Week13
Assignment: Molding and Casting
Introduction to Molding and Casting
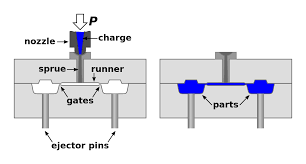
The molding and casting process is a fundamental manufacturing technique used to create objects by pouring a liquid material into a mold, which then solidifies into the desired shape.
Mold Creation: A mold is a hollow cavity that dictates the final shape of the casting. Molds can be made from various materials like sand, metal, plaster, or rubber, and are often reusable or expendable depending on the process. The mold is typically created based on a pattern or a 3D model of the desired object.
Material Preparation: The material to be cast (e.g., molten metal, liquid plastic resin, plaster, concrete) is prepared. This may involve melting, mixing with catalysts, or ensuring the correct viscosity and temperature for pouring.
Example: Plastic pellets are used in the injection molding process.
Example: Resin material used in art casting
Pouring/Injection: The prepared liquid material is carefully poured or injected into the mold cavity. This step requires precision to ensure the material fills all parts of the mold without trapping air bubbles.
Demolding/Ejection: Once the material has fully solidified or cured, the mold is opened or broken away, and the solidified part (the casting) is removed.
Finishing: The casting often undergoes finishing operations such as trimming excess material (flash), sanding, machining, or polishing to achieve the final desired dimensions and surface finish.
Casting is a specific type of molding process where a liquid material (most commonly molten metal, but also plaster, concrete, or liquid resins) is poured into a mold cavity. The material then cools and solidifies within the mold, taking its shape. Once solidified, the "casting" (the finished part) is removed from the mold.
Design of Mold:
For this assignment, a resin mold is made using the following steps. First step, a solid model of the Forge Logo is designed in SolidWorks, and a 3d milling tool path is generated using ArtCAM.
During the Extrude feature, a draft angle of 4 degrees is required for the casted product to release from the mold. |
To avoid sharp corners, add fillets to edges as required. Parting line edge should not have fillets or chamfers, and finally, save it in STL file format. |
For milling, MDF is used as the base material. The tool path is generated using ArtCAM. The workpiece size is 100x150mm |
First step, save the relief layer. Then add the STL file, which will be later used for creating the 3D toolpath |
Aligning to the center of the workpiece. |
Create the rectangle for 70x70 |
Machine Process:
Still in progress
3D Printed Mold Process:
About the Mold design
This mold features the logo of Forge Innovation and Ventures. This is a 2.5 mold with a taper of 3 degrees. Casted with the resin with a few failed electronics components like resistors, capacitors, and a few ICs. Since this is my first mold, the complexity is less.
I am still improving my design in a complex mold, as shown below
This is going to be a 2 part mold design to develop a 3d casted model.
Working the progress.
Prints have failed last night, will reprint and cast it with silica to develop a 3d tube model, as you can see hidden lines in the imagesmc.
Link to Files: Link