19. Invention, intellectual property and income
Assignment: Develop a plan for dissemination of your final project prepare drafts of your summary slide (presentation.png, 1920x1080) and video clip (presentation.mp4, 1080p HTML5, < ~minute, < ~10 MB) and put them in your root directory
Presentation slide and Video
Click to see the Video to my final presentation.
Intellectual Property
Intellectual property refers to creations of the mind: inventions; literary and artistic works; and symbols, names and images used in commerce. Intellectual property is divided into two categories:
Industrial Property includes patents for inventions, trademarks, industrial designs and geographical indications.
There are also more specialized or derived varieties of exclusive rights, such as circuit design rights and supplementary protection certificates for pharmaceutical products (after expiry of a patent protecting them) and database rights (in European law).
Patents
A patent is a form of right granted by the government to an inventor, giving the owner the right to exclude others from making, using, selling, offering to sell, and importing an invention for a limited period of time, in exchange for the public disclosure of the invention.
An invention is a solution to a specific technological problem, which may be a product or a process and generally has to fulfill three main requirements: it has to be new, not obvious and there needs to be an industrial applicability.To enrich the body of knowledge and stimulate innovation, it is an obligation for patent owners to disclose valuable information about their inventions to the public.
Copyright
A copyright gives the creator of an original work exclusive rights to it, usually for a limited time.
Copyright may apply to a wide range of creative, intellectual, or artistic forms, or "works".Copyright does not cover ideas and information themselves, only the form or manner in which they are expressed
Industrial design rights
An industrial design right (sometimes called "design right" or design patent) protects the visual design of objects that are not purely utilitarian. An industrial design consists of the creation of a shape, configuration or composition of pattern or color, or combination of pattern and color in three-dimensional form containing aesthetic value. An industrial design can be a two- or three-dimensional pattern used to produce a product, industrial commodity or handicraft. Generally speaking, it is what makes a product look appealing, and as such,
it increases the commercial value of goods.
Plant varieties
Plant breeders' rights or plant variety rights are the rights to commercially use a new variety of a plant. The variety must amongst others be novel and distinct and for registration the evaluation of propagating material of the variety is considered.
Trademarks
A trademark is a recognizable sign, design or expression which distinguishes products or services of a particular trader from the similar products or services of other traders
Trade dress
Trade dress is a legal term of art that generally refers to characteristics of the visual and aesthetic appearance of a product or its packaging (or even the design of a building) that signify the source of the product to consumers.
Trade secrets
A trade secret is a formula, practice, process, design, instrument, pattern, or compilation of information which is not generally known or reasonably ascertainable, by which a business can obtain an economic advantage over competitors and customers. There is no formal government protection granted; each business must take measures to guard its own trade secrets (e.g., Formula of its soft drinks is a trade secret for Coca-Cola.)
OPEN SOURCE LICENSE
MIT License
The MIT License is a permissive free software license originating at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT). As a permissive license, it puts only very limited restriction on reuse and has, therefore, an excellent license compatibility. The MIT license is also compatible with many copyleft licenses, such as the GNU General Public License (GPL); MIT licensed software can be integrated into GPL software, but not the other way around.
The common form of MIT License .
GNU General Public License
The GNU General Public License (GNU GPL or GPL) is a widely used free software license, which guarantees end users the freedom to run, study, share and modify the software. There are currently three versions of license are available under GNU. The terms and conditions of the GPL must be made available to anybody receiving a copy of the work that has a GPL applied to it ("the licensee"). Any licensee who adheres to the terms and conditions is given permission to modify the work, as well as to copy and redistribute the work or any derivative version. Software under the GPL may be run for all purposes, including commercial purposes and even as a tool for creating proprietary softwares.
Copyleft
The distribution rights granted by the GPL for modified versions of the work are not unconditional. When someone distributes a GPL'd work plus his/her own modifications, the requirements for distributing the whole work cannot be any greater than the requirements that are in the GPL. This requirement is known as copyleft.Copyleft applies only when a person seeks to redistribute the program. Developers may make private modified versions with no obligation to divulge the modifications, as long as they do not distribute the modified software to anyone else.
Note that copyleft applies only to the software, and not to its output (unless that output is itself a derivative work of the program)
Creative Commons (CC) is an American non-profit organization devoted to expanding the range of creative works available for others to build upon legally and to share.The organization has released several copyright-licenses known as Creative Commons licenses free of charge to the public. These licenses allow creators to communicate which rights they reserve, and which rights they waive for the benefit of recipients or other creators. An easy-to-understand one-page explanation of rights, with associated visual symbols, explains the specifics of each Creative Commons license. Creative Commons licenses do not replace copyright, but are based upon it. They replace individual negotiations for specific rights between copyright owner (licensor) and licensee, which are necessary under an "all rights reserved" copyright management, with a "some rights reserved" management employing standardized licenses for re-use cases where no commercial compensation is sought by the copyright owner. The result is an agile, low-overhead and low-cost copyright-management regime, profiting both copyright owners and licensees[wiki] The CC licenses all grant the "baseline rights", such as the right to distribute the copyrighted work worldwide for non-commercial purposes, and without modification. The details of each of these licenses depend on the version, and comprises a selection out of four conditions:
Attribution (BY)
Licensees may copy, distribute, display and perform the work and make derivative works and remixes based on it only if they give the author or licensor the credits (attribution) in the manner specified by these.here you can view View license deed and View legal code
Share-alike (SA)
Licensees may distribute derivative works only under a license identical ("not more restrictive") to the license that governs the original work. Without share-alike, derivative works might be sublicensed with compatible but more restrictive license clauses, e.g. CC BY to CC BY-NC.) here you can view View license deed and View legal code
No Derivative Works (ND)
Licensees may copy, distribute, display and perform only verbatim copies of the work, not derivative works and remixes based on it.here you can view View license deed and View legal code
Dissemination Plan
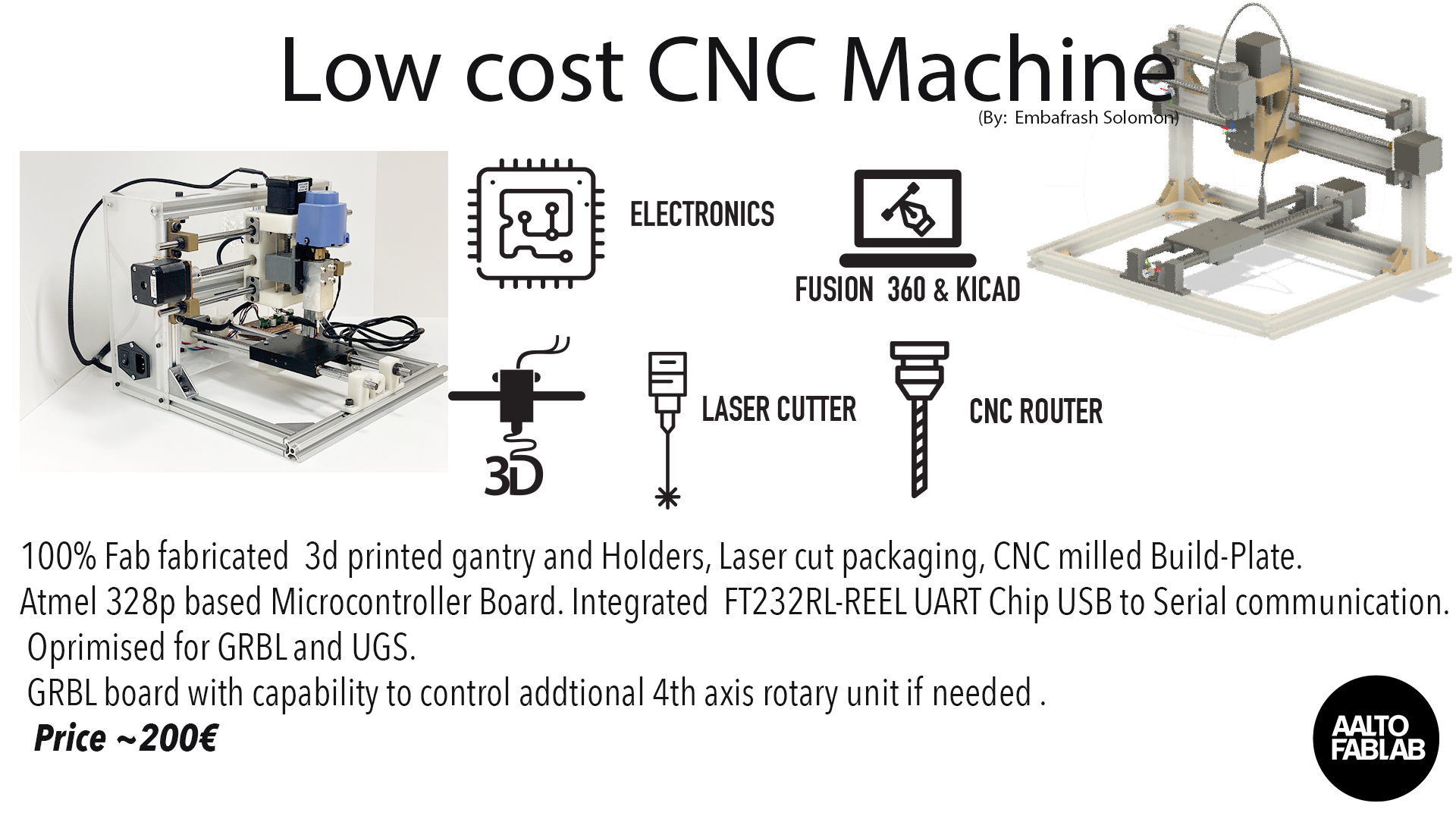
For my Final project I am preparing for a prototype V1.0 of a Low Cost CNC Machine.
The final project, much like many of my DIY activities, are more about learning new things and having fun than making money. That said, if it turns out that there is a market for a custom Low Cost CNC Machine, a services approach may result. (I am not holding my breath on it). Given that my work is based on many other open source efforts, I feel it is important to contribute this effort to help anyone else that may be looking at a similar problem..
More details on the steps , intention and design ideas behind this project can be found at my Final Project page.
Product Licensing
Attribution ShareAlike CC BY-SA
This license lets others tweak, and build upon the work even for commercial purposes, as long as they credit you and license their new creations under the identical terms. This license is quite similar to open source software licenses execept this licence is irrevocable SO Licensors should read and understand the terms and conditions of the license before applying it.. All new works based on the work will also carry the same license, so any derivatives will be forced to allow commercial use.
As a product my CNC machine is not unique and relied so much on other open source products like GRBL and UGS this could fit well in this catagory.
I designed this product not as a business concept - but to be able to give people (FAblab users) an option of a better designed, safer and transportable product that has competative performance.
As a product, this would have never reached this prototyping stage without building on the intellectual capital of others who deserve high level of attribute within the stream of knowledge via the Fab Academy.
While the share-alike license allows full remix and reuse of all product features, the attribute should be give to the creator.
Fab License: IP Protection
Attribution — You must give appropriate credit, provide a link to the license, and indicate if changes were made. You may do so in any reasonable manner, but not in any way that suggests the licensor endorses you or your use.
NonCommercial — You may not use the material for commercial purposes.
ShareAlike — If you remix, transform, or build upon the material, you must distribute your contributions under the same license as the original.
No additional restrictions — You may not apply legal terms or technological measures that legally restrict others from doing anything the license permits.
Licensees may copy, distribute, display and perform only verbatim copies of the work, not derivative works and remixes based on it.here you can view View license deed and View legal code
For Licensing all my works in fab academy 2021 i am using Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-SA 4.0)
It is much easier to create and satisfies most of my needs.we can easly create a license using creativecommons.org
This work by Embafrash Solomon is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Draft Summary Video
This short Video gives an overview of the different components of my low cost CNC machine design, fabrication and actuation.