3.Computer Controlled Cutting
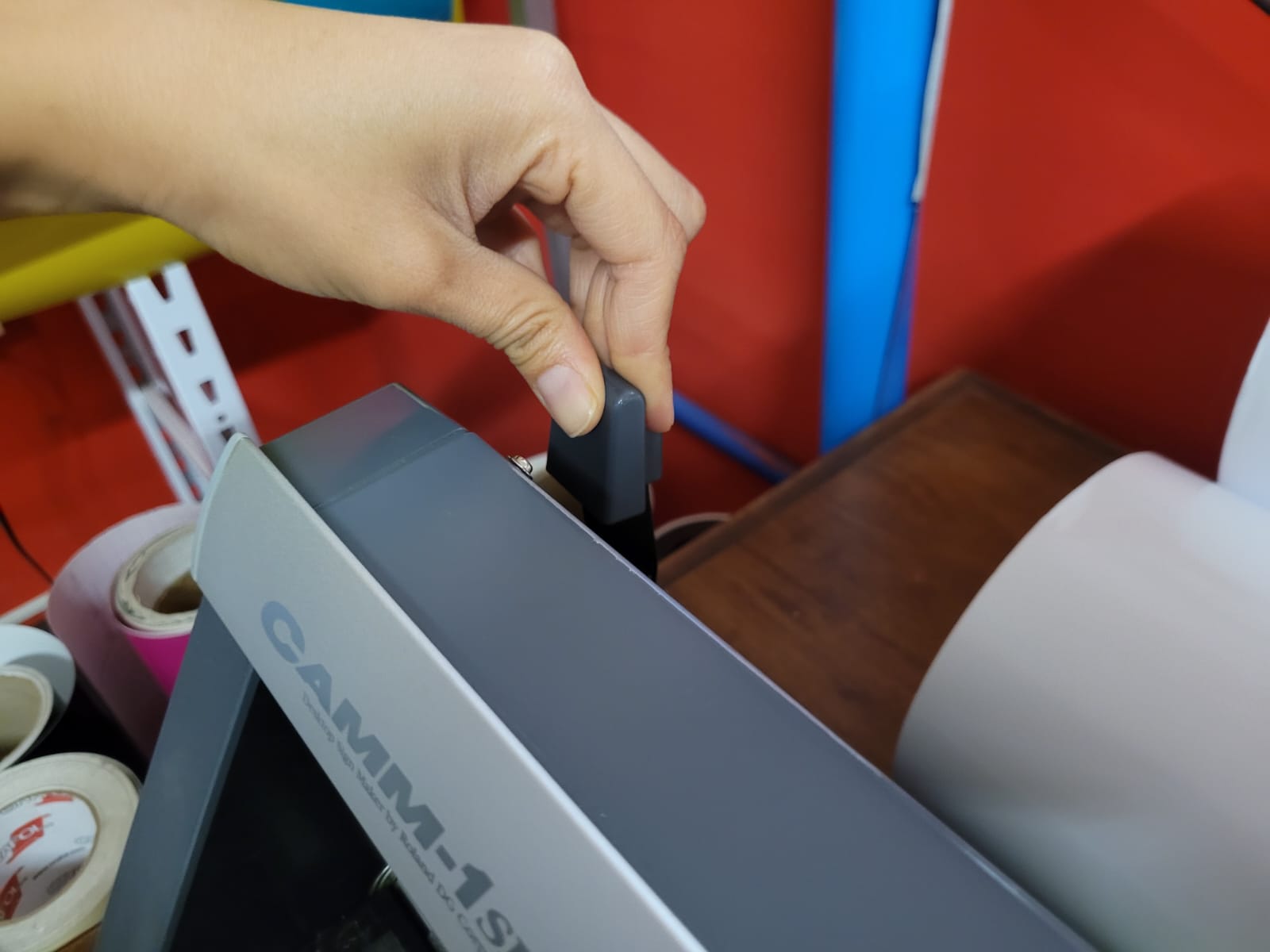
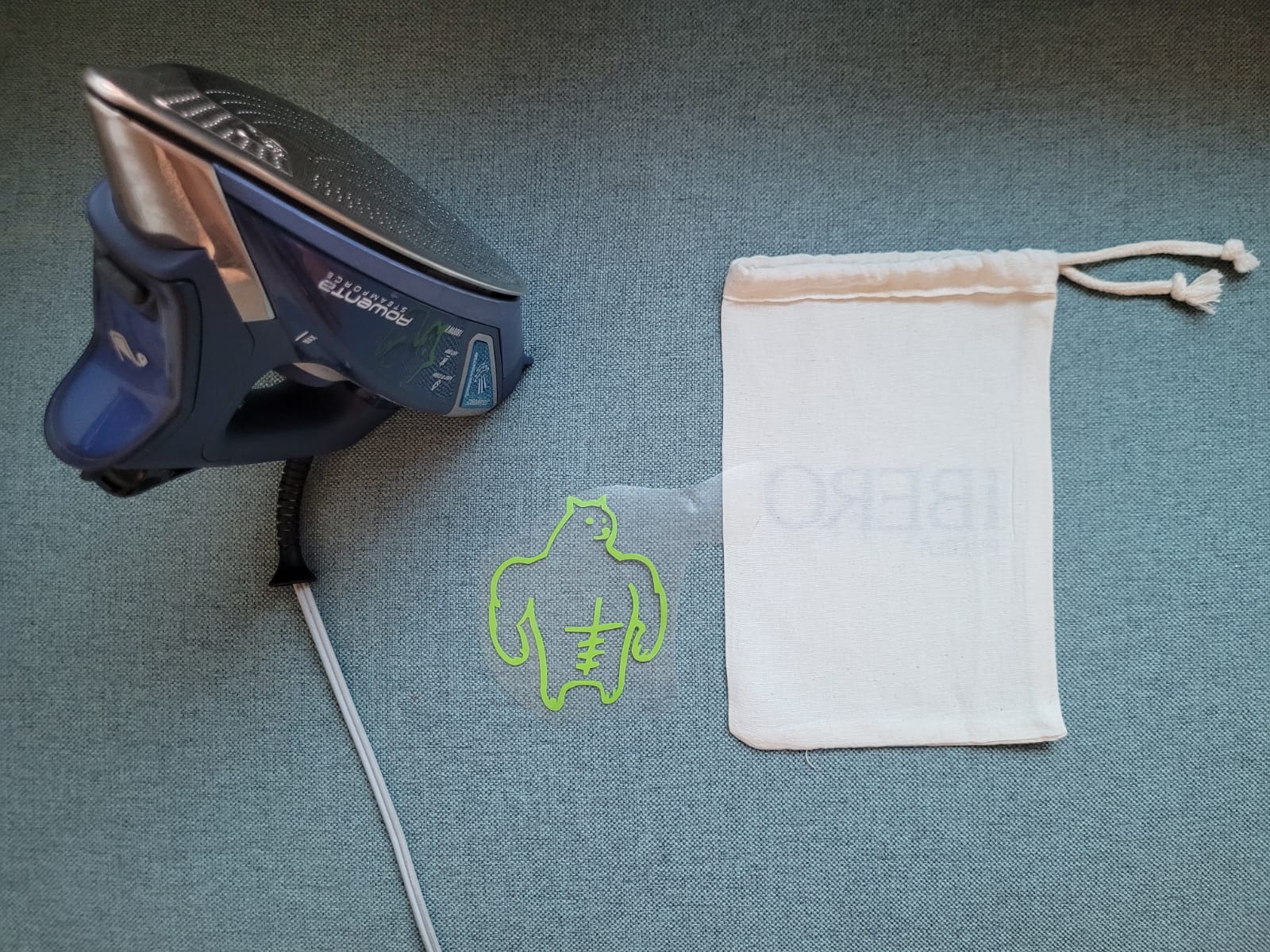
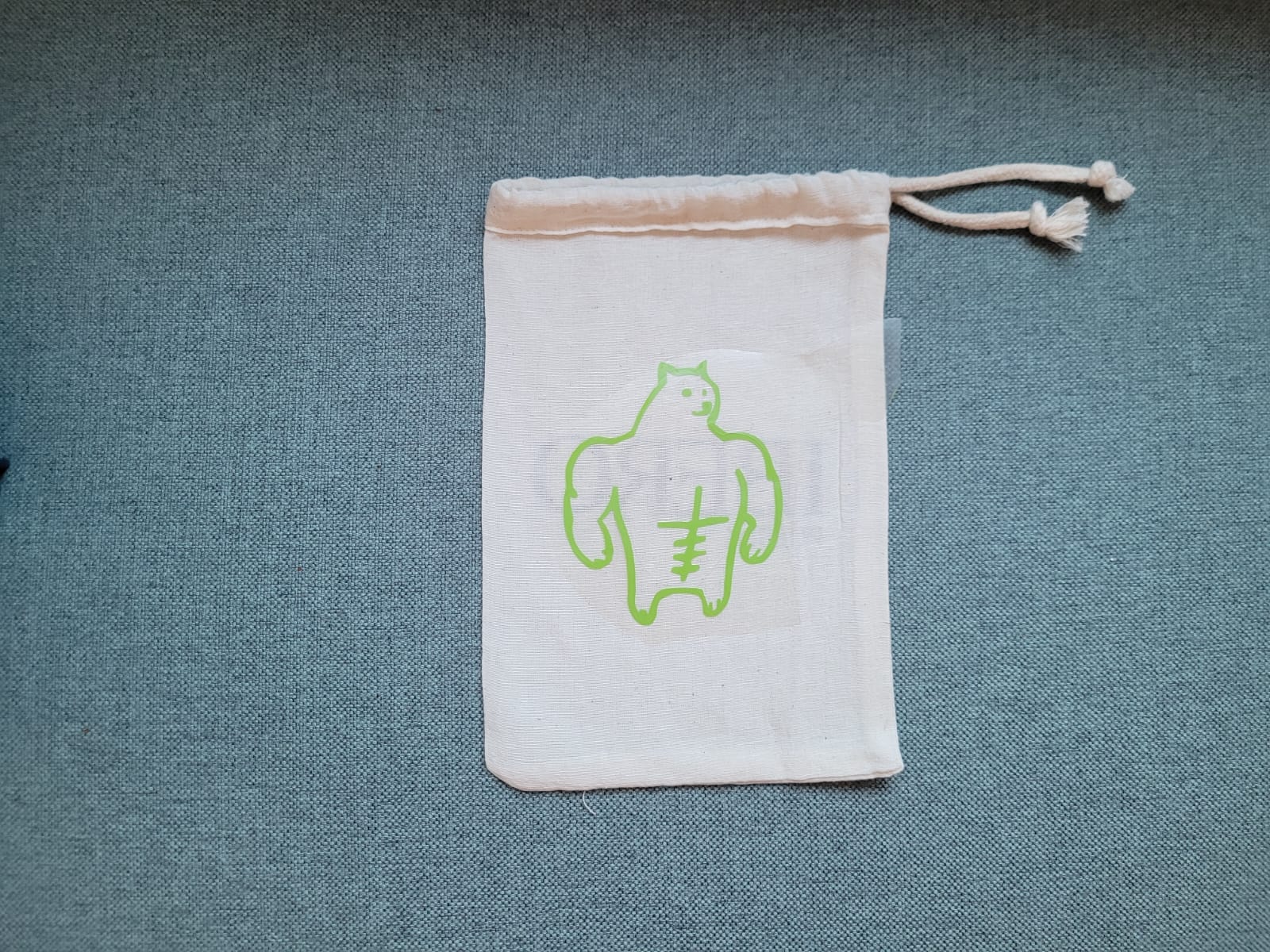
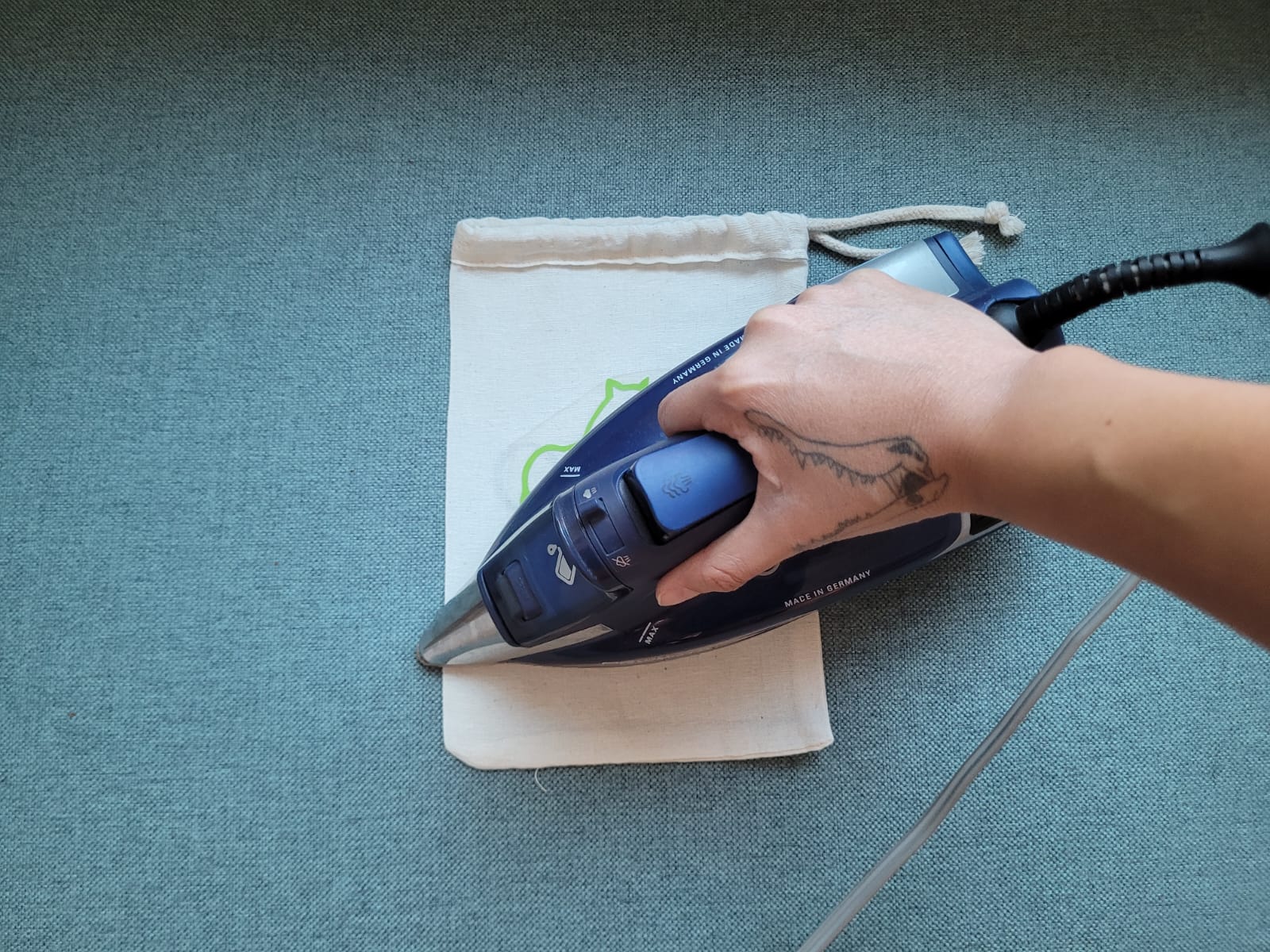
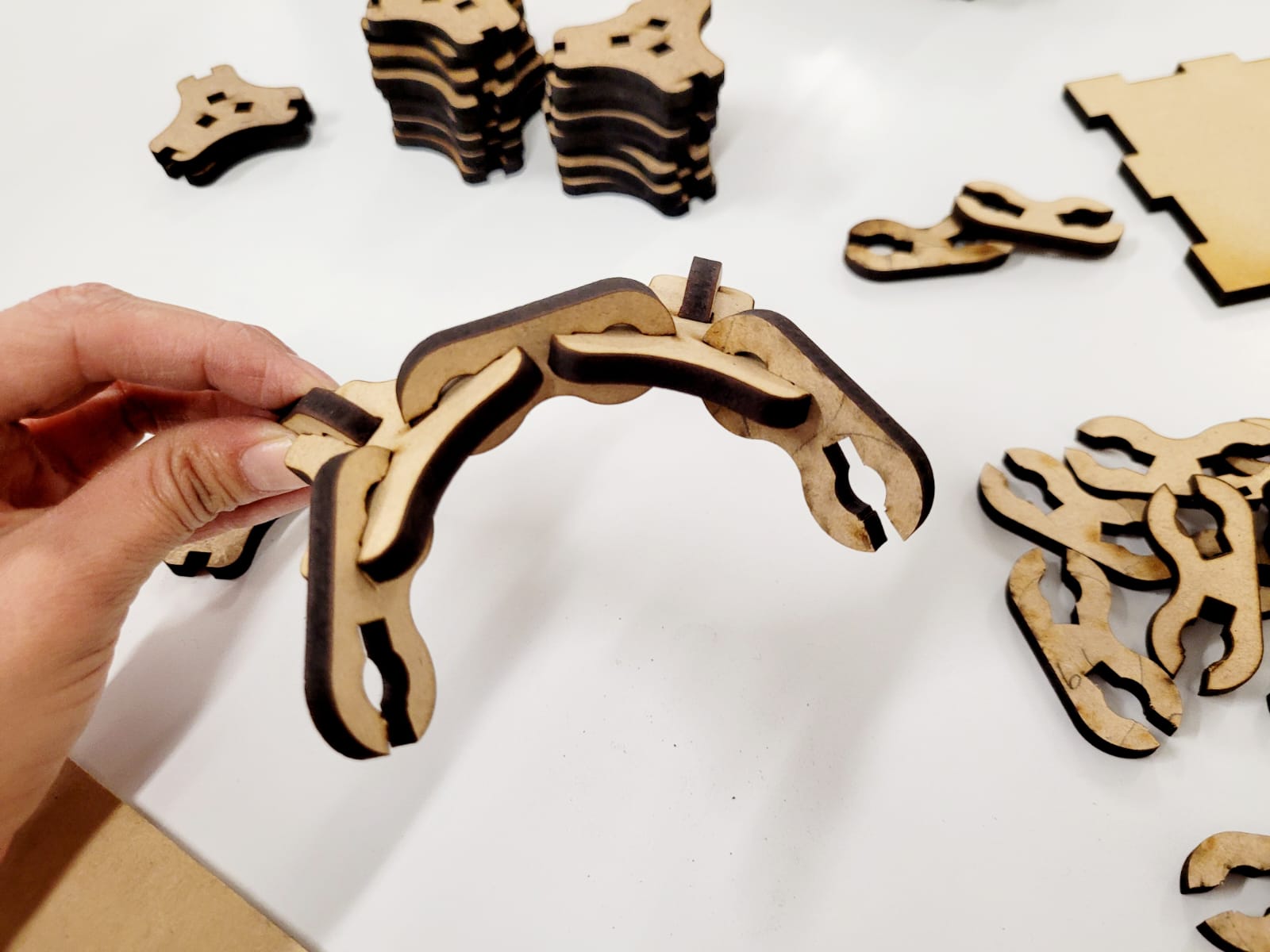
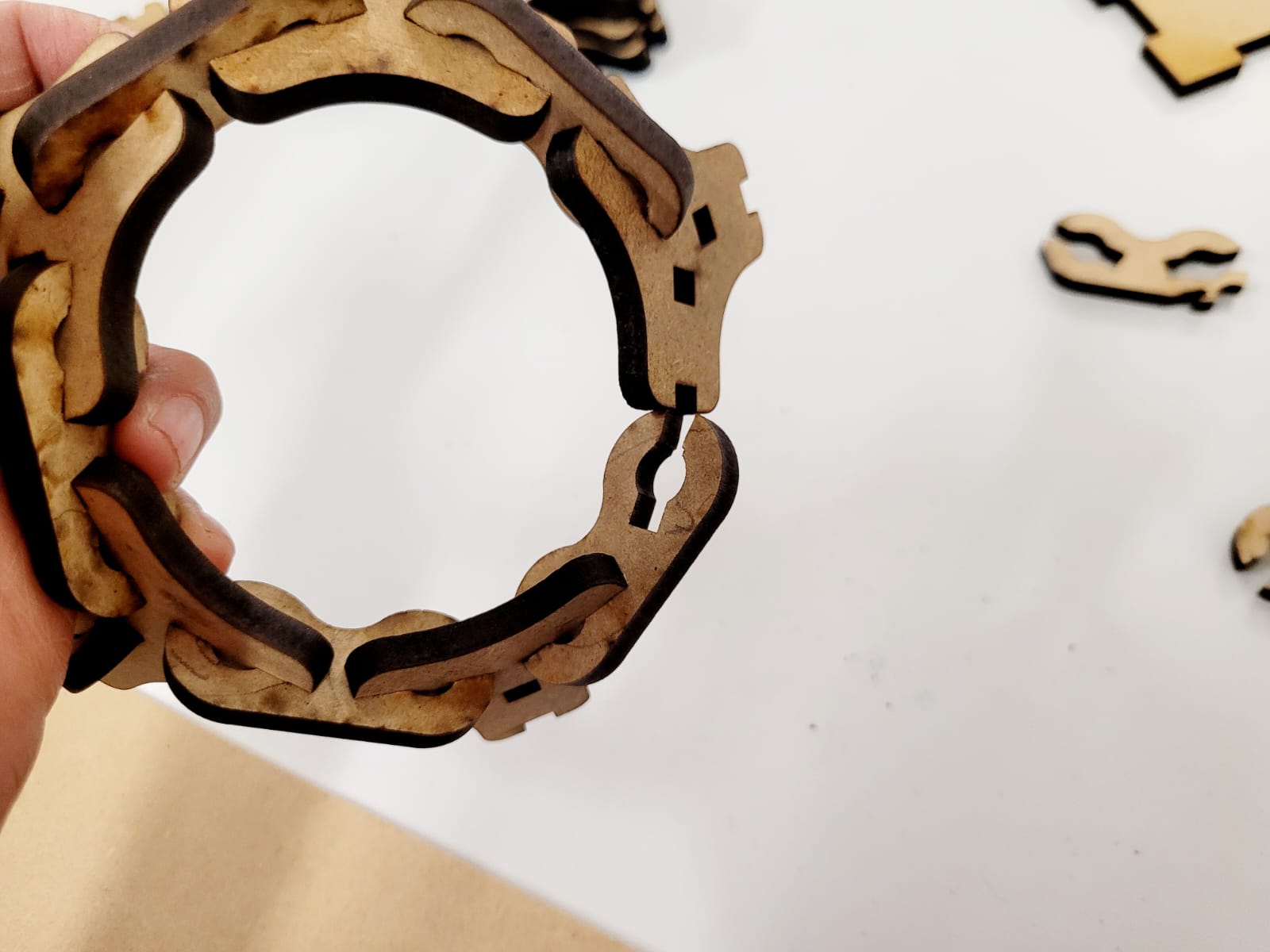
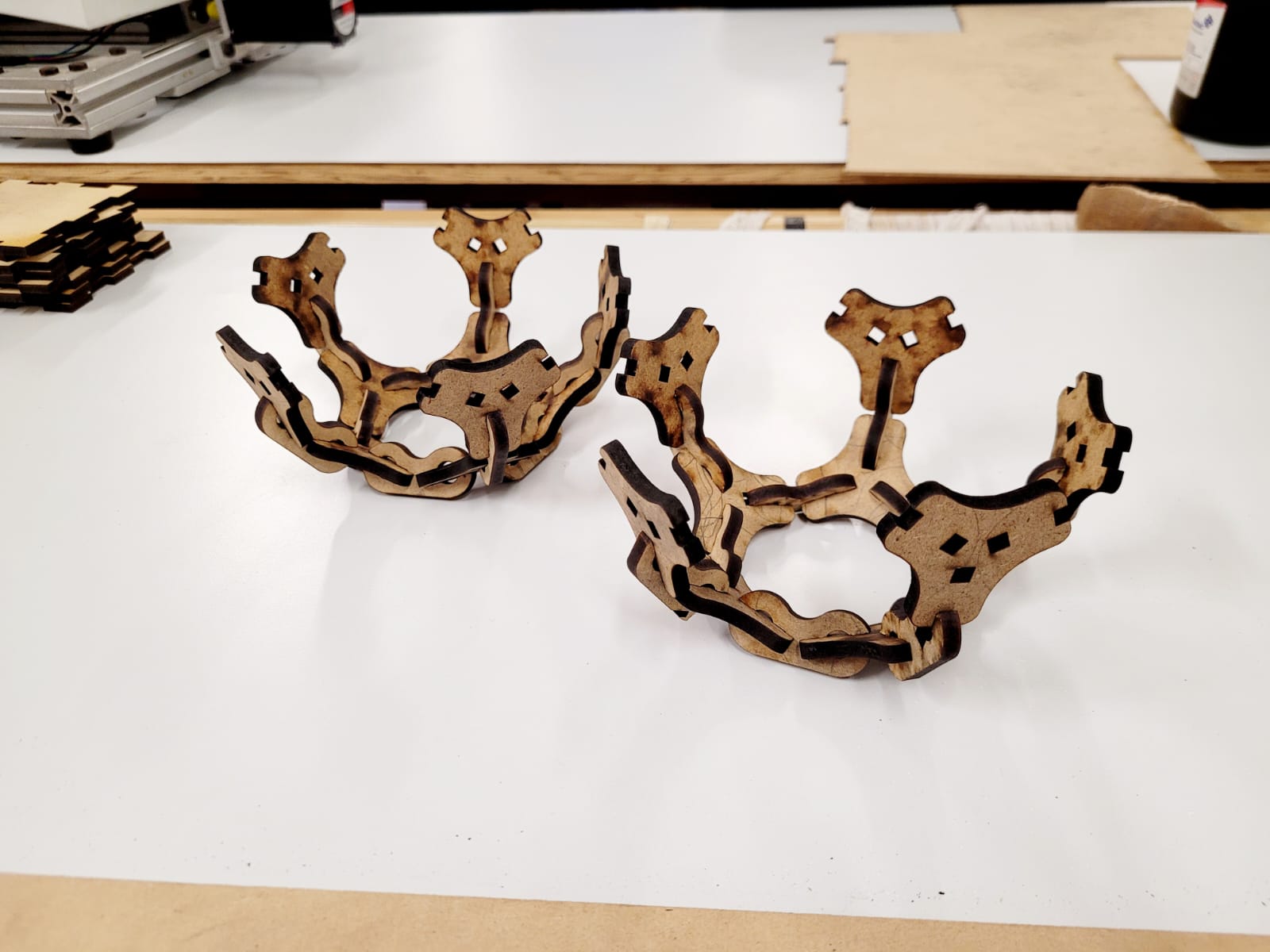
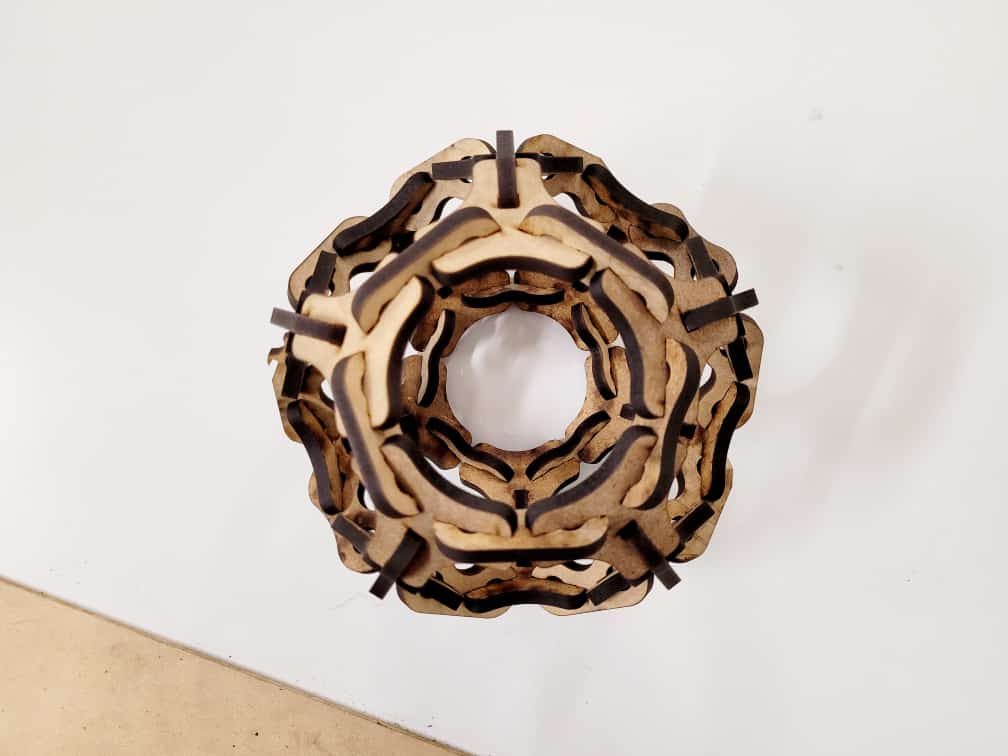
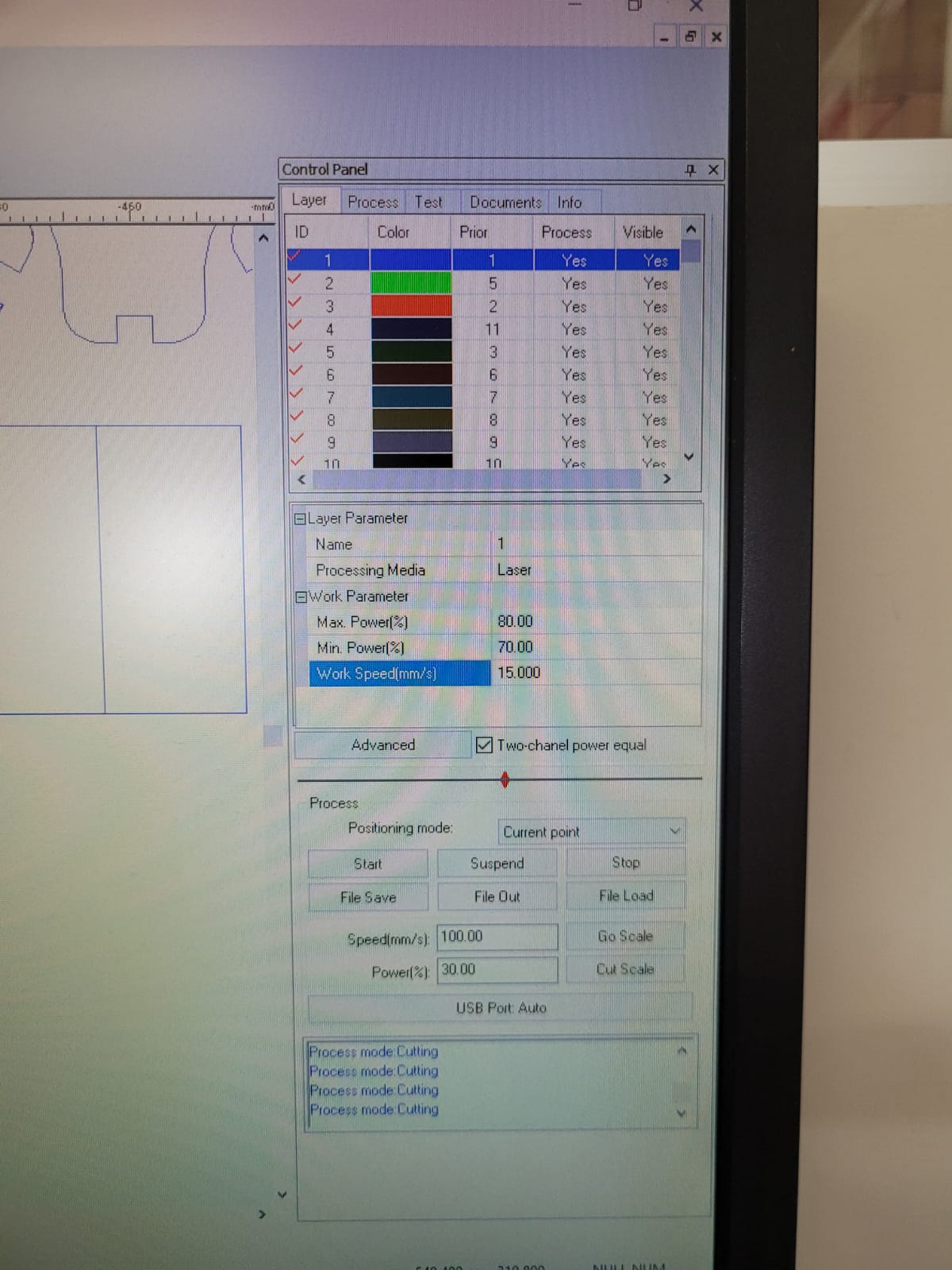
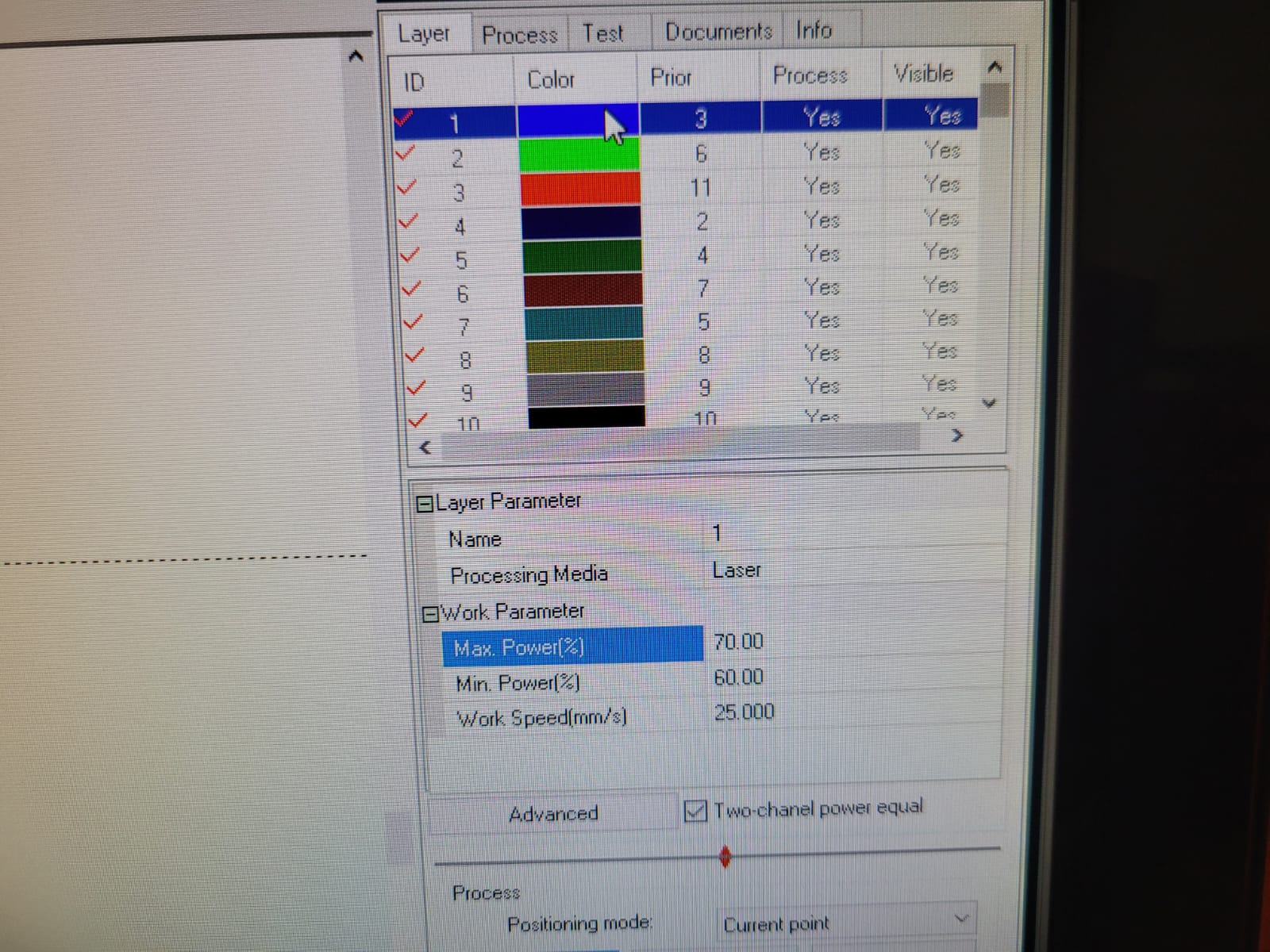
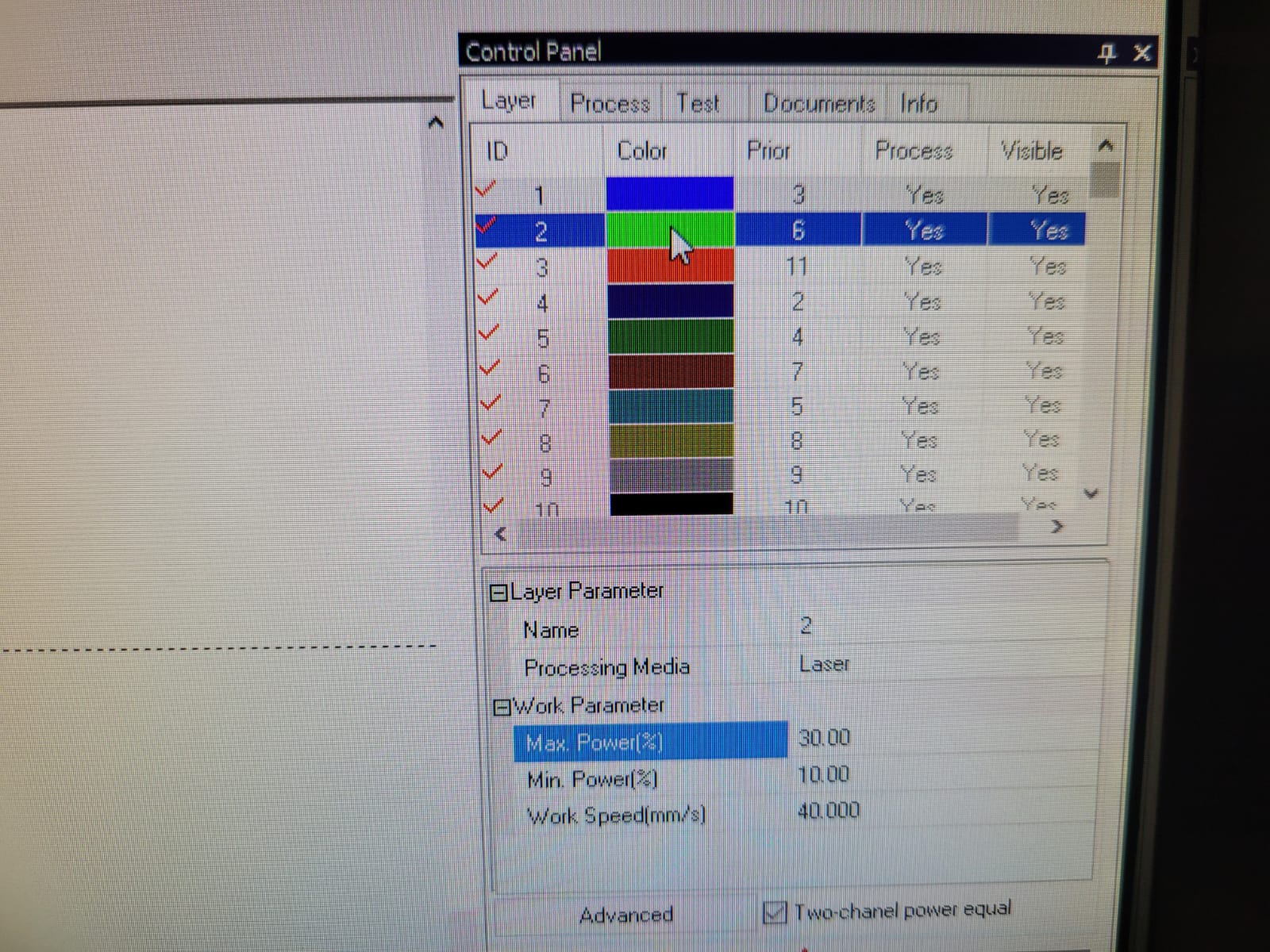
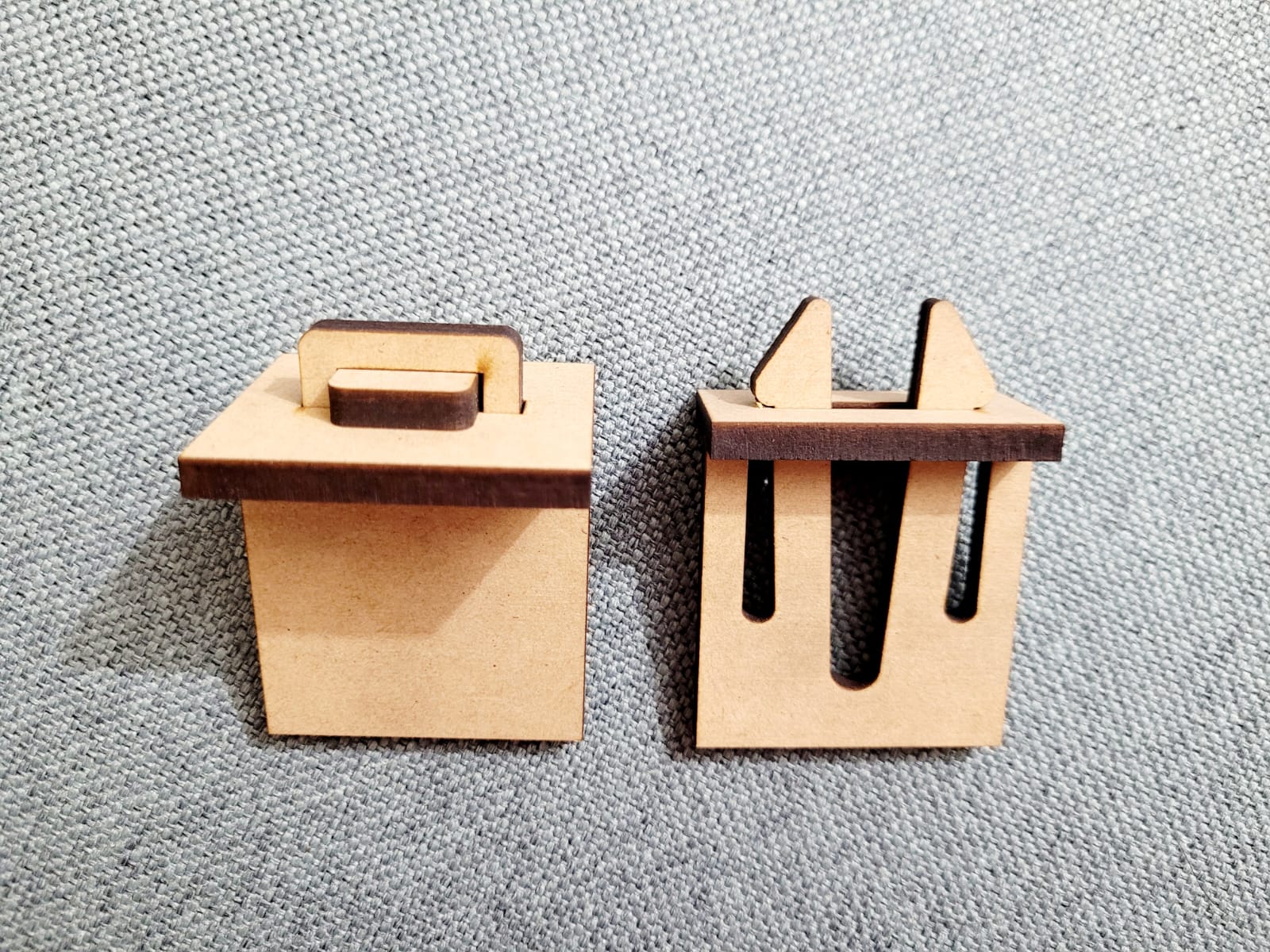
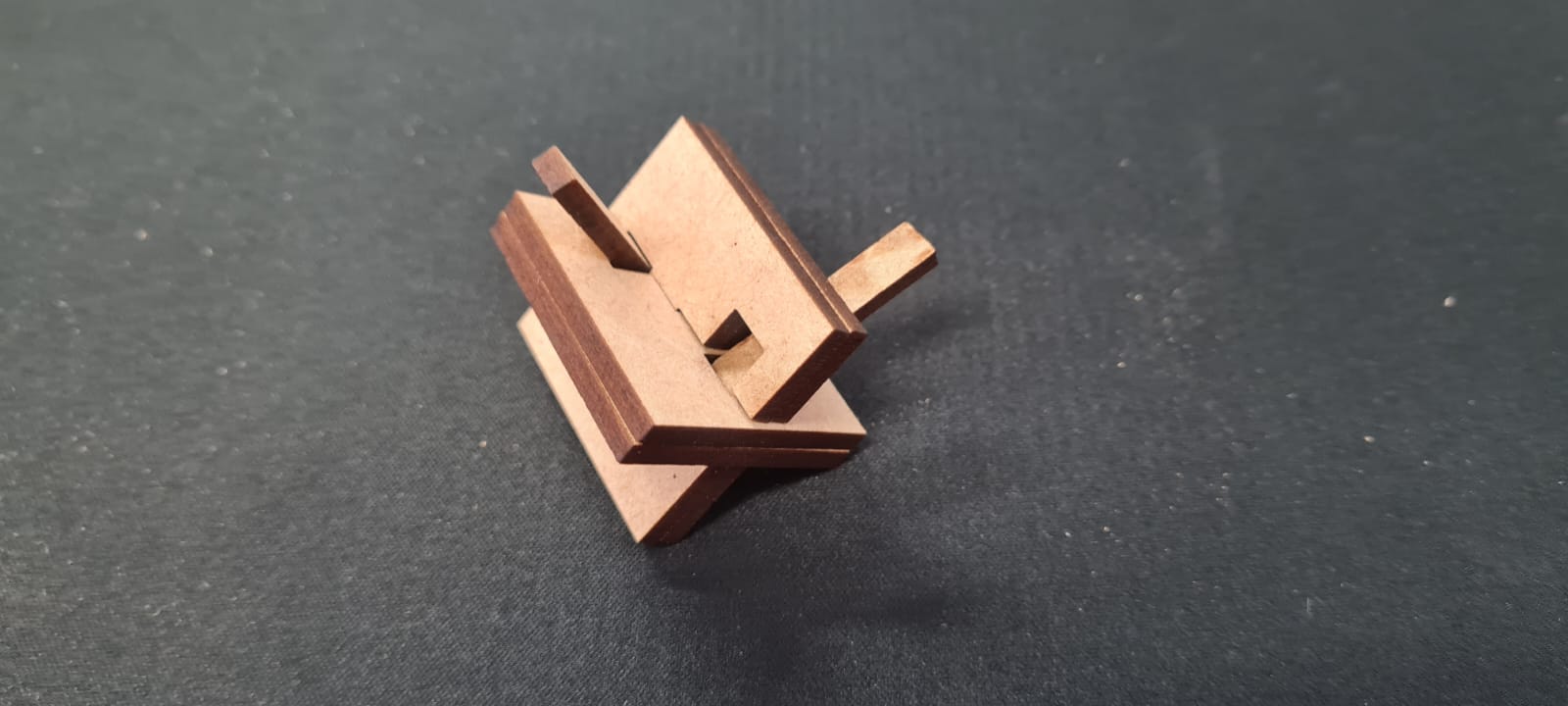
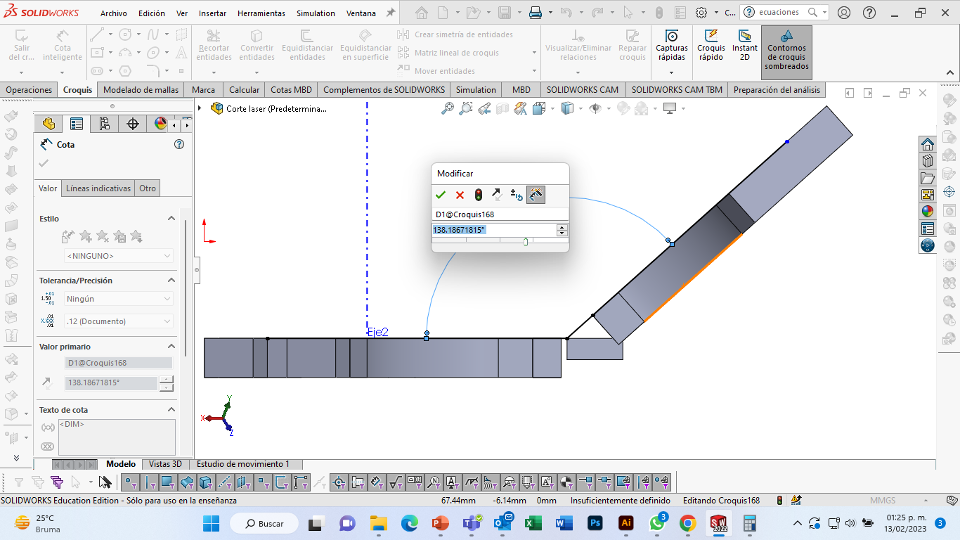
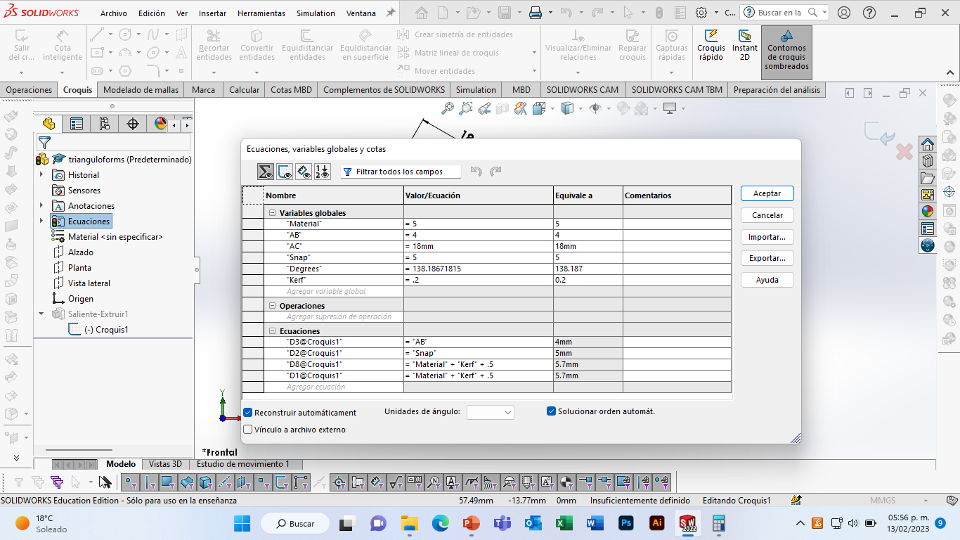
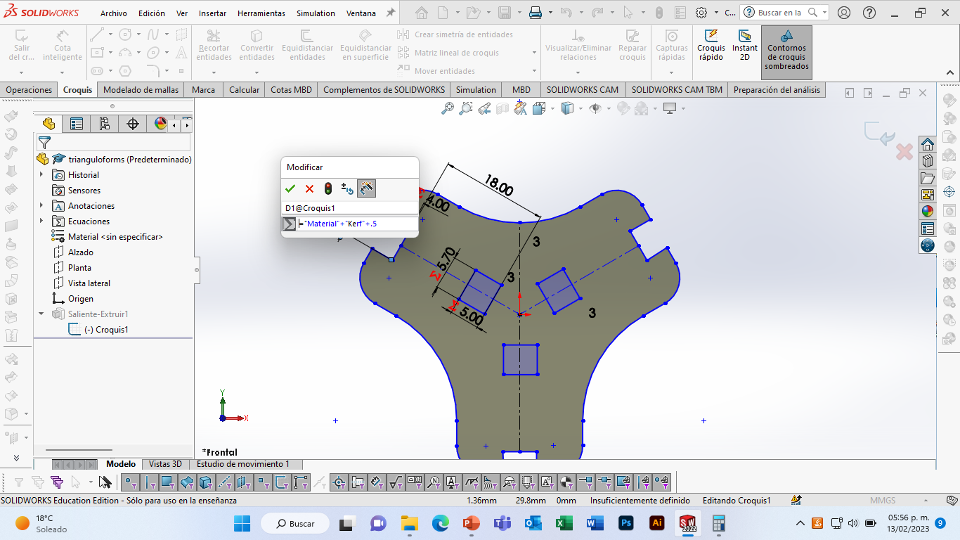
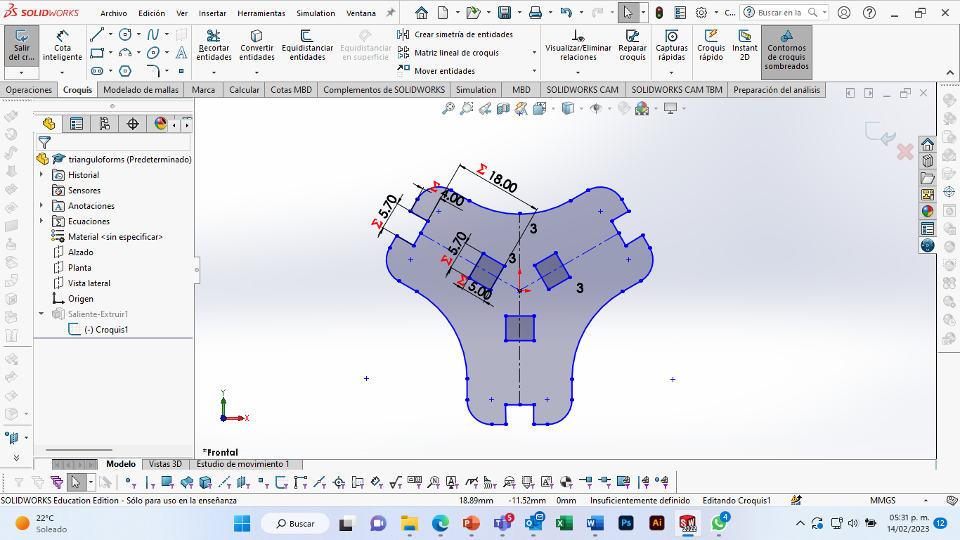
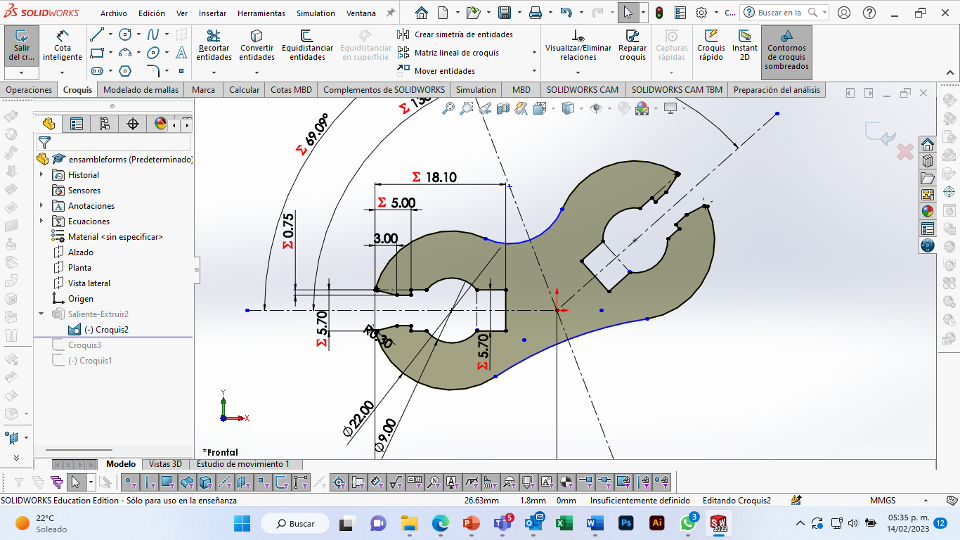
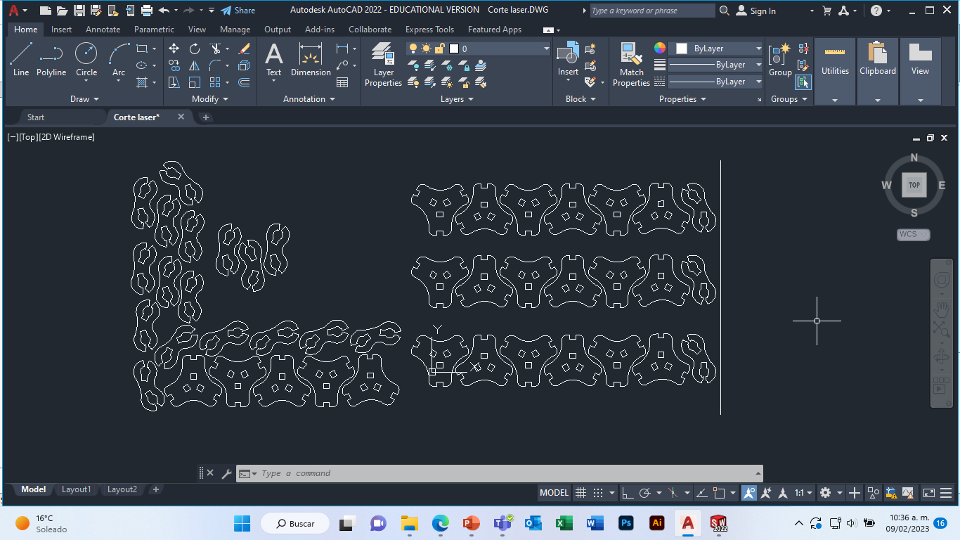
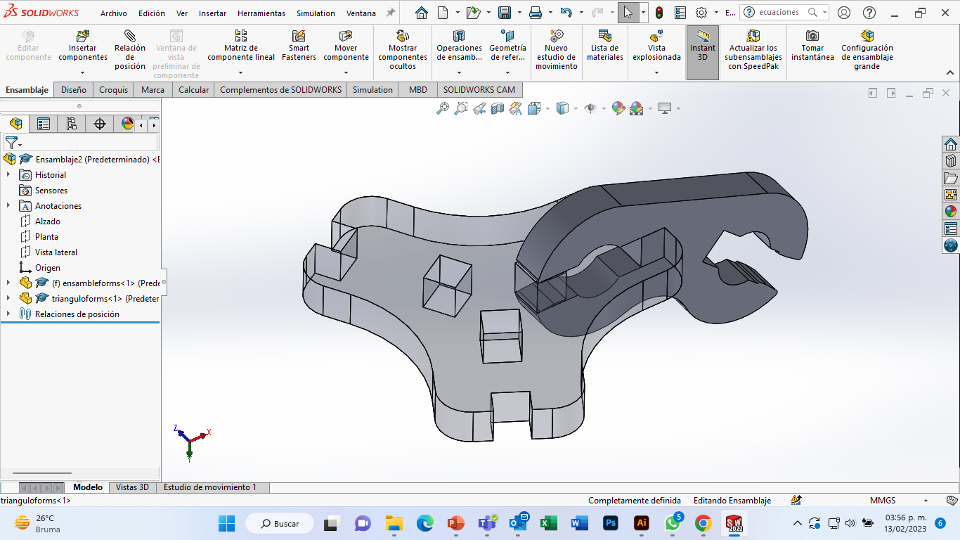
For this week we did the characterization of the laser cutting machine, we designed a parametric equipment that can be attached using only with your own sets. We also did a vinyl cutting exercise. Cutting machines are a tool used in a wide range of industries for precision cutting and designing projects.