- Logged in as: fablabtaipei (fablabtaipei)
- Recent changes
- Media Manager
- Sitemap
- Admin
- User page
- Update Profile
- Logout
User Tools
- Logged in as: fablabtaipei (fablabtaipei)
- Admin
- User page
- Update Profile
- Logout
Site Tools
Table of Contents
Embedded Programming
Embedded Programming
Goal
* read a microcontroller data sheet * program your board to do something, with as many different programming languages and programming environments as possible
Microcontroller
I intended to use Attiny 45 and therefore I read the datasheet of Attiny 25/45/85. One of the most important thing in the sheet is the functions of the pins. This matters when you lay components and wiring them.
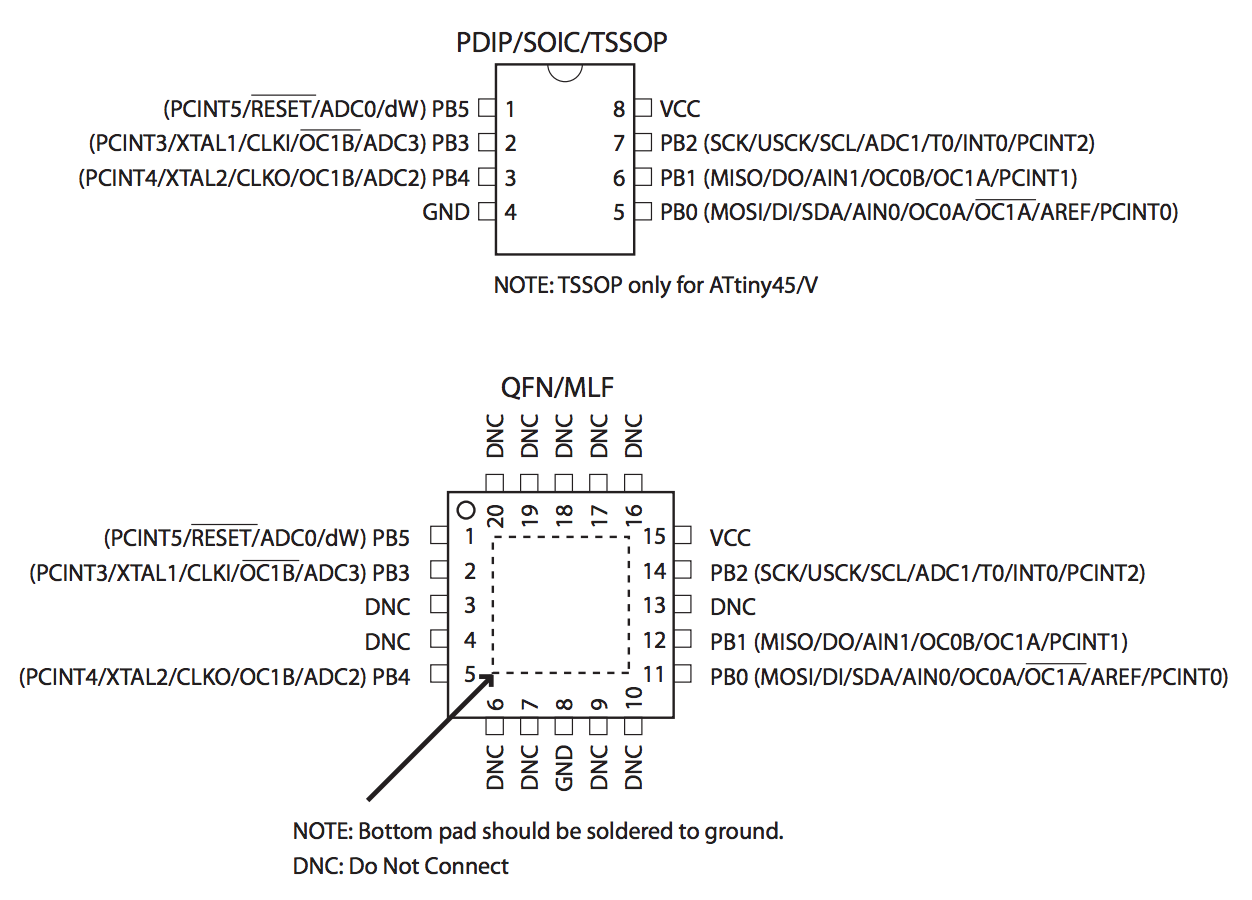
 Based on the datasheet, I made another board with a compact design. I used the following pins:
Based on the datasheet, I made another board with a compact design. I used the following pins:
- RESET
- XTAL1 (crystal)
- XTAL2 (crystal)
- GND
- MOSI
- MISO / Arduino Pin 1
- Not used.
- VCC
—-
Programming
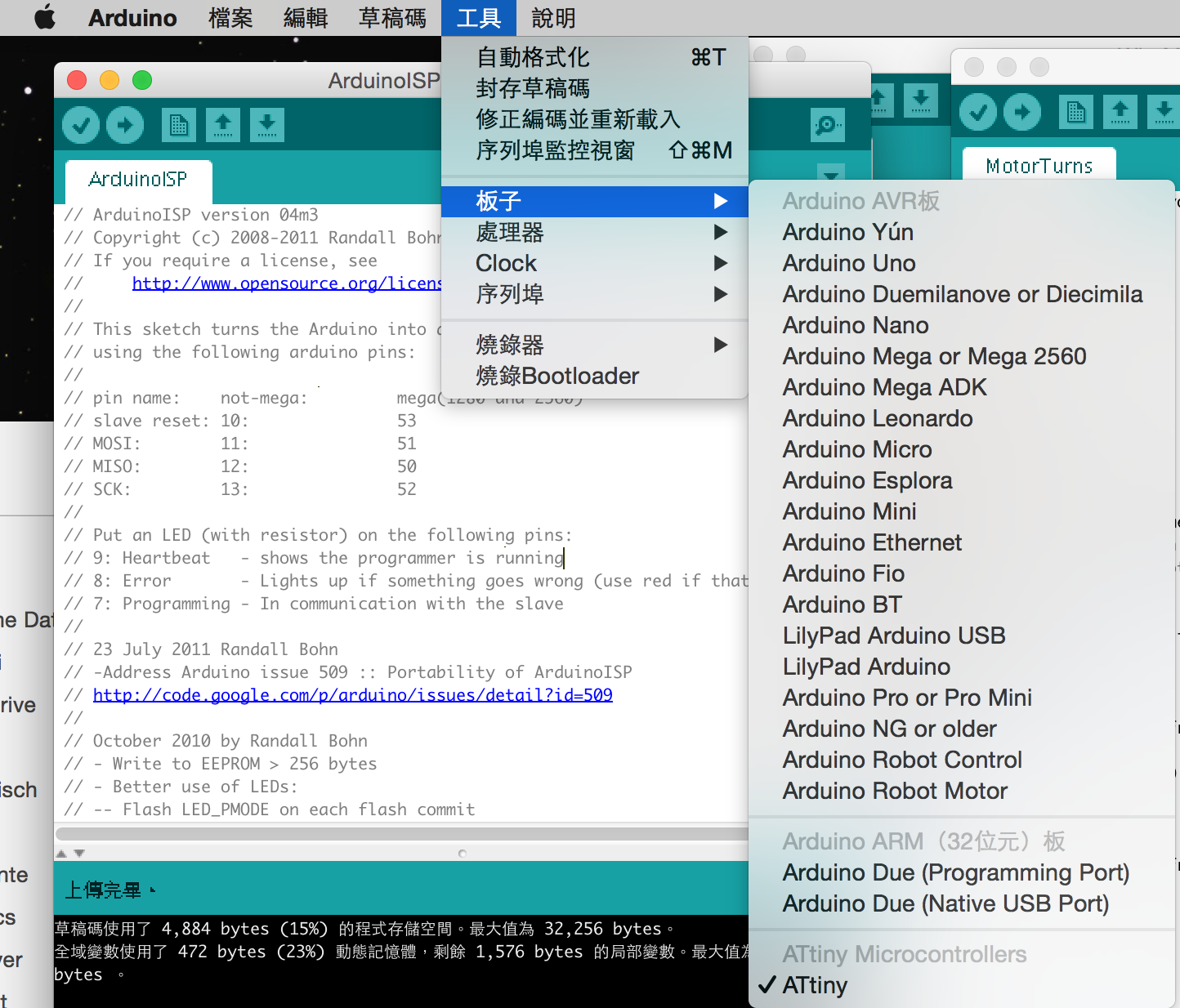 I used Arduino as ISP because I could not make it work in electronics production after several attempts. I installed Arduino and Arduino as ISP package in
----
Manager. After uploading the Arduino as ISP example to Arduino Uno, I selected 'Attiny 45' as board to upload the program to Attiny via Arduino with the following pins connected.
I used Arduino as ISP because I could not make it work in electronics production after several attempts. I installed Arduino and Arduino as ISP package in
----
Manager. After uploading the Arduino as ISP example to Arduino Uno, I selected 'Attiny 45' as board to upload the program to Attiny via Arduino with the following pins connected.
pin name: not-mega: mega(1280 and 2560) slave reset: 10: 53 MOSI: 11: 51 MISO: 12: 50 SCK: 13: 52
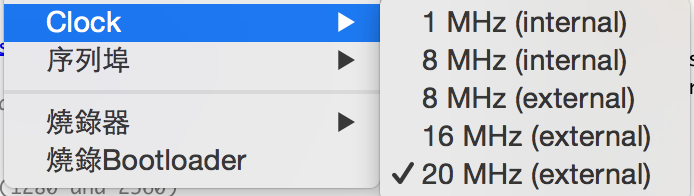 My board had an external 20 Mhz oscillator. Therefore I could set my Attiny 45 to run 20 Mhz. I checked 20 Mhz clock and burned bootloader in Arduino IDE.
My board had an external 20 Mhz oscillator. Therefore I could set my Attiny 45 to run 20 Mhz. I checked 20 Mhz clock and burned bootloader in Arduino IDE.
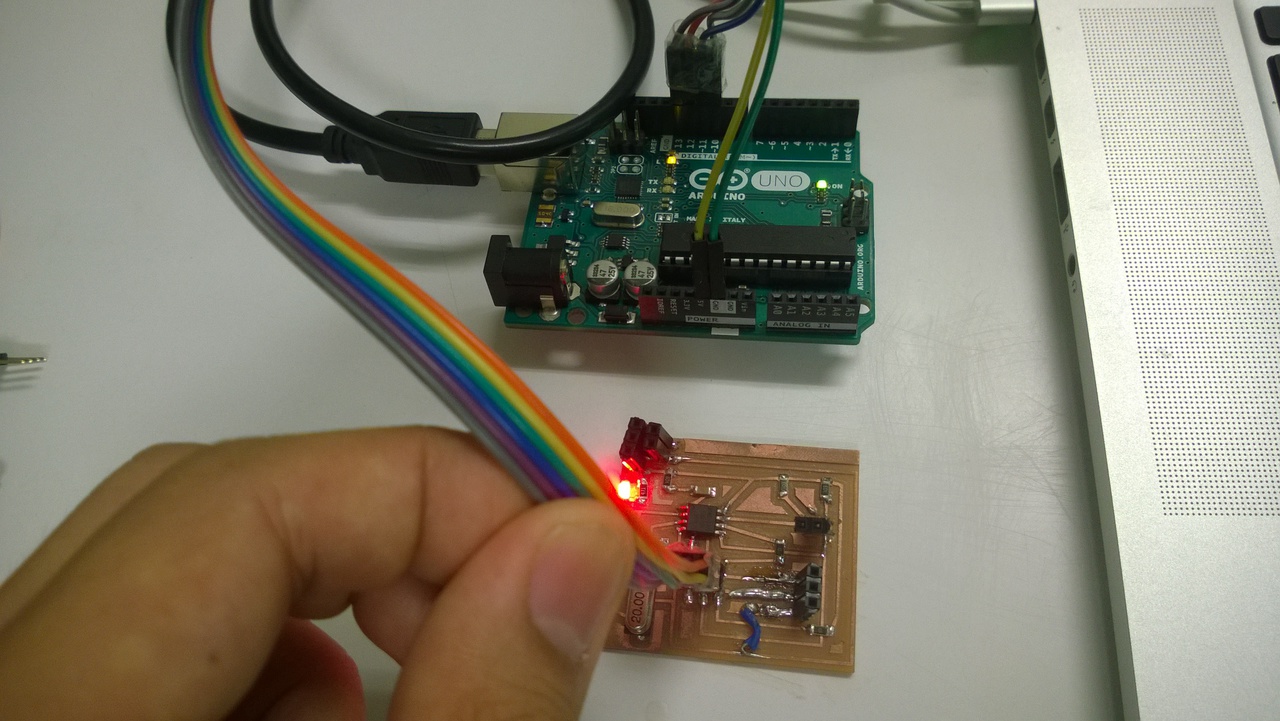 Then it was ready to upload to my board. I uploaded the following code. This was a modified code of Sweep example. The servo motor will continuously turn in one direction for a few seconds and then turn to the other.
Then it was ready to upload to my board. I uploaded the following code. This was a modified code of Sweep example. The servo motor will continuously turn in one direction for a few seconds and then turn to the other.
#include <SoftwareServo.h>
SoftwareServo myservo; // create servo object to control a servo
void setup() {
myservo.attach(1); // attaches the servo on pin 1 to the servo object
}
void loop() {
turn(5);
delay(1000);
}
void turn(int delayTime) {
// turn the servo with speed decided by delayTime
// delayTime should not be smaller than the time the servo needs to reach the position (about 5 miliseoncds)
int i=0;
for(i = 0; i < 180; i++) { // goes from 0 degrees to 180 degrees, in steps of 1 degree
myservo.write(i); // tell servo to go to position in variable 'pos'
delay(delayTime); // waits for the servo to reach the position
SoftwareServo::refresh();
}
for(i = 180; i >= 0; i--) { // goes from 180 degrees to 0 degrees
myservo.write(i); // tell servo to go to position in variable 'pos'
delay(delayTime); // waits 15ms for the servo to reach the position
SoftwareServo::refresh();
}
}
Or watch the video at Youtube