Climate Simulator in Greenhouse for organic products
The problem
The development of agriculture in the high Andean areas of Cusco that are above 3,500 meters above sea level is quite limited and with difficulties in adapting many products that require special conditions of temperature, dosed water, humidity and the presence of Substances that fertilize the soil. In the last 10 years, the use of greenhouses has increased, creating more favorable conditions for certain products to be grown at heights, where the cold and conditions are not favorable.
This type of agriculture is carried out in an artisanal way and guided by the experience and good judgment of the members of the communities, some of whom have the technical advice of the local authorities.
Purpose
My project aims to achieve an alternative solution for the large amount of use of phytotoldo in the high Andean region of Cusco Peru, above four thousand three hundred (4300 meters above sea level)It is intended to collect data from each fitotoldo on a Raspberry server of many parameters measured with Arduino sensors: water, humidity, temperature, fertilizer, mineral salts that are necessary for a more technical crop.
What is the Greenhouse or Fitotoldo?
The fitotoldos facilitate the control of the technical and environmental conditions (temperature, relative humidity, luminosity) for the production of species such as carrots, lettuce, spinach, beets, aromatic plants, among others, which will guarantee food safety and contribute to the farming.1. In the region of Cusco Peru, there are provinces called high Andean whose location is from 3400 meters above sea level to 4500 meters above sea level, where the cultivation of some products is practically impossible.2. The so-called fitotoldos have been used in which cultivation is carried out in an artisanal way to simulate climatic conditions more or less similar to those of lower ecological floors in the so-called inter-Andean valleys.3. The idea arises from the use of non-conventional energies such as solar energy, to build a phytosol and be able to control, through a climate simulator, all the parameters in the cultivation of organic products whose growth depends on external factors such as temperature, humidity, irrigation water, the amount of light that is required.
Who will use
The development and implementation of the final project will be used mainly by small farmers who are dedicated to the cultivation of organic products and need to increase their productivity and improve the quality of the products they grow in greenhouses. As the main crop parameters can be controlled, they can be used to improve agriculture.
The district municipality, through a government program called Pro-compete, supports the communities in its jurisdiction and we are already in talks with the local government to support the implementation and use of the climate simulator for the production of organic products that require special temperature conditions. , humidity and dosage of drip or sprinkler irrigation water.
Initial Sketch
Some components that are required
Sensors with arduino
In this project, it is proposed to connect our Arduino board with different sensors. We will explore and investigate the following sensors:
1.- Humidity sensor (DHT22)
2.- Temperature sensor (LM35)
3.- Water detector sensor (simple water triggerHumidity sensor (DHT22)
Humidity Sensor (DHT22)
The DHT-22 (also called AM2302) is a digital output, relative humidity and temperature sensor. It uses a capacitive humidity sensor and a thermistor to measure the surrounding air and sends a digital signal on the data pin.
In this project we will learn how to interface our Arduino board with different sensors . The temperature and humidity of the room will be printed on the serial monitor.
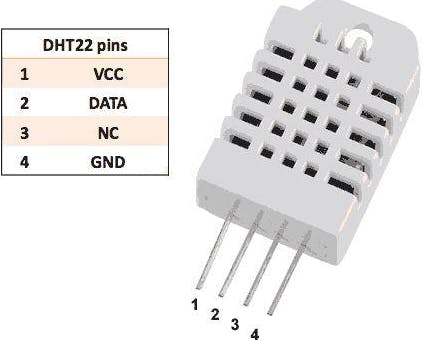
The connections are simple. The first pin on the left to 3-5V power, the second pin to the data input pin and the right-most pin to the ground.
Technical Details
-
Power − 3-5V
- Max Current − 2.5mA
- Humidity − 0-100%, 2-5% accuracy
- Temperature − 40 to 80°C, ±0.5°C accuracy
Components Required
You will need the following components −
- 1 × Breadboard
- 1 × Arduino Uno R3
- 1 × DHT22
- 1 × 10K ohm resistor
PROCEDURE
Follow the circuit diagram and hook up the components on the breadboard as shown in the image below.
Solar energy converter into electrical energy
It is defined as an electrical device that converts light energy into electrical energy through the photovoltaic effect. It is basically a p-n junction diode.
When sunlight strikes the PV cell, the photons of light excite the electrons on the cell and make them flow, producing usable energy (electrical energy).
Previous experiences
1.- Qorichacra Project
This Guide for the construction and management of greenhouses for the production of vegetables and fruits in high Andean areas is a tool that provides the small farmer with a step-by-step guide to the implementation of protected agriculture technology (greenhouses), with technical irrigation and with the application of Good Agricultural Practices, within a commercial agriculture approach.
The objective of the Guide is to disseminate and promote, in Peru and other countries in the region, these work methodologies already tested by peasant families and by agricultural technicians, which facilitate scaling processes to improve the performance of small family agriculture in the Andes.
The Guide has been prepared based on the learning validated in the "Qorichacra" project and in the project "Development of the technical assistance market for the efficient use of solar energy in greenhouses in the Cusco Region", initiatives to promote small agricultural producers that the Bartolomé de Las Casas Center in Cusco (CBC) has implemented in recent years, thanks to its accumulated knowledge and experience, which demonstrated the viability of technological change at the level of family farming above 3,500 meters above sea level.
The Qorichacra project was carried out between 2010 and 2015, promoted by the Syngenta Foundation for Sustainable Agriculture (SFSA) and the company Arcos Dorados (AD). With Qorichacra, the promotion of the use of greenhouses for the production of vegetables was resumed and the implementation of Good Agricultural Practices with small producers was promoted, in order to ensure the obtaining of high quality and safe vegetables, which the market demands every year again.
Protected agriculture in greenhouses has important advantages for the development of family farming, such as:
- Obtaining more than one harvest per year per product (up to 2 or 3, depending on factors such as variety, soil, water, etc.), translating into greater production and productivity per surface unit.
- A stable supply of products throughout the year, which allows, on the one hand, to articulate with formal clients in a medium and long-term supply relationship, and on the other hand, it gives you the opportunity to obtain high prices in the times of scarcity.
- It makes it easier for you to obtain safe and quality vegetables and fruits, as well as their traceability, allowing you to certify them.
- Facilitates the management of records and information for the traceability and monitoring of cultural activities. These records allow early detection of bad practices and take the necessary preventive or corrective actions.
METHODOLOGY
Backtracking destination to origin + Iterative Approach with deliveries Partial.