Final Project Documentation
4. Embeded Programming
Testing sensors
1. HCHO (VOC) sensor

For Data reading of VOC sensor I could use the manufacturer code as to see below. First Code shows the Part 1 of the programming the sensor, which is the calibrating part.
demo of Grove - HCHO Sensor by seeds studio
#include // load the math.h library
#define Vc 4.95
#define R0 34.28 // the number of R0 you detected just now
void setup() // At the begining of the programm connect to the serial port
{
Serial.begin(9600);
}
void loop()
{
int sensorValue=analogRead(A1); // read the signal (voltage value) from the pin A1 (analog)
double Rs=(1023.0/sensorValue)-1; // calculate Rs out of the read voltage value of pin A1
Serial.print("Rs = ");
Serial.println(Rs); // Print the real value of Rs
double ppm=pow(10.0,((log10(Rs/R0)-0.0827)/(-0.4807))); // calculate the HCHO level withs this callculation (ppm)
Serial.print("HCHO ppm = "); // Print the VOC value
Serial.println(ppm);
delay(10000); //wait 10 seconds bevor you read the next value
}
After the calibration, when I was sitting in the garden, there was a car nearby that started the engine. Immediately, even if I did not think about it, the sensor data has risen enormously. A few minutes later, a neighbor started the barbecue and the sensor data went up immediately ...
After the calibration in the outside air, I could bring the sensor into the room and measure the data of the room air. The sensor data kept rising as I was in the room with the door closed and after opening the window, the value of HCHO quickly dropped off.
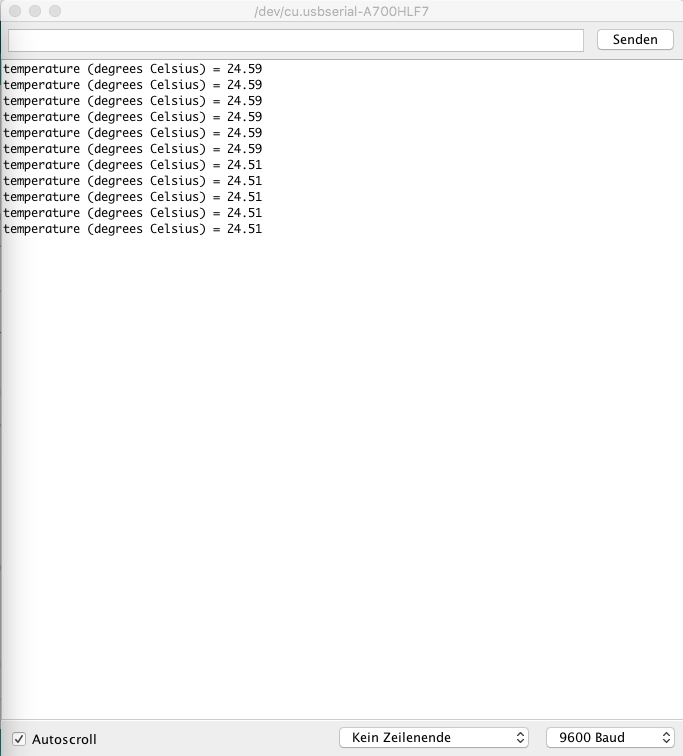
2. Temperature sensor
Grove temperature sensor v1.2 Seeds Studio .

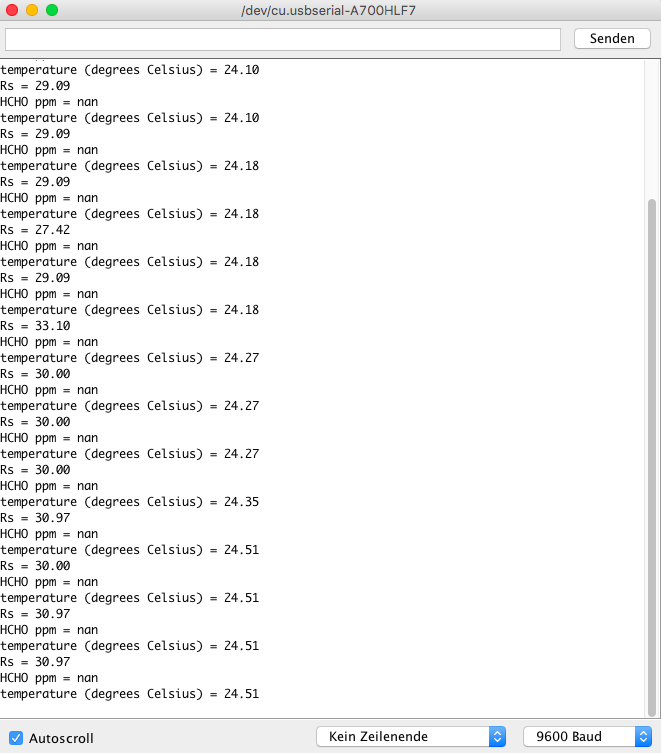
Here you can find the simple temperature and HCHO data reading code:
// Demo code for Grove - Temperature Sensor V1.1/1.2 // Loovee @ 2015-8-26 #include// Following two constants belonge to the HCHO sensor: #define Vc 4.95 #define R0 34.28 //the number of R0 you detected during the calibration const int B = 4275; // B value of the thermistor const int Rinit = 100000; // Rinit = 100k const int pinTempSensor = A0; // temperature sensor connect to A0 void setup() { Serial.begin(9600); } void loop() { int a = analogRead(pinTempSensor); float R = 1023.0/a-1.0; R = Rinit*R; float temperature = 1.0/(log(R/Rinit)/B+1/298.15)-273.15 - 2; // convert to temperature via datasheet int sensorValue=analogRead(A1); // read the signal (voltage value) from the pin A1 (analog) double Rs=(1023.0/sensorValue)-1; // calculate Rs out of the read voltage value of pin A1 Serial.print("Rs = "); Serial.println(Rs); // Print the real value of Rs double ppm=pow(10.0,((log10(Rs/R0)-0.0827)/(-0.4807))); // calculate the HCHO level withs this callculation (ppm) Serial.print("HCHO ppm = "); // Print the VOC value Serial.println(ppm); Serial.print("temperature (degrees Celsius) = "); Serial.println(temperature); delay(2000); }
3. Dust sensor

In the following you can find the data reading code for dust sensor from the seedsstudio.com .
int pin = 8;
unsigned long duration;
unsigned long starttime;
unsigned long sampletime_ms = 30000;//sampe 30s ;
unsigned long lowpulseoccupancy = 0;
float ratio = 0;
float concentration = 0;
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(9600);
pinMode(pin,INPUT);
starttime = millis();//get the current time;
}
void loop()
{
duration = pulseIn(pin, LOW);
lowpulseoccupancy = lowpulseoccupancy+duration;
if ((millis()-starttime) > sampletime_ms)//if the sampel time == 30s
{
ratio = lowpulseoccupancy/(sampletime_ms*10.0); // Integer percentage 0=>100
concentration = 1.1*pow(ratio,3)-3.8*pow(ratio,2)+520*ratio+0.62; // using spec sheet curve
Serial.print(lowpulseoccupancy);
Serial.print(",");
Serial.print(ratio);
Serial.print(",");
Serial.println(concentration);
lowpulseoccupancy = 0;
starttime = millis();
}
}

4. Stepper Motor
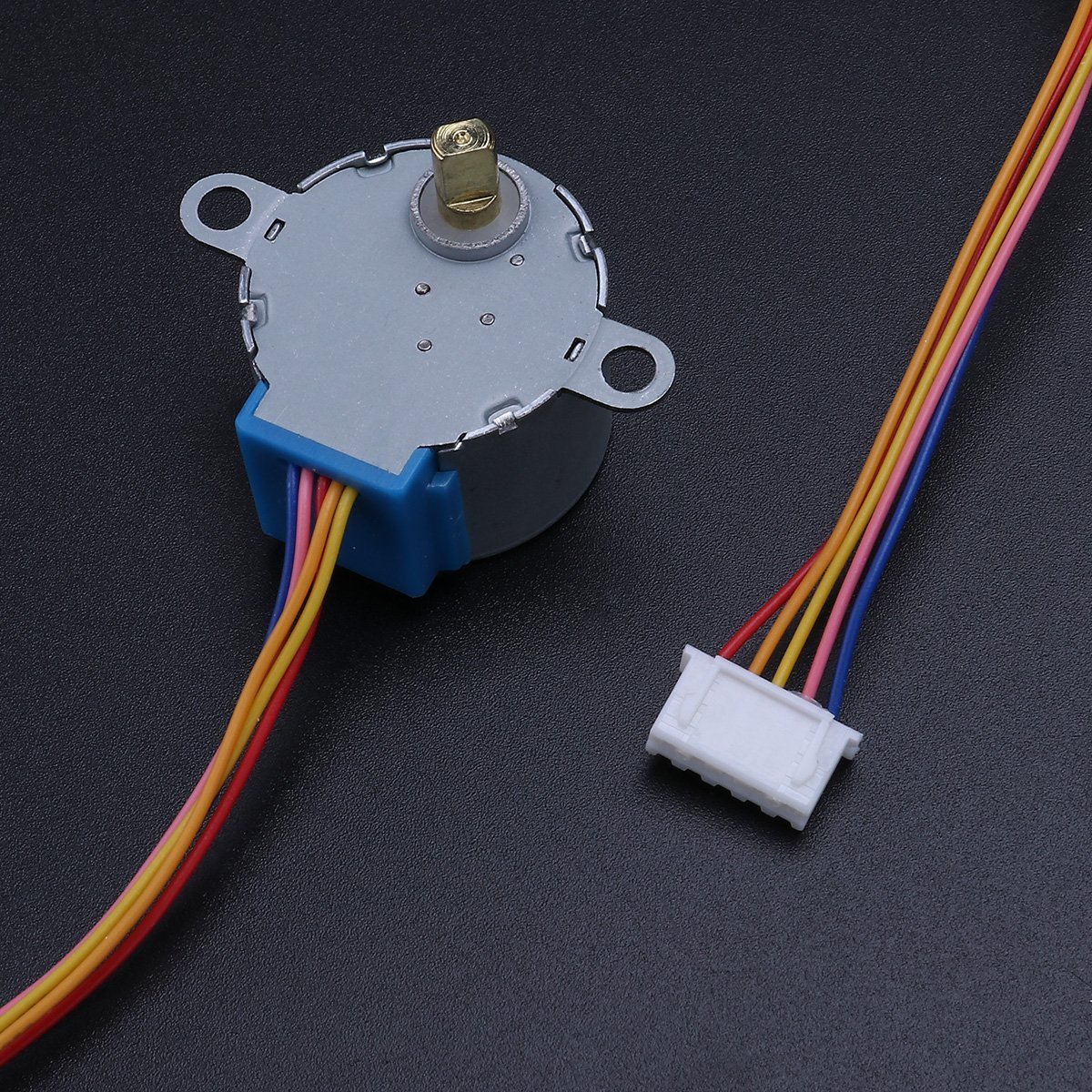

Simple stepper motor code:
/*
Stepper Motor Demonstration 1
Stepper-Demo1.ino
Demonstrates 28BYJ-48 Unipolar Stepper with ULN2003 Driver
Uses Arduino Stepper Library
DroneBot Workshop 2018
https://dronebotworkshop.com
*/
//Include the Arduino Stepper Library
#include
// Define Constants
// Number of steps per internal motor revolution
const float STEPS_PER_REV = 32;
// Amount of Gear Reduction
const float GEAR_RED = 64;
// Number of steps per geared output rotation
const float STEPS_PER_OUT_REV = STEPS_PER_REV * GEAR_RED;
// Define Variables
// Number of Steps Required
int StepsRequired;
// Create Instance of Stepper Class
// Specify Pins used for motor coils
// The pins used are 8,9,10,11
// Connected to ULN2003 Motor Driver In1, In2, In3, In4
// Pins entered in sequence 1-3-2-4 for proper step sequencing
Stepper steppermotor(STEPS_PER_REV, 10, 8, 9, 7);
void setup()
{
// Nothing for stepper (Stepper Library sets pins as outputs)
}
void loop()
{
// Rotate CW 1/2 turn slowly
StepsRequired = 2*STEPS_PER_OUT_REV ;
steppermotor.setSpeed(400);
steppermotor.step(StepsRequired);
delay(1000);
// Rotate CCW 1/2 turn quickly
StepsRequired = - 2* STEPS_PER_OUT_REV ;
steppermotor.setSpeed(700);
steppermotor.step(StepsRequired);
delay(2000);
}
5. RGB LED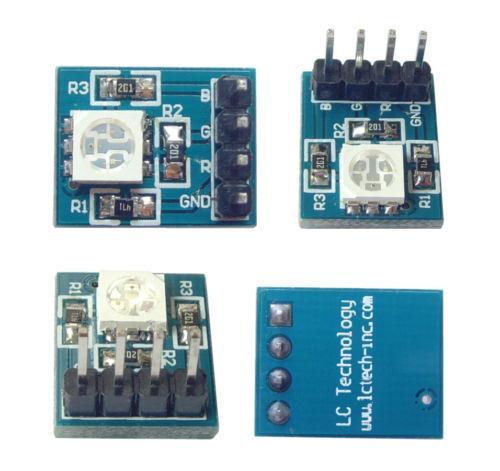 
Here is a simple RGB LED testing code for Arduino IDE:
int LEDred = PD5; // Colour red is connected on Pin PB2
//int LEDgreen = PD3; // Colour blue is connected on Pin PB1 (PWM)
int LEDblue = PD6; // Colour gruen an Pin 6
int p = 3000; // p is a pause with 3000ms (3 seconds)
int brightness1a = 200; // Value zwibetween 0 und 255 gives the information about the Brightness of each colour
int brightness1b = 200;
int brightness1c = 200;
int dark = 0; // Value 0 means Voltage 0V Spannung (LED off).
void setup()
{
pinMode(LEDblue, OUTPUT);
pinMode(LEDgreen OUTPUT);
pinMode(LEDred, OUTPUT);
}
void loop()
{
analogWrite(LEDred, dark); // now the red LED will be turned off
analogWrite(LEDgreen, brightness1b); // green LED on
delay(p);
analogWrite(LEDgreen, dark); // green LED off
analogWrite(LEDblue, brightness1c); // blue LED on
delay(p);
analogWrite(LEDblue, dark); // blue LED off
analogWrite(LEDred, brightness1a);
delay(p);
} Downloads
| HCHO sensor (ino) | download |
| RGB LED (ino) | download |
| Dust sensor (ino) | download |
| Steppermotor and RGB LED (ino) | download |
| Sensors and steppermotor plus LED simple code(ino) | download |