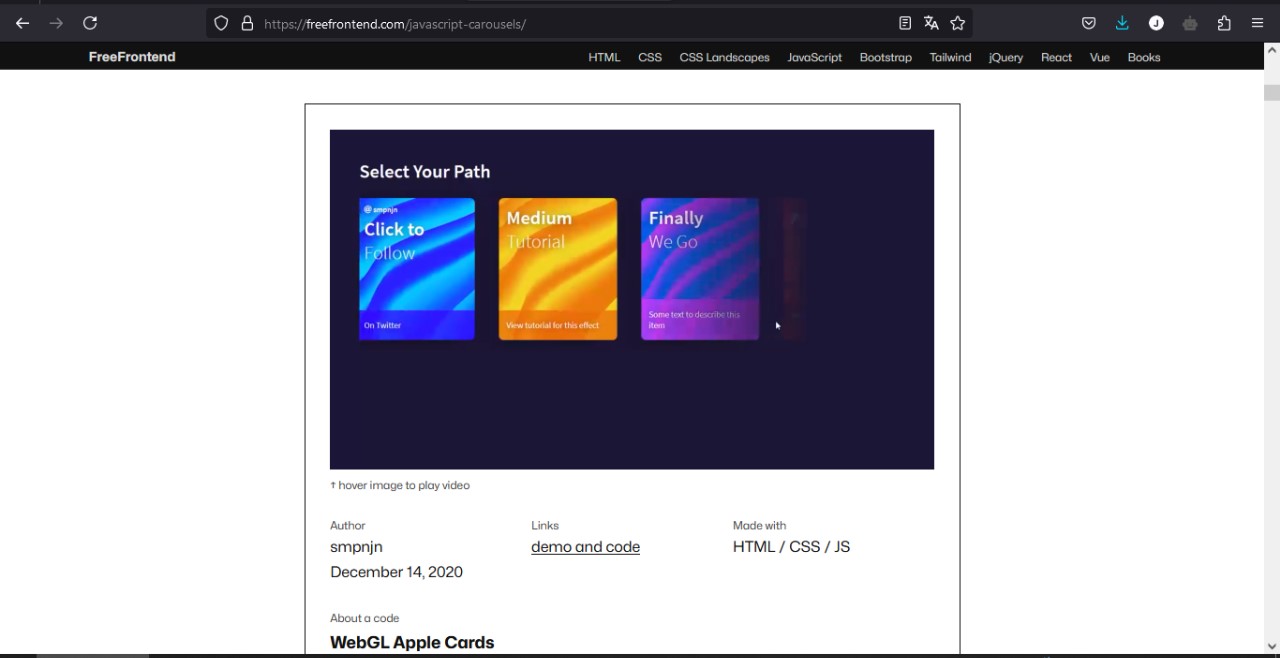
Giving my style to the webpage.
The first step (as it's permitted) is to clone a template to use as my working bench, the template provided by our local instructor, Rafael Perez template looks elegant and easy to edit in order to create my own design.
Things to change:
- Twist the page style
- Edit the landing page first block
- Change the weekly Assignments looks
- Add night mode
- Create gallerys.
- Create containers style
The base .html file
Click the link to download the .css, the .js and the webfonts, with a raw html to edit, to give style and build your html page you can use one or more of the elements combined or alone presented below, you can also create unique ones in the .css with bigger names for an easier understood.
| Element | Name | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| <a> | Anchor | Used for creating hyperlinks |
| <abbr> | Abbreviation | Represents an abbreviation or acronym |
| <address> | Address | Represents contact information for the author or owner of a document or article |
| <area> | Area | Defines an area inside an image map |
| <article> | Article | Represents a self-contained composition in a document |
| <aside> | Aside | Represents content indirectly related to the main content |
| <audio> | Audio | Used for embedding sound content |
| <b> | Bold | Makes text bold without implying any extra importance |
| <base> | Base | Specifies the base URL for relative URLs in a document |
| <bdi> | Bidirectional Isolate | Isolates a part of text that might be formatted in a different direction from other text outside it |
| <bdo> | Bidirectional Override | Overrides the current text direction |
| <blockquote> | Blockquote | Represents a section quoted from another source |
| <body> | Body | Represents the content of an HTML document |
| <br> | Break | Inserts a line break |
| <button> | Button | Represents a clickable button |
| <canvas> | Canvas | Used for drawing graphics via scripting (usually JavaScript) |
| <caption> | Caption | Defines a table caption |
| <cite> | Citation | Represents the title of a work |
| <code> | Code | Displays a fragment of computer code |
| <col> | Column | Specifies column properties for each column within a <colgroup> element |
| <colgroup> | Column Group | Specifies a group of one or more columns in a table for formatting |
| <data> | Data | Links a piece of content with a machine-readable translation |
| <datalist> | Datalist | Contains a set of <option> elements that represent the permissible or suggested options available to other controls |
| <dd> | Description Detail | Provides the details or definition for the preceding term (<dt>) in a description list (<dl>) |
| <del> | Deleted Text | Represents text that has been deleted from the document |
| <details> | Details | Represents a disclosure widget from which the user can obtain additional information |
| <dfn> | Definition | Represents the defining instance of a term |
| <dialog> | Dialog | Represents a dialog box or other interactive component |
| <div> | Division | A generic container for flow content |
| <dl> | Description List | Represents a description list |
| <dt> | Description Term | Represents a term in a description list |
| <em> | Emphasis | Marks text that has stress emphasis |
| <embed> | Embed | Embeds external content at the specified point in the document |
| <fieldset> | Fieldset | Groups related elements in a form |
| <figcaption> | Figure Caption | Represents a caption or legend for a figure |
| <figure> | Figure | Represents self-contained content, like illustrations, diagrams, photos, etc. |
| <footer> | Footer | Represents a footer for its nearest sectioning content or sectioning root element |
| <form> | Form | Represents a document section containing interactive controls for submitting information |
| <h1> to <h6> | Headings | Represent six levels of section headings |
| <head> | Head | Contains meta-information about the document |
| <header> | Header | Represents introductory content, typically a group of introductory or navigational aids |
| <hr> | Horizontal Rule | Represents a thematic break between paragraph-level elements |
| <html> | HTML | Represents the root of an HTML document |
| <i> | Italic | Represents text in an alternate voice or mood |
| <iframe> | Inline Frame | Represents a nested browsing context, embedding another HTML page into the current one |
| <img> | Image | Embeds an image into the document |
| <input> | Input | Used to create interactive controls for web-based forms to accept data from the user |
| <ins> | Inserted Text | Represents a range of text that has been added to a document |
| <kbd> | Keyboard Input | Represents user input, typically keyboard input |
| <label> | Label | Represents a caption for an item in a user interface |
| <legend> | Legend | Represents a caption for the content of its parent <fieldset> |
| <li> | List Item | Represents an item in a list |
| <link> | Link | Specifies relationships between the current document and an external resource |
| <main> | Main | Represents the dominant content of the <body> of a document |
| <map> | Map | Used with <area> elements to define an image map |
| <mark> | Mark | Represents highlighted text |
| <meta> | Meta | Represents metadata that cannot be represented by other HTML meta-related elements |
| <meter> | Meter | Represents a scalar measurement within a known range |
| <nav> | Navigation | Represents a section of a page that links to other pages or to parts within the page |
| <noscript> | Noscript | Defines a section of the document to be displayed if scripting is disabled or not supported |
| <object> | Object | Represents an external resource, which can be treated as an image, a nested browsing context, or a resource to be handled by a plugin |
| <ol> | Ordered List | Represents an ordered list of items |
| <optgroup> | Option Group | Groups a set of <option> elements within a <select> element |
| <option> | Option | Represents an option in a <select> element or a suggestion in a <datalist> element |
| <output> | Output | Represents the result of a calculation or user action |
| <p> | Paragraph | Represents a paragraph |
| <param> | Parameter | Defines parameters for an <object> element |
| <picture> | Picture | Contains zero or more <source> elements and one <img> element to provide versions of an image for different display/device scenarios |
| <pre> | Preformatted Text | Represents preformatted text |
| <progress> | Progress | Represents the completion progress of a task |
| <q> | Quotation | Represents a quoted section |
| <rp> | Ruby Parenthesis | Provides fallback parentheses for browsers that do not support display of ruby annotations |
| <rt> | Ruby Text | Represents the text of a ruby annotation |
| <ruby> | Ruby | Represents a ruby annotation |
| <s> | Strikethrough | Renders text with a strikethrough |
| <samp> | Sample Output | Represents sample output from a computer program |
| <script> | Script | Used to embed or reference executable code |
| <section> | Section | Represents a standalone section of functionality contained within an HTML document |
| <select> | Select | Represents a control that provides a menu of options |
| <small> | Small | Represents side comments or small print |
| <source> | Source | Specifies multiple media resources for <picture>, <audio>, or <video> elements |
| <span> | Span | A generic inline container for phrasing content |
| <strong> | Strong | Indicates that its contents have strong importance |
| <style> | Style | Contains style information for a document |
| <sub> | Subscript | Defines a subscript text |
| <summary> | Summary | Represents a summary or caption for the content of its parent <details> element |
| <sup> | Superscript | Defines superscript text |
| <table> | Table | Represents tabular data |
| <tbody> | Table Body | Groups one or more <tr> elements that are the body of the table |
| <td> | Table Data | Defines a cell of a table that contains data |
| <template> | Template | Defines a template for client-side content that is not to be rendered when the page loads |
| <textarea> | Textarea | Represents a multi-line plain-text editing control |
| <tfoot> | Table Foot | Groups one or more <tr> elements that are the footer of the table |
| <th> | Table Header | Defines a cell as header of a group of table cells |
| <thead> | Table Head | Groups one or more <tr> elements that are the head of the table |
| <time> | Time | Represents a specific period in time |
| <title> | Title | Defines the document's title that is shown in a browser's title bar or a page's tab |
| <tr> | Table Row | Defines a row of cells in a table |
| <track> | Track | Specifies text tracks for <audio> and <video> elements |
| <u> | Underline | Represents text with an unarticulated, though explicitly rendered, non-textual annotation |
| <ul> | Unordered List | Represents an unordered list of items |
| <var> | Variable | Represents a variable in a mathematical expression or a programming context |
| <video> | Video | Embeds a video into the document |
| <wbr> | Word Break Opportunity | Represents a word break opportunity |
This is the result of the styles in my page, in a raw page we can detail all the sections, on the top we normally link the libraries and style files (.css) for .html, if wee know for the name of cascade style sheet, that means that every style we define by the origin in the .css can have subvariants but is helpfull to have a pre defined style for each element.
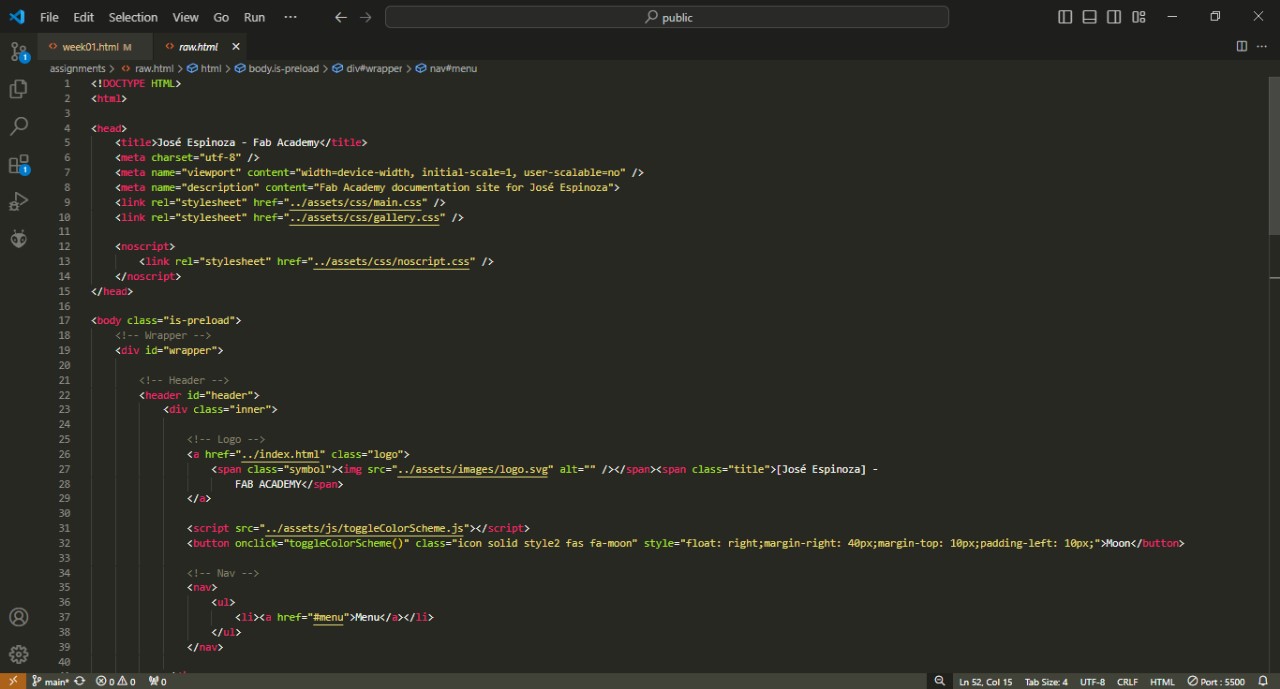
An HTML page is typically divided into several key sections to structure the content and improve user experience. The "header" tag, often contains introductory content or navigational links, like a logo, title, and menu. The *navbar* is a crucial component of the header, typically using "nav" tags, and it provides links to other sections of the website, ensuring easy navigation. The *main* section, denoted by the "main" tag, holds the primary content of the webpage. Following this, the *footer* section, represented by the "footer" tag, includes information such as contact details, copyright notices, and additional navigation links.
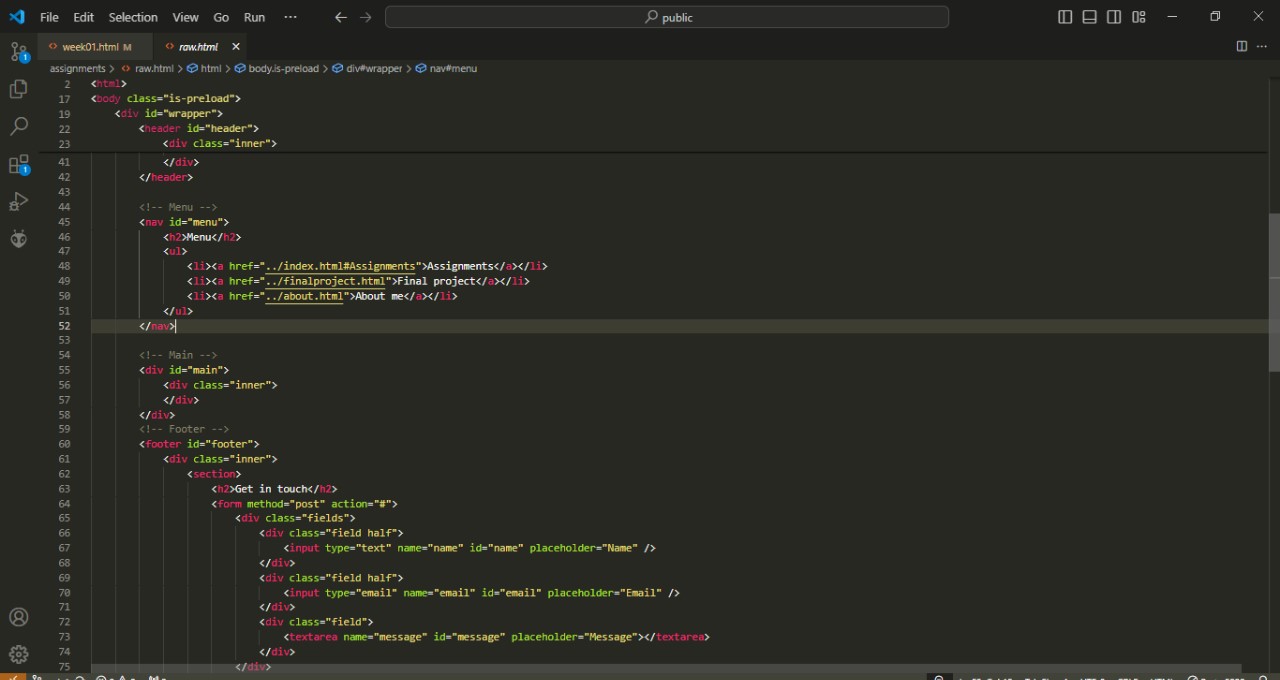
Scripts and JavaScript play a crucial role in adding interactivity and dynamic behavior to web pages. JavaScript, typically embedded within "script" tags, allows developers to manipulate the Document Object Model (DOM), respond to user events, validate forms, and communicate with servers through asynchronous requests. These scripts can be included directly within the HTML file or linked externally, enhancing maintainability and performance. By using JavaScript, we can create more engaging user experiences that go beyond the static capabilities of HTML and CSS alone.
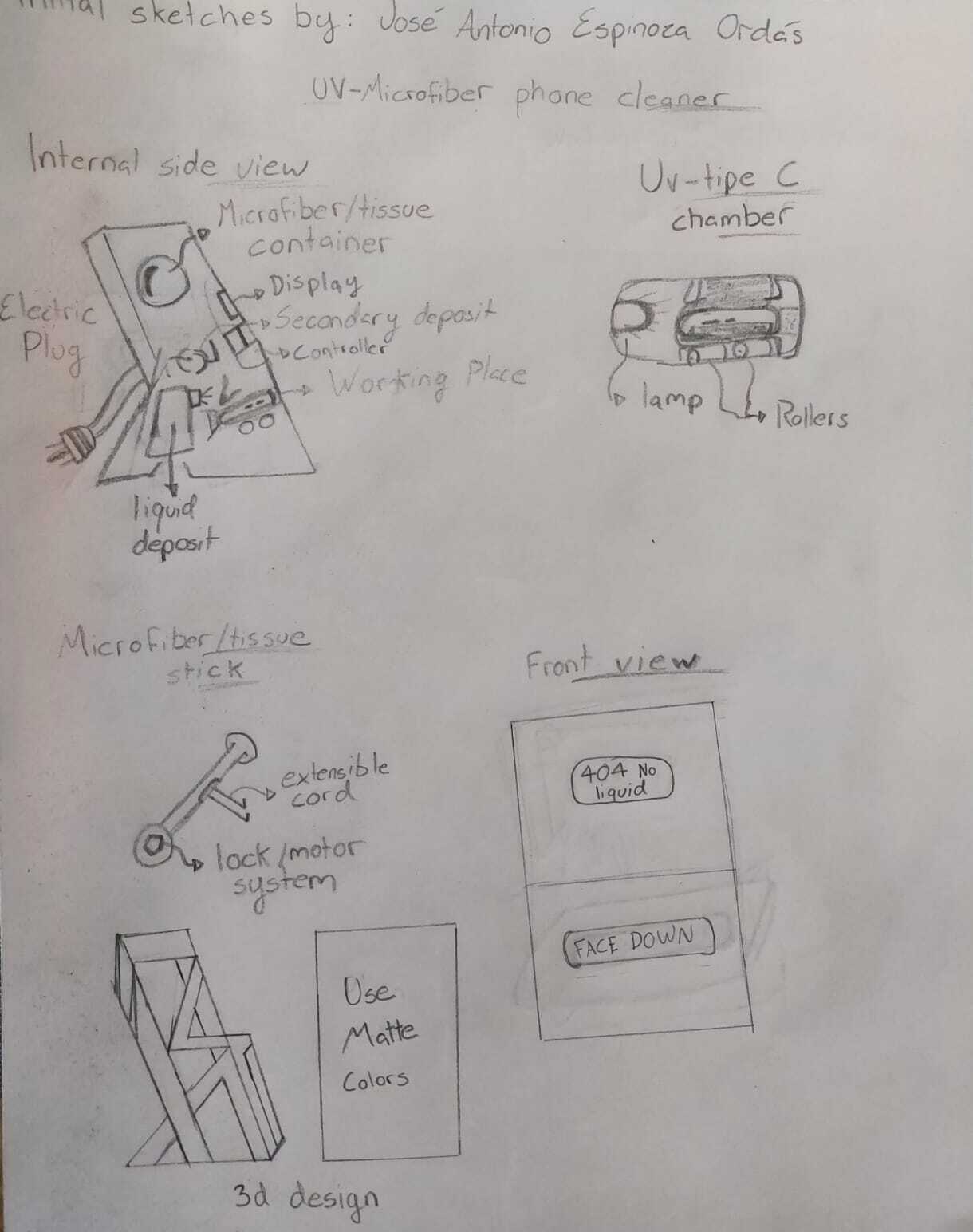
Thinking of a final project
I started thinking and sketching initial ideas for a future final project, then i asked my self the following questions:
- Target audience: The target could be every place with the number of adults enough, universities, shopping malls, sport centers, etcetera.
- Problem to solve: The number of different substances your phone carry in the day to day could help virus and infections to easily spread and harm you.
- Primary needs and pain points: You might think but it's as simple as buying phone wipes and having a cleaning habit, but no, if people forget to brush their teeth imagine their phone.
- Similar products and differentiative point: There are tons of similar products but they aren't safe enough, look at this video of the UV discussion as refference, also, the project has a different approach due to its ease of use and accessibility.
- How intuitive and user-friendly should be: I imagine it to be as simple as a toilet paper dispenser, that will help the project to easily adapt to predefined environments that didn’t initially have a designated place.
- Environmental impact: Another key point of this item is the ability to reuse microfiber towels, reducing the amount of paper and tissues used.
- Regulations and standards: I refer to this point when I say I’m not inventing a new UV disinfecting technic, the project will have applied only scientific tested examples.
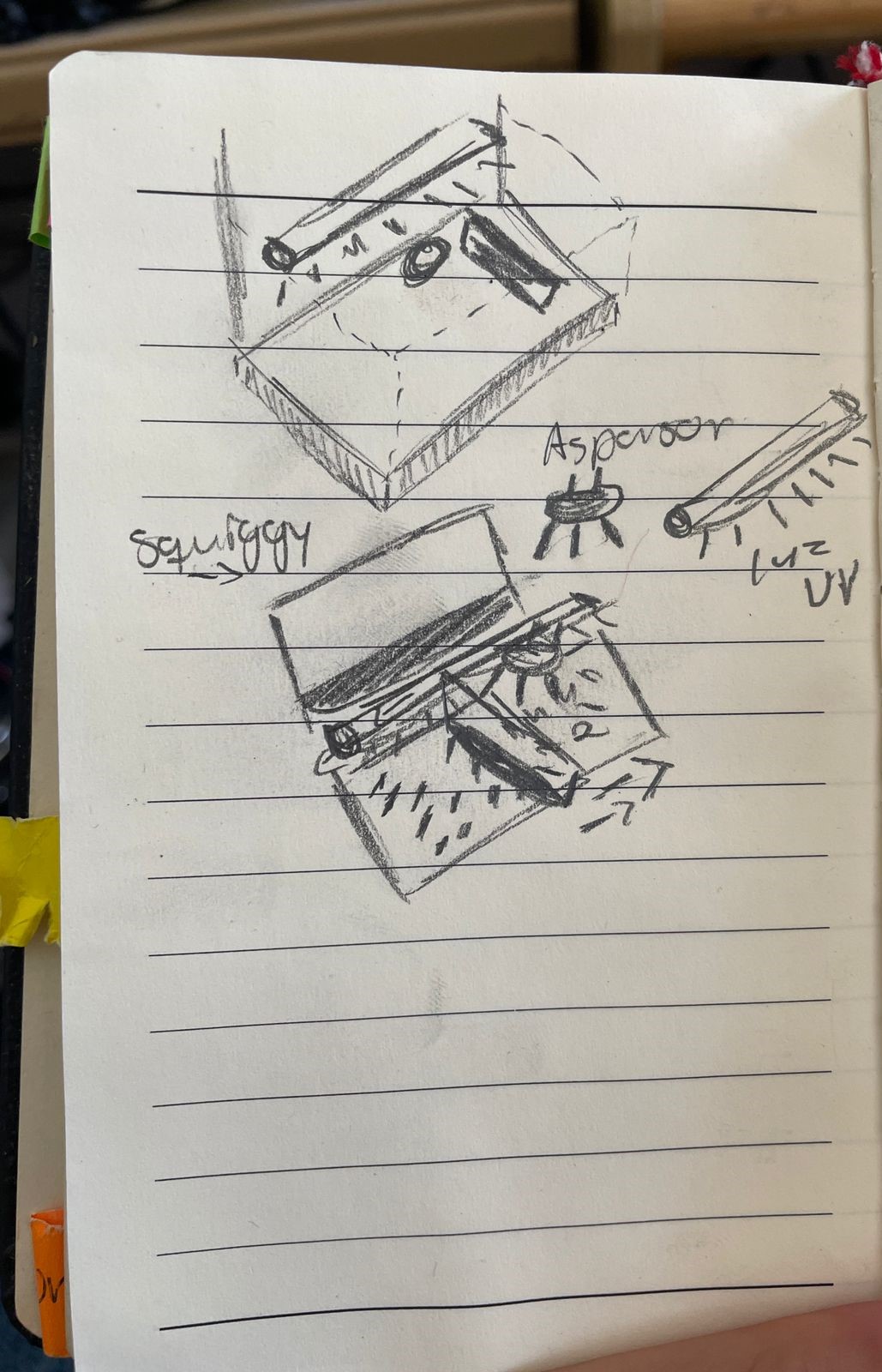
First sketches
The problem is that cell phones accumulate a lot of dirt, so we need a device that is in charge of disinfecting them. I have already seen that UV technology is very efficient for this, but I would like to add a way to clean the grease, so I need the system to include some way to spray some form of cleaner directly on the cell phone once inside, and it needs something that spreads it and cleans it, similar to a windshield wiper or that has a system of two rollers with microfibers to scrub it.
Section About me
I created a page specifically about me, just for you, to trying you know me a little more, I added what I decided oportune, the first that come to my mind to prentend being original, also remmember to compress all your images around 40-60 kb if possible, just google it and get thousand of options.
Student Agreement
You can easily see the document signed in the about me page.
