Project management & Principles and Practices
Assignment
Project Management
- read, sign the student/instructor/lab agreements, and commit to your repos
- work through a git tutorial
- build a personal site in the class archive describing you and your final project
Principles and Practices
- plan and sketch a potential final project
PC working environment
- PC: MacBook Pro(16-inch,2019)
- OS: Sonoma 14.7.2
- Terminal: zsh
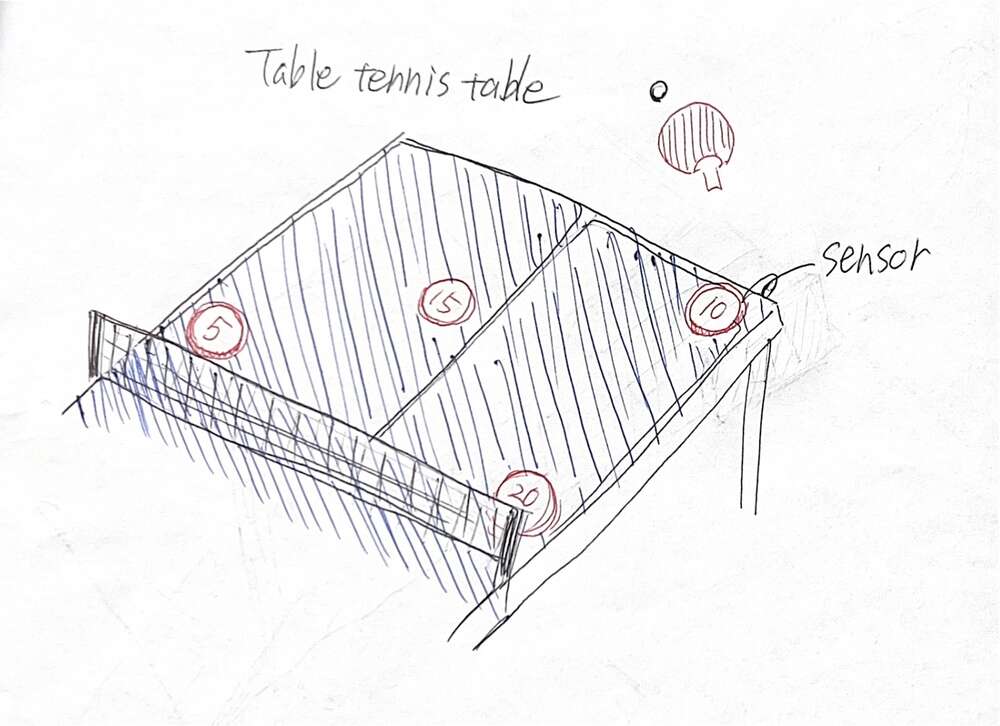
hero shot
my final project
What I did
- Sign up Agreement
- Sketch the final project
- Build environment
- Create a website
Git set up(to do only the first time)
First, install Homebrew, the Package Manager
1.Homebrew install
1.0 install
 From homebrew site
copy and paste the installation code into the terminal to install
install code↓
From homebrew site
copy and paste the installation code into the terminal to install
install code↓
/bin/bash -c "$(curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Homebrew/install/HEAD/install.sh)"
1.1 version check
brew --version

2.Git
2.0 Install using homebrew
brew install git
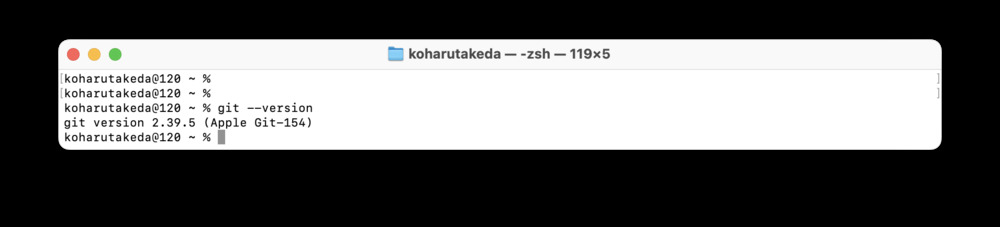
2.1 version check
git --version
2.2 Add my git username and set your email
git config –-global user.name “YOUR_USERNAME”
git config -–global user.email “xxxxxxxx@xxxxx.com”
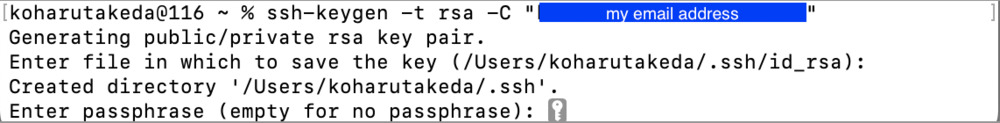
2.3 Generate my SSH key
ssh-keygen -t rsa -C "xxxxxxxx@xxxxx.com"
I typed my cloud address for “xxxxxxxx@xxxxx.com” for git. Then, appeared below phrase that Specify where to save the SSH key.
Enter file in which to save the key:
The SSH key is stored in the .ssh folder. The .ssh folder (default) is under your home directory, as tutorials.
Then, appeared below phrase, Enter my passphrase.
Enter passphrase (empty for no passphrase)
Enter same passphrase again;

2.4 Then Enter the command to display the contents of id_rsa.pub in order to see the SSH key.
cat ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub
2.5 Copy public key.
ssh-rsa ~~~~
...
~~~ xxxxxxxx@xxxxx.com
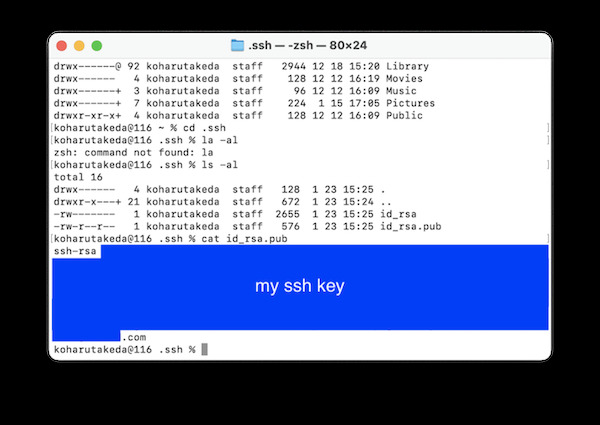
Confirmation shows that ssh has been generated
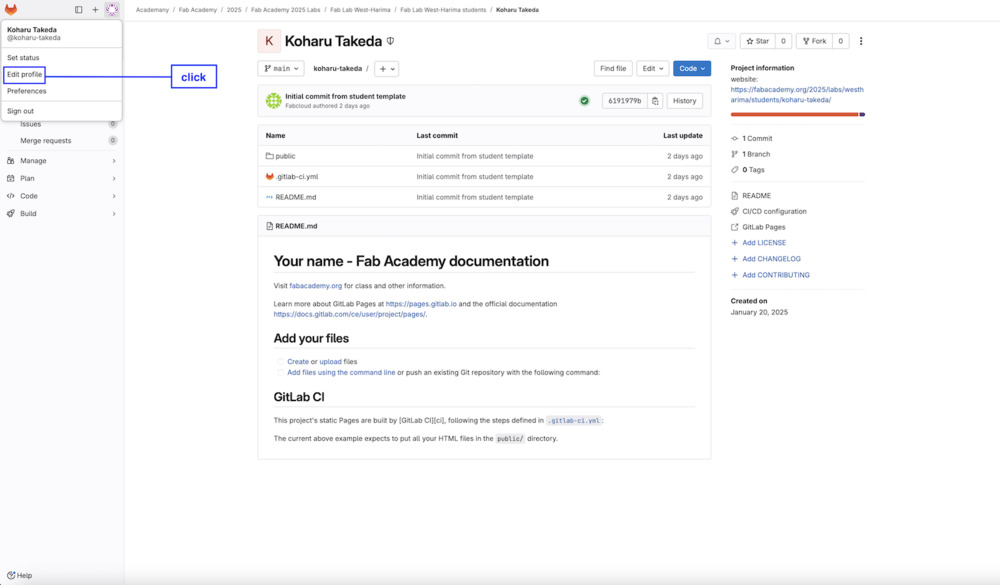
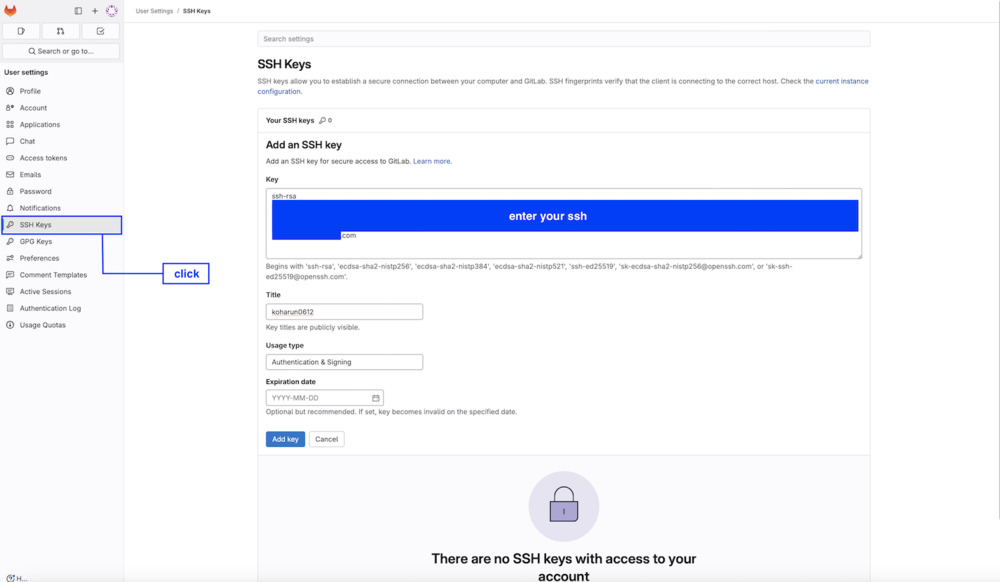
2.6 Finally add the copied key to GIT on the web version.
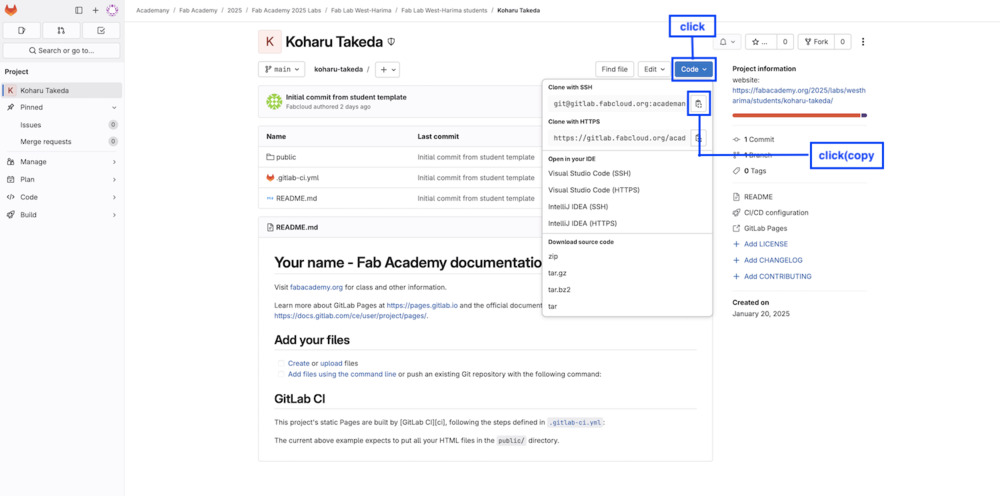
3.Copy my remote Repository
3.0 I bring (clone) the contents of a remote repository, do the following. The source address (git@~) is obtained from the remote repository (Gitlab project page). I do this only the first time, except I miss something.
git clone git@xxx.xxxxx

4.Codes when upload file to remote repository (at least)
Update the newest data to local (If the project join only me not necessary)
git pull
Check the add
git status
Add the changes
git add .
Commit(add) the update to the local repository, briefly describing the update in XXXX (in English)
git commit -m "XXXX"
Update to Remote repository
git push
Reference Links
5.Mkdocs
What is it?
This static site generator is designed to convert documents written in Markdown format into HTML sites. It is especially useful for project documentation, allowing you to easily create beautiful documentation sites.
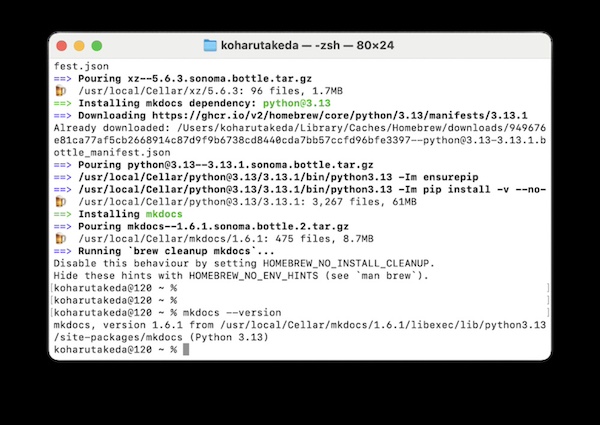
5.0 install
brew install mkdocs
5.1 version check
mkdocs --version
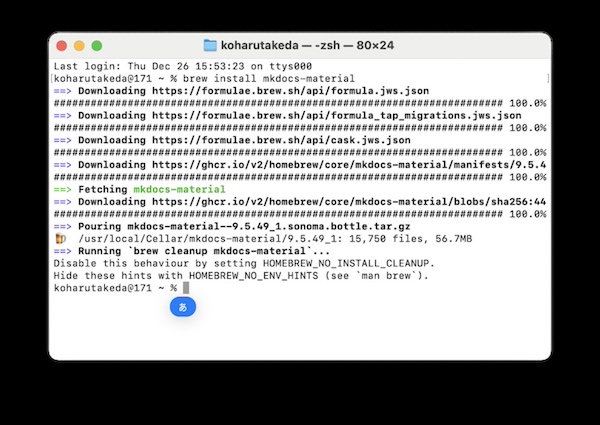
5.2 Install material, a mkdocs theme, with brew
brew install mkdocs-material
Reference Links
6.Bootstrap
Bootstrap5 is css framework. From Bootstrap site bootstrap provides pre-designed HTML, CSS, and JavaScript components to streamline web development.
Reference Links
7.gitignore
What is it? gitignore is a special filename used in Git, and files in this file are processed from the top down and are not subject to Git tracking.
7.0 First, open a terminal, type this in, and run it.
touch .gitignore

“touch .gitignore” is a command that creates a file called .gitignore in the Git repository. The “.gitignore file” is a file that specifies to Git which files and directories it will not track. Files and directories that match the pattern described in this file are not managed by Git and are ignored by Git when you commit or push them.
7.1 Edit with “nano” to add hidden files to gitignore.
nano .gitignore
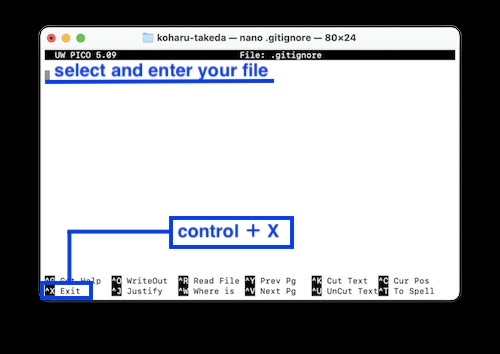
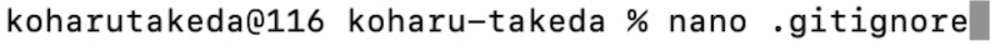 7.2 Next, when a screen like this appears, enter the file you want to remove from management and press Control X.
7.2 Next, when a screen like this appears, enter the file you want to remove from management and press Control X.
7.3 Next, press Y when a screen like this appears
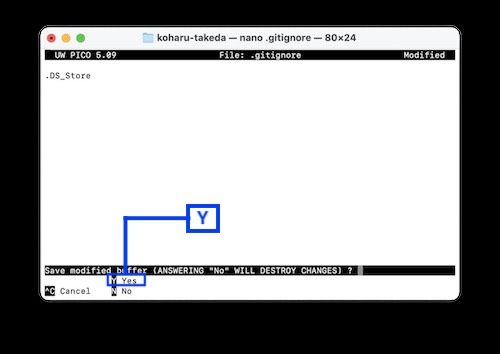
The file specified in 7.2 is now out of Git's control. In my case, everything with “.DS_Store” in the file is now ignored.
This command also allows you to delete hidden files
If you have a file that is managed in Git, and you subsequently add that file to your .gitignore, Git already keeps track of that file and will not immediately ignore it when you add it to your .gitignore. In other words, files that are already managed by Git are not automatically ignored when you add a .gitignore. If you want to delete the file itself, you can do so with the following command.
rm .DS_store
Reference Links
Impressions and What's I learned
- I felt there was a lot I didn't know about this Fabacademy. At the same time, I believe that I will have acquired a lot of knowledge and skills by the time I finish this curriculum!
- I am not good at English. Fabacademy is tough for me. But I am sure that my English will improve!
- I learned that gitignore can deliberately select files to be removed from Git's jurisdiction.