Computer Controlled Machining
Home ← →
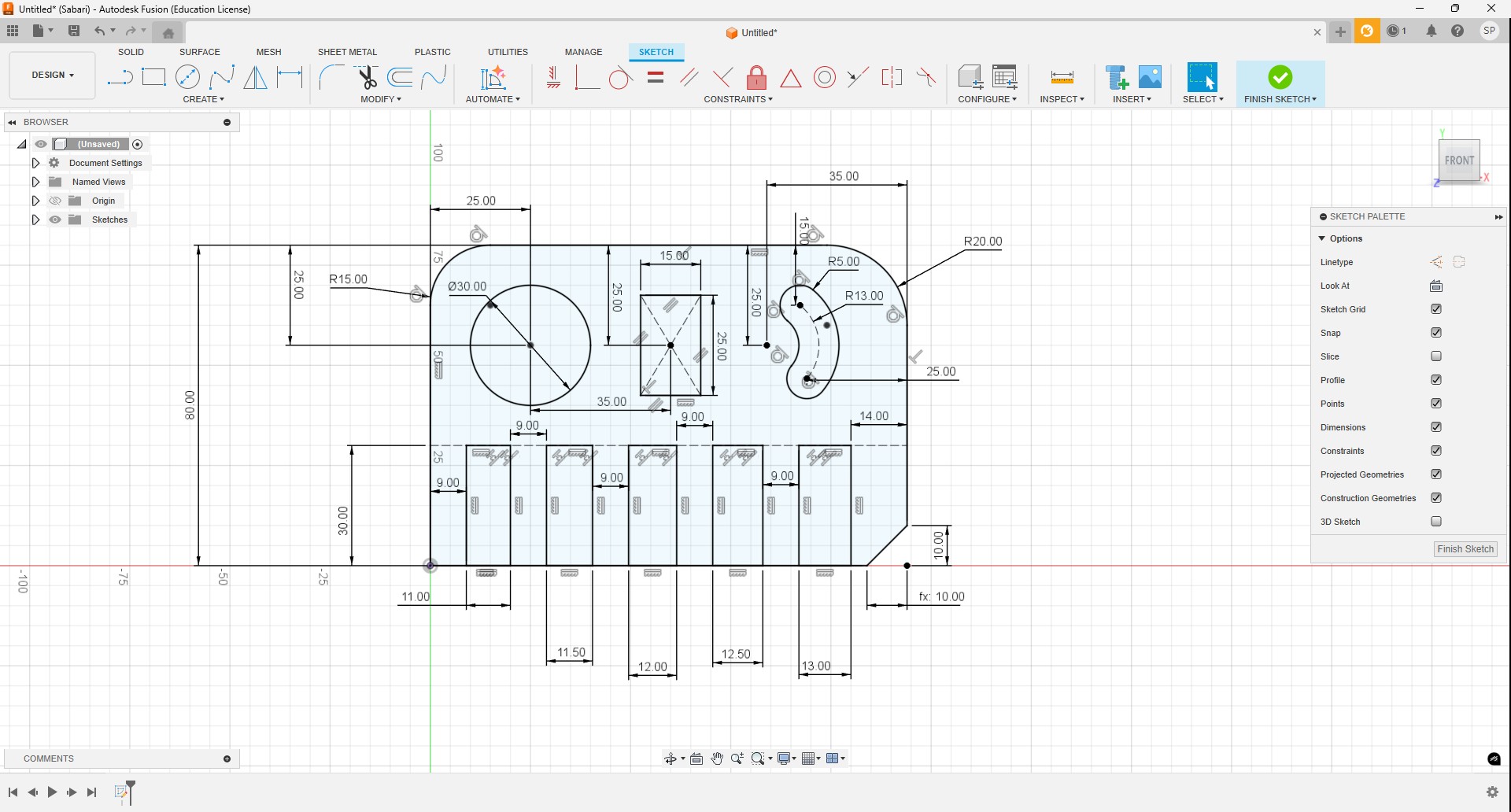
Objective of this Week
- Complete our lab's safety training
- Test runout, alignment, fixturing, speeds, feeds, materials and toolpaths for your machine
Our Fablab has CNC Wood Router STM 1325 Milling machine
CNC Milling Machine
A CNC (Computer Numerical Control) Milling Machine is used to precisely cut, carve, or engrave wooden components based on a computer-generated design. The machine operates using pre-programmed software to perform complex tasks with high accuracy, making it ideal for producing intricate patterns, furniture components, and decorative items.

Why we want
Traditional woodworking machines require manual operation, which demands a lot of skill, time, and effort. In contrast, a CNC milling machine offers precision, repeatability, and speed.
| Pros | Cons |
| High precision and repeatability | High initial cost |
| Increased productivity and speed | Requires skilled programming and operation |
| Can create complex and intricate designs | Regular maintenance needed for tools and machine |
| Efficient use of material with less waste | Produces wood dust and noise – needs dust collection |
| Compatible with CAD/CAM automation systems | Mostly limited to flat or shallow 3D workpieces |
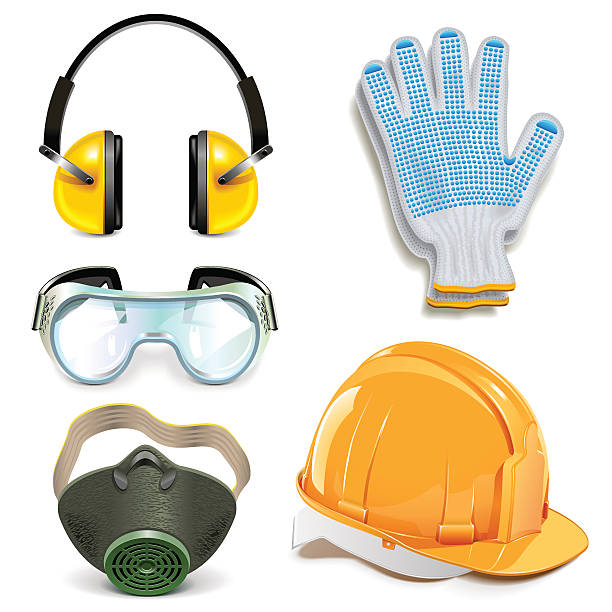
Safety Precaustions
- Always wear safety glasses and ear protection whenever we operate the milling machine, the wooden parts sometimes will be affected our eyes and also close your ears the machine will make more noise while it running.
- Don’t touch the machine while its fuctioning hands and keep loose clothing away from moving parts otherwise it may lead to severe accident happen.
- Ensure the workpiece is tightly clamped into the machine bed wihtout getting slip. In our machine we tightened by using the C clamp.
- Never allow any person while the machine running, keep eyes on nearby peoples also
- Only change the tools and cleaning operations after we turn off the power of the machine.
- Be alert to emergency stop procedures, if anything worst happens we must ready to do that immediately.
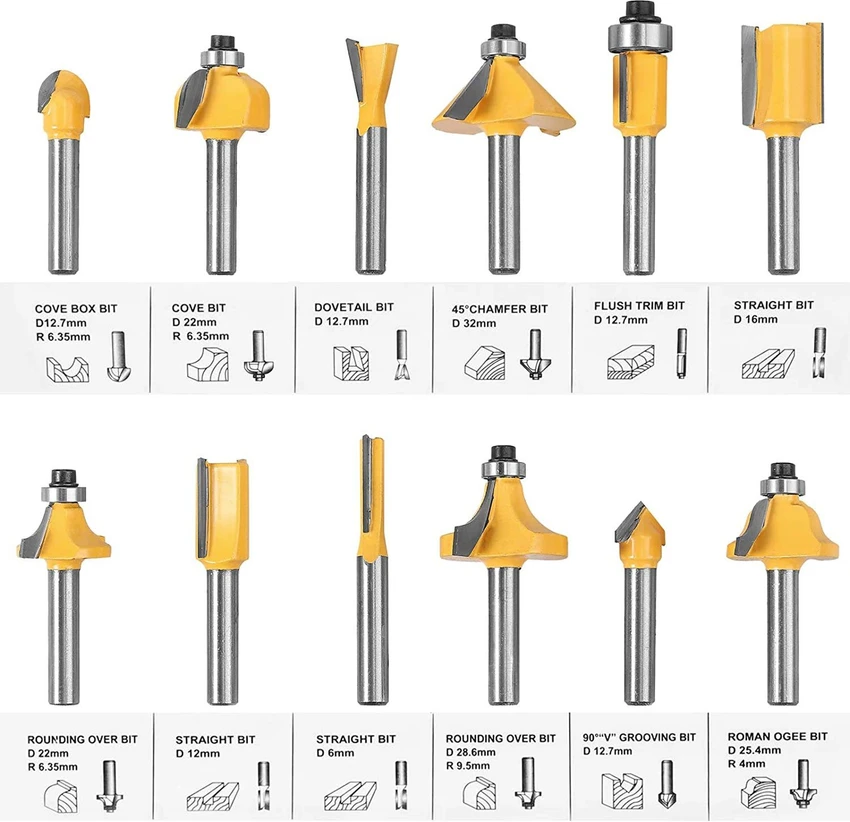
Tools
End Mill (Straight/Cutters)
It is used for cutting straight edges, pockets and contours to removes the materials cleanly with flat bottoms.
Ball Nose Bit
Ideal for 3D contouring and carving with smooth rounded finishes due to its hemispherical tip.
V-Bit (Engraving Bit)
Used for detailed engraving, lettering, and chamfering with V-shaped profiles.
Upcut Bit
Pulls chips upward; best for deep cuts with good chip removal, but may splinter wood surface.
Downcut Bit
Pushes chips downwards; gives clean top surface cuts, ideal for laminates and veneers.
Compression Bit
Combines upcut and downcut flutes; delivers clean top and bottom edges, great for plywood.
Fly Cutter (Surfacing Bit)
Used to flatten and surface large wooden boards or spoilboards quickly and evenly.
Tapered Ball Nose Bit
Used for fine detail 3D carving with added rigidity due to its tapered shape.
Dovetail Bit
Cuts angled slots for joinery work like dovetail joints in furniture making.
Drill Bit
Creates vertical holes; used for doweling or hardware installation in wood.
Machine Operation Training

Before starting the machine
- Machine – cutter should be in good condition, make sure no obstacles around the machine, bed also should be clean.
- Material – make sure it’s compatible and properly fixed into the mahine bed without getting slip.
- Movement – Check the machine movement in all axis(x,y and z) whether it is going properly or not.
- File – check speed/feed settings, cutting depth, machine limits by only give some gap in z axis without touching the tool in workpiece.Furhter try the pause before running the machine whether it is properly respond or not
- Human – be physically & mentally ready, wear proper clothes & protection (ears, face, hands).
During the machine operation
- Machine –Carefully watch tool path, spindle, and cutting depth
- Material – clear out debris after cut the workpice, avoid tool breakage.
- Human – stay away from machine little bit, notice any strange noise/smell, wear protection always.
After work
- Machine – clean dust/debris, check axis and dust box.
- Material – Check once the cutted layer and also check the sacrificial layer for next machine operation
- Tool – Check the tool if in case any breakage happens
Testing