The task list for this week:
- Develop a plan for dissemination of your final project.
- Prepare drafts of project summary slide (presentation.png, 1920x1080) and video clip (presentation.mp4, 1080p HTML5, < ~minute, < ~10 MB) and put them in your root directory
- Creative Commons (CC) license
- GNU General Public License
- BSD license
- MIT - Open Source license
- Apache License
- Creative Commons (CC) license
- GNU General Public License
- BSD license
- MIT - Open Source license
- Apache License
I have zero knowledge about legal things and business .So I decided to take help from someones webpage .For this assignment I reference kiran sir and rahul assignment page as a referance for completing this assigment.
What is Invention?:
Generally speaking, an invention is a new product or process that solves a technical problem. This is different from a discovery, which is something that already existed but had not been found.
An invention is a unique or novel device, method, composition or process. The invention process is a process within an overall engineering and product development process. It may be an improvement upon a machine or product or a new process for creating an object or a result. An invention that achieves a completely unique function or result may be a radical breakthrough. Such works are novel and not obvious to others skilled in the same field. An inventor may be taking a big step toward success or failure.Some inventions can be patented. The system of patents was established to encourage inventors by granting limited-term, limited monopoly on inventions determined to be sufficiently novel, non-obvious, and useful. A patent legally protects the intellectual property rights of the inventor and legally recognizes that a claimed invention is actually an invention. The rules and requirements for patenting an invention vary by country and the process of obtaining a patent is often expensive.(Wikipedia)
Type of Invention
Inventions are of three kinds: scientific-technological (including medicine), sociopolitical (including economics and law), and humanistic, or cultural.
Scientific-technological inventions include railroads, aviation, vaccination, hybridization, antibiotics, astronautics, holography, the atomic bomb, computing, the Internet, and the smartphone.
Sociopolitical inventions comprise new laws, institutions, and procedures that change modes of social behavior and establish new forms of human interaction and organization. Examples include the British Parliament, the US Constitution, the Manchester (UK) General Union of Trades, the Boy Scouts, the Red Cross, the Olympic Games, the United Nations, the European Union, and the Universal Declaration of Human Rights, as well as movements such as socialism, Zionism, suffragism, feminism, and animal-rights veganism.
Humanistic inventions encompass culture in its entirety and are as transformative and important as any in the sciences, although people tend to take them for granted. In the domain of linguistics, for example, many alphabets have been inventions, as are all neologisms (Shakespeare invented about 1,700 words).(Source-Wikipedia)
Intellectual Property
A brand, invention, design, or other type of production that a person or company has legal rights to is referred to as intellectual property (IP). Almost all companies have some kind of intellectual property, which may be a valuable asset.
Intellectual property rights, such as a patent, copyright, or trademark, give the creator an exclusive, time-limited right to use his or her original work. To safeguard their intellectual property, business owners who want to register their intellectual property must understand the differences between the three registrations.
What is patent?
A patent is an exclusive right granted by the law to the patentee for a specific period of time with regard to an invention. By obtaining a patent for an innovation, the inventor gains the right to prevent others from using, importing, selling, or manufacturing the protected good without their permission. India allows for the patenting of innovative products and processes that involve inventive step and have potential for industrial use.
What is Copyright?
The legislation grants the makers of cinematograph films and sound recordings, as well as authors of literary, theatrical, musical, and aesthetic works, the right to use the term "copyright." Brands, names, slogans, brief phrases, techniques, stories, or factual material are not covered by copyright. Additionally, thoughts or ideas are not covered by copyright. Therefore, copyright is primarily employed to safeguard the original works of authors, composers, designers, dramatists, and other creatives as well as those who create sound recordings, motion pictures, and computer software.
What is Trademark?
A trademark is a graphic symbol that may be a word signature, name, device, label, numbers, or combination of colours that is used by one enterprise to identify its products or services from those of other businesses that provide comparable goods or services. Therefore, trademarks are frequently used to protect company names, slogans, brand names, and more.
Trade secrets :
Trade secrets are a category of intellectual property that includes formulas, procedures, methods, designs, tools, patterns, or information compilations that have inherent economic value because they are not widely known or easily discoverable by others, and which the owner takes reasonable precautions to keep secret. Such material is referred to as confidential information in some jurisdictions.
Right of publicity :
The right of publicity, often known as personality rights, is the individual's ability to restrict how their name, picture, likeness, or other unmistakable identifiers are used for commercial purposes. The right of publicity can continue to be valid after a person's death because it is typically viewed as a property right rather than a personal one (to varying degrees depending on the jurisdiction).
DIFFERENT COPYRIGHT LICENSES :
Creative Commons (CC):
A Creative Commons (CC) license is one of several public copyright licenses that enable the free distribution of an otherwise copyrighted "work". A CC license is used when an author wants to give other people the right to share, use, and build upon a work that the author has created. CC provides an author flexibility (for example, they might choose to allow only non-commercial uses of a given work) and protects the people who use or redistribute an author's work from concerns of copyright infringement as long as they abide by the conditions that are specified in the license by which the author distributes the work.
GNU General Public License:
The GNU General Public License (GNU GPL or simply GPL) is a series of widely used free software licenses that guarantee end users the freedom to run, study, share, and modify the software. The licenses were originally written by Richard Stallman, founder of the Free Software Foundation (FSF), for the GNU Project, and grant the recipients of a computer program the rights of the Free Software Definition. The GPL series are all copyleft licenses, which means that any derivative work must be distributed under the same or equivalent license terms. This is in distinction to permissive software licenses, of which the BSD licenses and the MIT License are widely used, less restrictive examples. GPL was the first copyleft license for general use.
BSD licenses:
BSD licenses are a family of permissive free software licenses, imposing minimal restrictions on the use and distribution of covered software. This is in contrast to copyleft licenses, which have share-alike requirements. The original BSD license was used for its namesake, the Berkeley Software Distribution (BSD), a Unix-like operating system. The original version has since been revised, and its descendants are referred to as modified BSD licenses.BSD is both a license and a class of license (generally referred to as BSD-like). The modified BSD license (in wide use today) is very similar to the license originally used for the BSD version of Unix. The BSD license is a simple license that merely requires that all code retain the BSD license notice if redistributed in source code format, or reproduce the notice if redistributed in binary format. The BSD license (unlike some other licenses e.g. GPL) does not require that source code be distributed at all
MIT licenses:
The MIT license gives users express permission to reuse code for any purpose, sometimes even if code is part of proprietary software. As long as users include the original copy of the MIT license in their distribution, they can make any changes or modifications to the code to suit their own needs. It is one of the most simple open source license agreements. The intent was for the text to be understandable by average users and to avoid extensive litigation, which may arise from other similar Free and Open Source Software (FOSS) licenses.
Apache License :
The Apache License is a permissive free software license written by the Apache Software Foundation (ASF).] It allows users to use the software for any purpose, to distribute it, to modify it, and to distribute modified versions of the software under the terms of the license, without concern for royalties. The ASF and its projects release their software products under the Apache License. The license is also used by many non-ASF projects.
Creating license on Creative Common for my Final project:
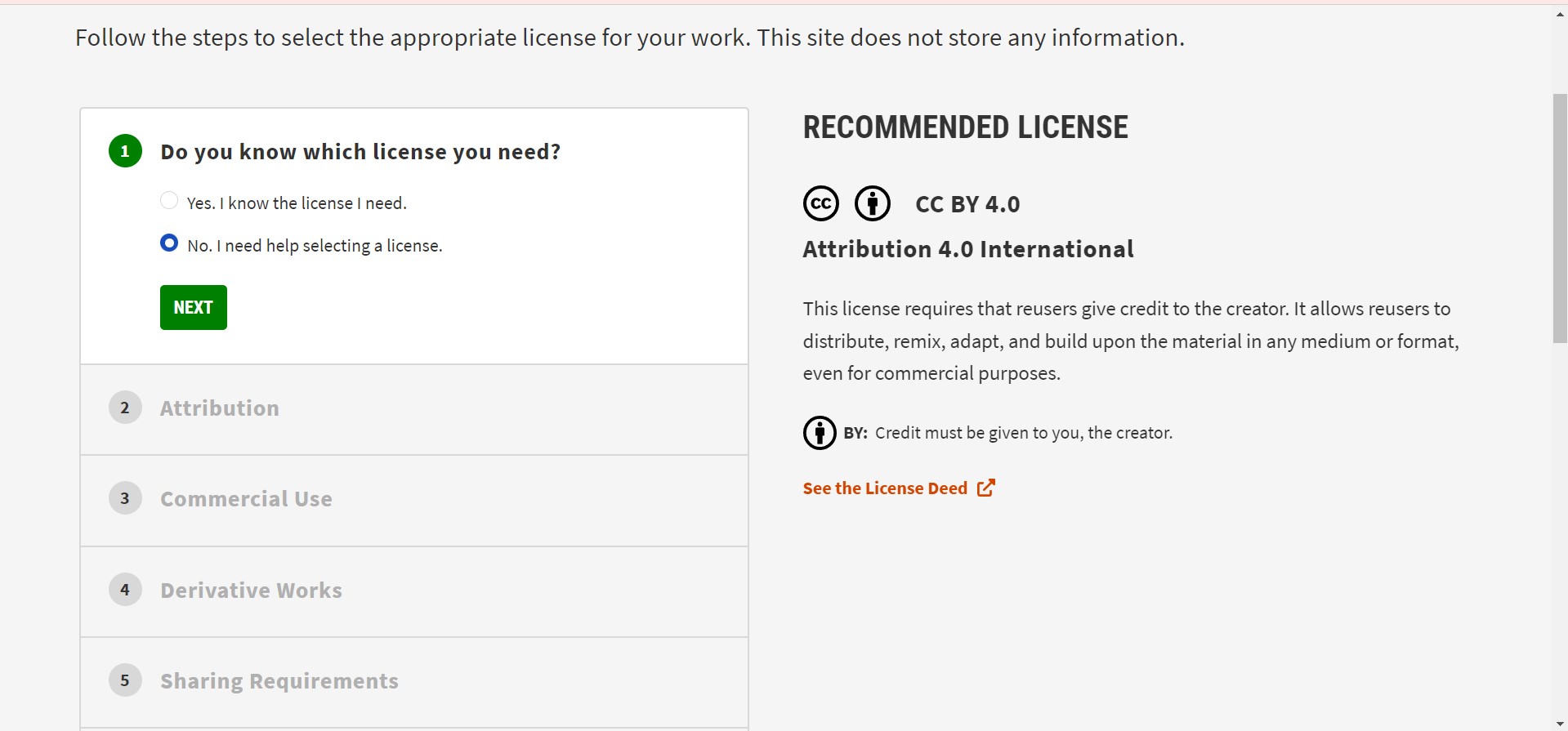
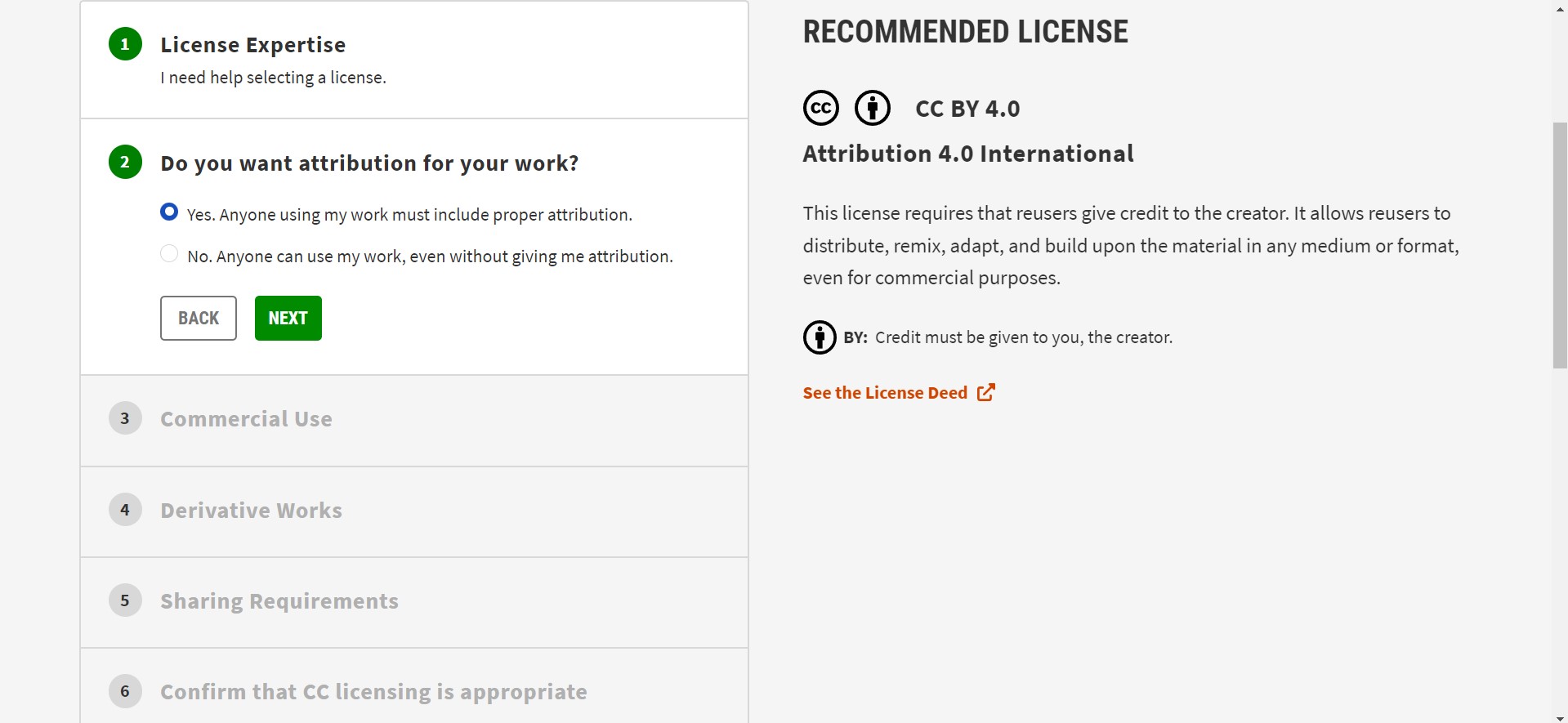
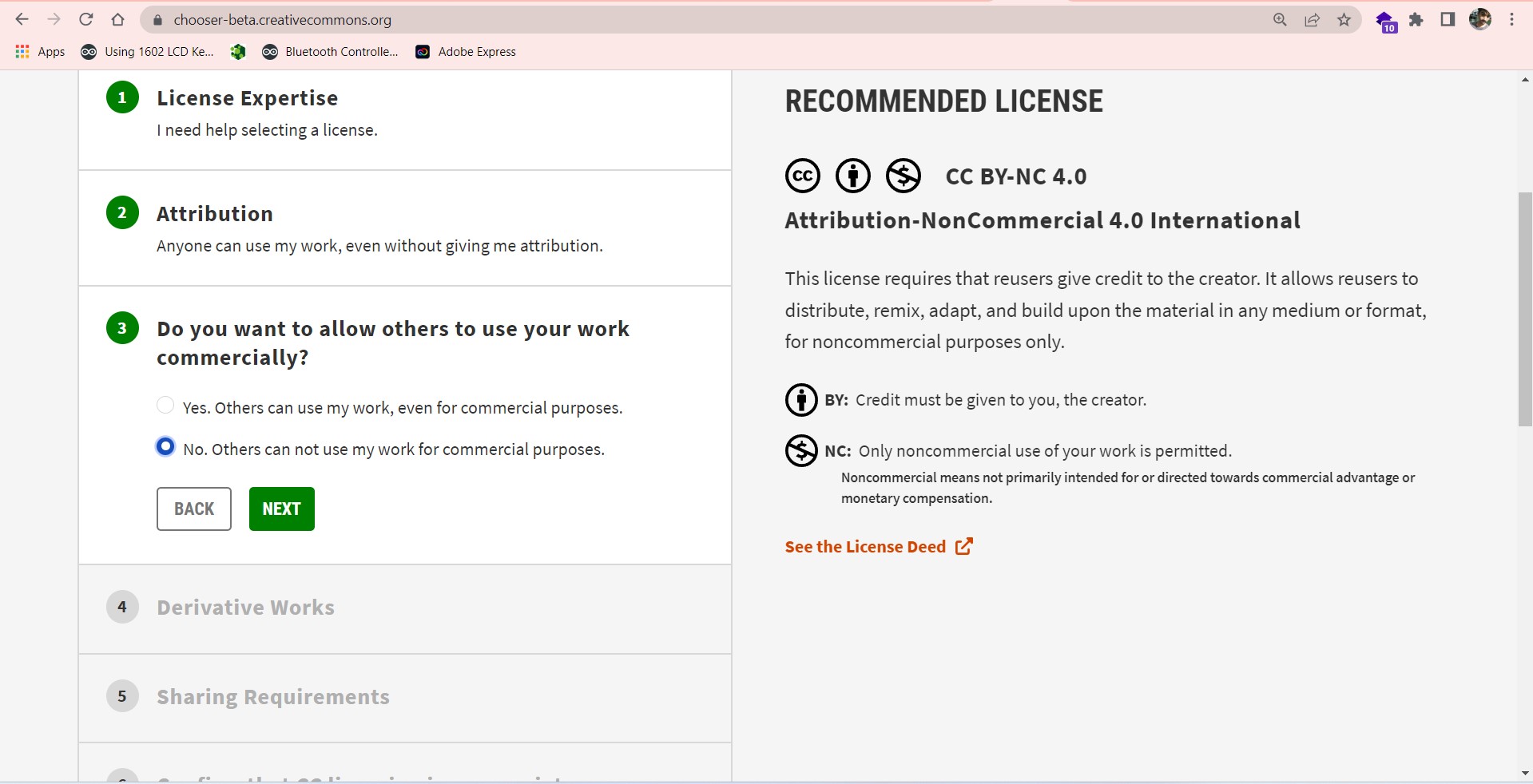
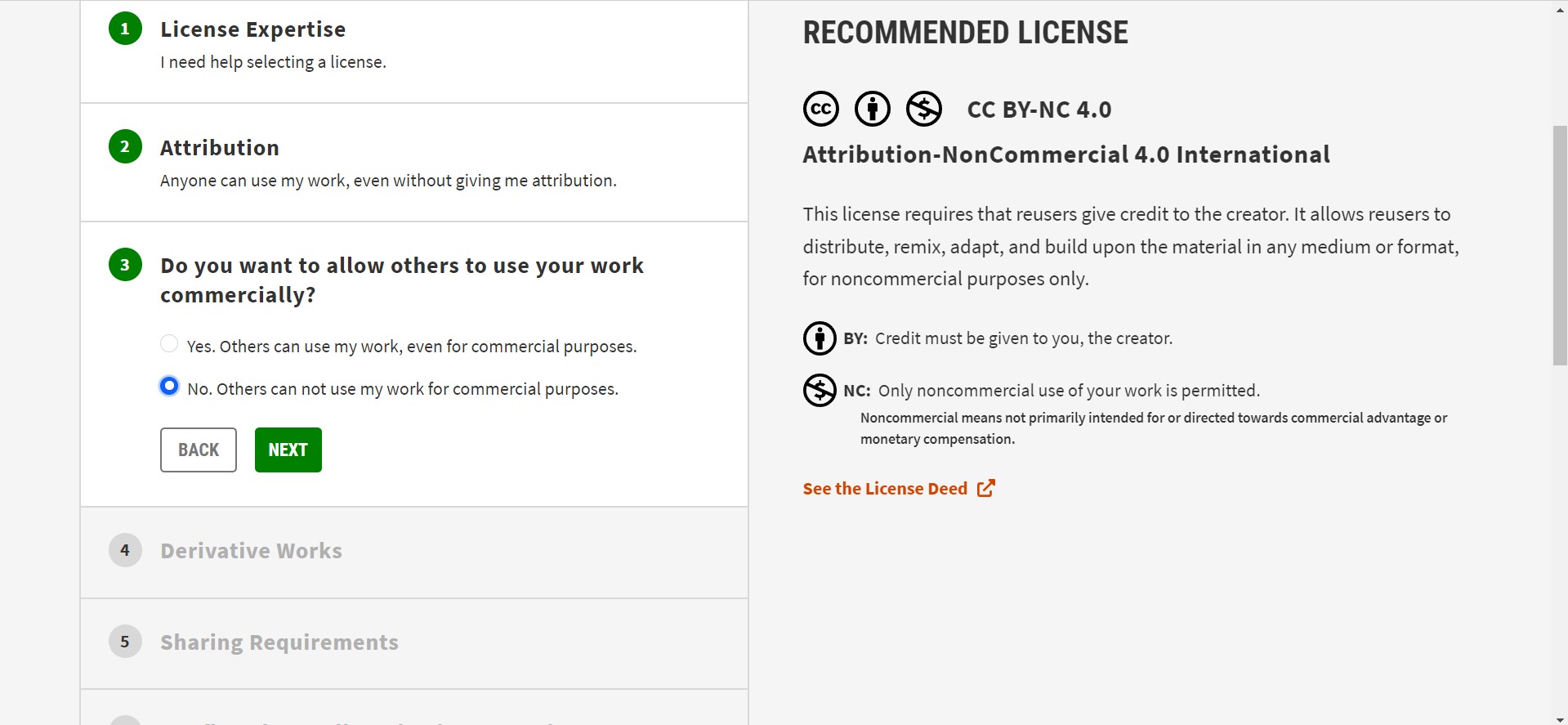
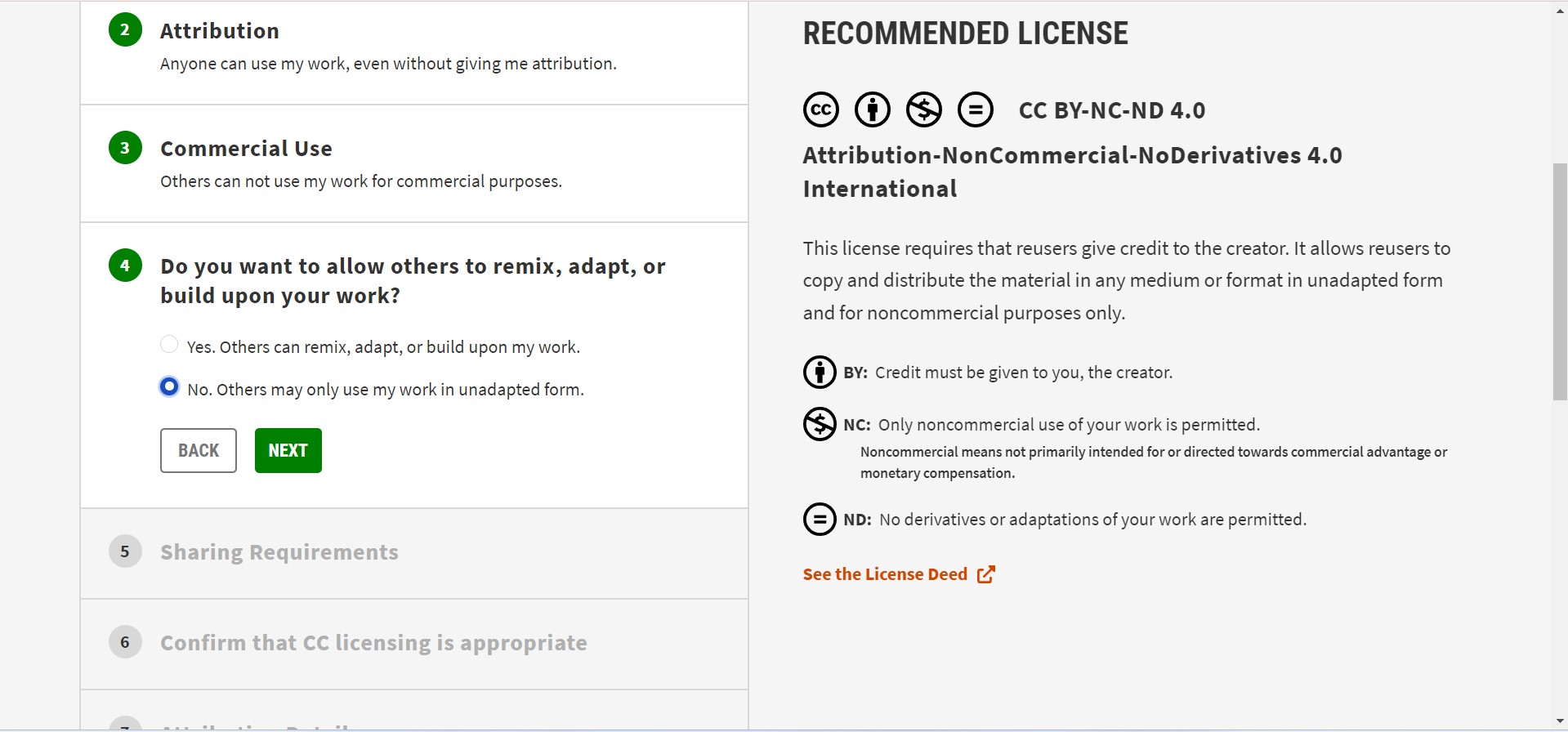
I try to creat a created creative commons license for my Project.I did the following steps to make one.
Go to creativecommons.org license website.
.
.
.
.
.

.
.
.
.
.
.
.
I copy and past the HTML embedded code as you can see follow.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
LPG Sanitary Pad Incinerator by Vrushabh Zunjurkar is licensed under Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International
LPG Sanitary Pad Incinerator by Vrushabh Zunjurkar is licensed under CC BY-NC-ND 4.0
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
I pest this url at the footre of my Index.html page .
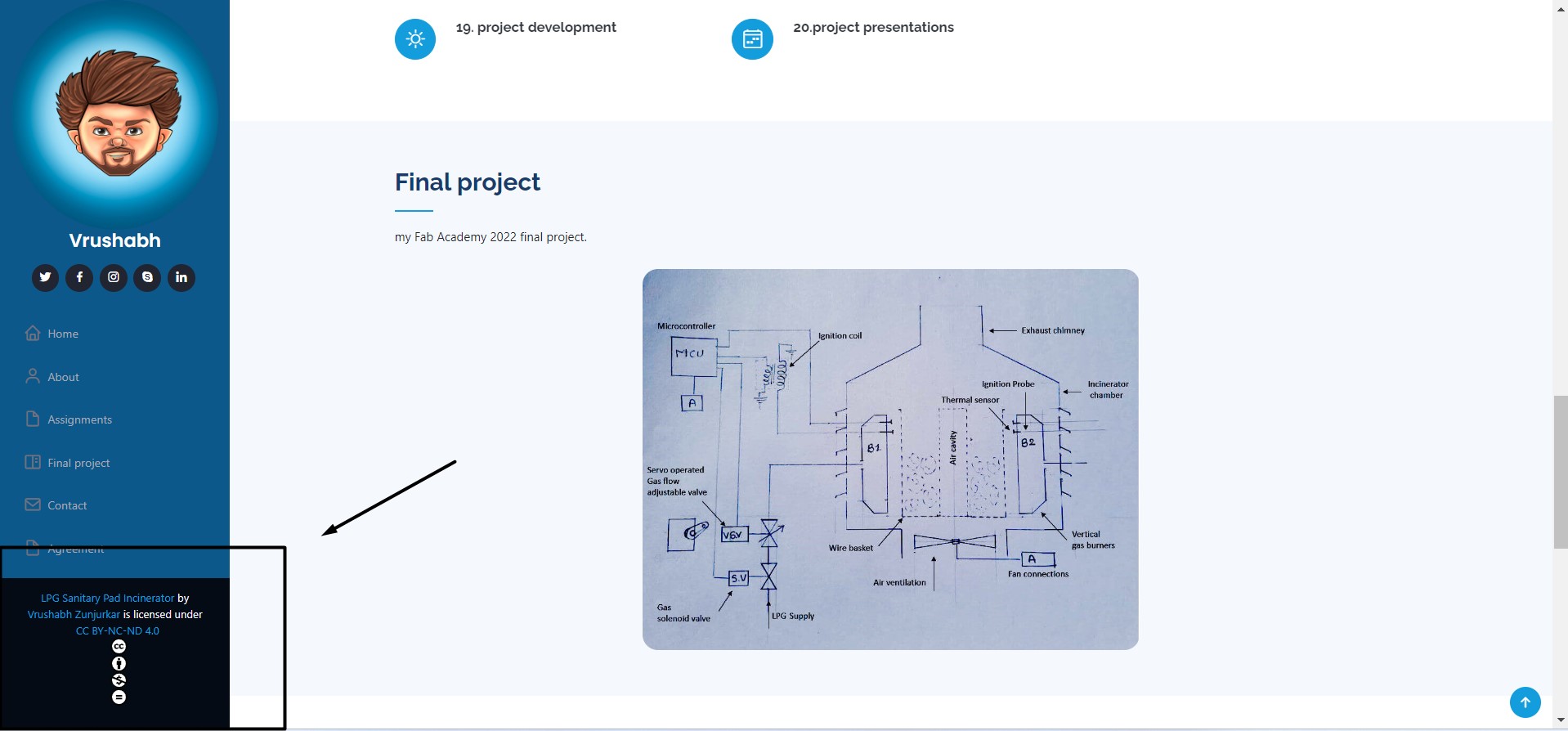
.
I also added it below my final project page as you can see.
.
Plan for dissemination:
To take this project up to societal use I designed a Theory of change with my friend prasad patil from vigyan ashram .He has some business sance and he also was a part of this project.
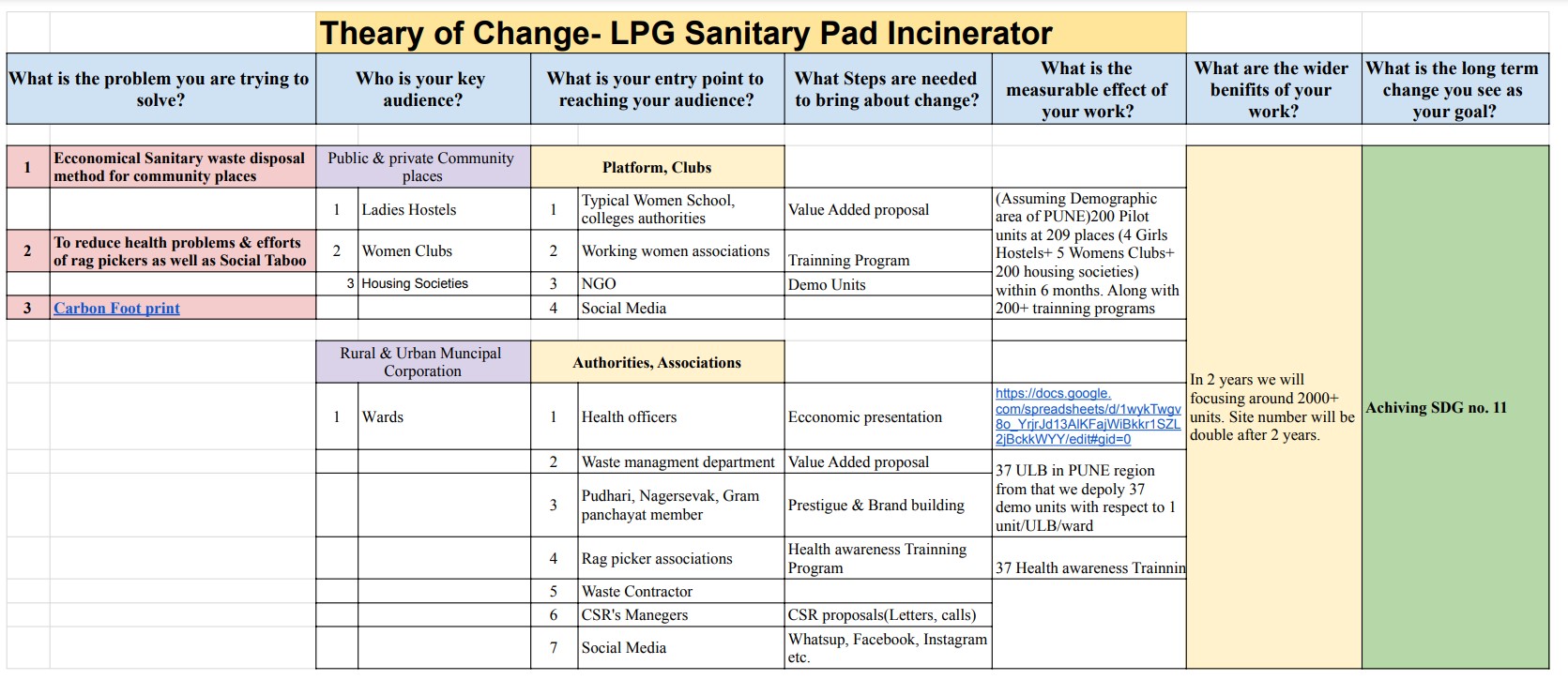
Theary of Change- LPG Sanitary Pad Incinerator.
