Introduction into reasons and structure of G-Code - a language for controlling machines.
why
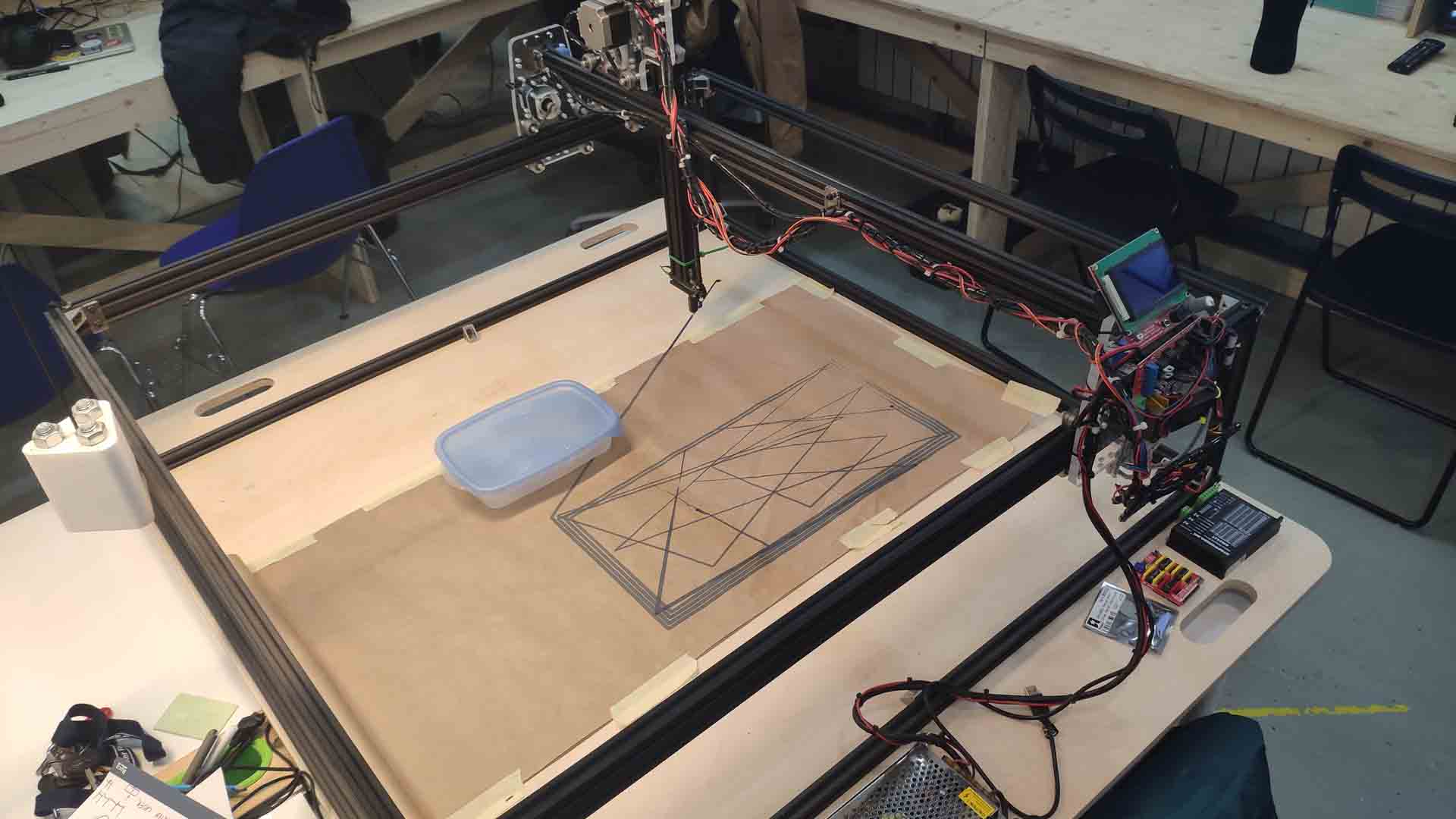 – CNC overview –
– CNC overview –
G-Code - a common language for many types of machines from CNC, to laser, to robot-manipulator, etc. It is established to create standardization - while different devices might need to be configured differently same set of instructions will do same outcome; abstraction - raises base level so you don’t have to do everything from scratch every time; protection - provides structure for many of most common dangers to be controlled (like boundary, speed limitations etc.); ease of use - common between devices, though might be slightly different based on capabilities and configurations; complex geometry simplification - huge geometry will easily overwhelm device if put all together into RAM, which is usually is too small to even handle large SD cards (not enough memory for addresses).
M-Code - firmware override commands
machines
Types:
- Open loop - prone to misalignment but simle, thus more common;
- Closed loop - can react to a problem in loop and go into auto-pause for machine and user safety.
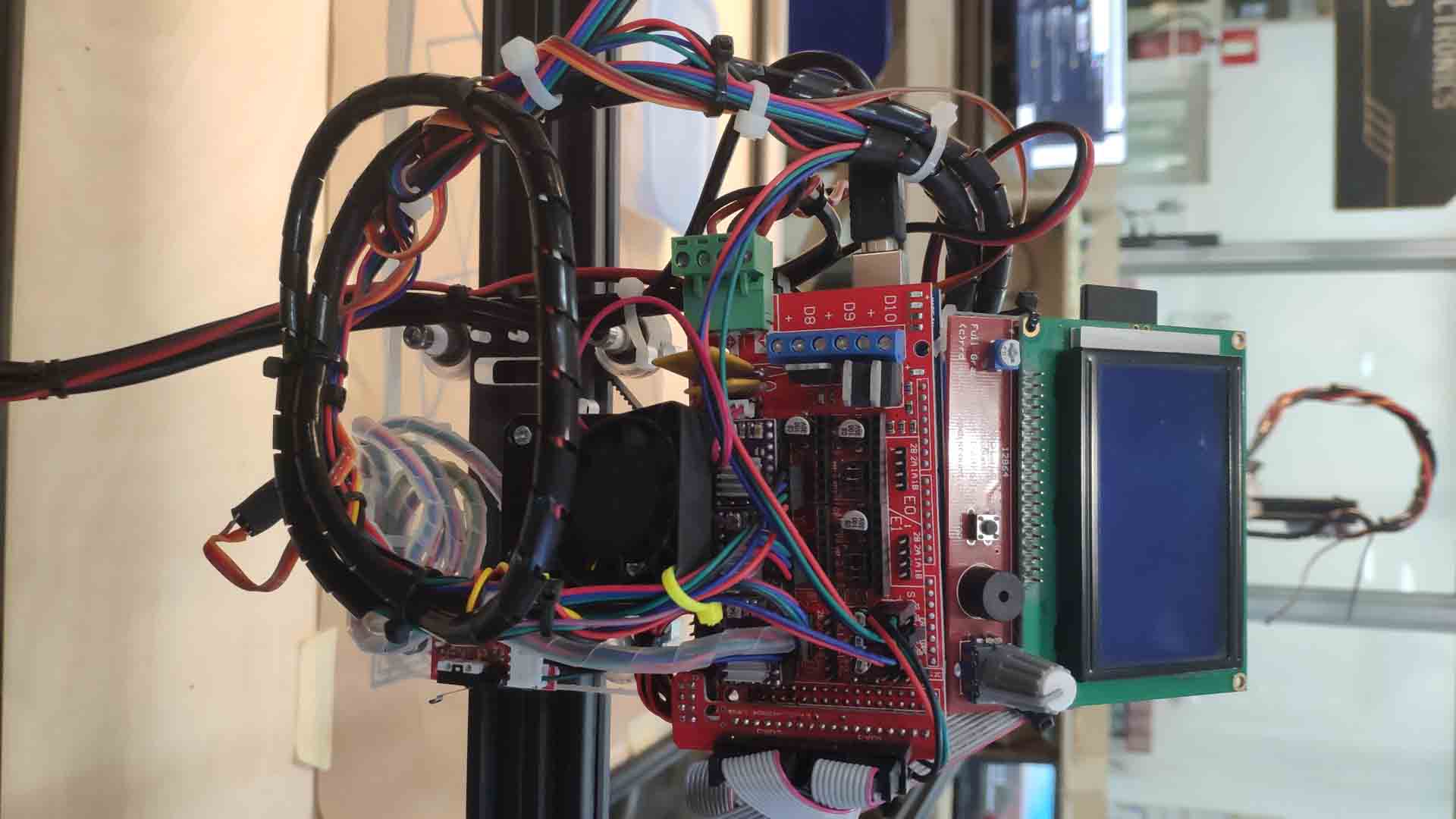 – CNC controller –
– CNC controller –
Parts:
- Microcontroller - brain of machine (pin power output is tiny, analog of a couple of LEDs).
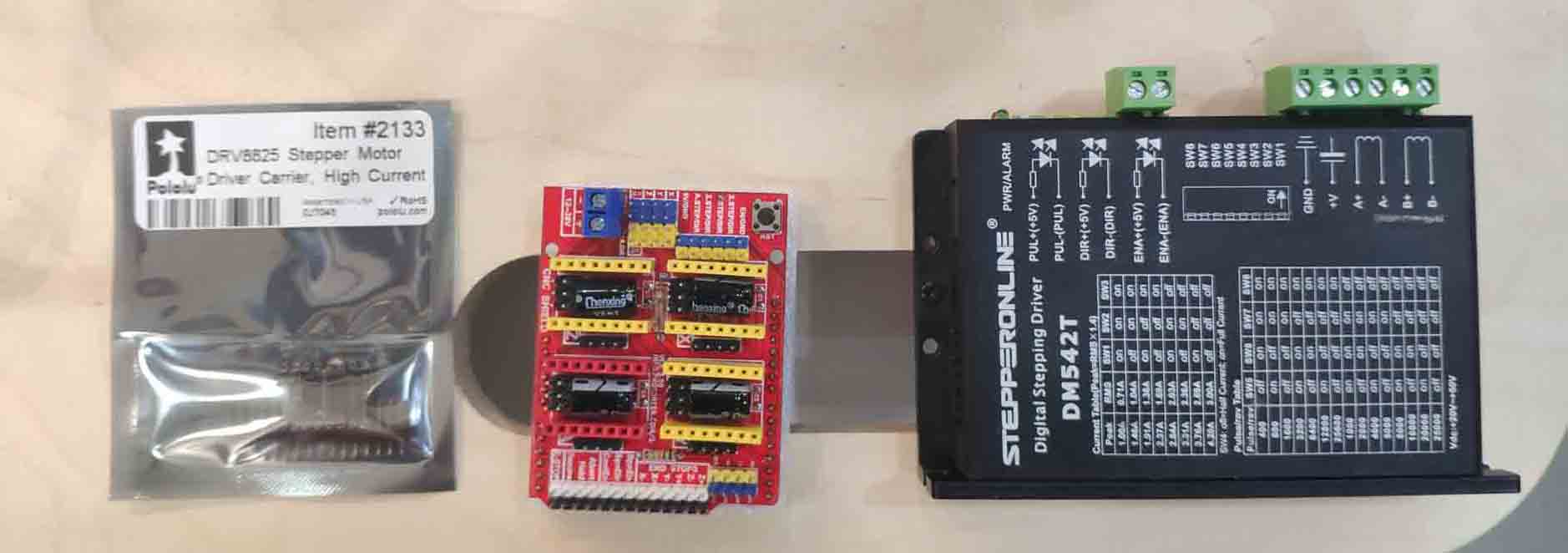
- Shield - smart breadboard. Exist to extend and organize connections. Can pass more power than normal output.
- Step-sticks - micro version of shield for a specific case.
- Driver - a dumb but powerful piece to work with steppers (can withstand a lot more power: analog of 3000 LEDs).
- Sensors (i.e. clicker for setting 0) - machine way of interacting with environment. Could be connected directly to microprocessor or to a shield.
- Tools (i.e. laser, drill, etc.) - act in a controlled way.
- Motors and Stepper-motors - most common way to activate the environment. Most often require drivers to power them. Steppers consist of two counter-aligned magnetic coils and a core with discrete stable positions - steps.

Native steps - stable positions of stepper-motor. Micro-stepping - software based subdivisions (combine positive and negative signals to create fractional position). With modern control is fairly reliable but nonetheless is not as accurate as stepper with more resolution.
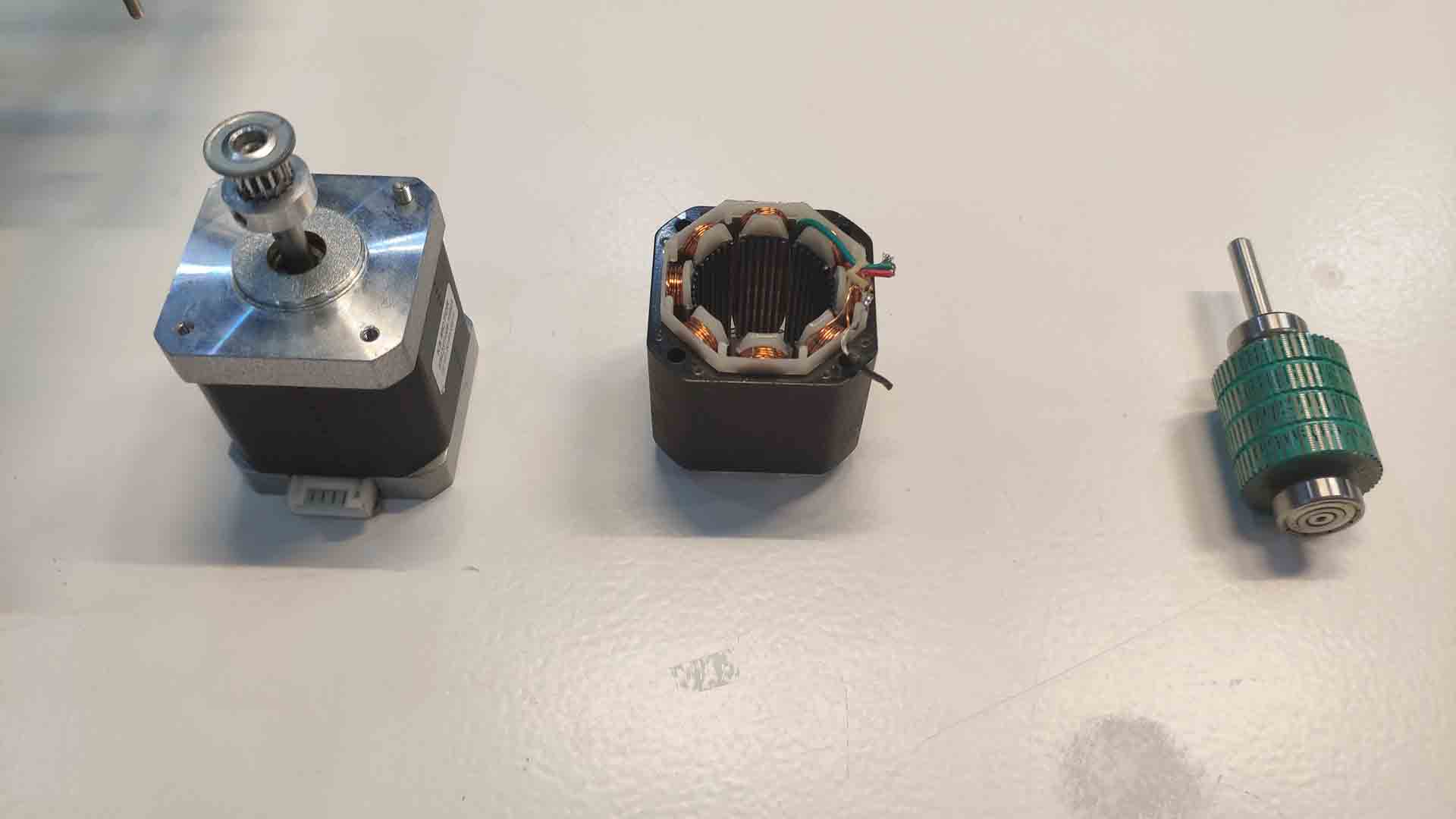 – Disassembled stepper-motor –
– Disassembled stepper-motor –
code structure
- Setup and prepare (i.e. heat up the bed, heat up the filament and wait, go to 0, define new 0, etc.);
- Commands (various types of movement, activating, deactivating sensors and tools)
firmware
- Marlin - GCode interpreter
- GRBL - heavy duty tasks (could be slower to execute but machines can go much faster)
Benefit of these both is that they are both opensource. Both have many flavors - versions and variable functionality. Can be further edited through configurations.
common commands
Normally G-Code is generated (foe example, by slicer), but many tools (robot-manipulator, CNC, etc.) can show it so it’s important to at least approximately understand it.
- G0 + coordinates relative to 0 - moving without counterforces
- G1 + coordinates + F speed controlled movement
- G2, G3 - arc commands clockwise or counterclockwise
- G> - Presets
F - speed
S - spindle speed
T - tool
It is possible to switch between relative or absolute coordinates by other commands. NB! Always double check - this is most common error.
- M400 - finish moves
- M701 - load filament
Common process - prepare g-code file, store on SD-card, read on machine and execute. However, can be done directly by interacting with machines over USB over serial:
- Arduino IDE;
- ChilliPepper - more visual;
- Repetier - send full code set;
Suggestion: Play around with it and G-Code instructions side by side.
// TODO: results of experimentation