Learning Outcomes
- Demonstrate workflows used in the chosen process.
- Select and apply suitable processes (and materials) to do your assignment.
Checklist
- Documented the workflow(s) and process(es) used.
- Explained how your process is unique compared to other assignments.
- Described encountered problems and solutions.
- Included original design files and source code.
- Included a ‘hero shot’ of the result.
Objective
My wildcard assignment focuses on sheet metal laser cutting and other mild steel welding I am going to use in my final project which are not covered in other Fab Academy assignments.While laser cutting is used in the computer-controlled cutting week, it's limited to non-metal materials like wood and acrylic. Cutting metal sheets involves different machine settings, safety precautions, and handling. Additionally, I incorporated welding to assemble the metal frame and perform other small joining tasks, introducing fabrication methods beyond the scope of standard assignments.
‘Hero Shot’
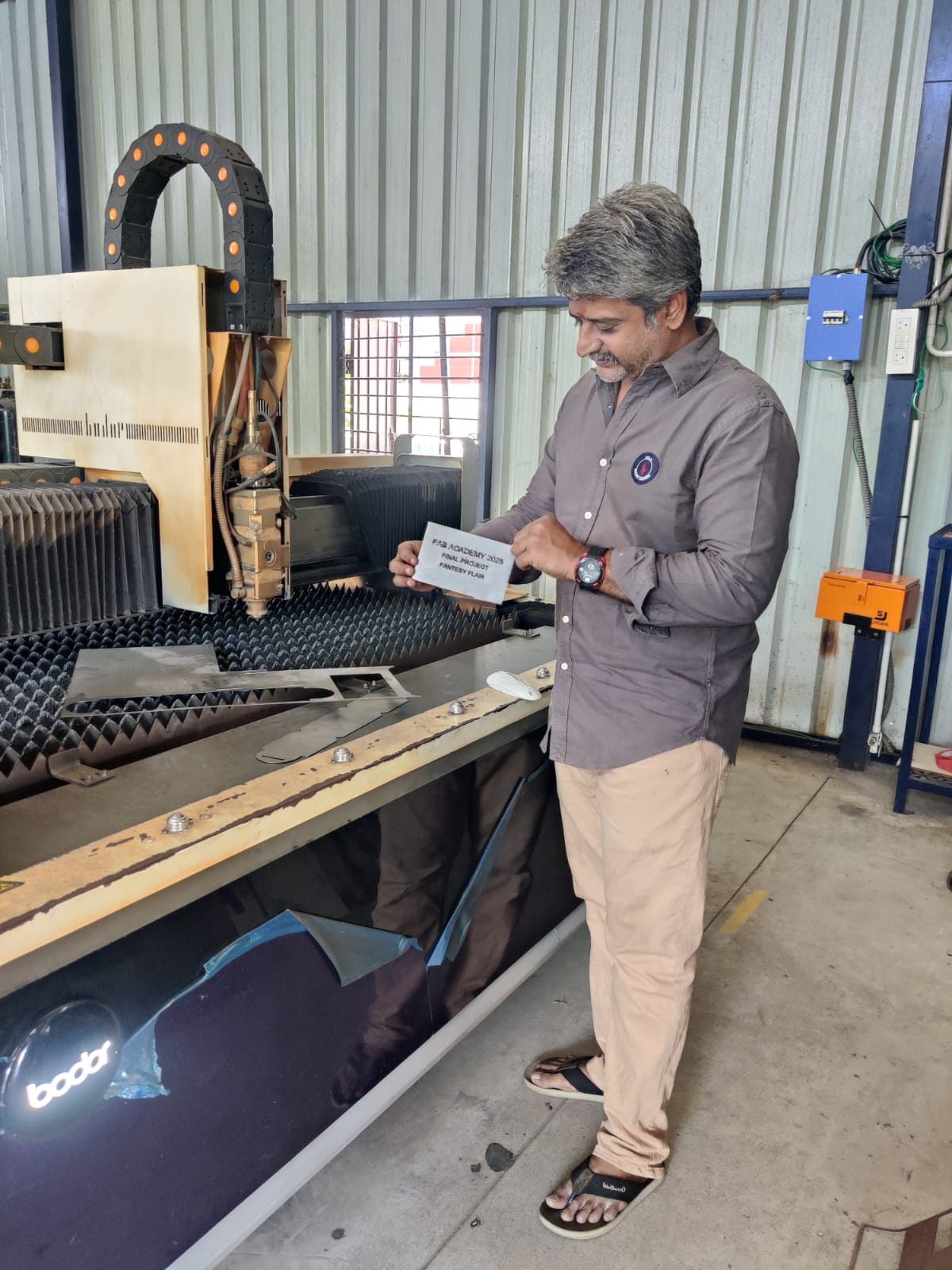
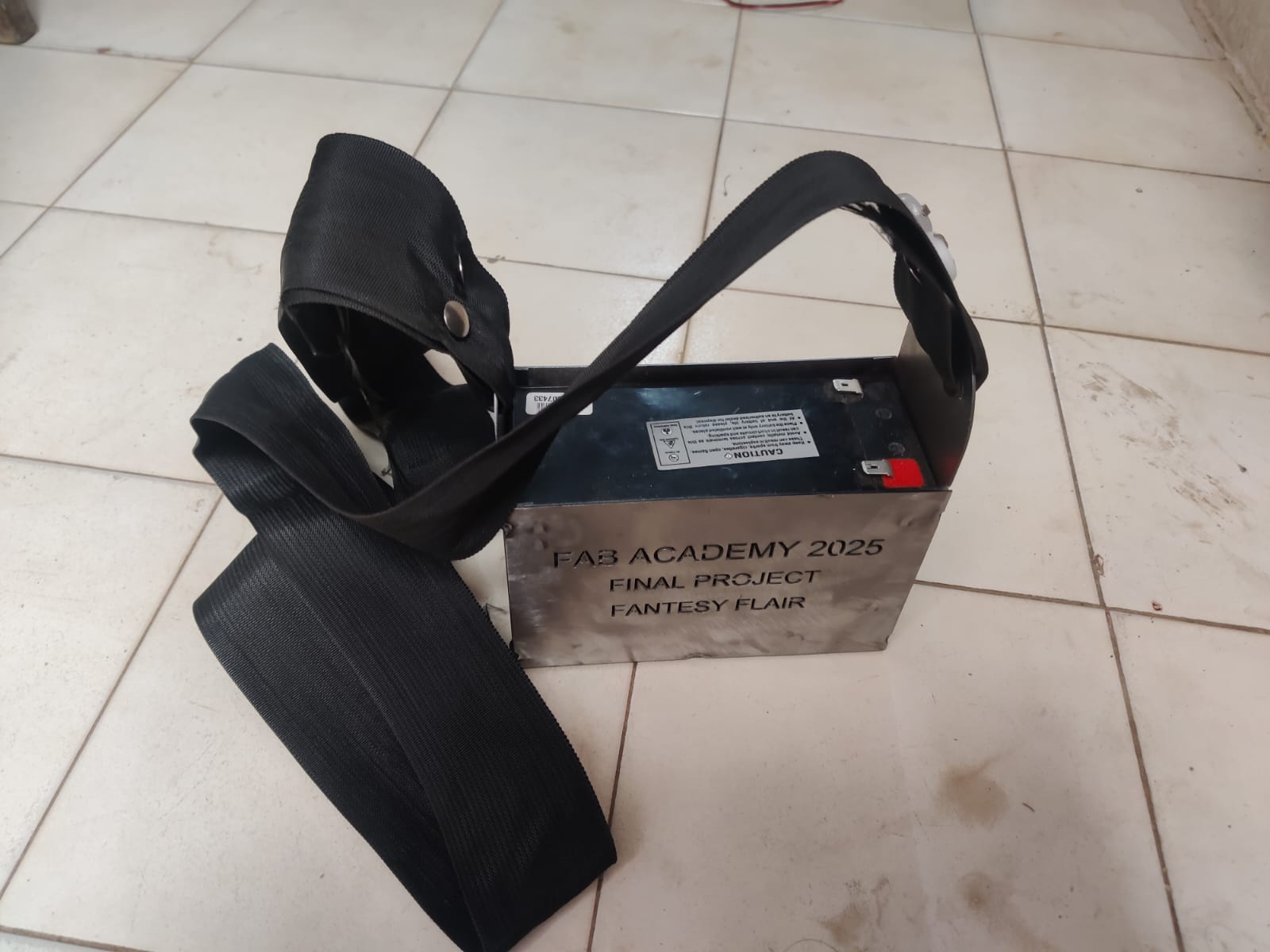



Motivation:
During my animatronic and robotics builds, I often use battery packs. However, I found that metal enclosures provide better durability, heat resistance, and electromagnetic shielding than plastic ones. I decided to fabricate a custom steel battery cover for one of my control units using metal laser cutting.
Tools & Materials
- Software Used: Autocad (CAD), CypCut Laser Cutting System (CAM for laser)
- Machine Used: Fiber Laser Metal Cutter (IPG 1000W)
- Material: 1.5mm Mild Steel Sheet
- Finishing Tools: Deburring tool
Design Process
-
Autocad (CAD)
- Measured battery pack dimensions (7×3×4 all in inch)
- Designed the enclosure with:
- Rounded corners
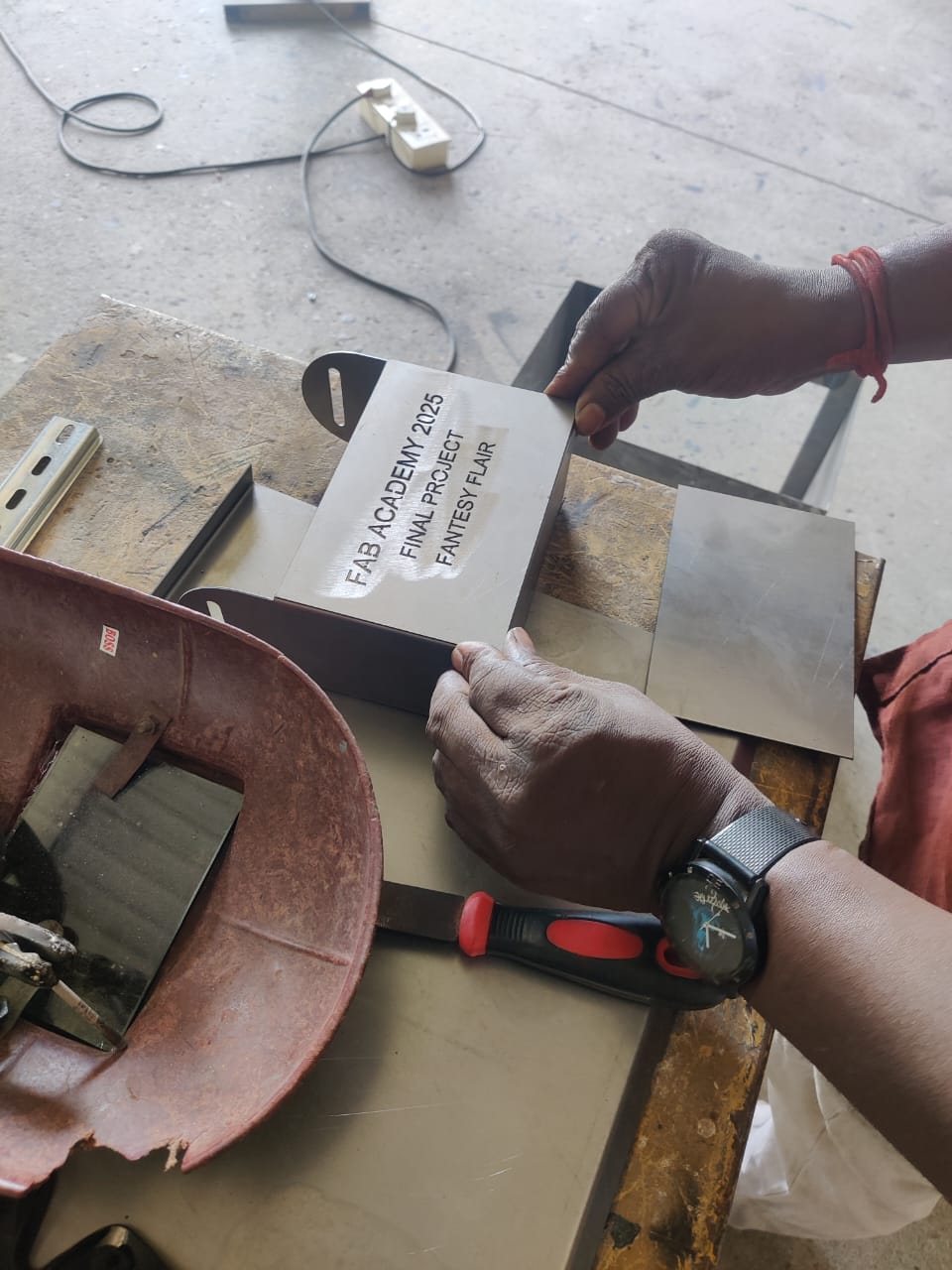
- Engraving: “FAB ACADEMY 2025 – FINAL PROJECT – FANTASY FLAIR” on the top plate
- A locking notch for the snap-fit
- Exported the 2D profile as DXF for laser cutting
-
CAM Preparation ( CypCut Laser Cutting System )
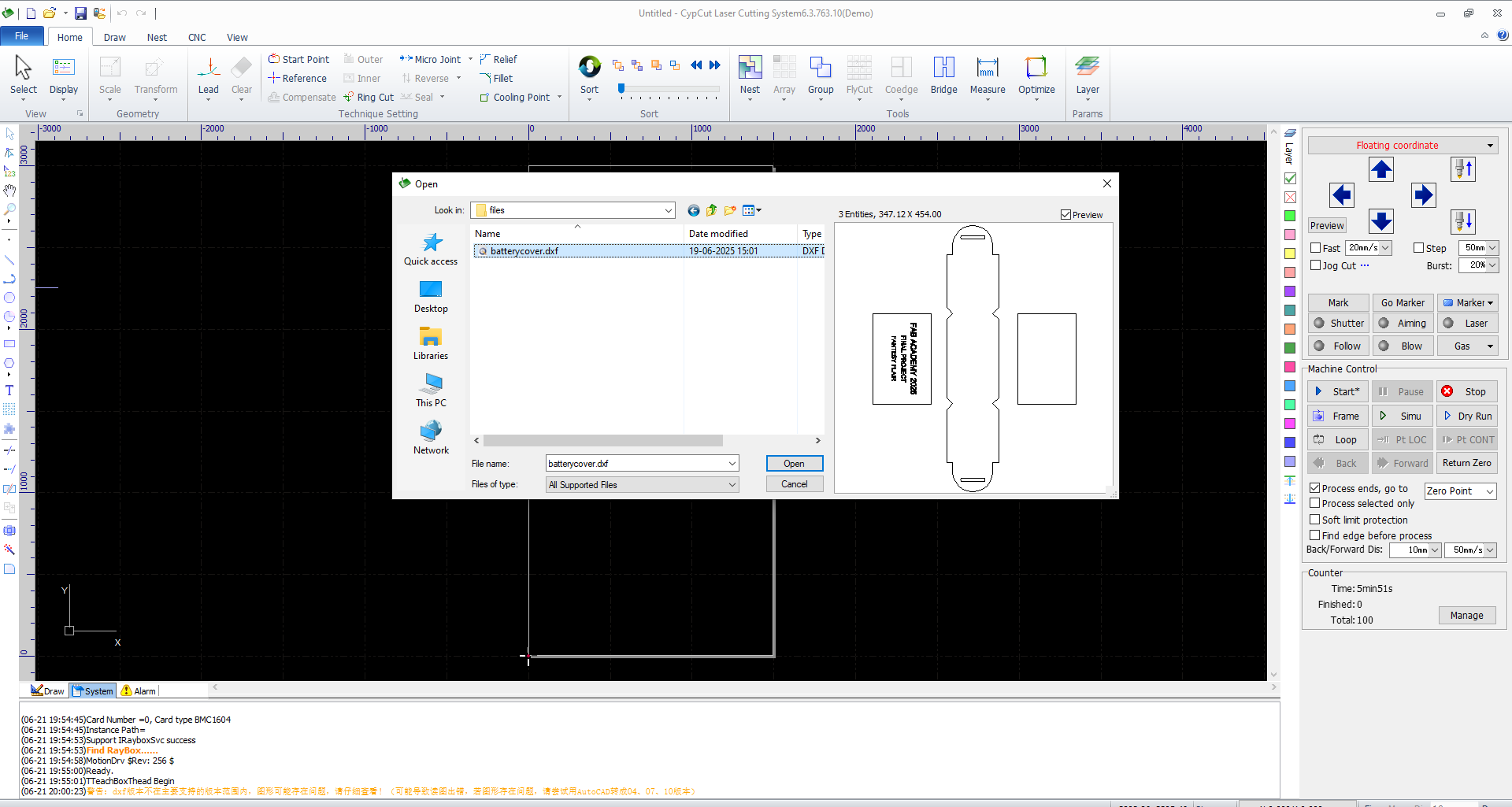
- Imported DXF into CypCut Laser Cutting System
- Assigned layer colors:
- Red: Cut (outer profile)
- Blue: Cut (slots and holes)
- Set machine parameters:
- Power: 80%
- Speed: 25 mm/s
- Assist Gas: Air/Nitrogen
A dry run test is performed without activating the laser to ensure the cutting path stays within the sheet boundaries. The machine follows the programmed toolpath, allowing the operator to check alignment, part placement, and fit. This prevents material wastage and ensures accurate positioning before actual cutting begins.
Fabrication Steps
For fabricating a battery case using 1.5 mm sheet metal with a CypCut Laser Cutting System, begin by designing interlocking or tab-based parts in CAD software, ensuring proper clearance for bending and fitting. Export the design as a DXF and import into CypCut. Use suitable settings—Power: 1000–1500W, Speed: 6–10 mm/s, Gas: Nitrogen—for clean cuts. Secure the sheet metal on the bed and focus the laser. Once cut, deburr the parts, then use a press brake for bending as per the design. Assemble using screws, rivets, or welding. Ensure cutouts for connectors, ventilation, and battery fit.
When the Start button is clicked, the machine receives a signal to begin operation. The controller activates the motors and initiates the pre-programmed cutting or movement sequence. Safety checks are verified, and the process starts automatically, ensuring smooth execution of the task according to the selected parameters.
Metal Laser Cutting
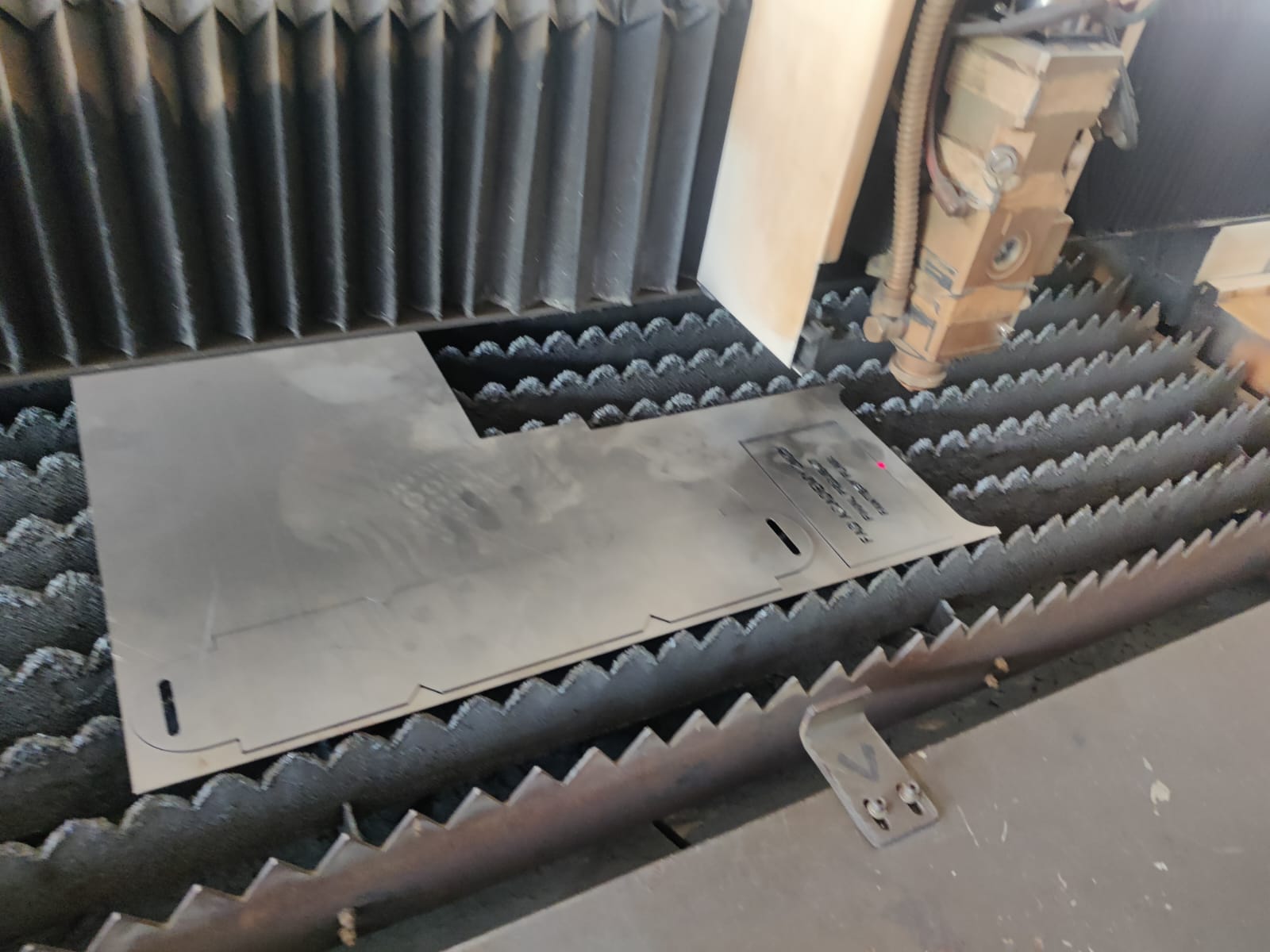

- Loaded 1.5mm mild steel sheet
- Performed dry-run (no cut) to confirm alignment
- Executed cut using air-assist to avoid burn marks
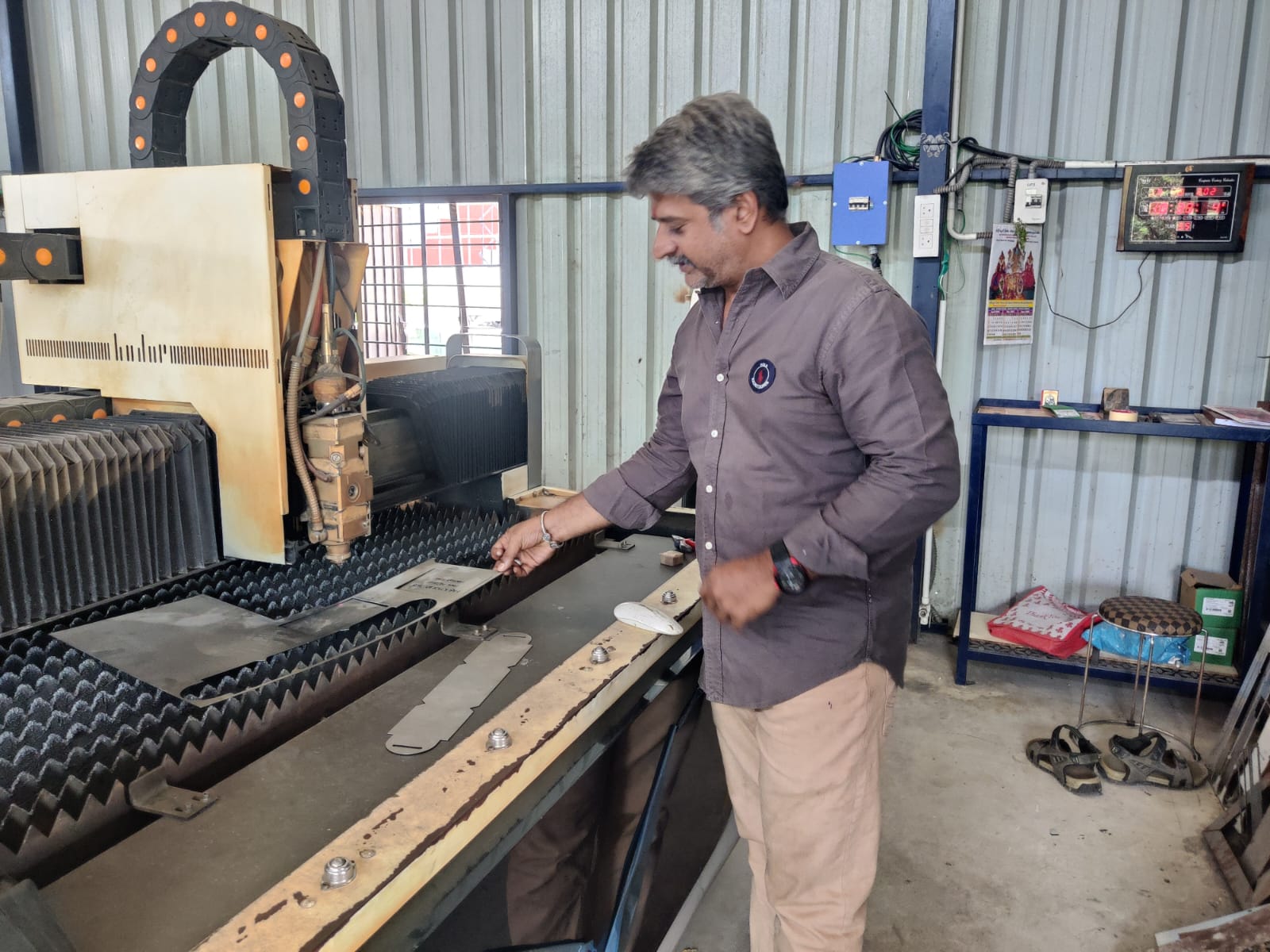

Post-processing

- Deburred sharp edges using a handheld file and rotary tool
- Cleaned the surface using alcohol
CNC Bending Machine
Material Setup
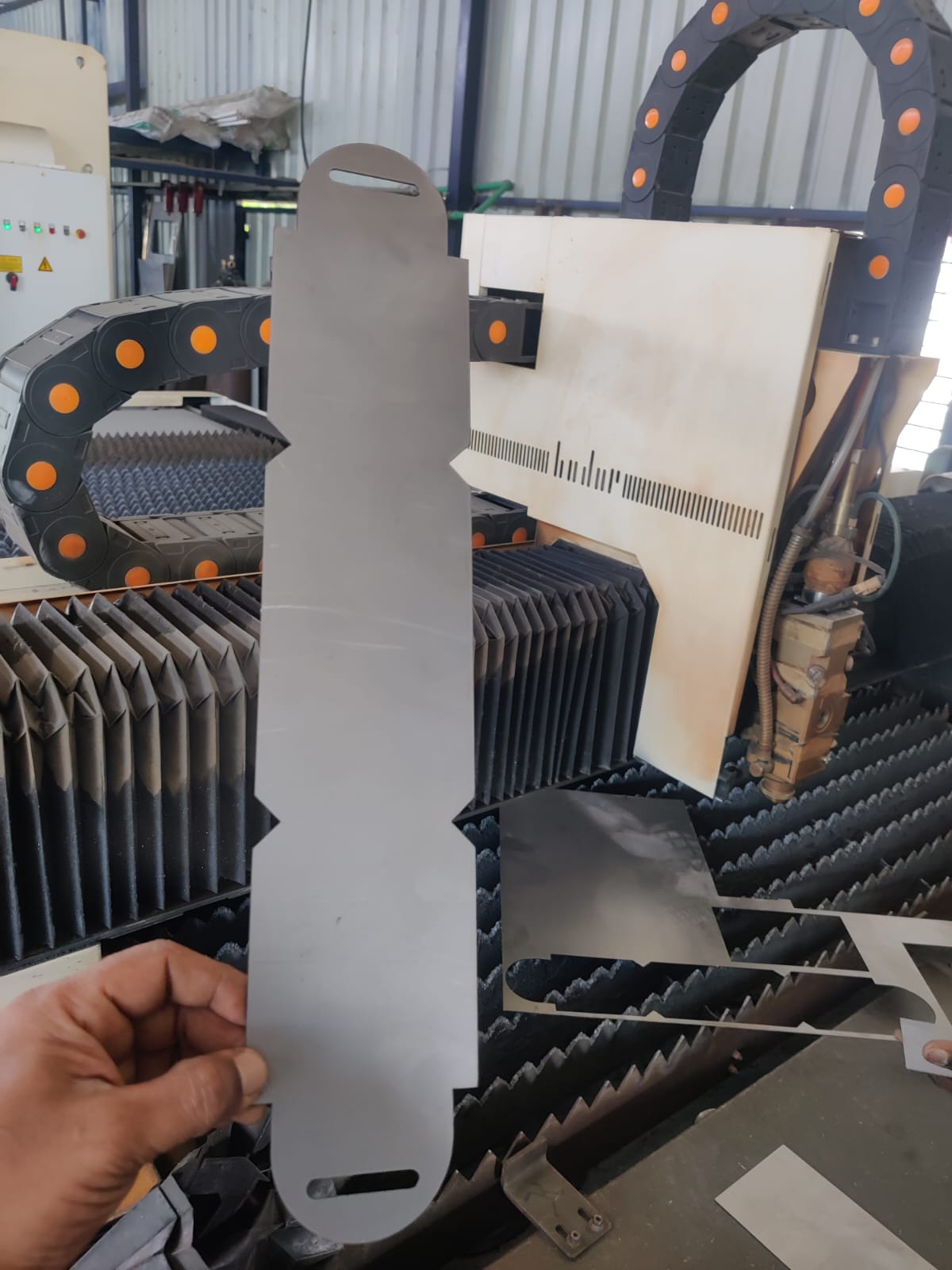
- LaserCut sheet metal to size .
- Place the material correctly on the CNC bender table.
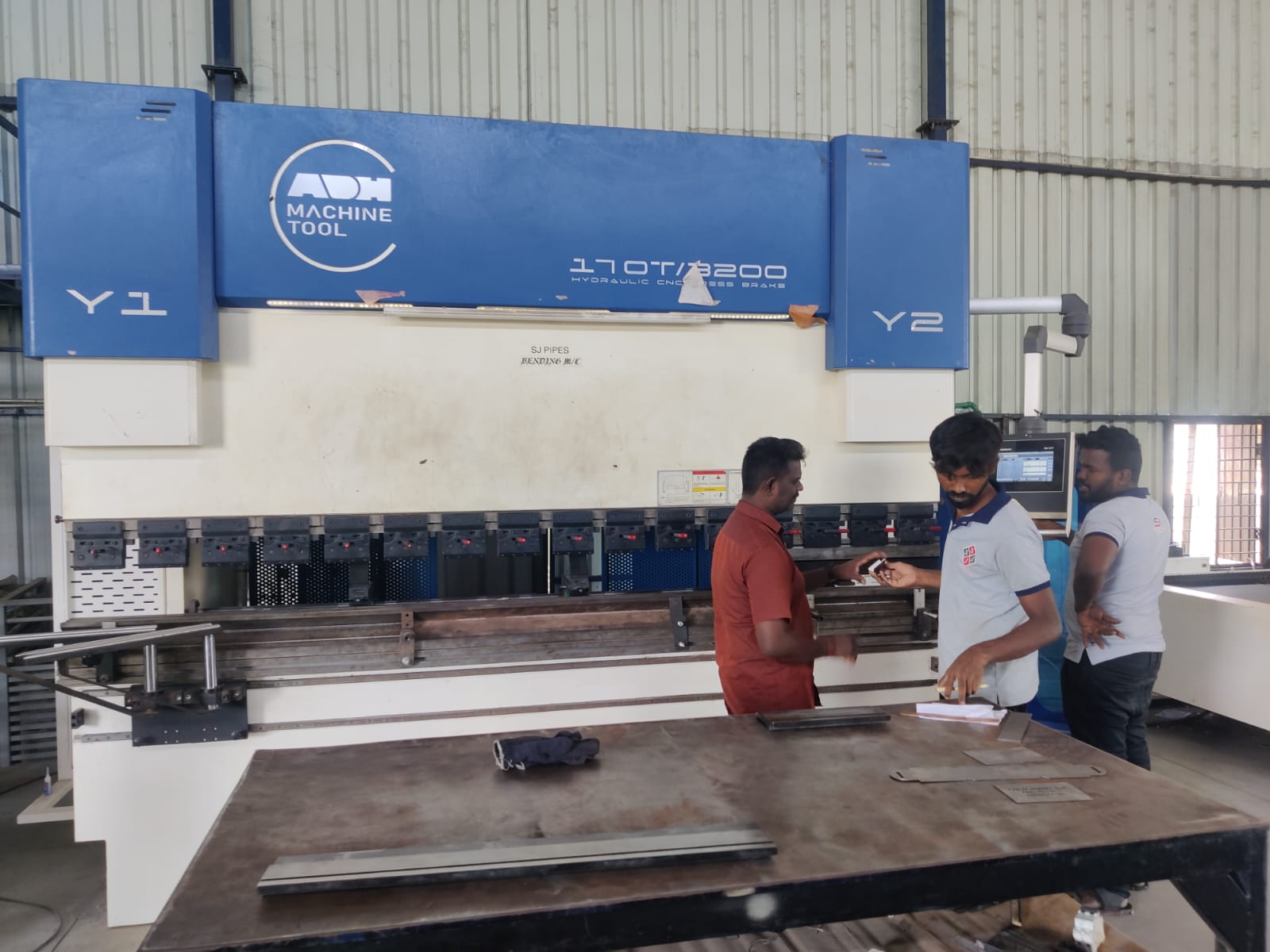


A CNC bending machine is a computer-controlled tool used to bend sheet metal with high precision and repeatability. It uses programmable controls to adjust angles, force, and bending sequences, reducing human error and increasing productivity. The machine typically operates through a hydraulic or electric press brake system, where a punch and die form the desired bend. Operators input the design using CAD/CAM software, and the machine automatically positions the sheet for each bend. CNC benders are essential in industries like automotive, aerospace, and metal fabrication for producing consistent, accurate parts. They support complex geometries and multi-angle bending operations efficiently.
Tool Setup
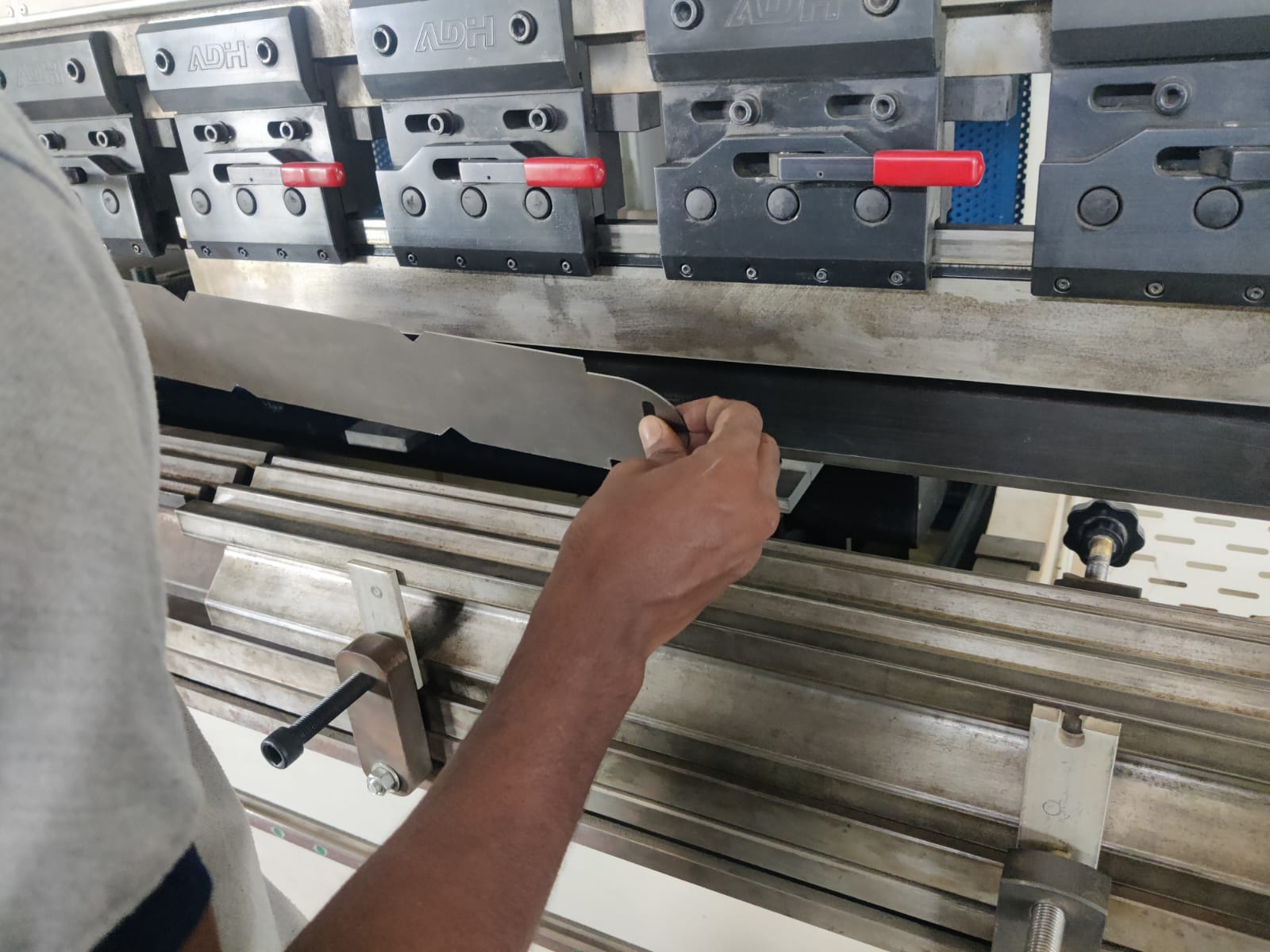

- Install the proper punch and die based on bend radius and sheet thickness.
- Align the tooling carefully to ensure accuracy.
Program Execution

- Load the program into the CNC bender.
- The machine positions the back gauge to the correct point for each bend.
- The press applies force to form the bend based on the programmed angle.
Sequential Bending

- The operator follows the bend sequence (displayed on-screen).
- The CNC press automatically adjusts the position and angle for each step.
Quality Check

- After bending, check bend angles and dimensions with a protractor and caliper.
- Adjust the program if fine-tuning is needed for springback or tolerance.
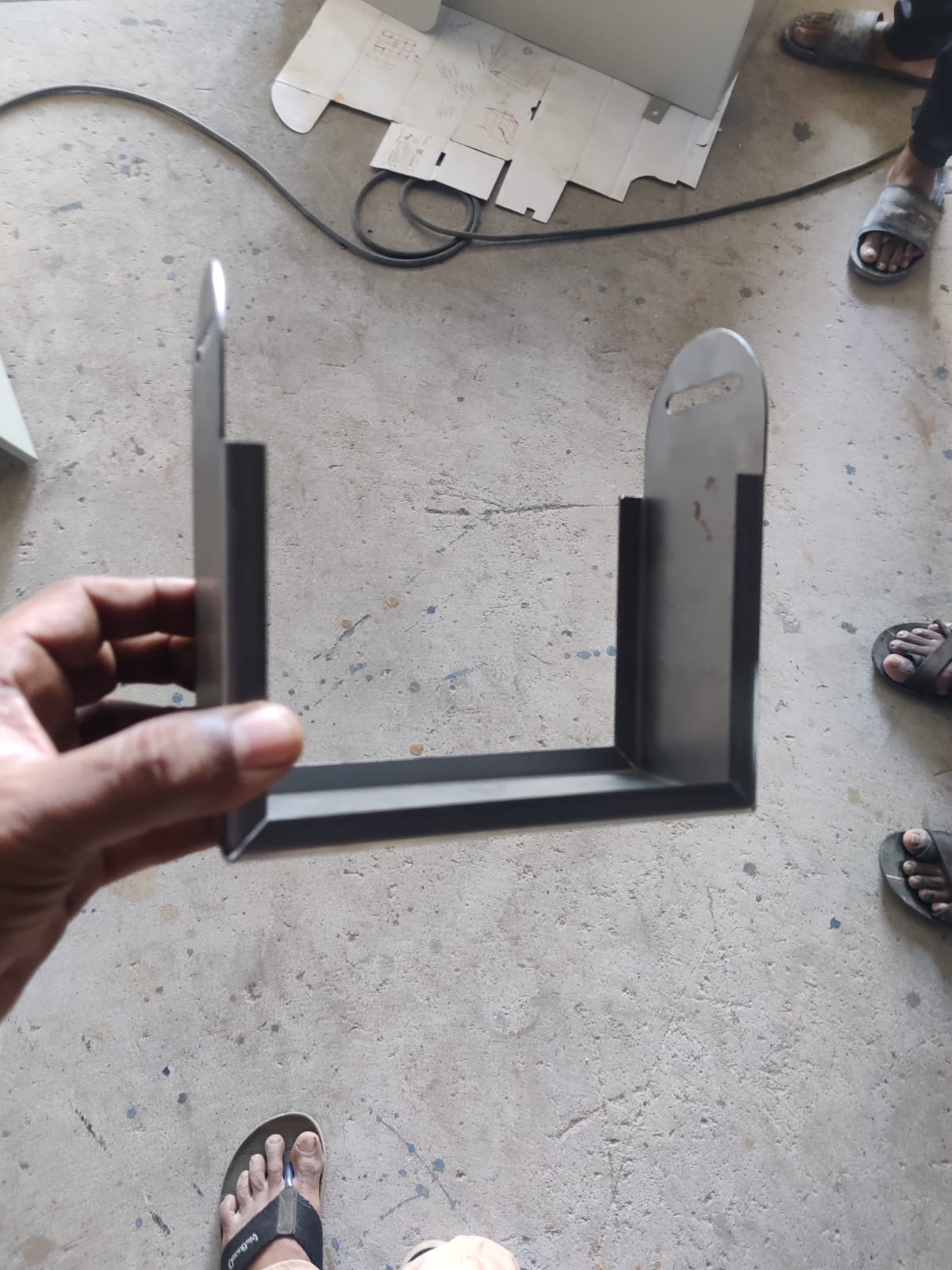
Battery Enclosure – Fabrication & Welding
This custom-fabricated metal enclosure houses a 12V, 7Ah battery, which serves as the main power source for the Fantasy Flair animatronic wing system.
- Material: 1.5mm Mild Steel
- Method: TIG Welding
- Engraving: “FAB ACADEMY 2025 – FINAL PROJECT – FANTASY FLAIR” on the top plate
Assembly Process

- Laser-cut metal pieces were bent to shape as per the design.
- Side flanges were aligned and clamped manually.
- Arc welding was done along two seams to ensure structural integrity.
- Engraved top plate was placed during assembly to maintain alignment.

Purpose
- Protects the battery from mechanical damage during operation and transport.
- Ensures safe and clean integration with the animatronic wing wearable system.
How this Sheet metal laser cutting, cnc bending and Fabrication process is not covered on other assignments
For my Fab Academy Wildcard Week assignment, I focused on sheet metal laser cutting, CNC bending, and fabrication—a process not covered in other assignments. While previous tasks involved digital fabrication methods like CNC routing for wood and 3D printing for plastic, they did not address metalworking techniques. This assignment introduced precision sheet metal processing, including designing flat metal patterns, using a laser cutter to cut stainless steel, and performing CNC-controlled bending to achieve complex geometries. Unlike subtractive machining or additive manufacturing, this method involves cutting and reshaping rigid metal sheets, which requires understanding material properties, bend allowances, and fabrication tolerances. It also included welding and assembly, adding a manual fabrication layer not emphasized in other digital-only assignments. Overall, this process expanded my knowledge of industrial-grade digital fabrication beyond Fab Lab’s typical tools, showcasing how digital design translates into functional metal components used in real-world applications.
Problems Encountered and Fixed
-
Material Warping After Laser Cutting:
The Mild steel sheet warped slightly due to the heat generated during laser cutting, affecting accuracy and alignment.
Fix: Adjusted laser power and speed, allowed cooling, and used clamps to flatten the sheet before bending.
-
Incorrect Bend Angles:
Initial bends didn’t match the design due to unaccounted bend allowance and springback.
Fix: Recalculated bend allowance using online tools and conducted test bends on scrap to calibrate settings.
-
Misalignment During Welding:
Heat distortion during welding caused parts to misalign.
Fix: Used spot welds and metal jigs to hold the parts in place during full welding.