Start of Design.
As mentioned previously the design was inspired by the Pavillion press fit design. To reach the final design I have made different sketches. I have also used the circular pattern feature as shown below.
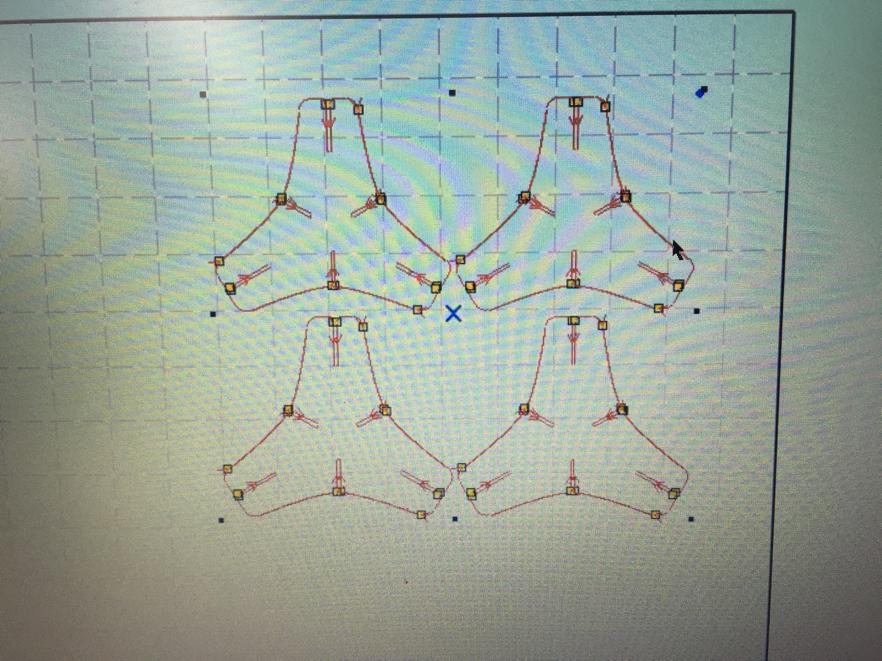
After multiple iterations, I have reached the final design. I started with 3 patterns and then varied by changing the values on the parametric options. Below shown the design with joints thickness of 2.9 mm.
Once the 2D design was made,
the parametric feature was used to control the width, thickness of the joints and the number of circular and rectangular patterns of the design.
Picture below shows the rectangular 4X4 pattern with 3 circular patterns.
Picture below shows the rectangular 4X4 pattern with 4 circular patterns.
Start of Fabrication
I have decided to test the Plywood 3.2 mm in this assignment to be able to try different materials. Based on the conclusion obtained from the group assignment, the kirf value of MDF wood was taken in consideration to be able to get a tight joint thickness. Assuming the kirf value (MDF) is 0.8 mm, I have set the thickness to be 2.4 mm as shown below.
After performing the first trial, I found out that the kirf value should be varied and this because I was using plywood instead of MDF, which will result in a different kirf value. That being said, the thickness was set to 2.9 mm as shown below.
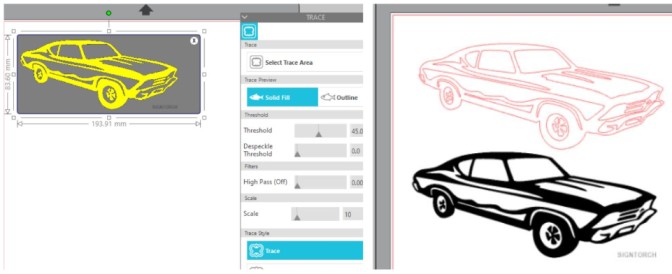
Once the design was ready, the file was saved as DXF and imported to Lasercut software (detailed procedure of how to use the laser cutter were presented previously).
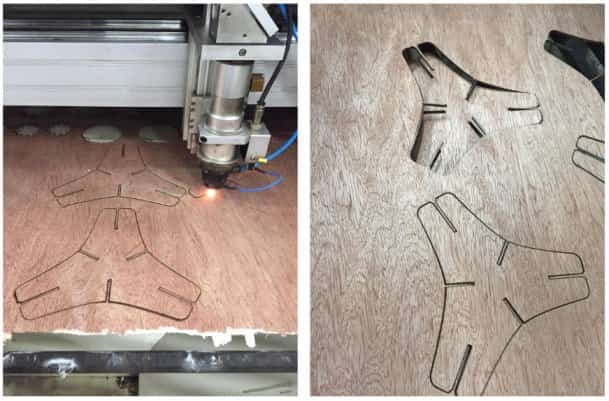
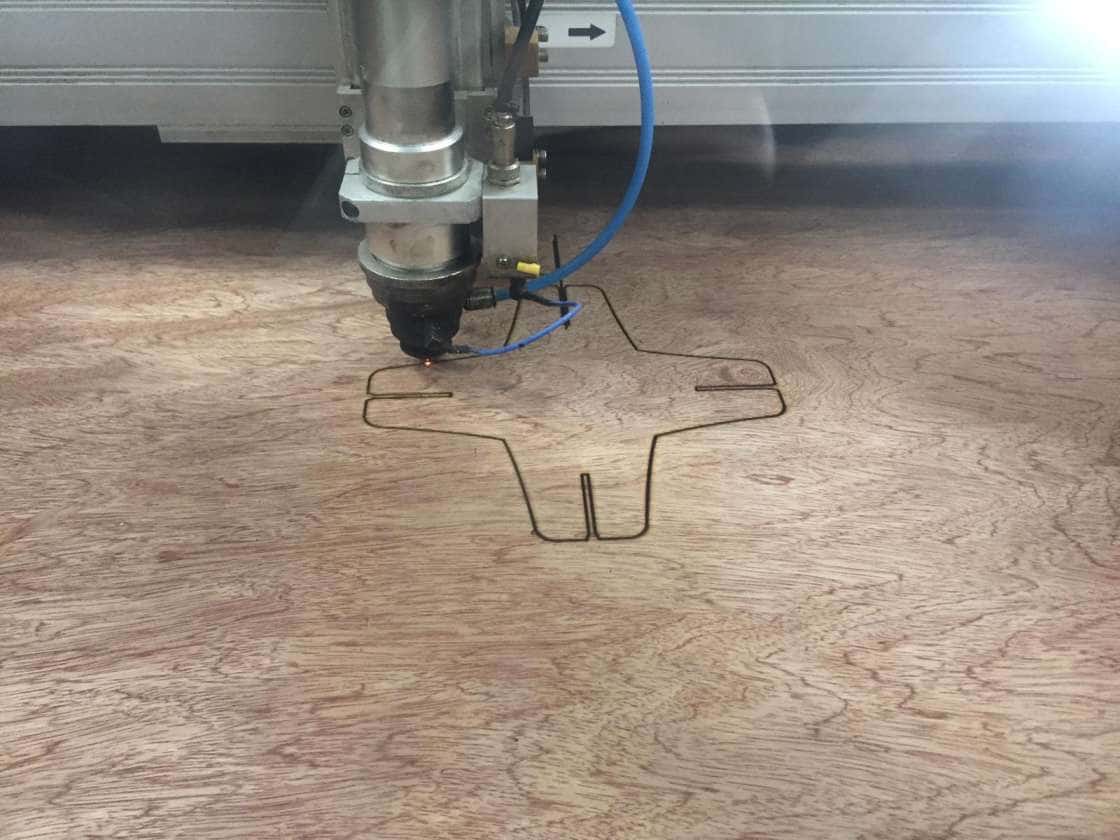
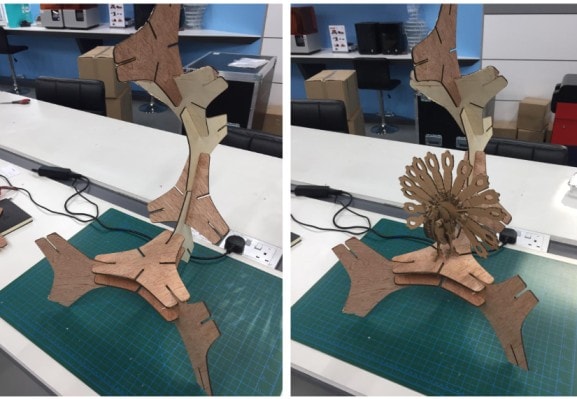
The power of the laser machine was set to 100% with a speed of 20 % and then the machine was operated. Below shown the laser cutting for the construction kit of 3 patterns designed.
I have faced some difficulties during the laser cutting process as the plywood sheet was bent, so the distance between the laser head and plywood sheet was not symmetric all over the cutting area. To solve this problem, I had to change the z-axis laser head distance depending on the position of cutting.
The next step was to cut the design with 4 joints as shown below.
Once the design was ready, the file was saved as DXF and imported to Lasercut software. During the cutting I have faced a second issue which caused failure of the cutting. The laser was burning the edges and not cutting it, as shown below.
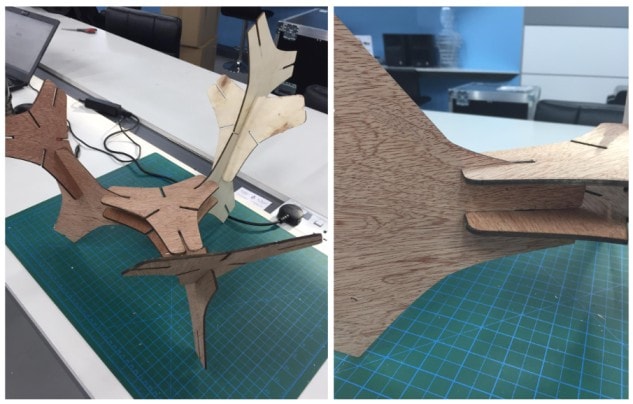
Since there was an issue with the lase machine, I have decided to use the 3 patterns design to construct simple 1 of my kit.
Simple 2 of different shape for the the kit
Click on text to download 2D file:
- Parametric design file download link
- 4 Pattern design file download link
- 3 Patter design file download link