Week 13: Networking and Communications
Assignment
For this assignment the objective is to make two microcontroller communicate whether wireless or wire to each other.
I designed a board with ESP8266 chip and LED to communicate wireless with another copy of the same design.
From the same process as week 6 of designing a PCB in KiCAD, I designed the board was going to use by importing all components needed and aligning and connecting parts that supposed to connect.
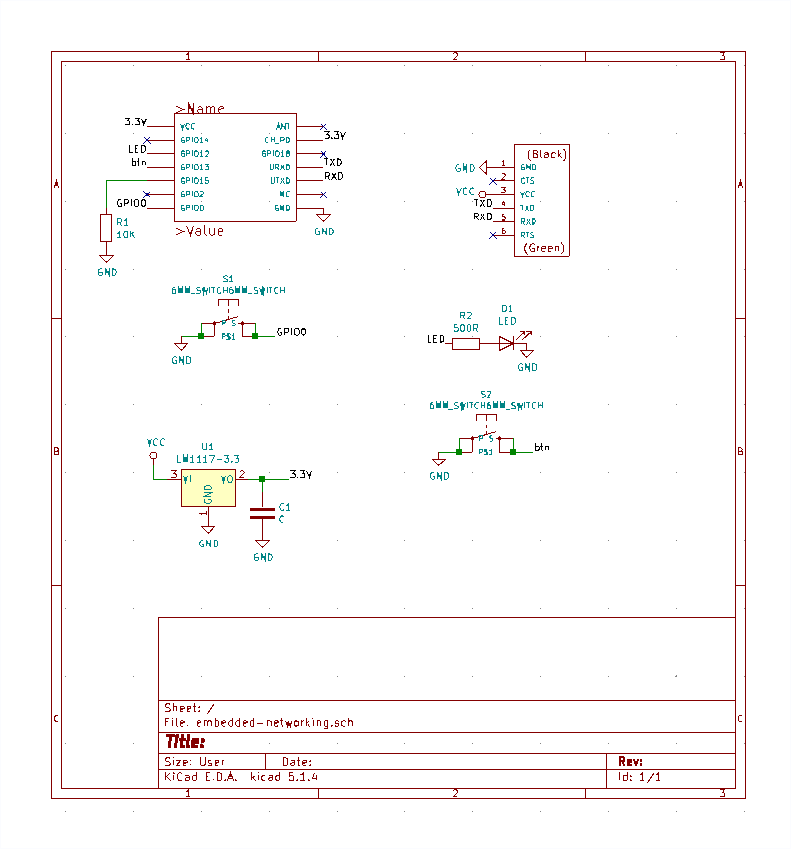
I continued to design the board layout for making a PCB.
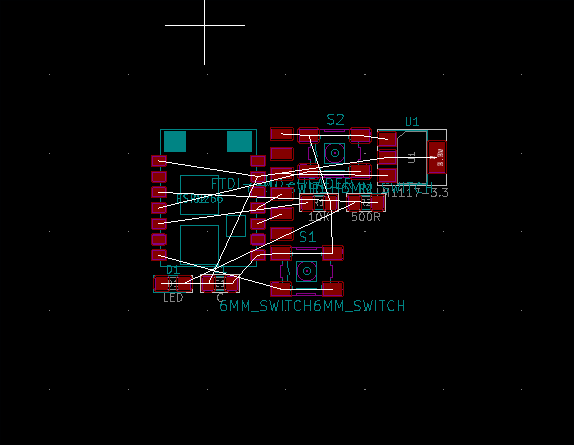
I aligned components and made an edge cut of the PCB.
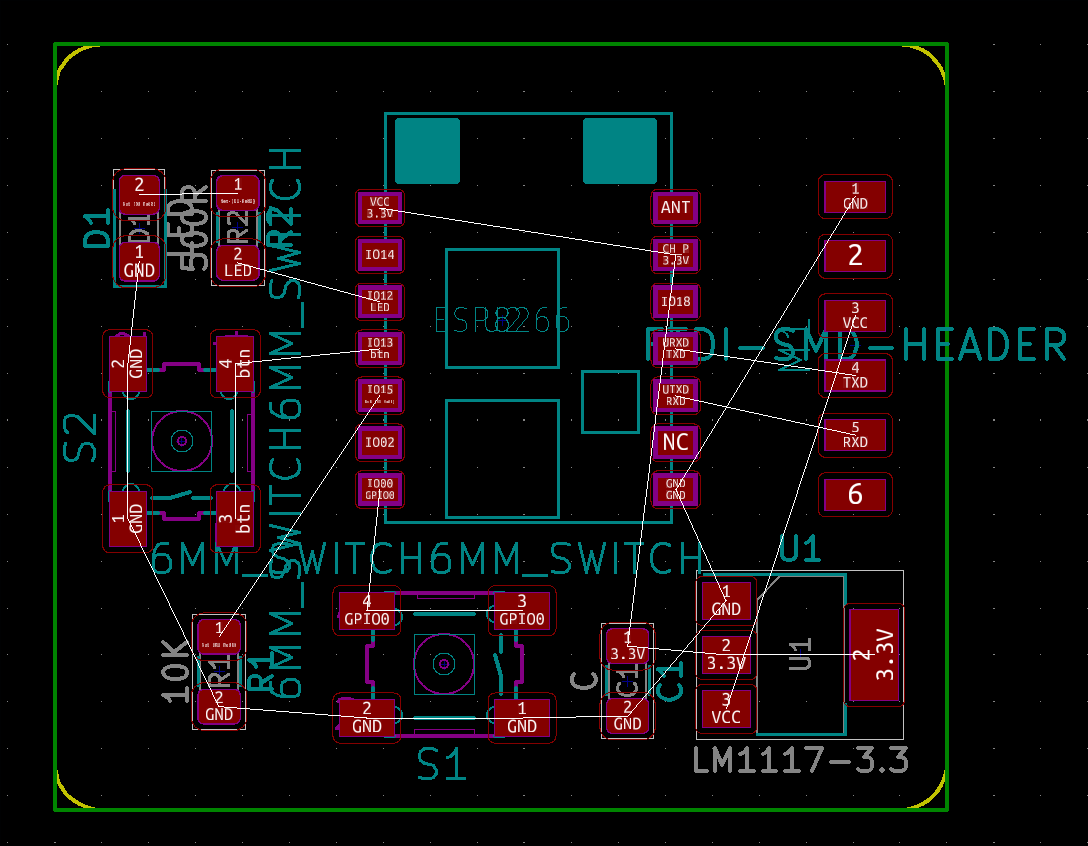
When components are aligned correctly it is easy to create layouts.
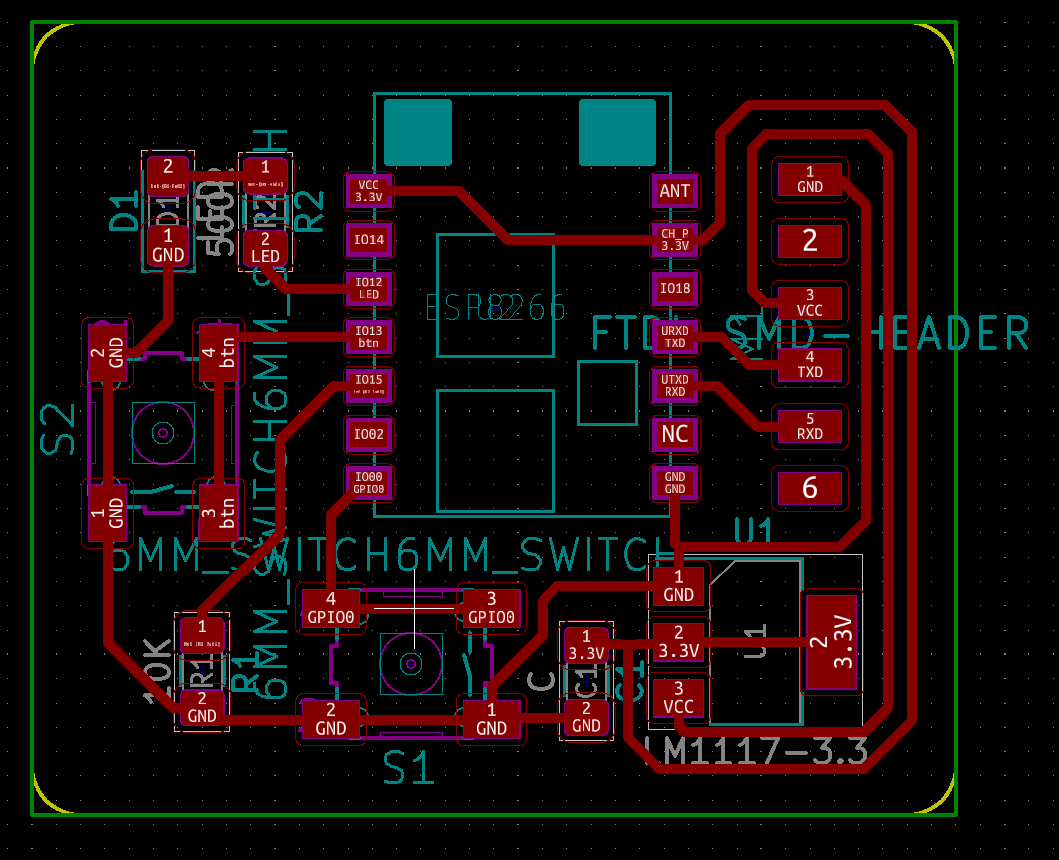
This is a 3D view of the final board.
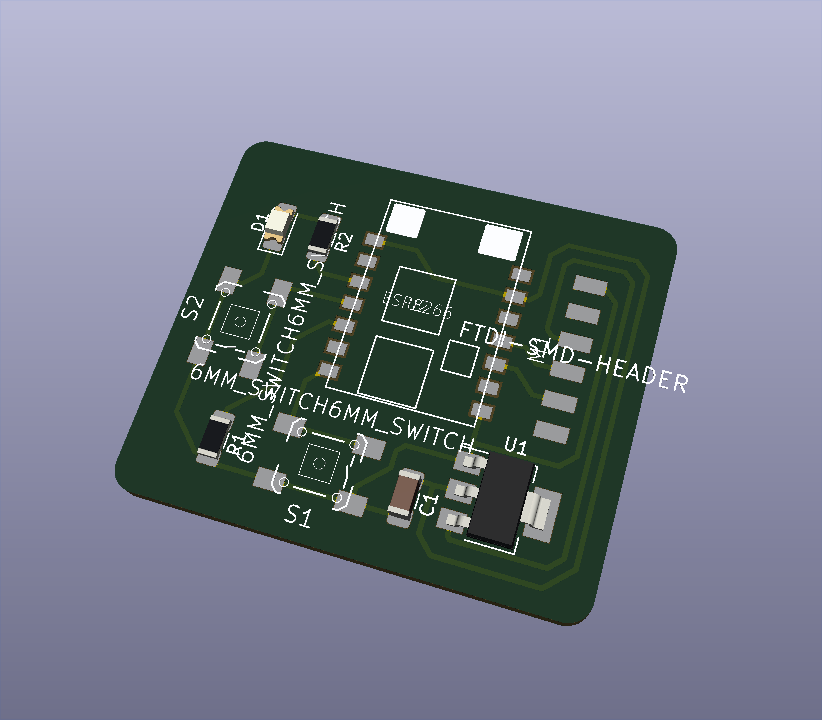
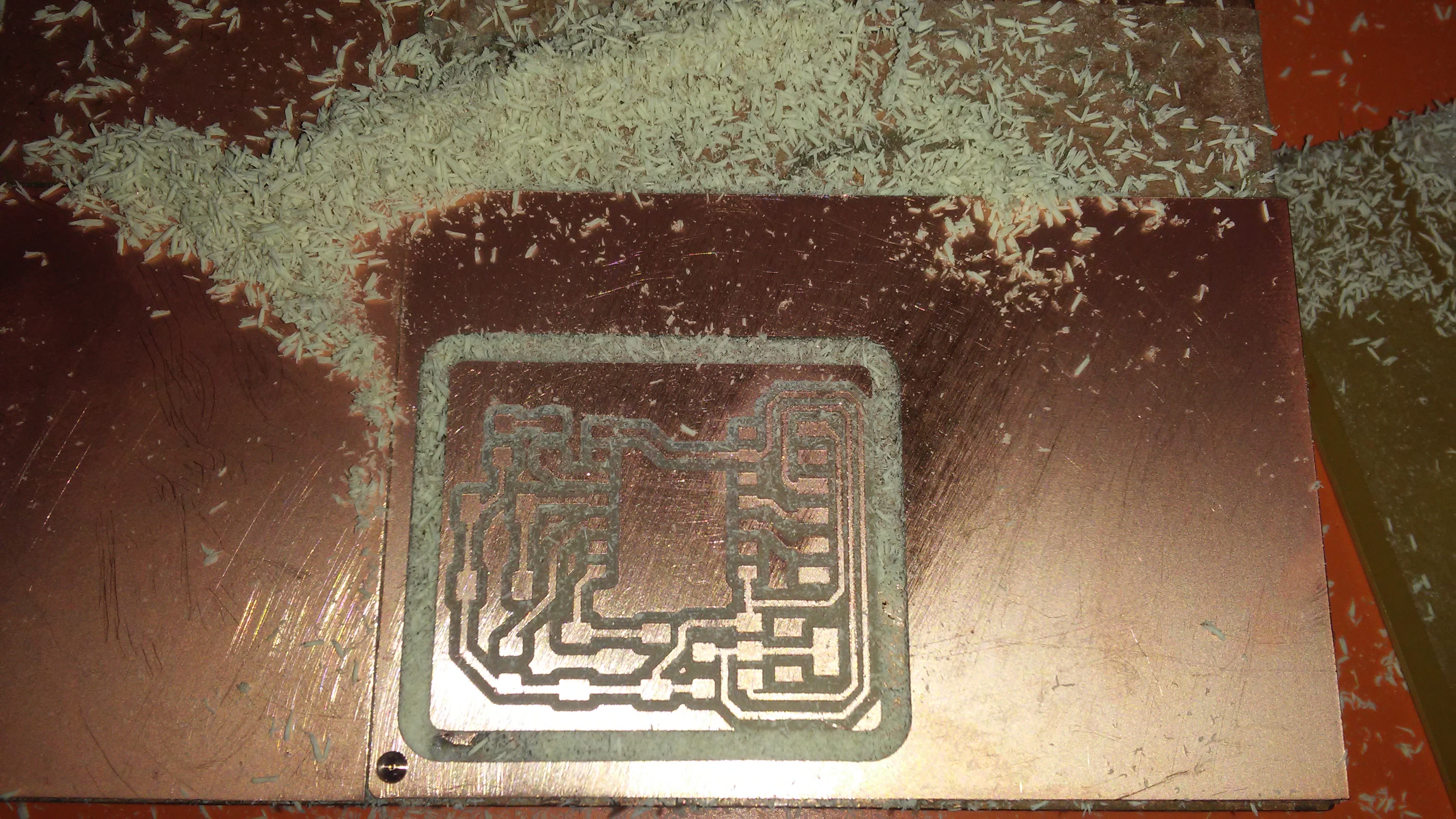
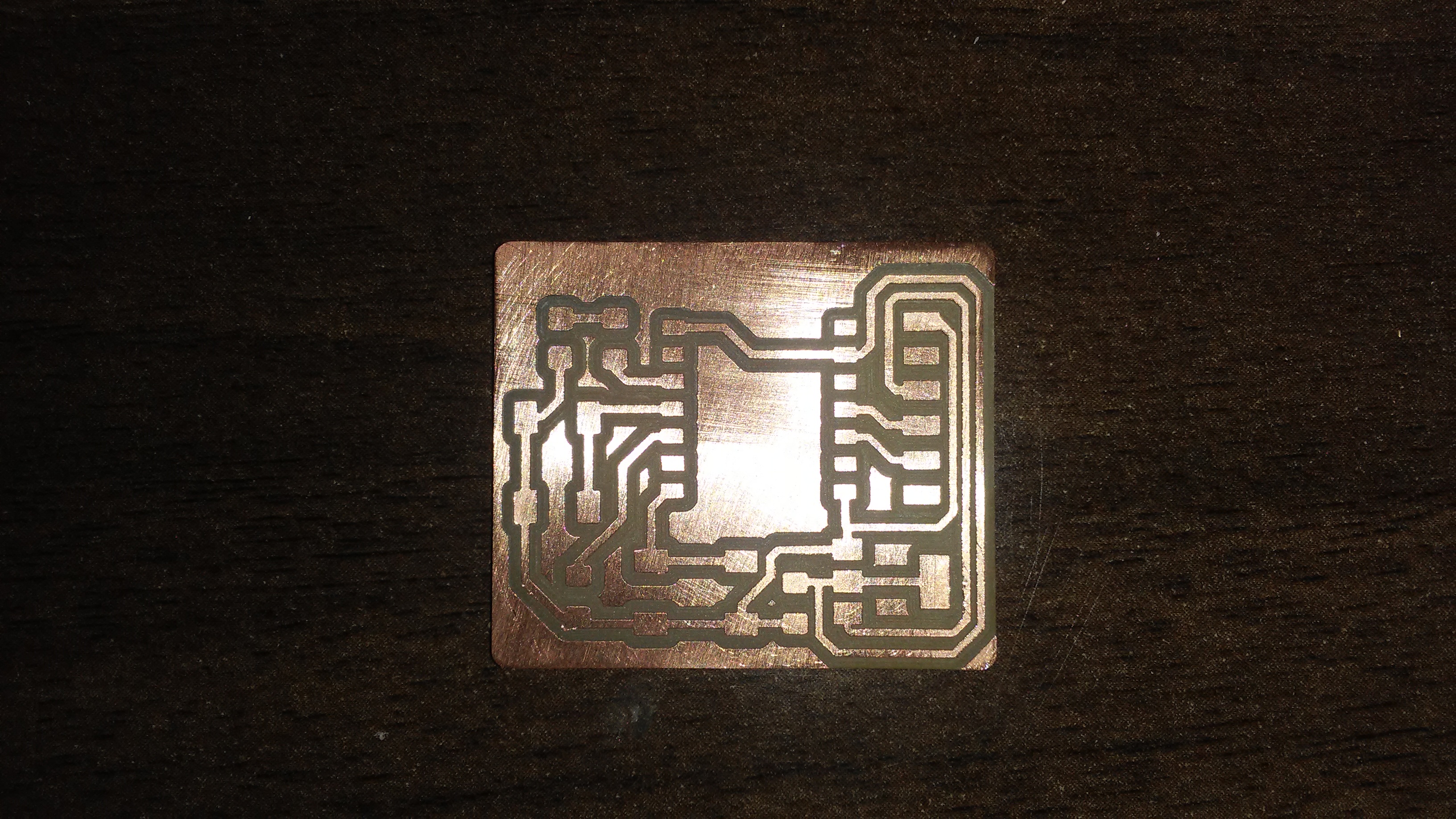
I moved to the next step of milling the board.

This is the final look of the board after being milled.
I soldered all the components in their place.
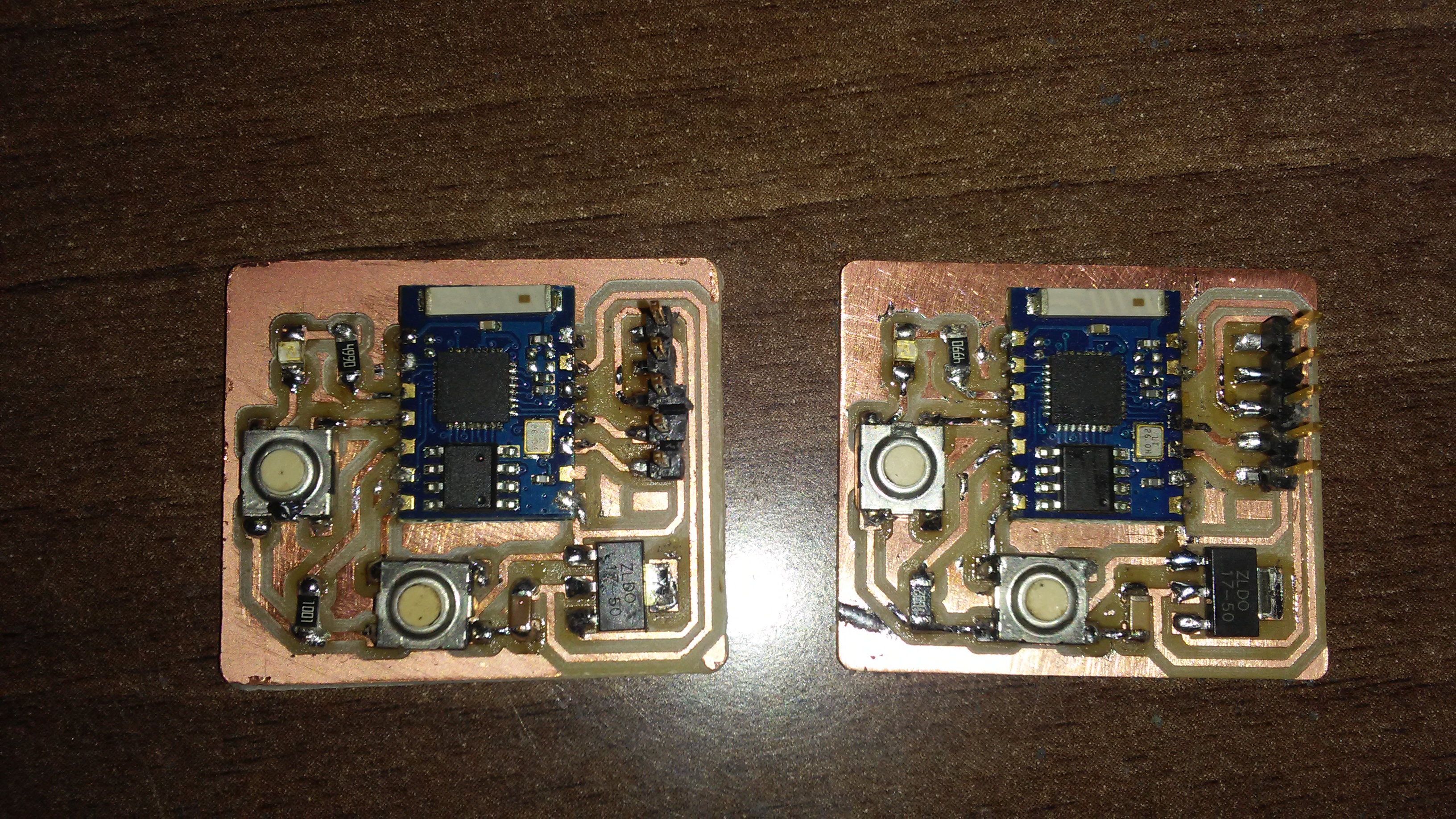

This is the list of components used for each board.
| No | Component Name | Pieces |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | ESP8266 ESP-3 | 1 |
| 2 | FTDI connector | 1 |
| 3 | LM1117-3.3 | 1 |
| 4 | Tactile button | 2 |
| 5 | LED | 1 |
| 6 | Resistor | 2 |
| 7 | Capacitor | 1 |
To program this board I used the arduino IDE and I had to add the board in the IDE. I did it using this guide. The library I used were include when I installed the board in the IDE.
Server side program.
#include <ESP8266WiFi.h>
WiFiServer server(80); // Server Port
IPAddress ip(192,168,43,100); // Fixed IP address for server
IPAddress gateway(192,168,43,1); // Router's IP address
IPAddress subnet(255,255,255,0);
char ssid[] = "YourSSIDhere";
char pass[] = "YourPassWordHere";
int ledPin = 9;
int button = 10;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
WiFi.config(ip, gateway, subnet);
WiFi.begin(ssid, pass);
while(WiFi.status() != WL_CONNECTED) {
Serial.print(".");
delay(500);
}
Serial.println();
server.begin();
Serial.println("Server Started");
Serial.print("Server's IP address: ");
Serial.println(WiFi.localIP());
Serial.println();
}
void loop() {
// Check if a client has connected
WiFiClient client = server.available();
if (!client) {
return;
}
// Wait until the client sends some data
Serial.println("new client");
while (!client.available()) {
delay(1);
}
// Read the first line of the request
String request = client.readStringUntil('\r');
Serial.println(request);
client.flush();
// Match the request
if (request.indexOf("/led-on") > 0) {
digitalWrite(ledPin, HIGH);
}
if (request.indexOf("/led-off") > 0) {
digitalWrite(ledPin, LOW);
}
// stop connection with client
client.stop();
Serial.println("Client disonnected");
Serial.println("");
}
Client side program.
#include <ESP8266WiFi.h>
IPAddress server(192,168,43,100); // Fixed IP address of the server
WiFiClient client;
char ssid[] = "YourSSIDhere";
char pass[] = "YourPassWordHere";
int ledPin = 9;
int button = 10;
int lastBtnState = 0;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
pinMode(ledPin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(button, INPUT);
WiFi.begin(ssid, pass);
while(WiFi.status() != WL_CONNECTED) {
Serial.print(".");
delay(500);
}
Serial.println();
}
void loop() {
if (digitalRead(button) == HIGH) {
if (lastBtnState == 0) {
client.connect(server, 80);
client.write("/led-off");
lastBtnState = 1;
}
else {
client.connect(server, 80);
client.write("/led-on");
lastBtnState = 0;
}
}
}
Here I tested the code
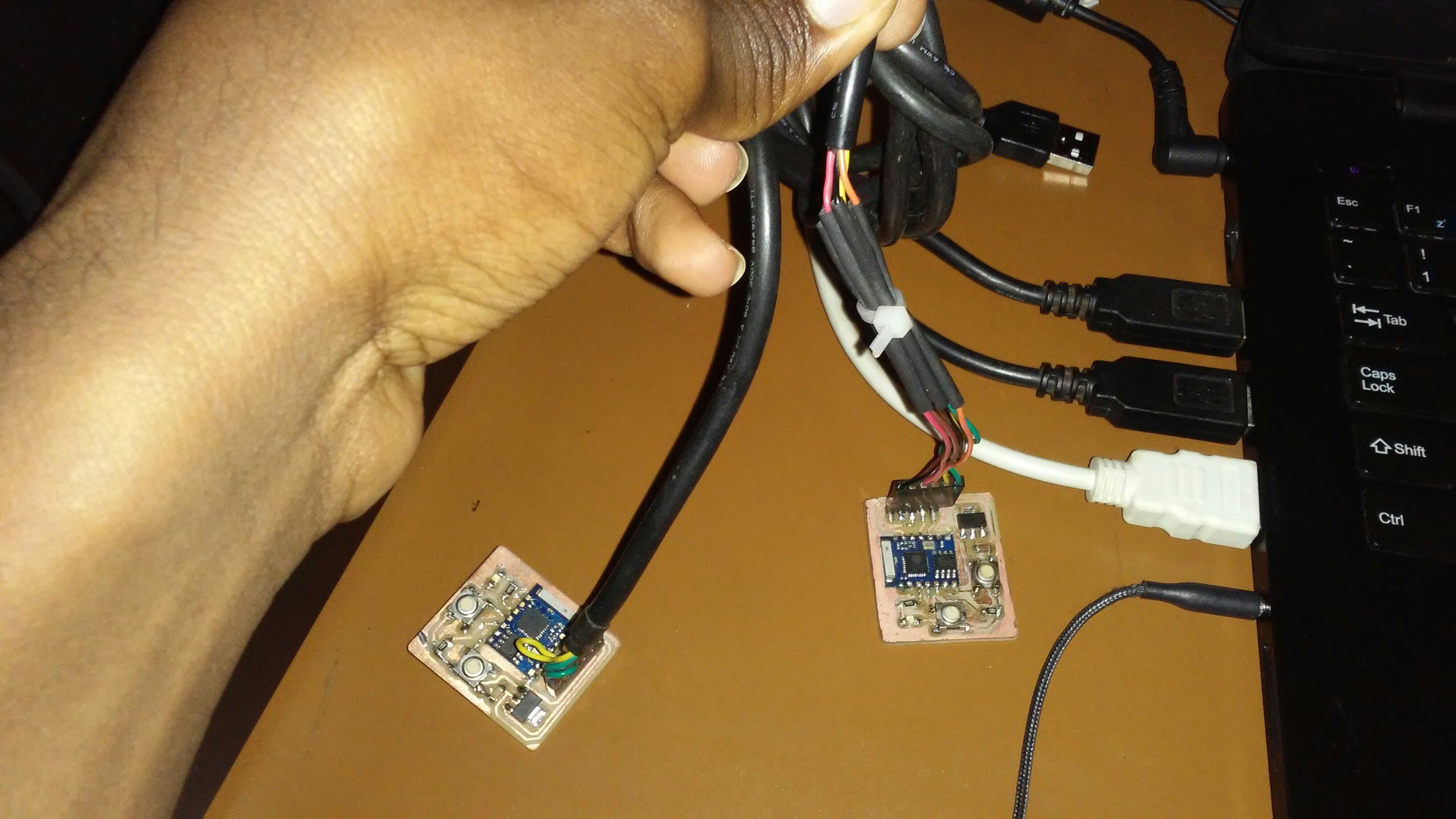
below it is the video of the project working
Conclusion
The purpose of the project was to communicate 2 boards so that each can turn on an LED on the other, they communicate through WiFi. I used ESP8266 chip which are WiFi enabled and works at low power like other microcontroller.
Files used to design and program the board can be found here.