Principles and Practices, Project Management
In the first week we worked on defining the final project and getting familiar with the documentation process.
Principles and Practices
Weareable Wireless Robotic Arm Controller
The goal of this project is to develop a portable control interface capable of operating a robotic arm in near real-time. By integrating motion tracking and flexion detection, the system offers an intuitive, human-like control experience, bridging the gap between user intent and mechanical execution. Beyond simple movement, this technology aims to decentralize the machine operator, enabling complex tasks to be performed from a safe distance or in specialized environments.
The inspiration for this project came from an earlier prototype: a wired glove for controlling a mouse. While that initial version successfully demonstrated the basic concept of gesture-based input, it was limited by its physical connection. My goal for the Fab Academy is to build this concept into a fully wireless system with optimized signal processing. This transition from a simple wired tool to a sophisticated wearable controller represents a significant personal achievement.
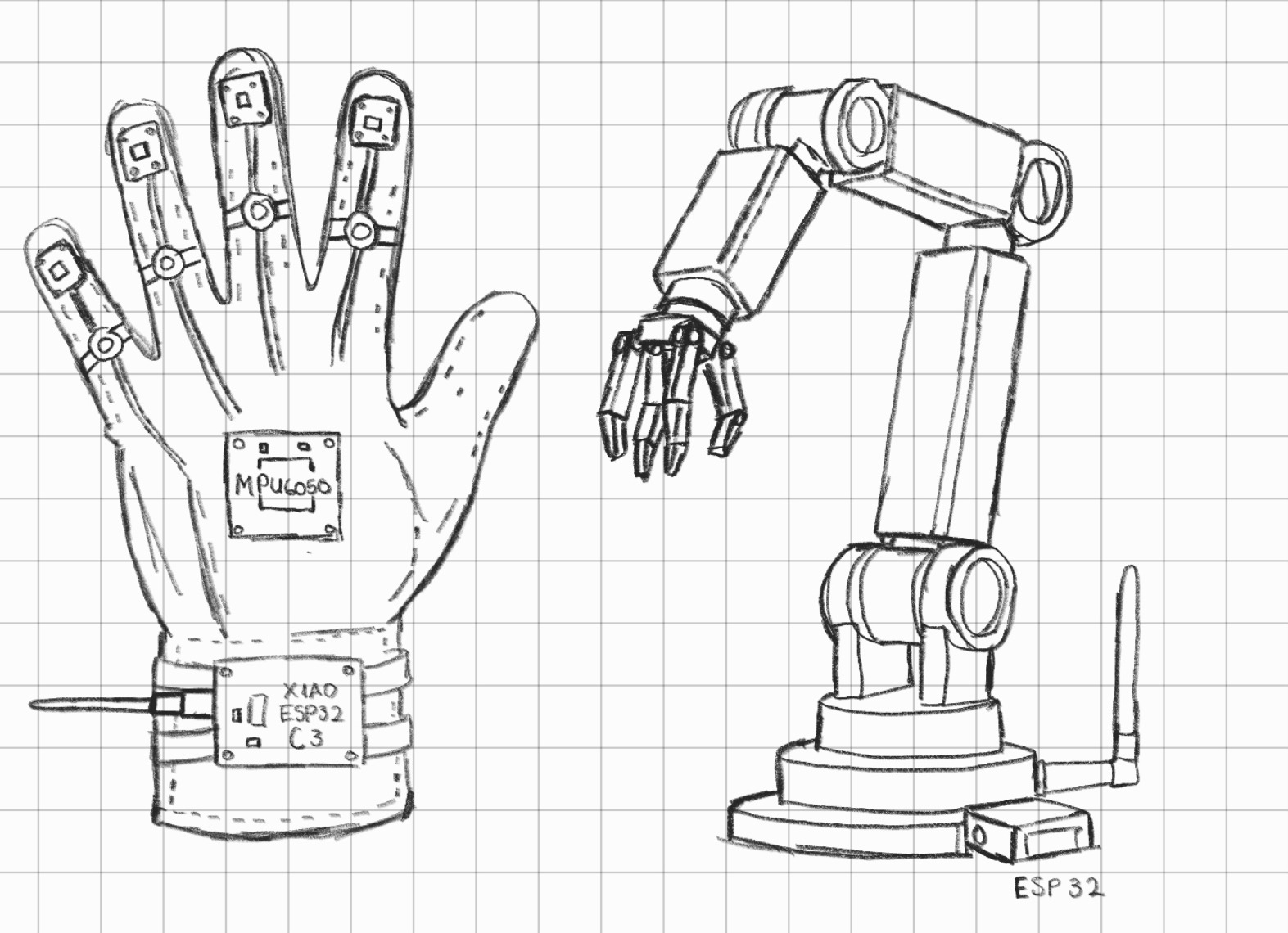
Possible Design Considerations
- Mechanical Structure: The robotic claw will be manufactured using 3D printing in PLA or PETG for complex geometries, while the structural base and arm segments will be laser-cut from MDF or Acrylic to ensure fast prototyping.
- Actuators: Movement will be driven by high-torque Servos for precise angular control in the joints, or Stepper Motors if continuous rotation and higher holding torque are required.
- Wearable Base: The glove will be constructed from a semi-rigid fabric or a combination of 3D-printed flexible TPU "exoskeleton" parts to provide both comfort and stable mounting points for the electronics.
- Custom Sensors: To monitor finger movement, DIY Flex Sensors can be fabricated using Velostat, a pressure-sensitive conductive material, offering a cost-effective alternative to commercial sensors.
- Control System: Real-time processing will be handled by the XIAO ESP32-C3, using its small form factor and built-in Wi-Fi/Bluetooth capabilities for wireless data transmission.
Challenges and Technical Heurdles
- Near-Zero Latency: Achieving a real-time response between the user’s hand movements and the robot’s execution.
- Signal Processing: Implementing digital filters (such as a Complementary Filter) to smooth out MPU6050 sensor noise without introducing additional delay.
- Ergonomics: Positioning the XIAO ESP32-C3 and battery strategically to ensure the "Smart Glove" is comfortable and avoids straining the user's wrist.
- Mechanical Consistency: Creating a mounting system that keeps flex sensors aligned with the knuckles to provide stable resistance readings during repeated bending.
- Wireless connection: Achieve stable and long-distance connection between the smart glove and the robotic arm via Wi-Fi/Bluetooth integrated into the ESP32 module.
To manage the development of this project, I established a structured schedule based on the Fab Academy's weekly requirements, defining specific goals and delivery dates for each phase.
