Discovering How to Produce an Electronic Board
We had a Group Assignment and an Individual Assignment this week.
- Group Assignment The group assginment was to characterize the specifications of our PCB production process.
- Individual Assignment The individual assignment was to make an in-cicuit programmer by milling the PCB.
You can check the Group Assignment on the following link: Group Assignment
Machines Used
The main machine used in this week's assignment is the Desktop CNC Machine.The Roland MDX-40 was used for cnc milling the coper board in this assignment. This Roland MDX-40 uses the a Computer Controlled Router to Mill the intended object.
Software Used
The following software were used in this week's assignment:- Eagle was used to edit the design of the PCB.
- GIMP was used to extract and enhance the image of the PCB design.
- Fab Module was the main online platform used to produce the g-code used by the CNC machine.
- Arduino IDE was used for downloading the firmware to the produced ISP.
1- Characterizing the Specifications of PCB Production
In order to discover the different specifications of PCB production, we first started by trying a test file that has various thickness. The step-by-step procedure of preparing the g-code and milling the copper board is described below. The same procedure followed will be used every time we want to mill a new PCB
Preparing the G-Code
The CNC machines usually recieves a g-code that controls the x, y and Z movement of the milling bit.
To mill on our CNC machine, the follwing procedure was followed:
- Preparing the Design In order to start milling a PCB, we have to prepare the design first on Eagle. After building the circuit first on Eagle, we then arrange the schematic of the PCB and assign the location of all component and the connections between them. After that, we extract the image to be used for extracting the g-code.
- Extracting the cicuit image and enhancing it on GIMP After finalizing the layout of the PCB, we extract the image in a monocrome setting. Then we insert the image in GIMP to enhance it and produce two different images, one for the internal path of the PCB and the other is for the external path of the PCB.
- Generating the g-code using Fab Modules After extracting both images, the next step is to generate the g-code. The g-code is generated on Fab Modules. I detailed step-by-step procedure will be described later in this chapter.
- Forwarding the Job Order After generating the g-code, the next step is to send the g-code to the CNC machine. But before doing that, we have to set up the coordinates of the CNC machine.
Setting Up the CNC Machine
After preparing the g-code and the relative settings we need, the next step is to place the material we want in the CNC machine and set it up according to the thickness of the material.
To mill on our CNC machine, the follwing procedure was followed:
- Zeroying the X and Y axis The first step is to set the zero location where the milling bit will start on the copper board. This step is done using the control panel on the computer and the location is set manually.
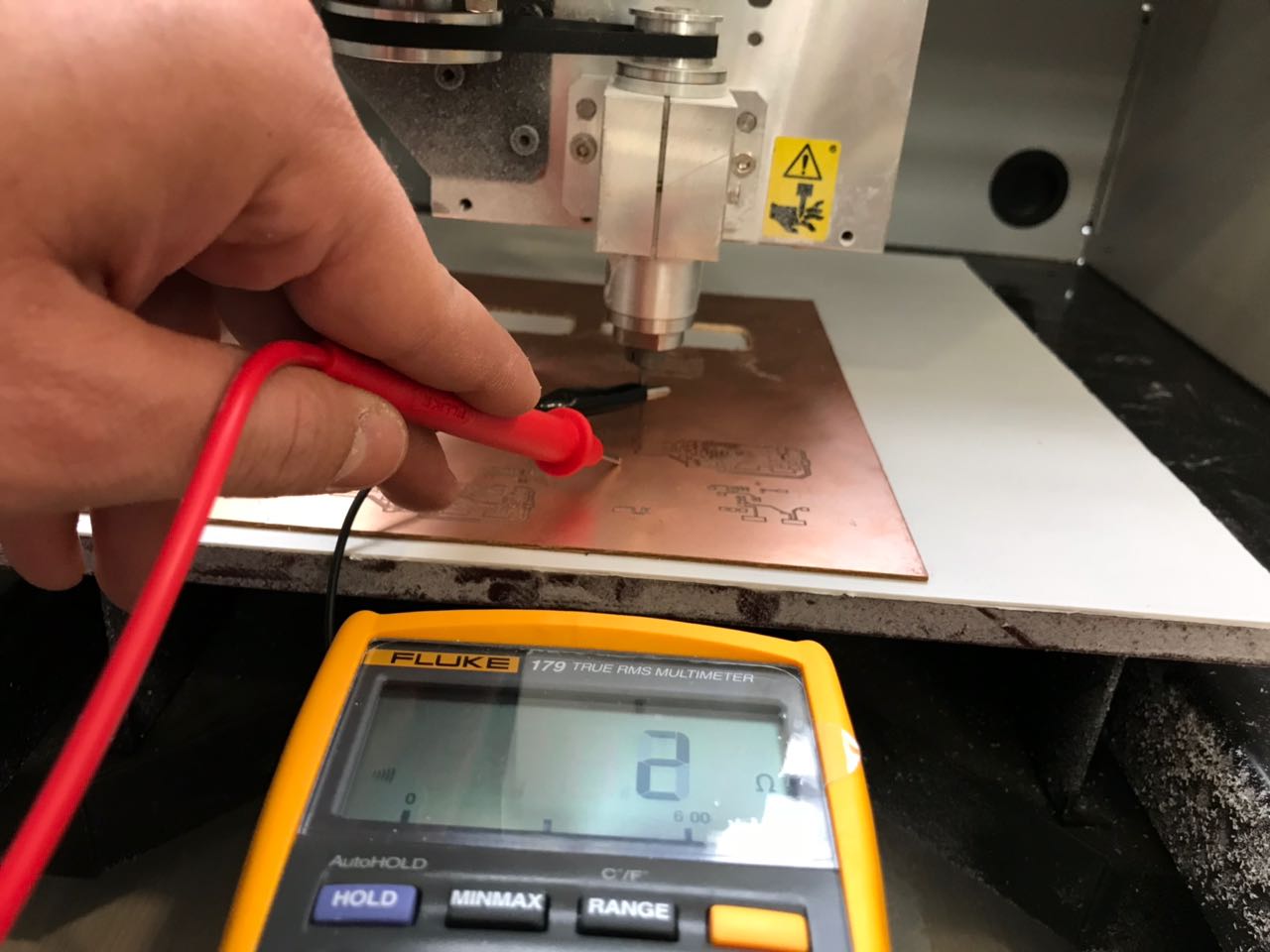
- Zeroying the Z axis Next, we should zero the milling bit at the top survace f the copper board. To do this step precisely, we use a multimeter. Once the drilling bit contacts the surface of the copper board, this will lead to a closed circuit and thus the mutlimeter will beep.
- Performing the Mill After setting up the coodinates of the machine, we output the g-code drectly using the "Drop Out" software. The CNC machine will then start the job.

Testing the CNC Machine
So the idea was to understand the different settings of the CNC milling process that could affect the output products.
There are many variables in the Milling process setting that could be changed and respectively affect the output of the machine.
The settings are:
- RPM of Milling Bit is the variable that controls the rotating speed of the milling bit.
- Mrilling Bit Diameter is the variable that is directy related to the bit diameter. The bigger the diameter, the less we can achieve thin connecting lines.
- Feed Rate is the variable that controls the rate the milling bit moves on the surface of the copper board. Milling the inner lines requires a normal feed rate. However, milling the outer parameter of the pcb required very slow feed rate.
- Offset Number is the variable that controls the number of passes the milling bit does over the same path. This setting majorely affects the final product. Paths that are not cut in the first pass post probably will be cut during the other passes.
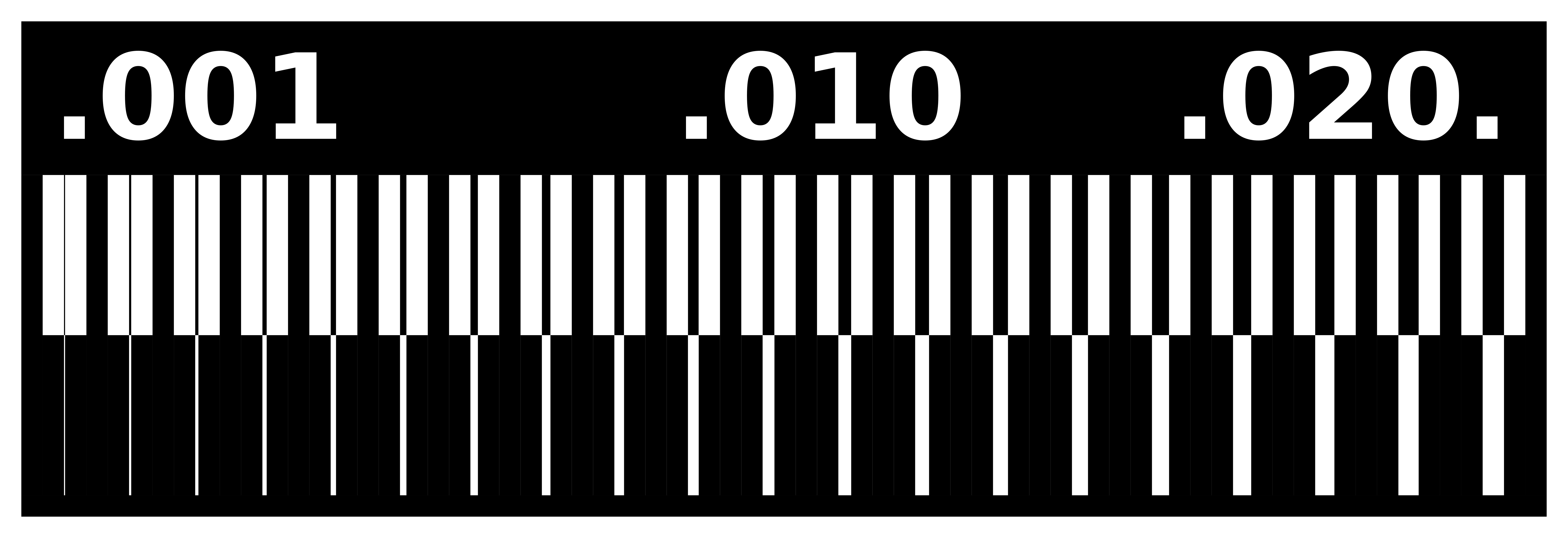
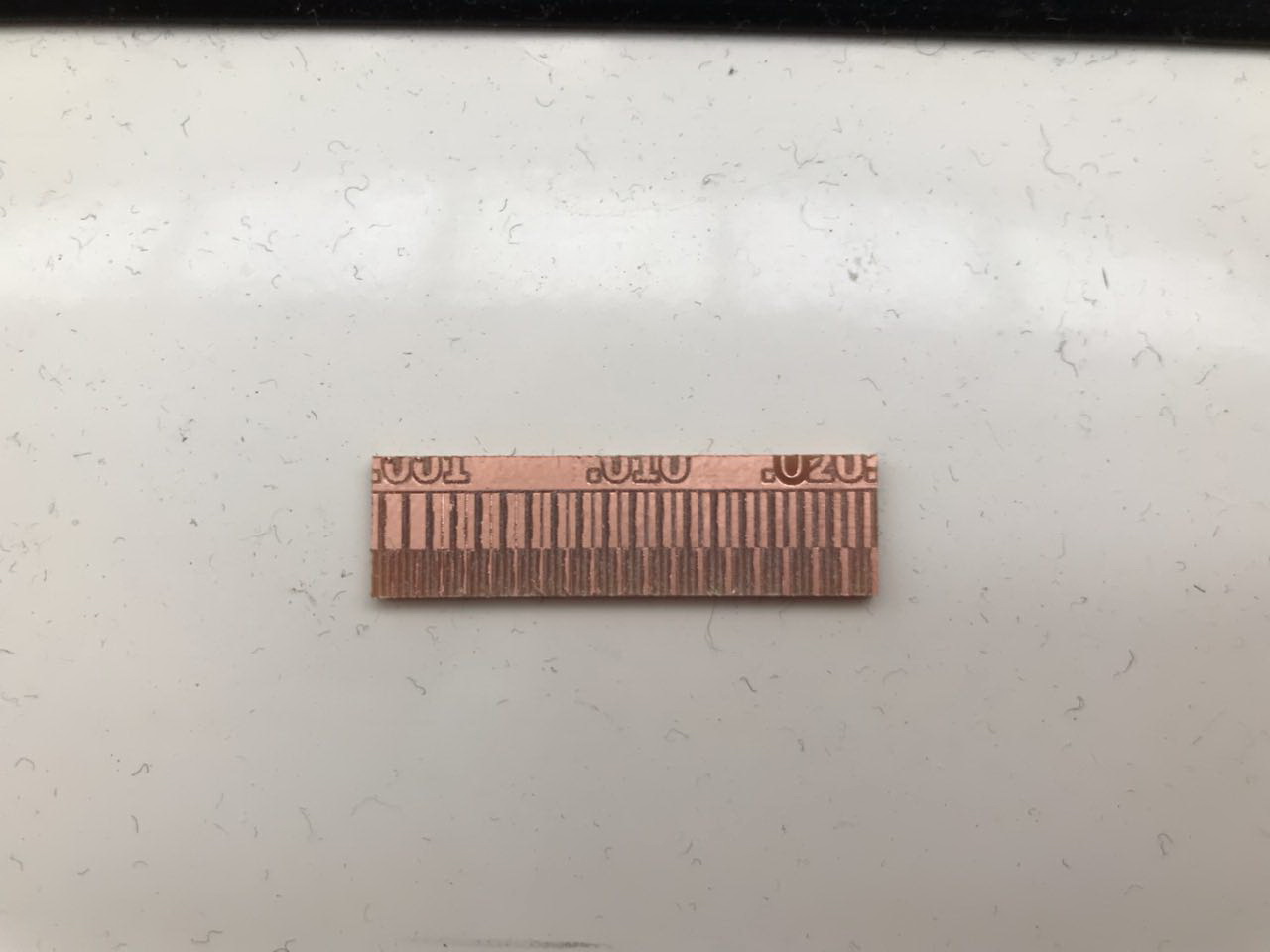
Saying that, we started by a Test File we got from the internet, that has different paths of vairious thicknesses. We tested milling this image using the milling bit of diameter 0.2mm.
The test file was downloaded from the following Link
After that, we noticed that not all paths stayed, and the thin paths (less than 0.005mm) were missing. Thus we deduced that our limitation is that the milling bit cannot mill paths less than 0.005 mm.
2- Making an In-cicuit Programmer ISP
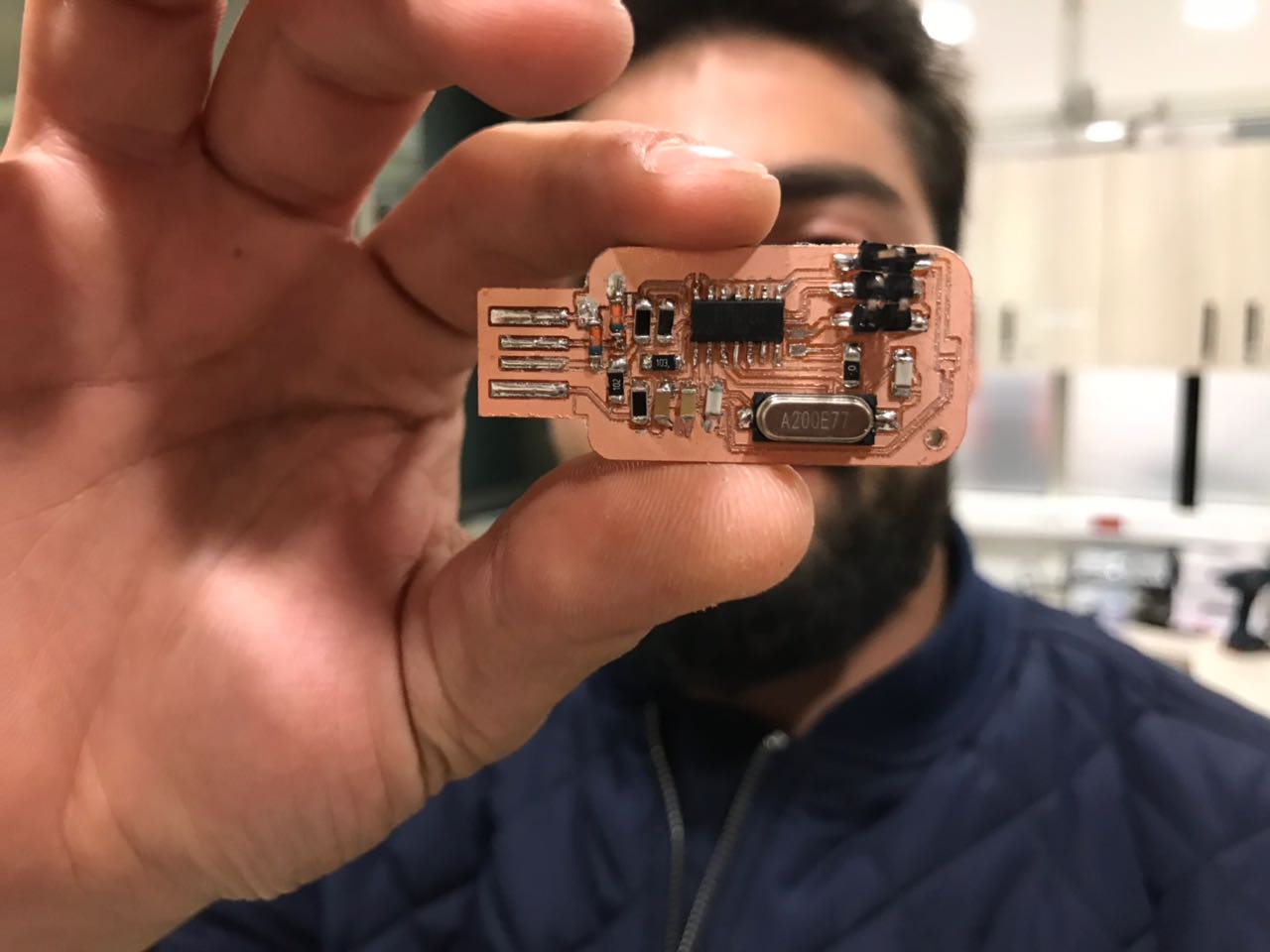
After checking the best settings that are used for milling, the next step was to start milling the Fab ISP.
To do that many steps were followed that will be described in details below.
The main steps that are followed to produce a fully functional ISP go as the following:
- Preparing the Design
- Extracting the PCB Layout Image
- Producing the G-Code
- CNC Milling the PCB Board
- Welding the Components
- Programming the Microcontroller
You can download the original Eagle file used for my ISP from the following links: Fab_ISP_Key
Step 1 - Preparing the Design
The first step in any PCB production process is preparing the design. In our case, we had access to many designs available in the Archive of the Fab Academy. However, we had we had to choose a design that fits the available inventory in our lab. So based on that, I chose to use the FabISPkey V1.0 as the design i want to use. But I had one component that differs from the downloaded design, which is the Crystal 20Hz. We did not have the XTal1 in our lab. So the solution was to change the design on Eagle, to fit the size of the Crystal we have. Based on this change, I needed to change Cappacitors C3 and C4 to meet the requirements according to the data sheet of the Crystal.
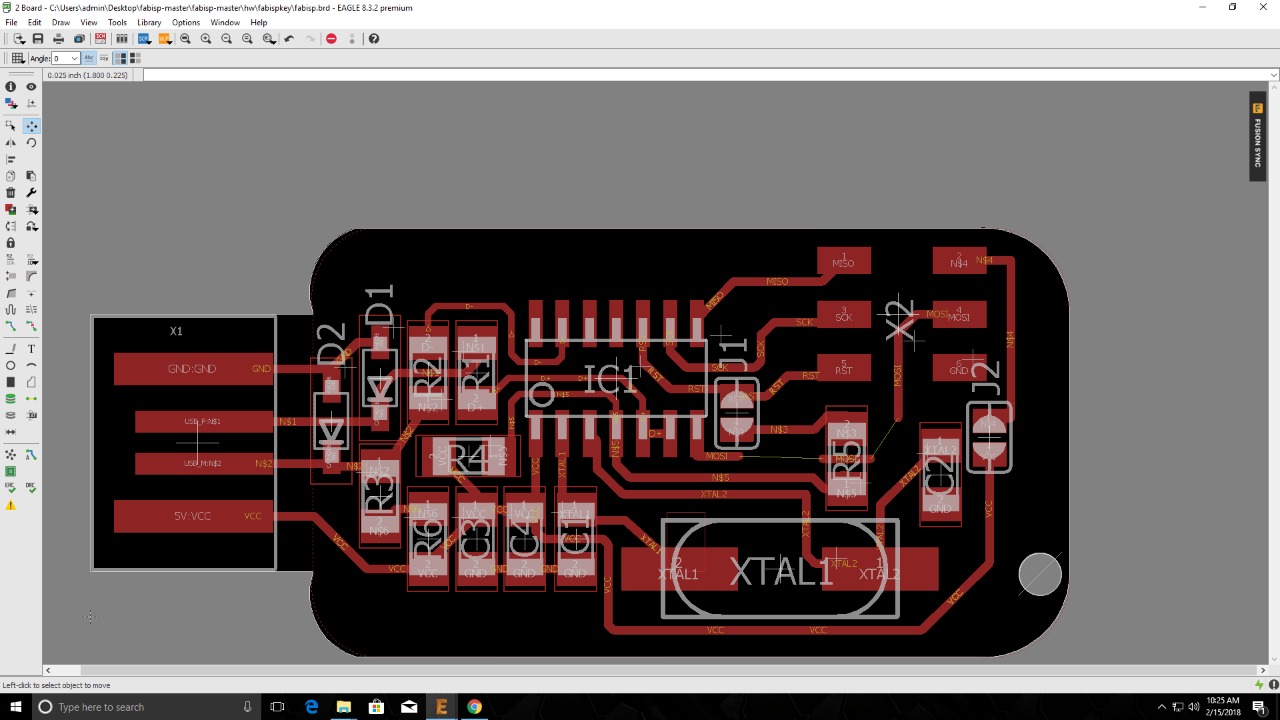
Step 2 - Extracting the PCB Layout Image
After finalizing the design, the next step is to extract the final layout of the PCB, which mainly represents the location of the different components and the connecting lines between them.
The image was extracted from Eagle in a Monochrome setting, and was then opened in GIMP. I mainly used GIMP to enhance the extracted layout and produce 2 different images:
- Image 1 that represents the internal layout of the PCB
- Image 2 that represents the external perimeter of the PCB
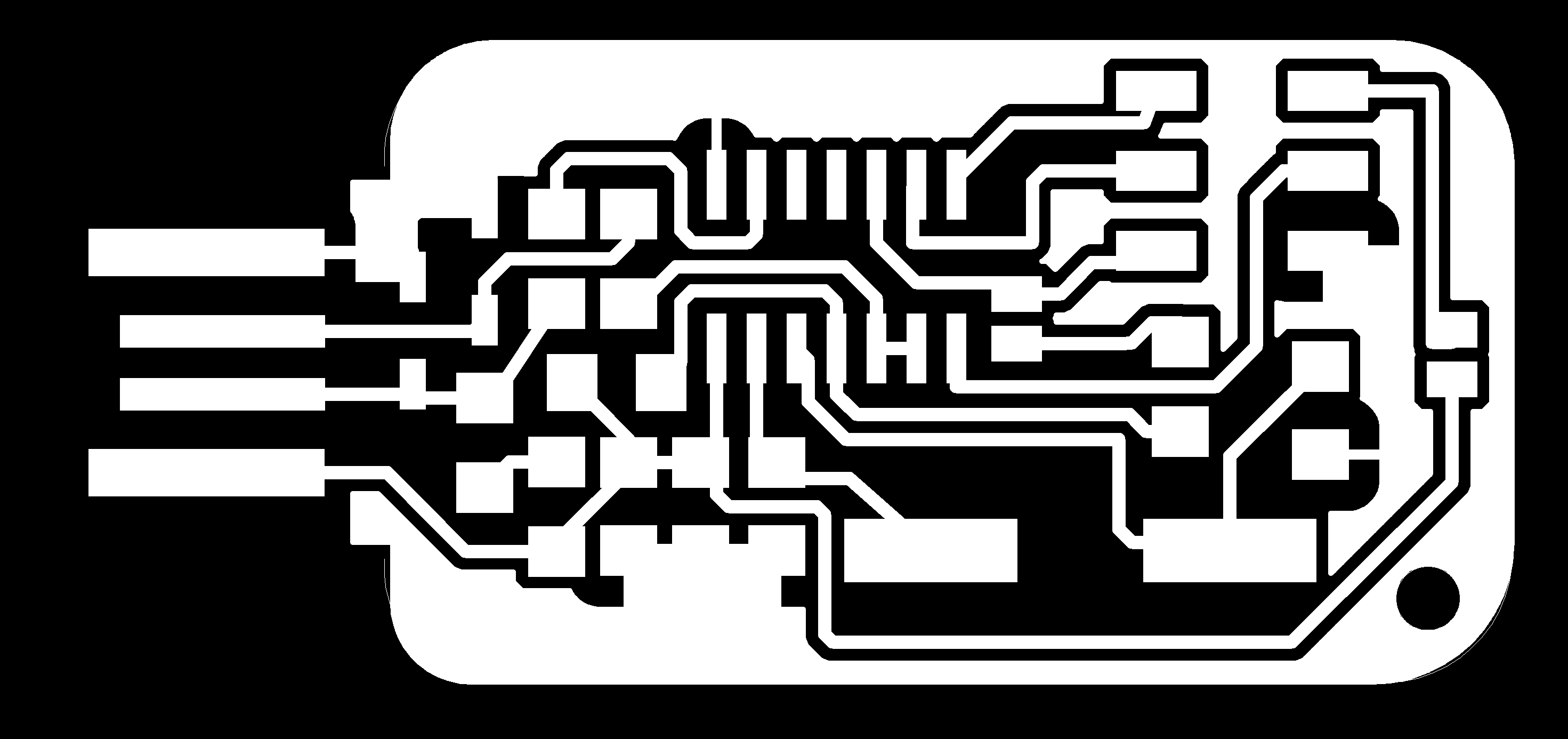

Step 3 - Producing the G-Code
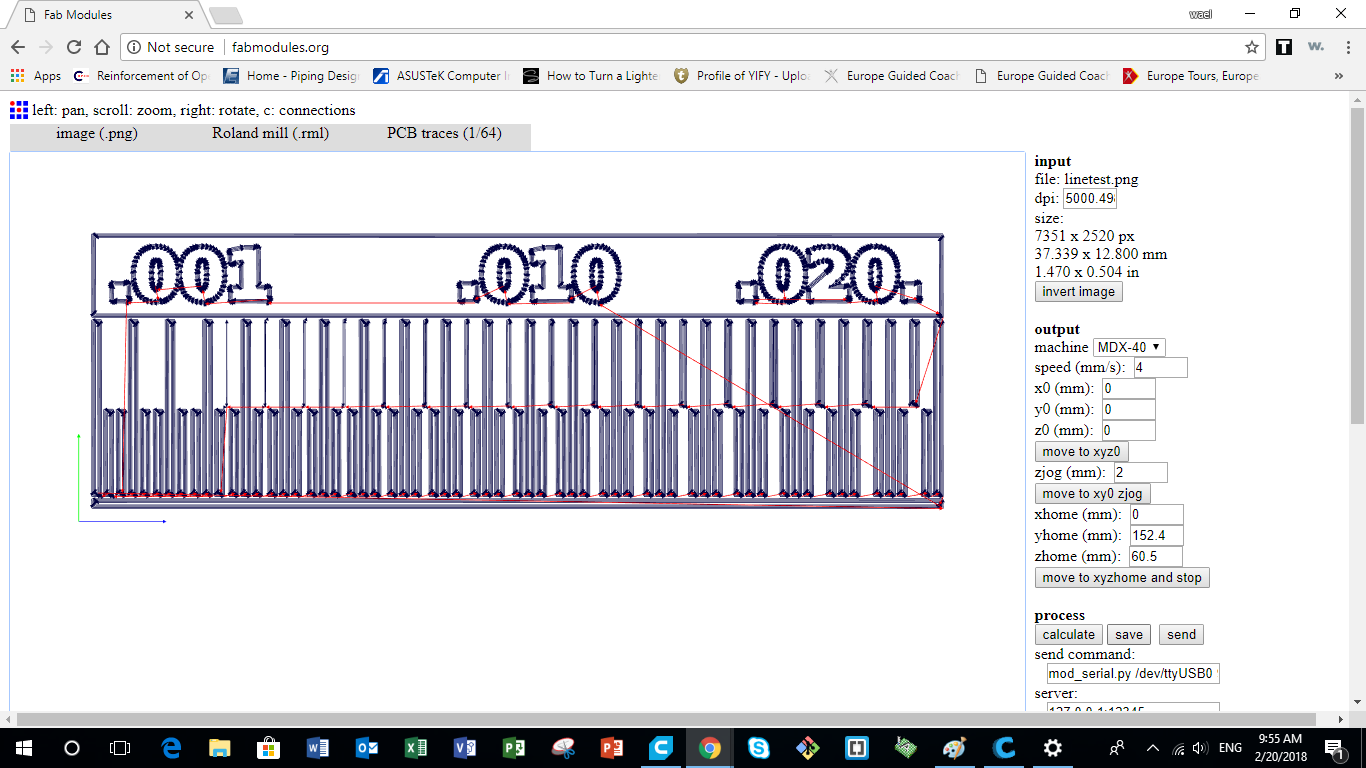
After exctracting the two images that represent the internal and external paths of the milling bit, it's time now to produce the g-code. I used Fab Modules to produce the g-code for PCB milling on the ROlang MDX-40.
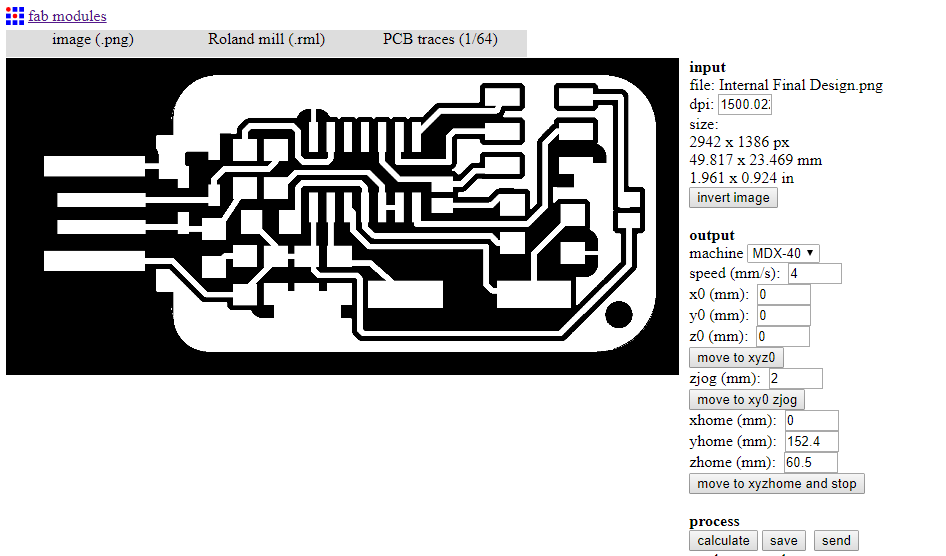
The following steps were followed on Fab Modules to generate the g-code:
- Choose input format and select image (png) that the g-code is going to be generated from
- Then select the file from the specific folder
- Then go on to Output format and select the format that applies to the CNC machine you are using, in our case it was Roland mill (.rml)
- Then select Process and choose PCB traces (1/64) for internal paths and PCB Outline (1/32) for the external parameter
- Then under Output, select the CNC machine you are using, it was a Roland MDX-40. Change the X0, Y0 and Z0 to save space on copper board used. Then check the Feed Speed. I was using 4mm/sec for the Internal Traces and 0.5mm/sec to the External Parameter.
- Then Under Process, adjust the cut depth which should be 0.0 mm for the internal tracing, and 1.7mm for the external parameter. The tool diameter (milling bit) which was 0.1 mm for the internal traces, and 1 mm for the external parameter.
The Number of offsets is 4 and the offset overlap used was 70%
No other adjustments were be made. - Once the Input, Output, and Process tabs are double have been adjusted and double checked. Go ahead and press the Calculate button
- Then finally click the Save button and save it to the designated folder. It would be saved as an .rml file
Step 4 - CNC Milling the PCB Board
After preparing the G-code, the following steps were taken to mill the layout onto the copper board:
- First I needed a software that would send the g-code directly to the Roland MDX-40. In my case I used the Drop-Out software to send the .rml file to the CNC machine
- On the Drop-Out application press the add button and choose the .rml file you created and press open
- Then go to File and select Print Setup
- On the Print setup first choose the name of your printer, in my case it was the Roland TS-30
- Then go to Properties and press the Tool tab, the only thing that should be adjusted are the Z down position and Z engraving pitch both should be at 0.00 mm. During the internal traces milling the RPM used was 4500, however, when milling the external parameter, iused an RPM of 6000.
- Then go on to the Options tab and select Operation Panel
- Set the X and Y-axis on the position where you want your PCB to be engraved on the copper board inside the CNC, then press the XY axis SET button
- As for the Z-axis, we needed to zero the tool at the top surface of the copper board. In order to do this delicate process we need to gradually bring it down onto the board, with the help of a multimeter with the beep mode on and have one of the cables on the copper board and the other on the drilling bit. In this case as soon as the drill-bit touches the copper board the multimeter would beep. Make sure to go extremely slow at the end so you dont risk breaking your drill-bit
- Once the beep is heard, you know that the drilling bit is right at the surface and you can go back to the operational panel (on Drop-out), select the Z-axis from the dropdown menu and set the Z-axis.
- Once everything is set press OK until you reach the first page of drop-out and press theOutputbutton. Your CNC machine should now start the process of milling/engraving the copper plate set inside. watch the process until its done
- Check the final result, using a multimeter with the beep setting to make sure components are isolated and all conductivity channels are connected
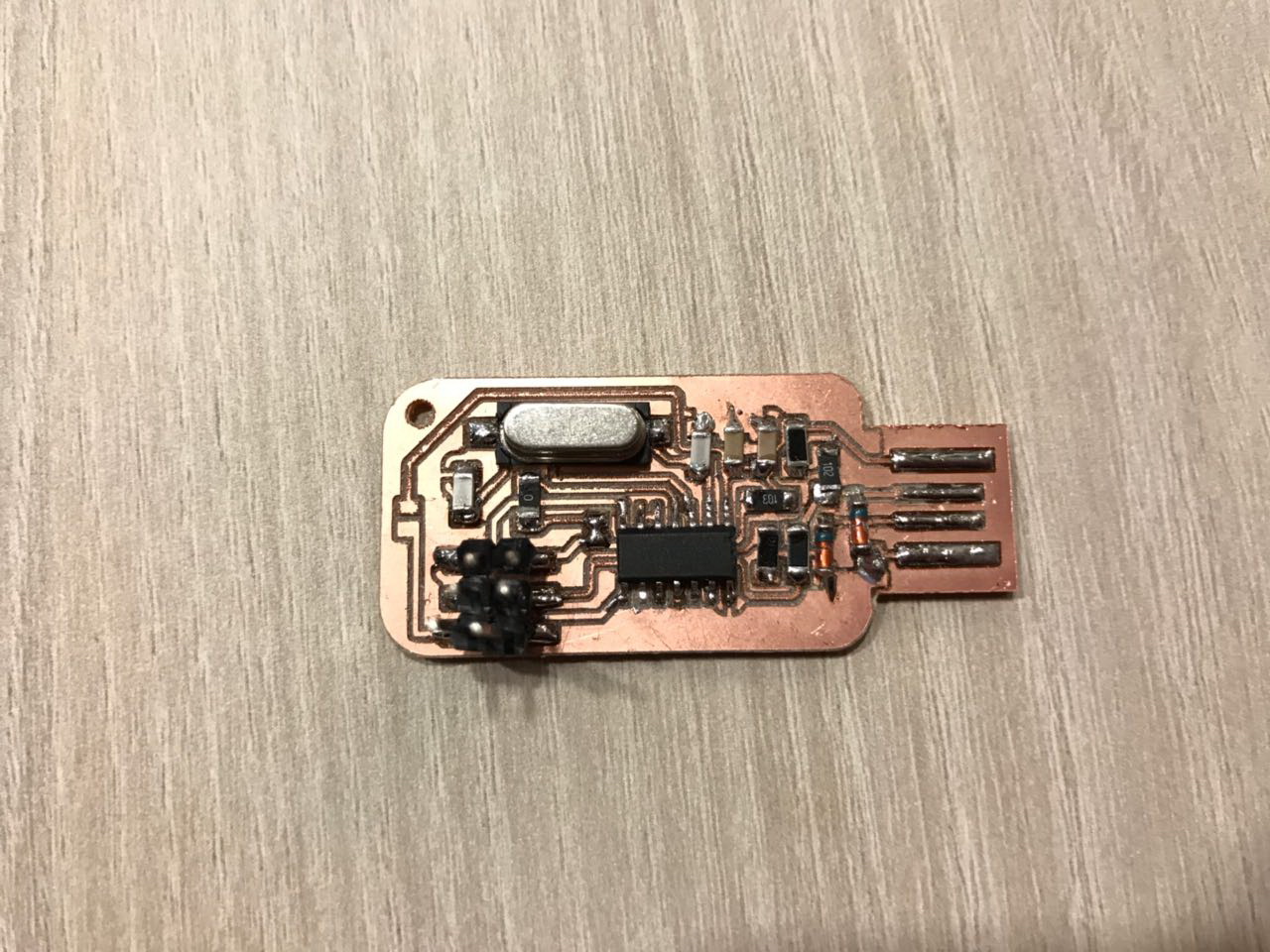
Step 5 - Welding the Components
Now that we have the PCB layout cut-out, the next stper is to start soldering. In order to do so we first need certain tools to proceed, find the list with specs below:
- Soldering Iron: set at 320 degrees celcius
- Solder wire: 0.5 mm
- Tweezers
- Desoldering copper
- Vacuum
- Tack-it
Then follows the list of components:
- Atiny44A Microchip
- 2 x 3.3V Zener Diodes
- 1 x 0 Ohm Resistor
- 1 x 499 Ohm Resistor
- 1 x 1 KOhm Resistor
- 1 x 10 KOhm Resistor
- 2 x 49.9 Ohm Resistor
- 1 x 20 MHz Crystal
- 1 x 0.1 uF Capacitor
- 1 x 22pF Capacitor
Now for the final step in this process, make sure all connections are ok using the multimeter on the beep option. And you should be set to move on to the next step.
Step 6 - Programming the Microcontroller
After finalizing all the required hardware components needed to build the PCB, the next step is to download the Software on the ISP. The following steps are followed to do that.
- First we need to connect the Arduino to the PC, open the Arduino IDE and make sure you have the right board and port under the tools tab
- Then under file and examples, you need to find the ISP program and upload it to the Arduino
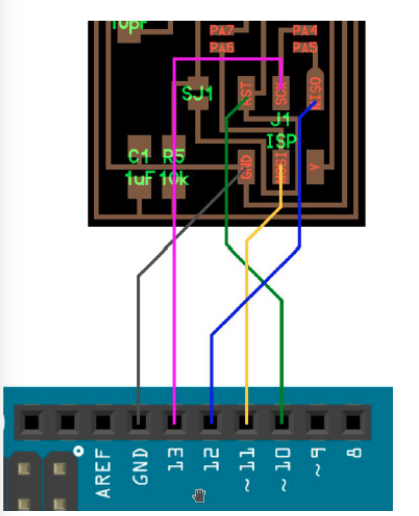
- Now disconnect the arduino form the PC and connect it to your ISP using the following schematic
- Once the connection between the arduino and your ISP is made, connect the arduino to the PC again. And run the terminal (on LINUX) and type the following commands
- sudo apt-get install flex byacc bison gcc libusb-dev avrdude
- sudo apt-get install gcc-avr
- sudo apt-get install avr-libc
- sudo apt-get install libc6-dev
- Press enter after each command and type 'y' if prompted
- Then you need to go to the Desktop directory through the terminal and download a zipped file and unzip it. using the following commands
- cd ~/Desktop
- wget http://academy.cba.mit.edu/classes/embedded_programming/firmware.zip
- unzip firmware.zip
- After you unzip the file, through the terminal enter the unzipped file named 'fabISP_mac.0.8.2_firmware/'
- Then add the following commands on the file's directory
- make clean
- make hex
- nano makefile
- Here you have to look for the AVRDUDE and add a hastag next to the last one so it goes as a comment
- And skip a line under it and add 'AVRDUDE = avrdude -c stk500v1 -P /dev/ttyACM0 -b19200 -p $(DEVICE)'
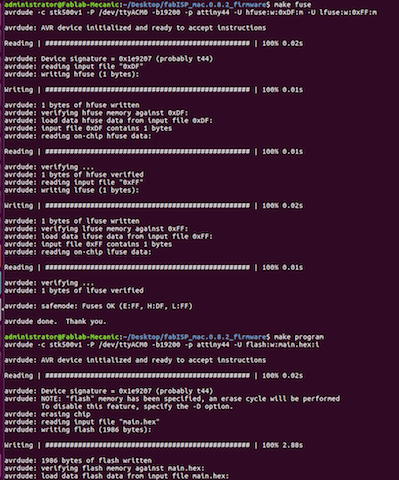
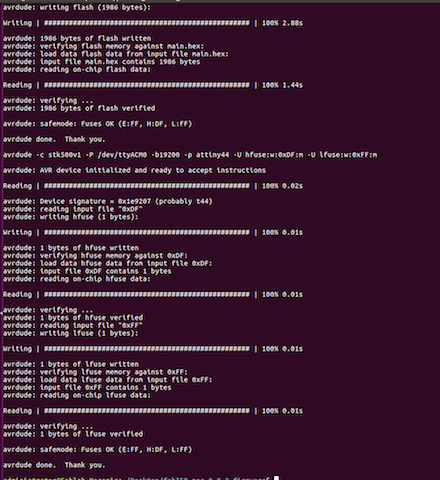
- make fuse
- make program
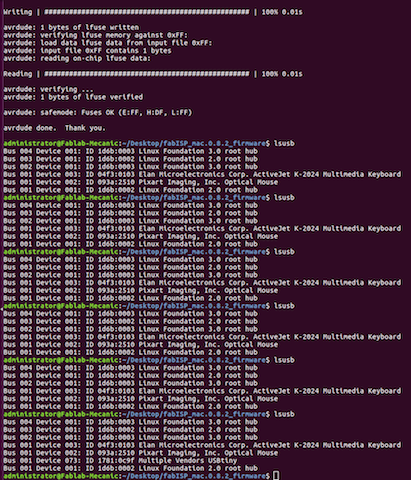
- Finally, disconnect your ISP from the Arduino, Unsloder the Jumpers and plug it into the PC
- Then type in the terminal, 'lsusb'
You can download the Firmware used for my ISP from the following links:Firmware