What is Embedded Programming?
It is the art of writing code specifically for hardware that isn't a "traditional" computer. It's about efficiency, real-time response, and controlling every single electron moving through the pins to make a device come to life.
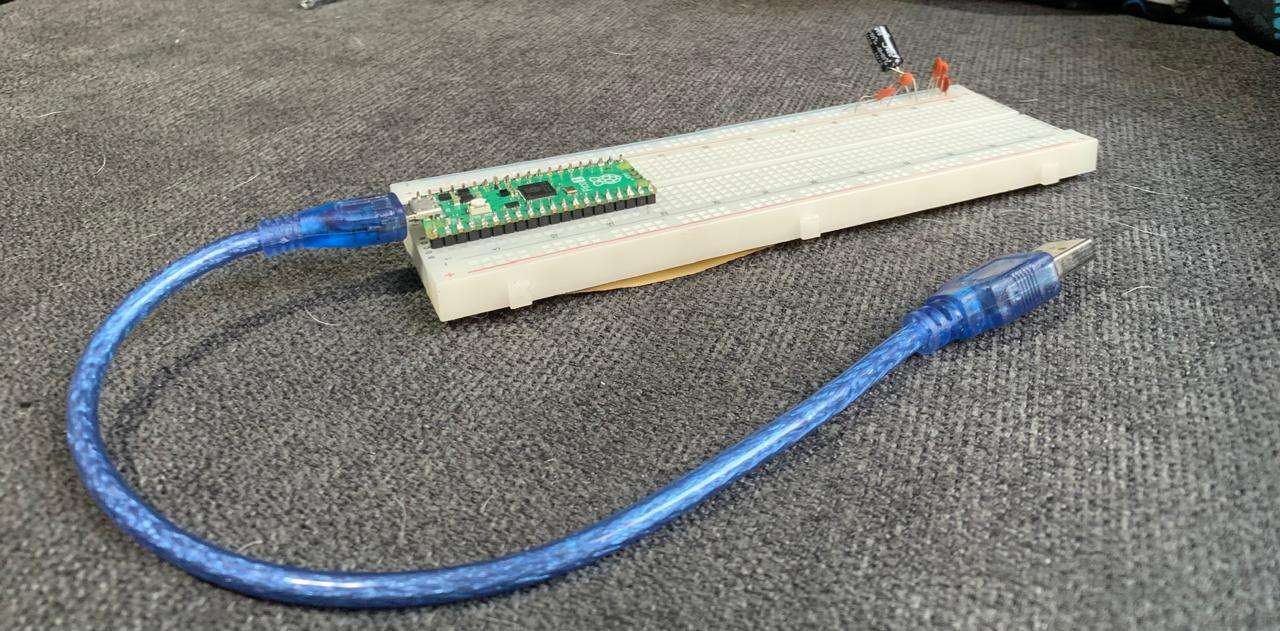
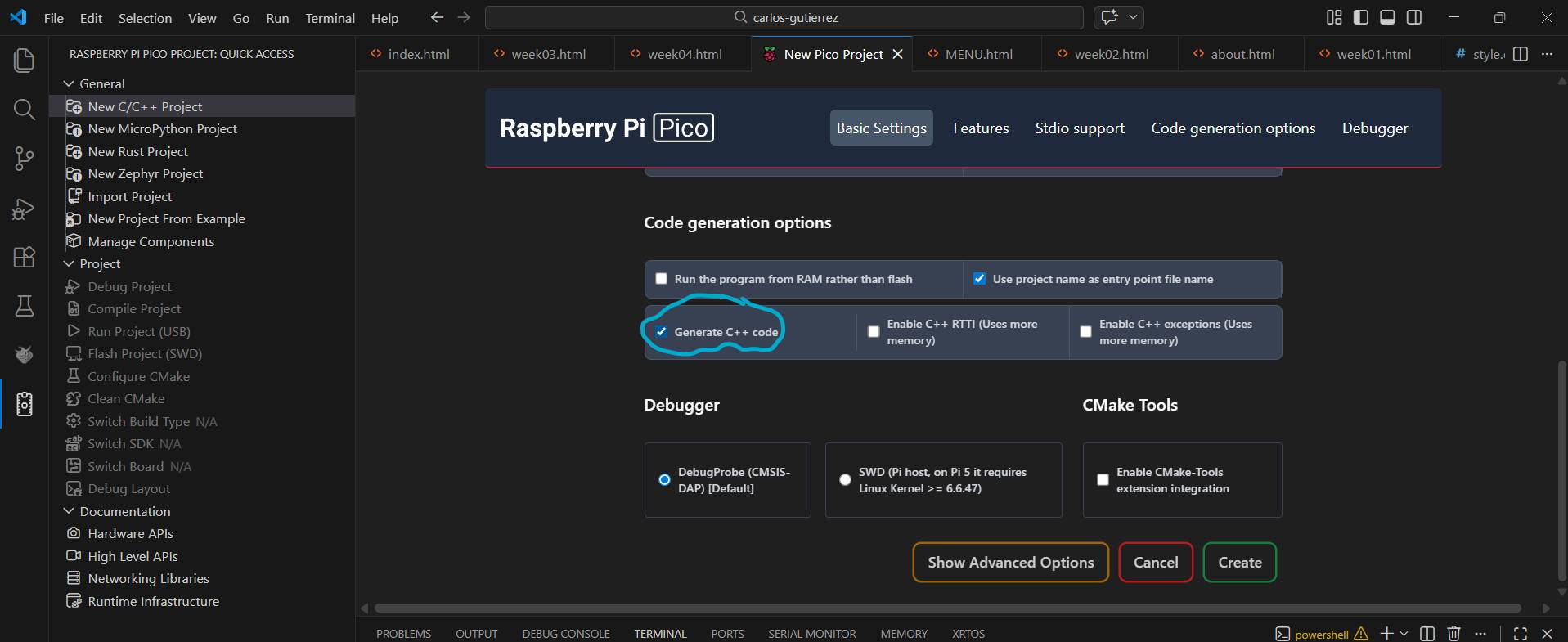
[ THE CONTROLLER: RASPBERRY PI PICO 2 ]
For this mission, I chose the Pico 2. I love the workflow using VS Code with the Pico extension—it makes the process much more professional and streamlined.
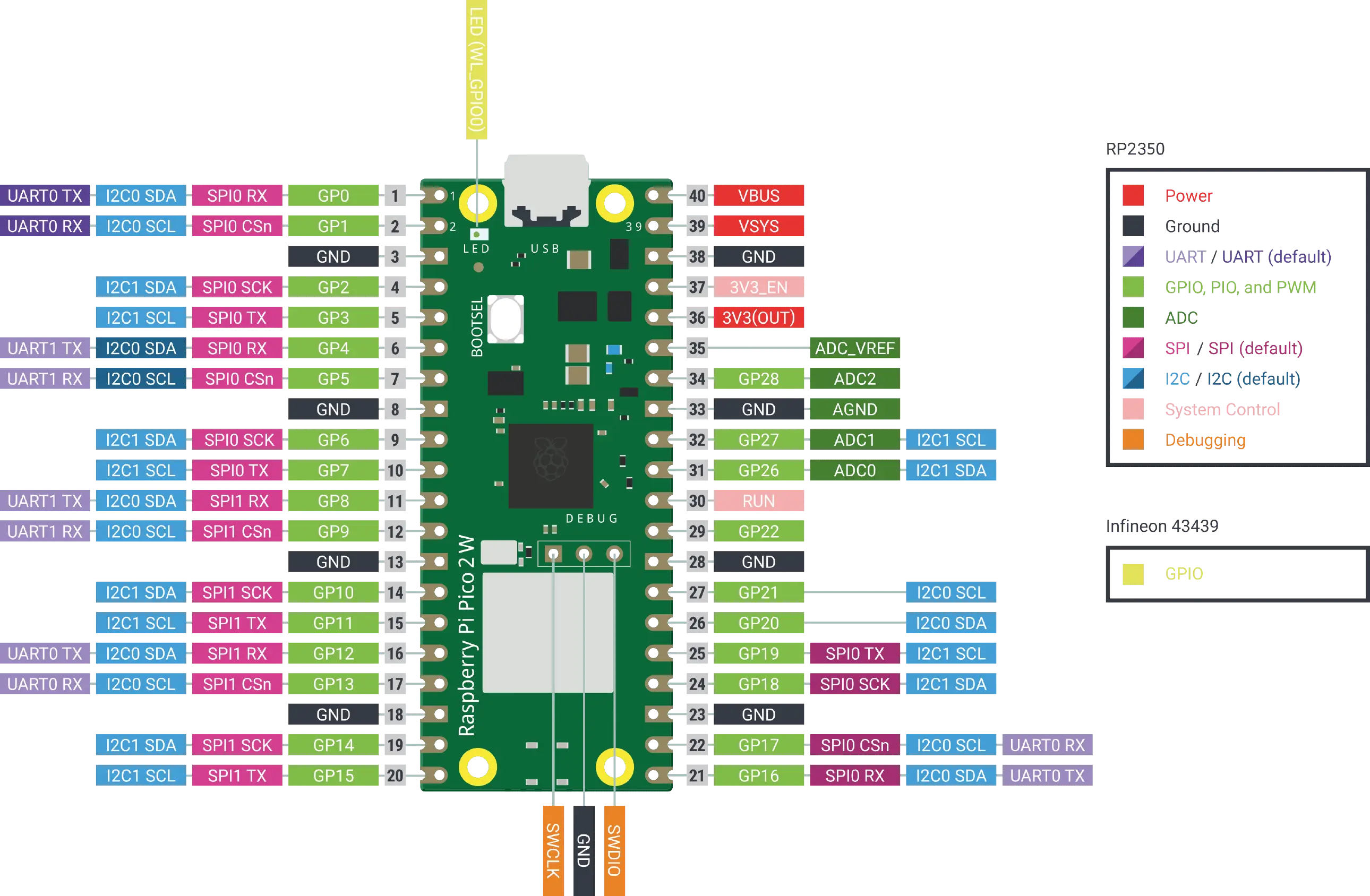
> FIG 01: PINOUT_DIAGRAM
| PIN TYPE | FUNCTION |
|---|---|
| Power | VBUS (5V), 3V3, GND |
| GPIO | General purpose Input/Output (3.3V) |
| ADC | Analog to Digital Converter (12-bit) |
| PWM | Pulse Width Modulation (Motor/LED control) |
| SPECIFICATION | DETAILS |
|---|---|
| Microcontroller | RP2350 (Dual Core ARM Cortex-M33) |
| Clock Speed | 150 MHz |
| Memory (SRAM) | 520 KB Internal |
| Flash Memory | 4 MB Off-chip (via QSPI) |
| Languages | C/C++, MicroPython, Rust |
| Communication | 2x UART, 2x SPI, 2x I2C |
| Features | 8x PIO State Machines |
SELECT EXECUTION ENVIRONMENT.
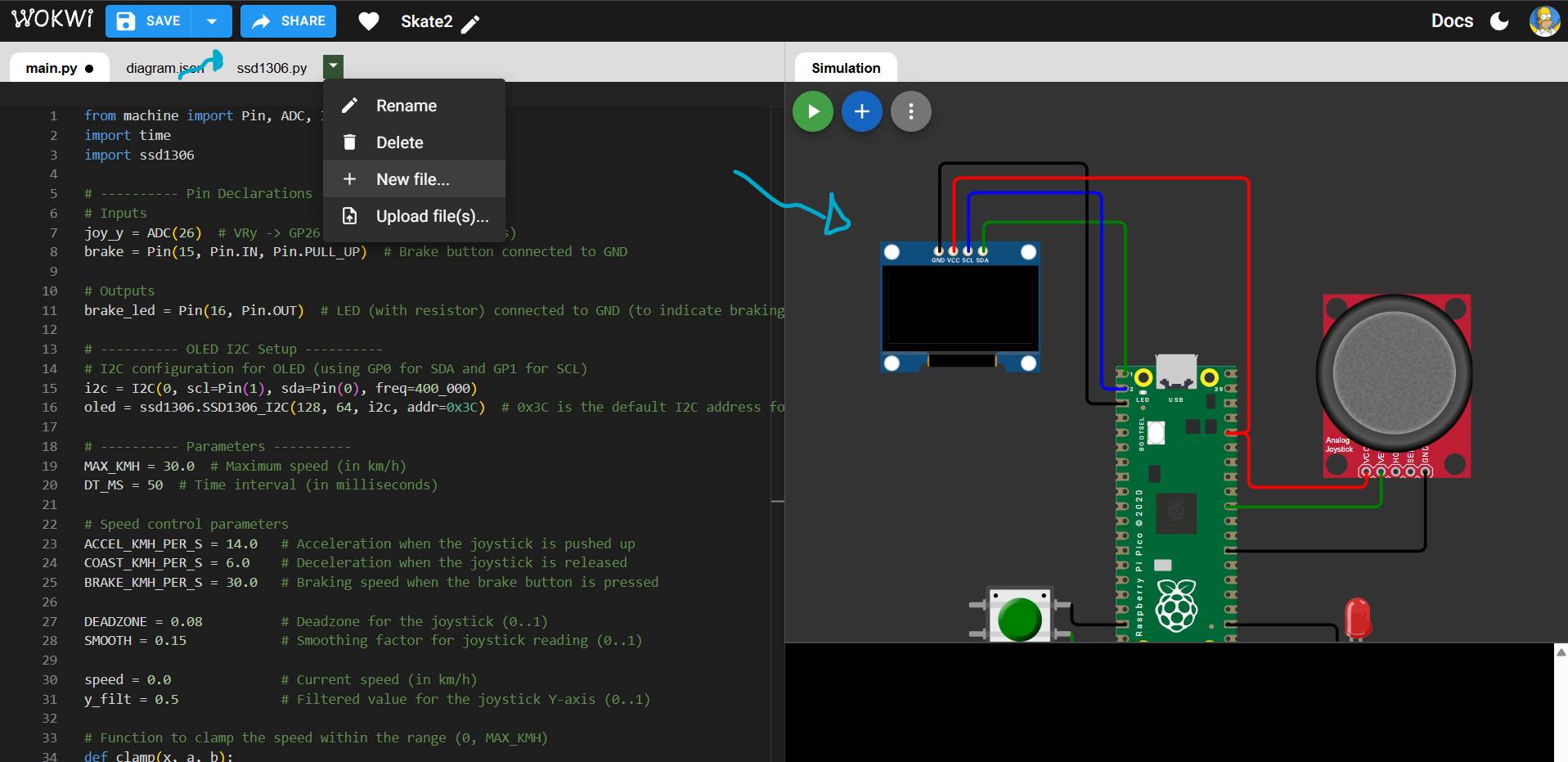
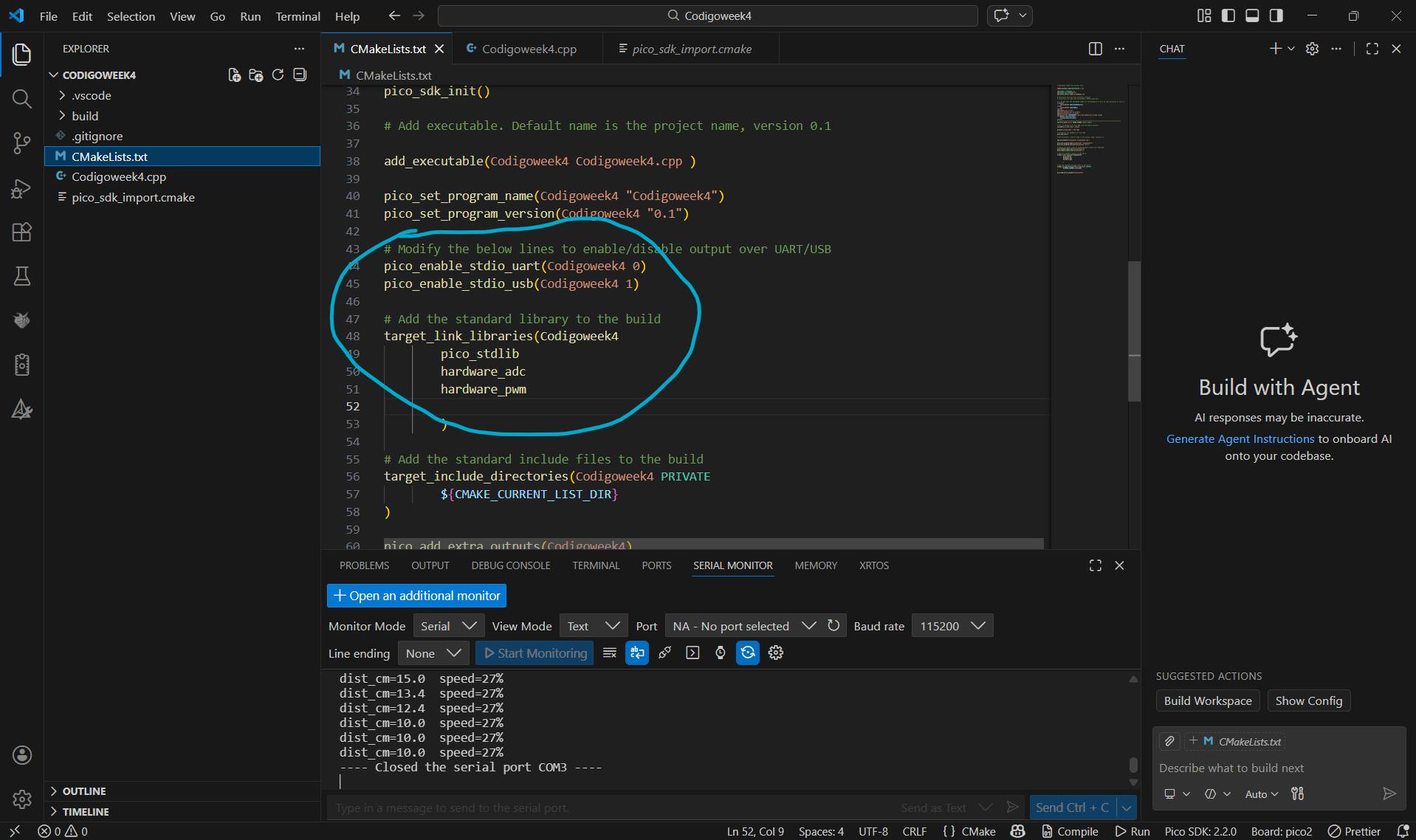
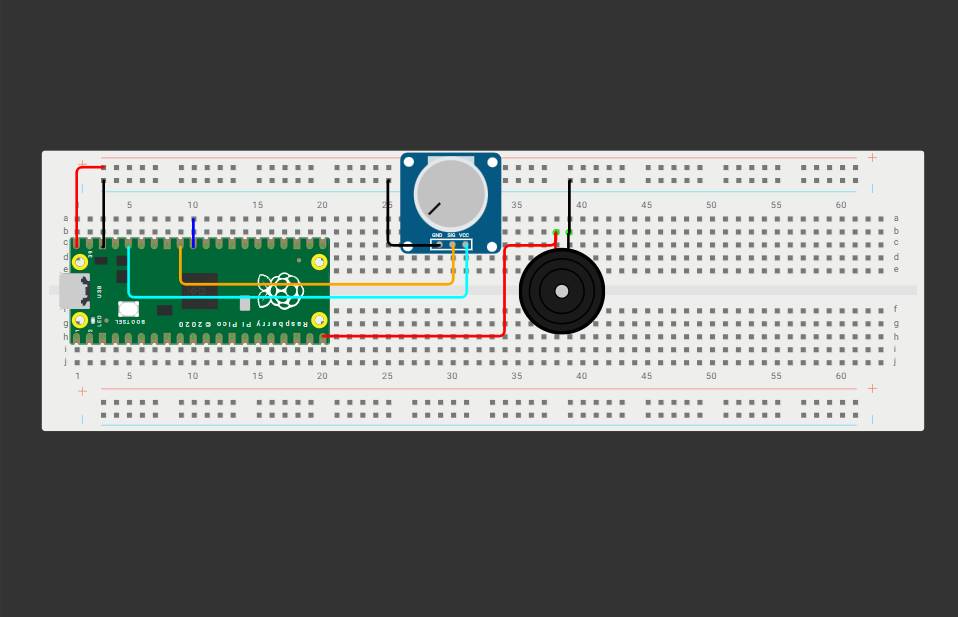
[ MISSION: WOKWI SIMULATION ]
MAIN.PY
from machine import Pin, ADC, I2C
import time
import ssd1306
# ---------- OLED ----------
i2c = I2C(0, scl=Pin(1), sda=Pin(0), freq=400_000)
oled = ssd1306.SSD1306_I2C(128, 64, i2c, addr=0x3C)
# ---------- Inputs ----------
joy_y = ADC(26) # VRy -> GP26 (ADC0)
brake = Pin(15, Pin.IN, Pin.PULL_UP) # botón a GND
# ---------- Output ----------
brake_led = Pin(16, Pin.OUT) # LED (con resistencia) a GND
# ---------- Params ----------
MAX_KMH = 30.0
DT_MS = 50
ACCEL_KMH_PER_S = 14.0
COAST_KMH_PER_S = 6.0
BRAKE_KMH_PER_S = 30.0
DEADZONE = 0.08
SMOOTH = 0.15
speed = 0.0
y_filt = 0.5
def clamp(x, a, b):
return a if x < a else (b if x > b else x)
while True:
dt = DT_MS / 1000.0
# leer joystick (0..1)
y = joy_y.read_u16() / 65535.0
y_filt = (1.0 - SMOOTH) * y_filt + SMOOTH * y
# comando -1..+1 (arriba positivo)
cmd = (y_filt - 0.5) * 2.0
if abs(cmd) < DEADZONE:
cmd = 0.0
braking = (brake.value() == 0)
brake_led.value(1 if braking else 0)
# dinámica de velocidad
if braking:
speed -= BRAKE_KMH_PER_S * dt
else:
if cmd > 0:
speed += (cmd * ACCEL_KMH_PER_S) * dt
else:
speed -= COAST_KMH_PER_S * dt # sueltas o jalas abajo: desacelera
speed = clamp(speed, 0.0, MAX_KMH)
# ---------- OLED ----------
oled.fill(0)
oled.text("JOY SPD", 0, 0)
oled.text(f"{int(speed + 0.5)} km/h", 0, 20)
oled.text(f"cmd:{cmd:+.2f}", 0, 48)
if braking:
oled.text("BRK", 100, 0)
oled.show()
time.sleep_ms(DT_MS)
SSD1306.PY
# MicroPython SSD1306 OLED driver, I2C and SPI interfaces
from micropython import const
import framebuf
# register definitions
SET_CONTRAST = const(0x81)
SET_ENTIRE_ON = const(0xA4)
SET_NORM_INV = const(0xA6)
SET_DISP = const(0xAE)
SET_MEM_ADDR = const(0x20)
SET_COL_ADDR = const(0x21)
SET_PAGE_ADDR = const(0x22)
SET_DISP_START_LINE = const(0x40)
SET_SEG_REMAP = const(0xA0)
SET_MUX_RATIO = const(0xA8)
SET_COM_OUT_DIR = const(0xC0)
SET_DISP_OFFSET = const(0xD3)
SET_COM_PIN_CFG = const(0xDA)
SET_DISP_CLK_DIV = const(0xD5)
SET_PRECHARGE = const(0xD9)
SET_VCOM_DESEL = const(0xDB)
SET_CHARGE_PUMP = const(0x8D)
class SSD1306(framebuf.FrameBuffer):
def __init__(self, width, height, external_vcc):
self.width = width
self.height = height
self.external_vcc = external_vcc
self.pages = self.height // 8
self.buffer = bytearray(self.pages * self.width)
super().__init__(self.buffer, self.width, self.height, framebuf.MONO_VLSB)
self.init_display()
def init_display(self):
for cmd in (
SET_DISP | 0x00, # off
SET_MEM_ADDR, 0x00, # horizontal addressing
SET_DISP_START_LINE | 0x00,
SET_SEG_REMAP | 0x01, # rotate
SET_MUX_RATIO, self.height - 1,
SET_COM_OUT_DIR | 0x08, # rotate
SET_DISP_OFFSET, 0x00,
SET_COM_PIN_CFG, 0x12 if self.height == 64 else 0x02,
SET_DISP_CLK_DIV, 0x80,
SET_PRECHARGE, 0x22 if self.external_vcc else 0xF1,
SET_VCOM_DESEL, 0x30,
SET_CONTRAST, 0xFF,
SET_ENTIRE_ON,
SET_NORM_INV,
SET_CHARGE_PUMP, 0x10 if self.external_vcc else 0x14,
SET_DISP | 0x01 # on
):
self.write_cmd(cmd)
self.fill(0)
self.show()
def poweroff(self):
self.write_cmd(SET_DISP | 0x00)
def poweron(self):
self.write_cmd(SET_DISP | 0x01)
def contrast(self, contrast):
self.write_cmd(SET_CONTRAST)
self.write_cmd(contrast)
def invert(self, invert):
self.write_cmd(SET_NORM_INV | (invert & 1))
def show(self):
self.write_cmd(SET_COL_ADDR)
self.write_cmd(0)
self.write_cmd(self.width - 1)
self.write_cmd(SET_PAGE_ADDR)
self.write_cmd(0)
self.write_cmd(self.pages - 1)
self.write_data(self.buffer)
def write_cmd(self, cmd):
raise NotImplementedError
def write_data(self, buf):
raise NotImplementedError
class SSD1306_I2C(SSD1306):
def __init__(self, width, height, i2c, addr=0x3C, external_vcc=False):
self.i2c = i2c
self.addr = addr
self.temp = bytearray(2)
super().__init__(width, height, external_vcc)
def write_cmd(self, cmd):
self.temp[0] = 0x80
self.temp[1] = cmd
self.i2c.writeto(self.addr, self.temp)
def write_data(self, buf):
# 0x40 = data stream
self.i2c.writeto(self.addr, b"\x40" + buf)
[ SYSTEM LOG: AI COLLABORATION ]
LOG_01
"Optimized technical tables and unified slider layout for cross-environment consistency."
LOG_02
"Help me to improove the controls of the video logs"
> STATUS: SYSTEM_READY_FOR_DEPLOYMENT