Moulding and Casting
Assignments of the Week
- 1.Review the safety data sheets for each of your molding and casting materials.
- 2.Make and compare test casts with each of them.
- Hygroscopicity: Silicone resin has a strong hygroscopic nature, which may lead to the formation of a silicone gel when it absorbs moisture. Ingesting or inhaling a significant amount of silicone gel can cause blockage in the lungs, posing a severe medical emergency.
- Dust: During the handling of silicone resin, particularly in its preparation or processing, silicone dust may be generated. Prolonged inhalation of silicone dust can irritate the respiratory system, causing symptoms such as a sore throat and cough.
- Skin Contact: Direct contact with silicone resin is generally safe, but some individuals may be allergic to certain components of silicone. In rare cases, it might cause mild skin irritation or allergic reactions.
- Avoid Ingestion or Inhalation: Ensure that silicone resin is kept away from children and pets to prevent accidental ingestion or inhalation.
- Use Personal Protective Equipment: When handling silicone resin, especially during its preparation or processing, use appropriate personal protective equipment such as masks, gloves, and goggles to reduce the risk of dust inhalation and skin contact.
- Maintain Good Ventilation: Keep the workspace well-ventilated when working with silicone resin to reduce the accumulation of dust and the risk of inhalation.
- Follow Instructions: Read and follow the instructions and safety guidelines provided with the silicone resin product.
- Skin Contact: Epoxy resin can cause skin irritation and allergic reactions upon prolonged or repeated contact. Extended skin exposure may lead to dermatitis or allergic skin conditions.
- Respiratory System: In its liquid state, vapors from epoxy resin may irritate the respiratory system. High concentrations of vapors can cause symptoms such as headaches, eye irritation, and throat discomfort. Prolonged exposure may result in respiratory issues.
- Eye Contact: Direct contact of epoxy resin with the eyes can cause irritation, redness, and pain. Immediate rinsing is necessary, and in case of severe reactions, medical attention should be sought.
- Allergic Reactions: Some individuals may develop allergic reactions to certain components of epoxy resin, manifesting as skin symptoms, respiratory discomfort, and other allergic responses.
- Occupational Health Hazards: In industrial settings, prolonged exposure to high concentrations of epoxy resin and its hardeners may adversely affect workers' health, potentially leading to carcinogenic effects.
- Use appropriate personal protective equipment like gloves, goggles, and respirators.
- Work in well-ventilated areas and avoid confined spaces.
- Follow product instructions and safety procedures.
- Avoid prolonged skin contact, and clean skin promptly if contact occurs.
- Undergo regular health monitoring, especially for those working extensively with epoxy resin.
- Respiratory Issues: Dust generated during the handling and mixing of gypsum powder can pose a respiratory hazard. Prolonged inhalation may lead to respiratory irritation, coughing, and asthma-like symptoms.
- Skin Contact Concerns: Direct contact with wet gypsum or gypsum-based solutions may cause skin irritation or allergic reactions in some individuals. Prolonged exposure may result in skin conditions such as dermatitis.
- Eye Irritation: Gypsum dust or solutions coming into contact with the eyes can cause irritation, redness, and discomfort. Immediate rinsing is necessary, and medical attention may be required for severe reactions.
- Allergic Sensitivity: Certain individuals may develop allergic sensitivities to components of gypsum, leading to skin and respiratory issues.
- Temperature Risks: In some processes, gypsum may be heated. Contact with hot gypsum can cause burns or scalds.
- Use personal protective equipment, including respiratory protection, gloves, and eye protection.
- Work in well-ventilated areas and minimize dust generation.
- Adhere to product usage instructions and safety guidelines.
- Avoid direct skin contact with wet gypsum and promptly clean skin if contact occurs.
- Take appropriate precautions when working with hot gypsum.
Group assignment:
Group Assignment:
Material Datasheets
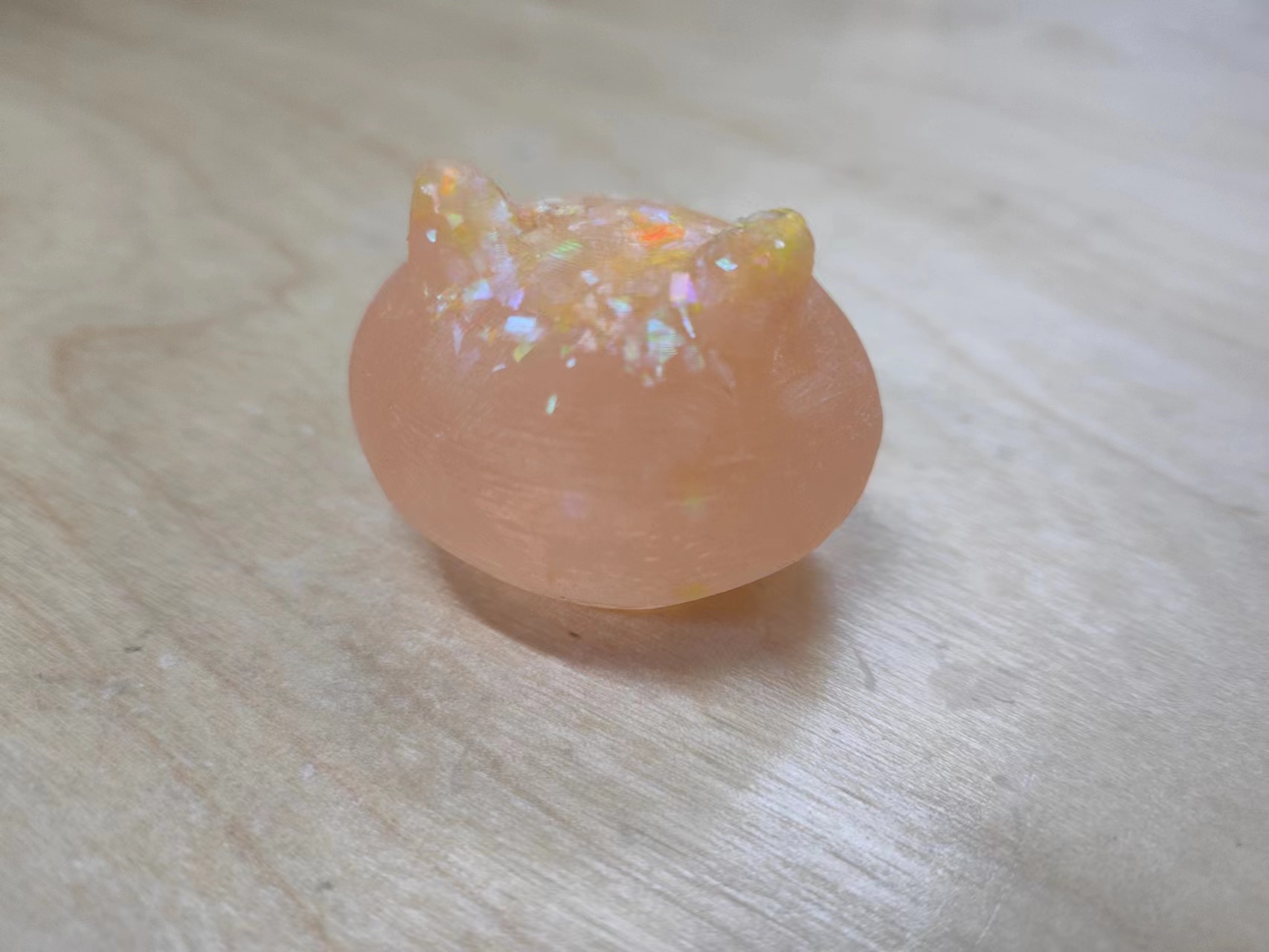
Food Grade Silicone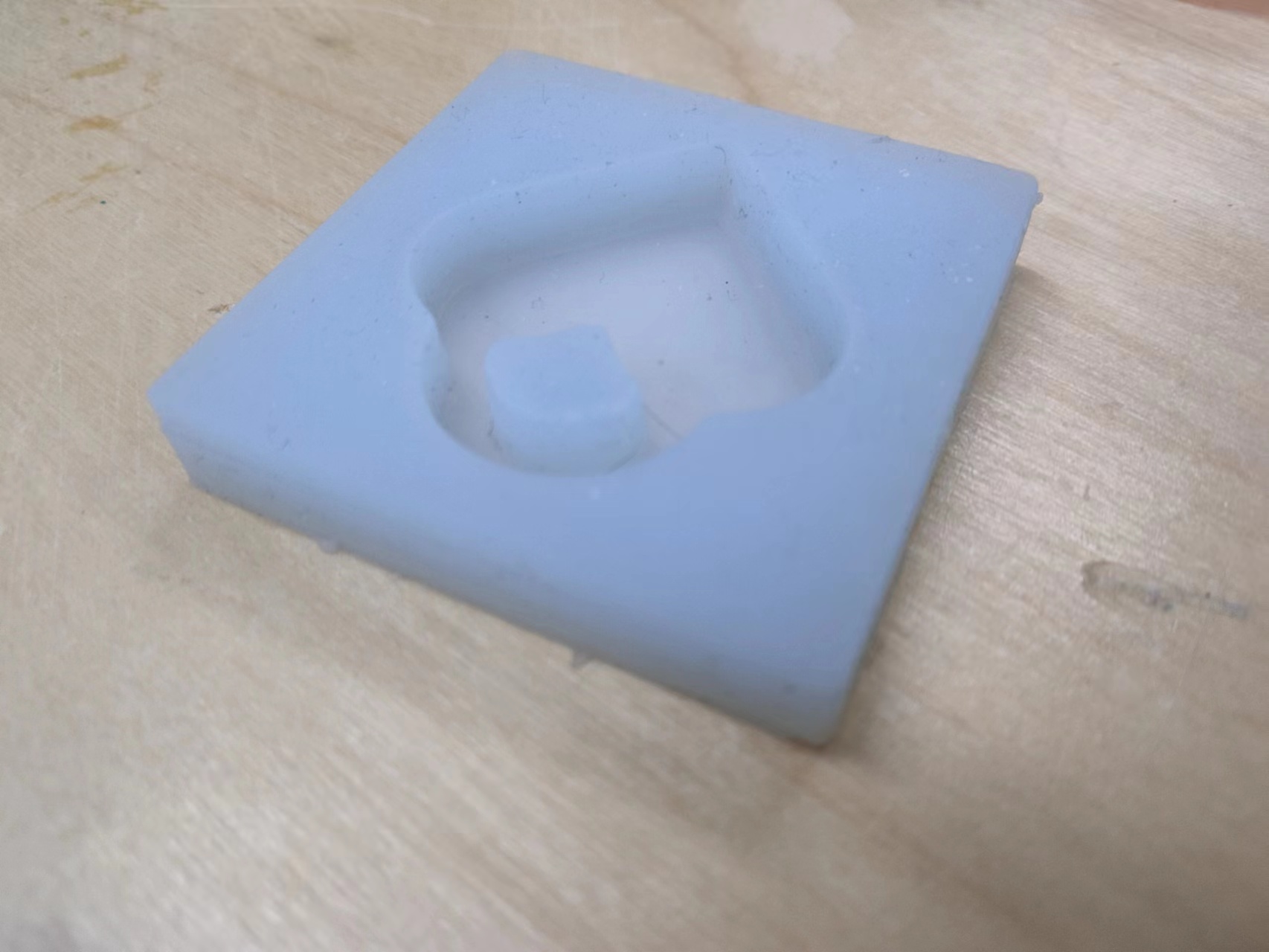
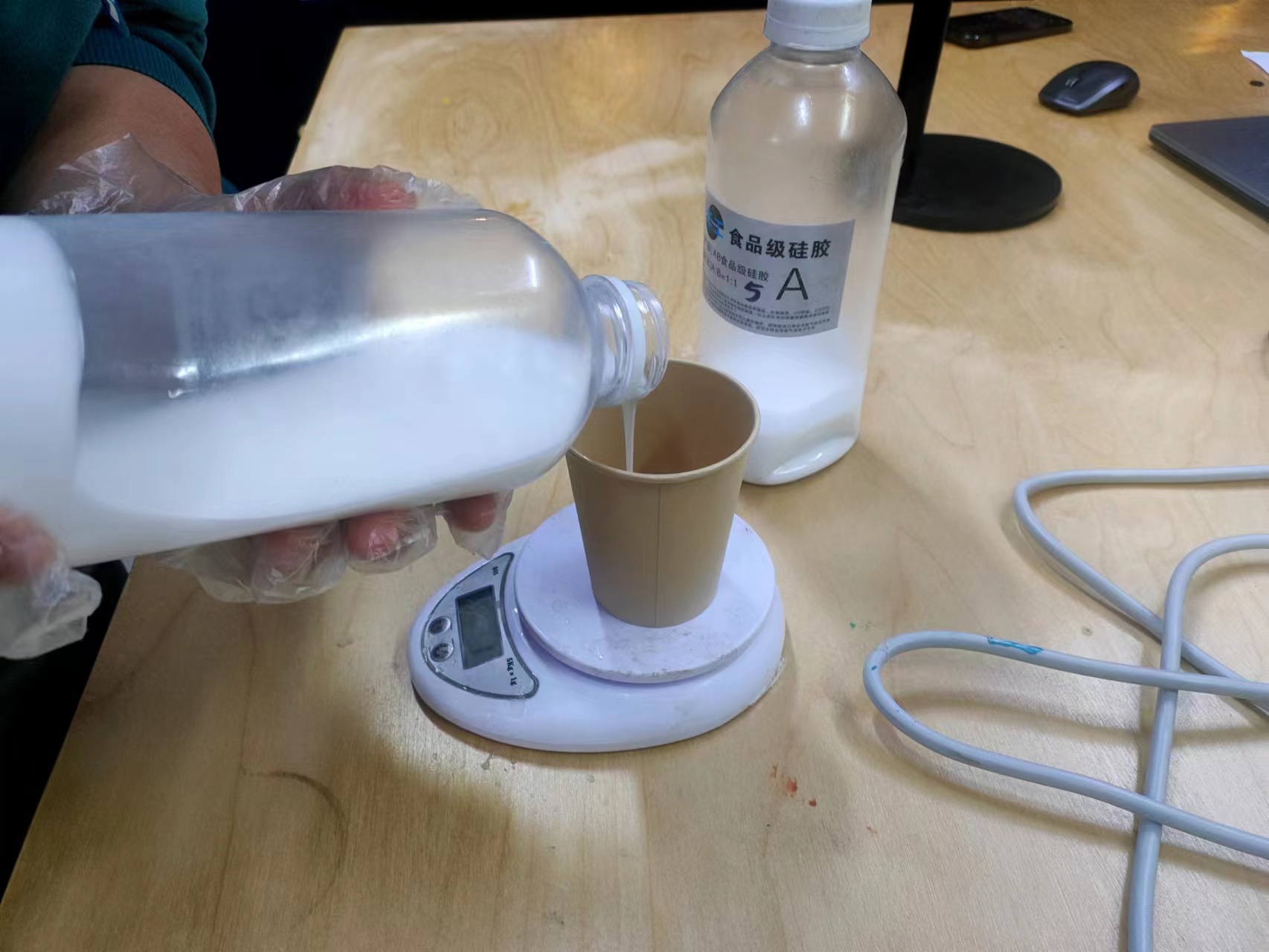
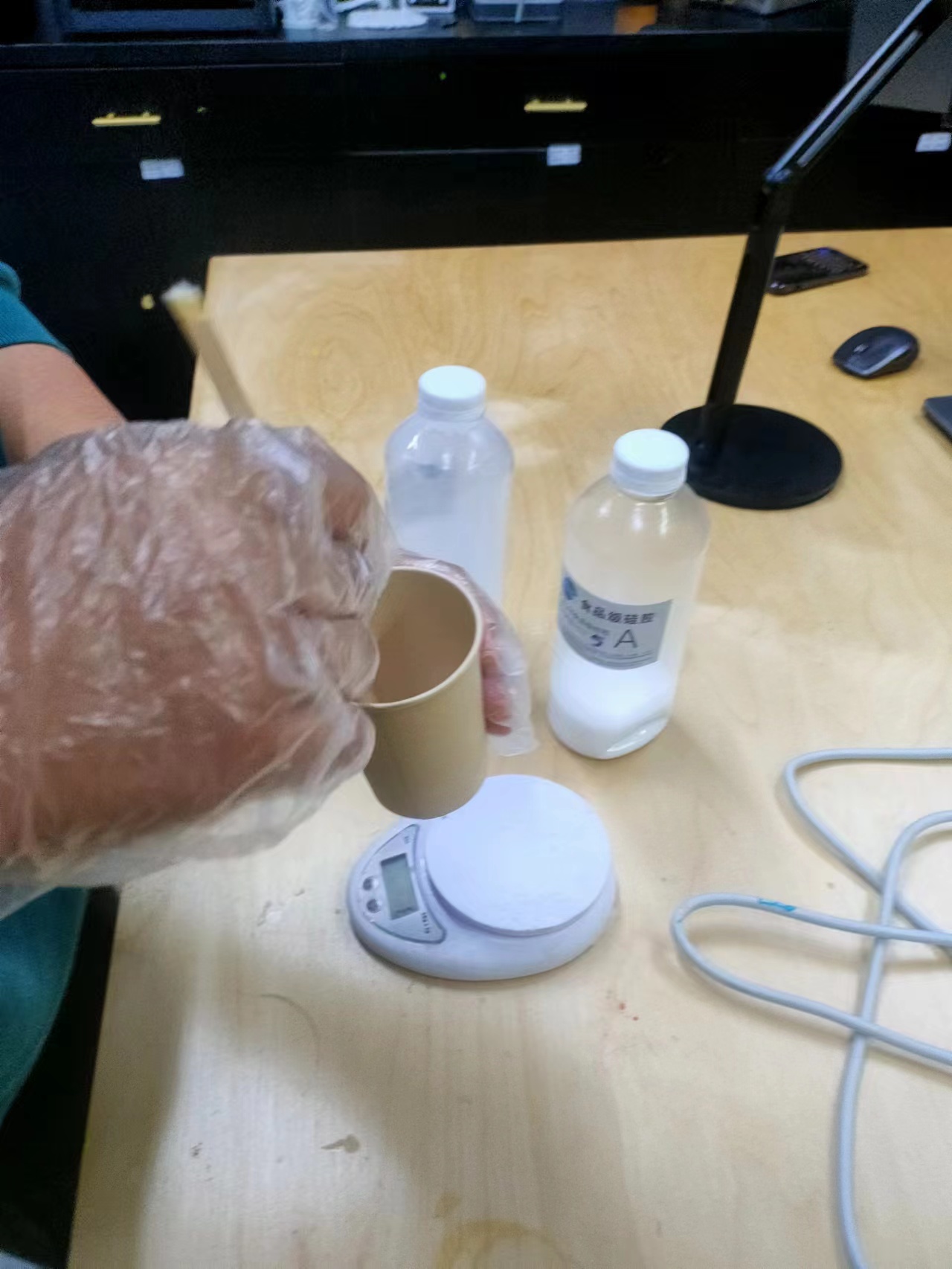


The mixing ratio:The ratio of Silica gel A to Silica gel B is 1:1.
Silicone resin is a common inorganic material often used for its moisture-absorbing, drying, and sealing properties. Overall, silicone resin is relatively safe under normal usage, but there are still some considerations:
To minimize potential hazards associated with silicone resin, the following precautions should be taken:
Epoxy Resin
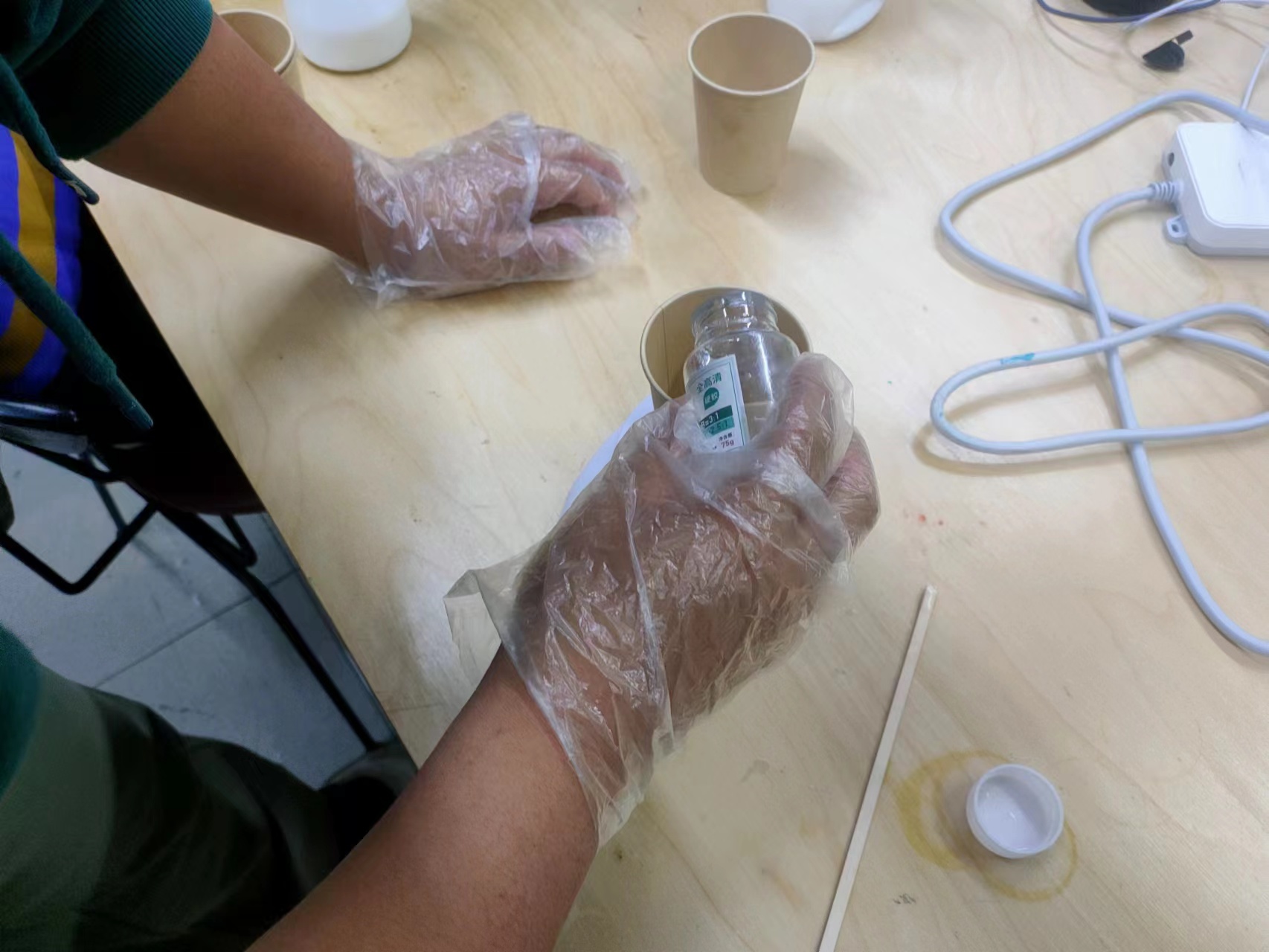
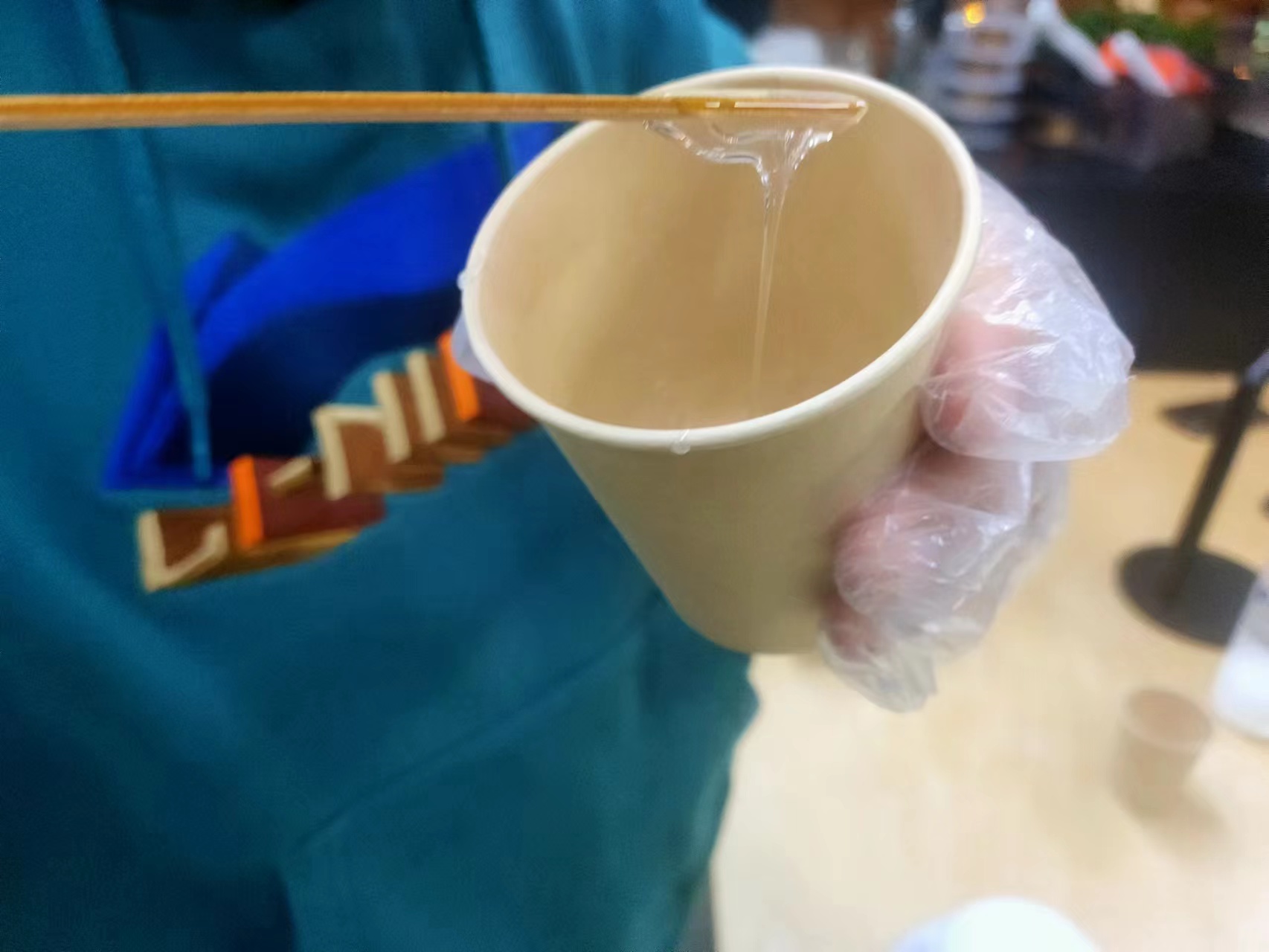




The mixing ratio:Epoxy resin A to epoxy resin B ratio is 1:3.
Epoxy Resin Hazards:
Epoxy resin is a commonly used chemical in various applications such as coatings, adhesives, and composite materials. While epoxy resin exhibits superior performance in many applications, it may also pose some potential hazards:
To minimize epoxy resin hazards, it is crucial to:
Gypsum
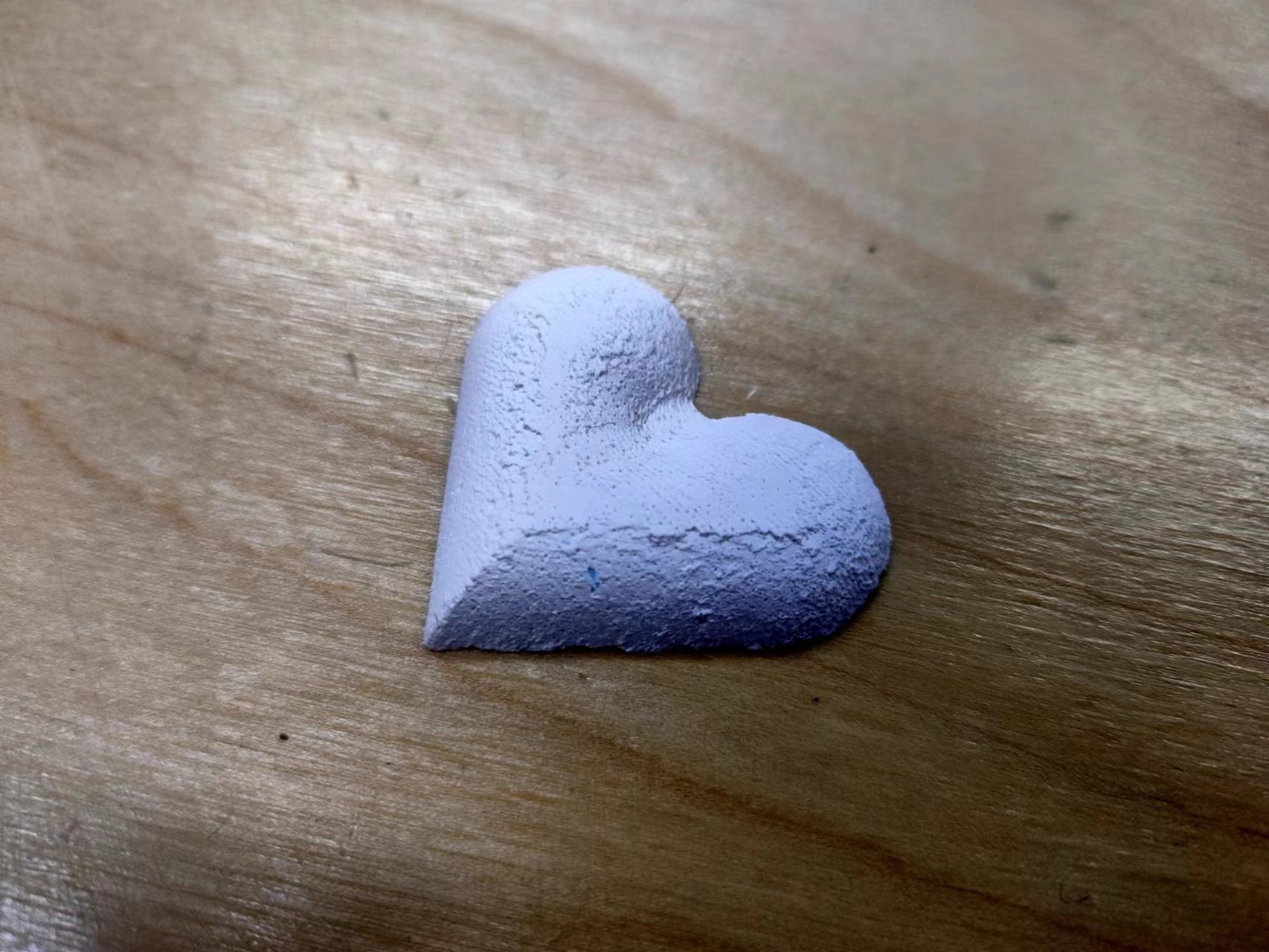
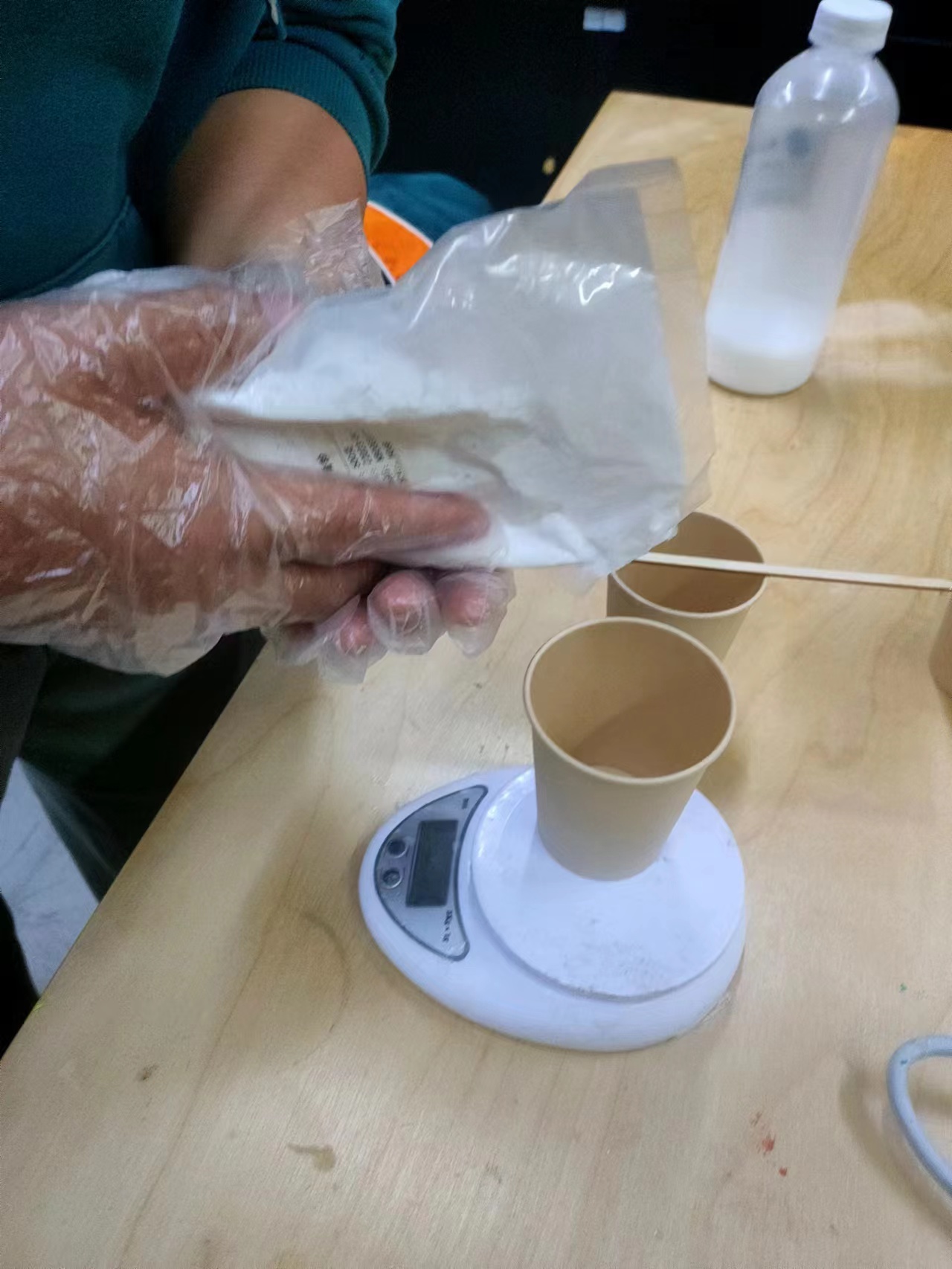


The mixing ratio:plaster 100g water 33g
Gypsum Hazards:Gypsum is a common material used in construction and crafts, often employed in the making of molds, decorations, and architectural repairs. While gypsum is generally safe when used appropriately, there are some considerations regarding potential hazards:
To minimize potential hazards associated with gypsum:
Individual assignments:
1.Design a mold around the stock and tooling that you'll be using, mill it (rough cut + (at least) three-axis finish cut), and use it to cast parts.
1. Modeling
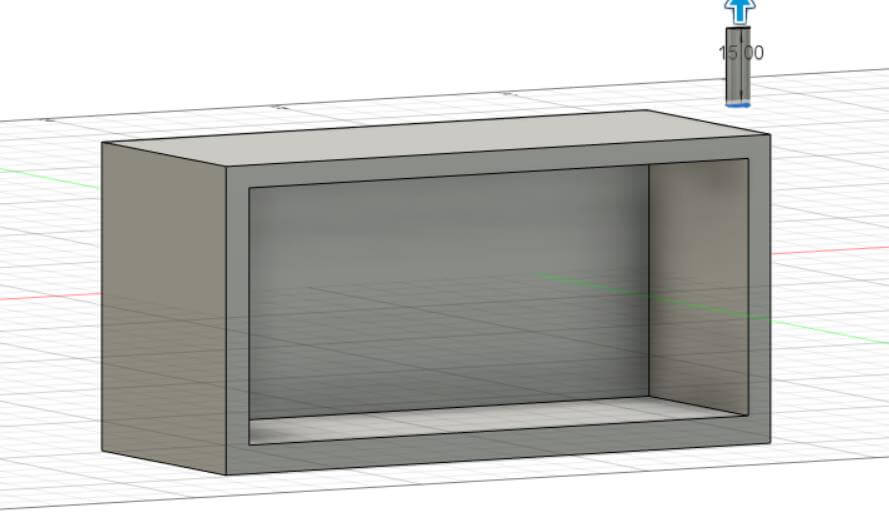
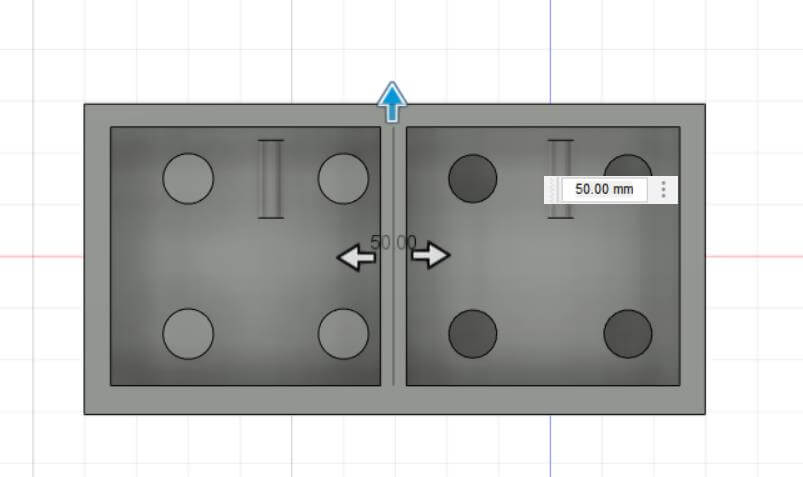
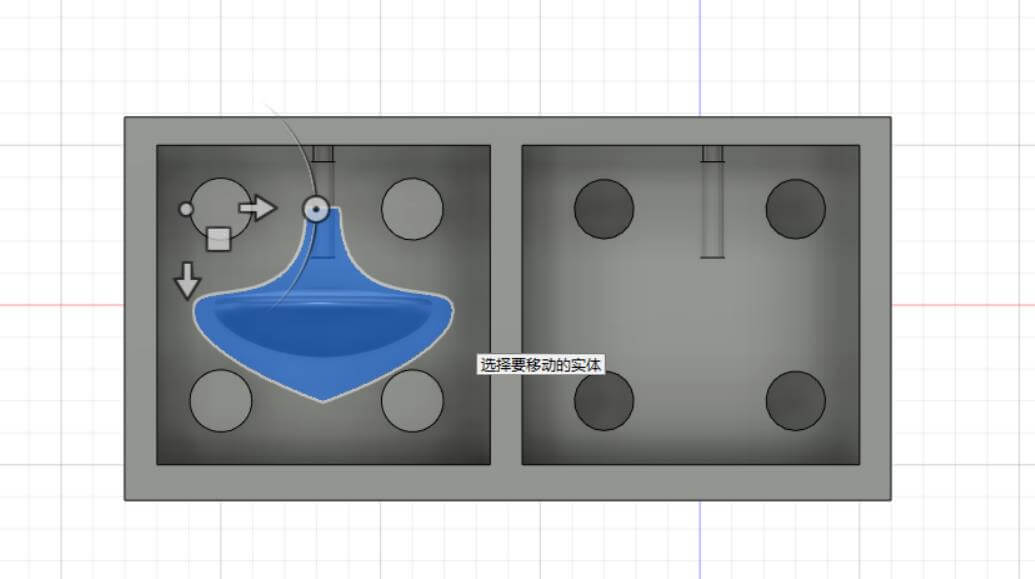
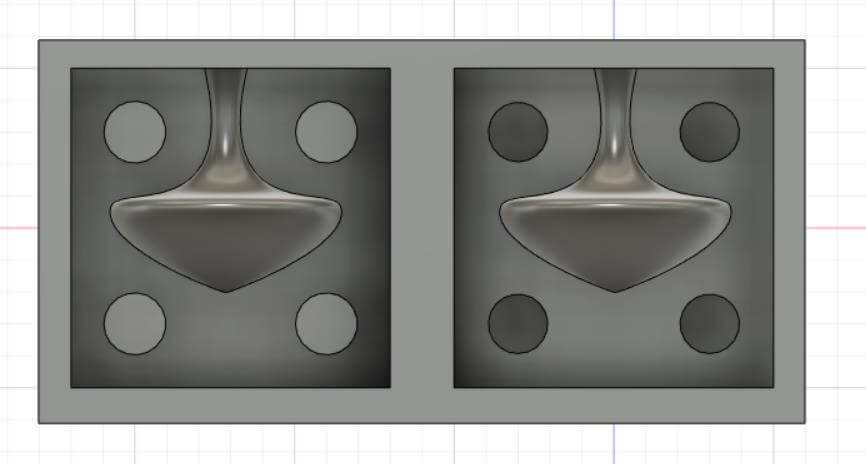
a. Modeling process.
2. Software settings for die cutting.
1、Before I start milling, I need to create a new setup..
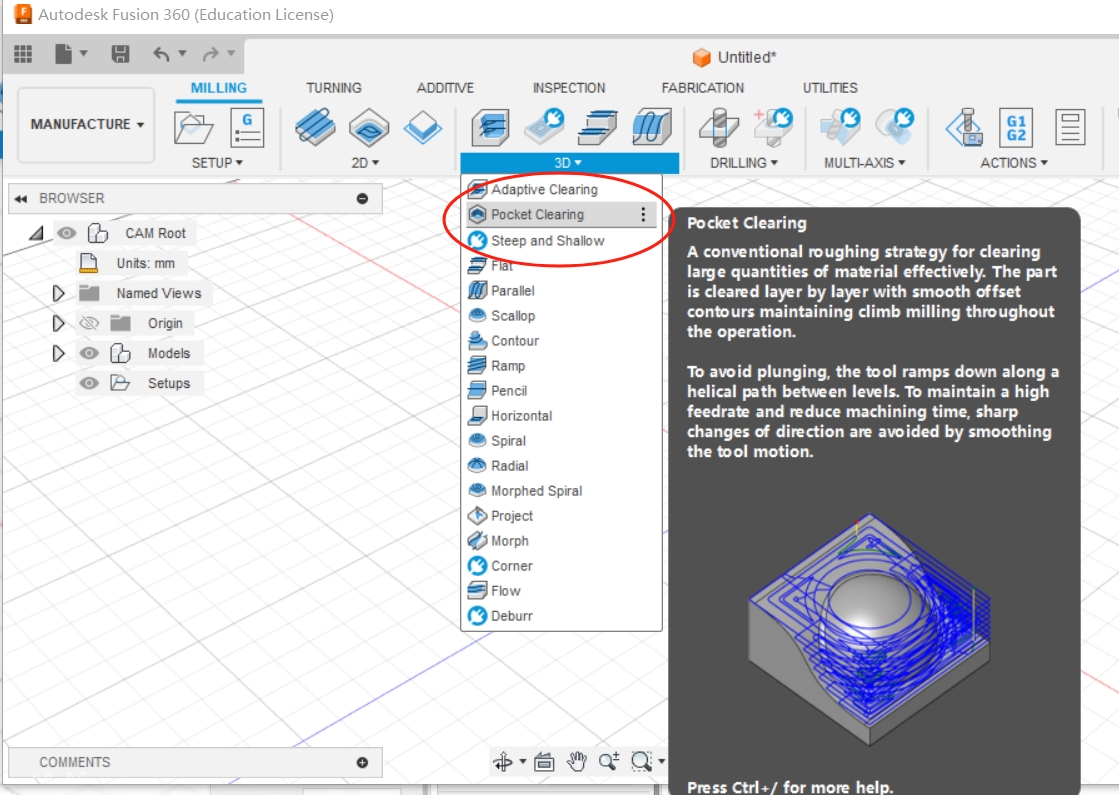
2、I chose the milling method of Pocket Clearing.
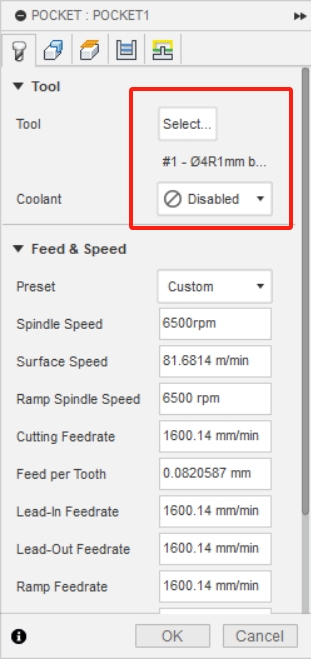
3、I selected the milling tool I wanted to use, and since our machine doesn't have a cooling system, I chose "None" for coolant.
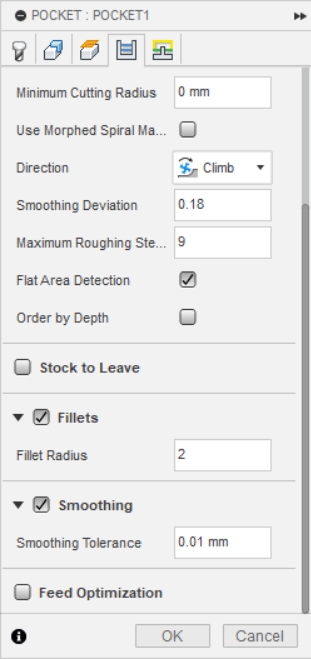
4、I made the following selections under the guidance of my supervisor.
4.1 Select Climb in Direction
4.2 Smoothing Deviaition 0.18
4.3 Maximum Roughing Stepdown 9
4.4 Deselect Stock to Leave
4.5 Check Fillets,Fillet Radius = 2
4.6 Check Smoothing,Values remain as default
5、Select Helix in Ramp Type
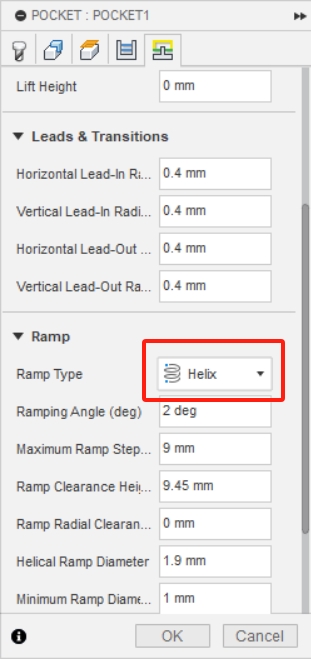
3. Die cutting process。
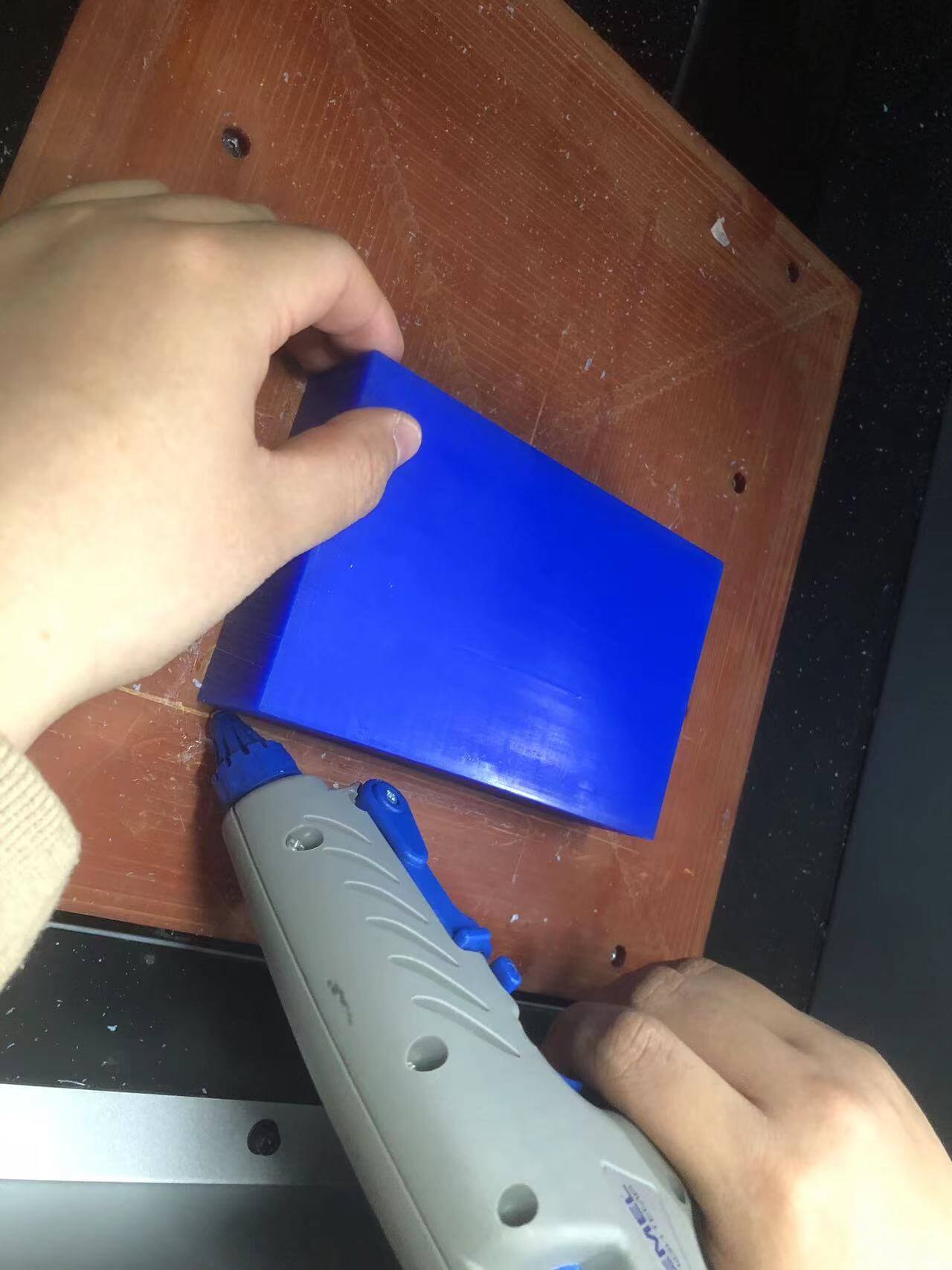
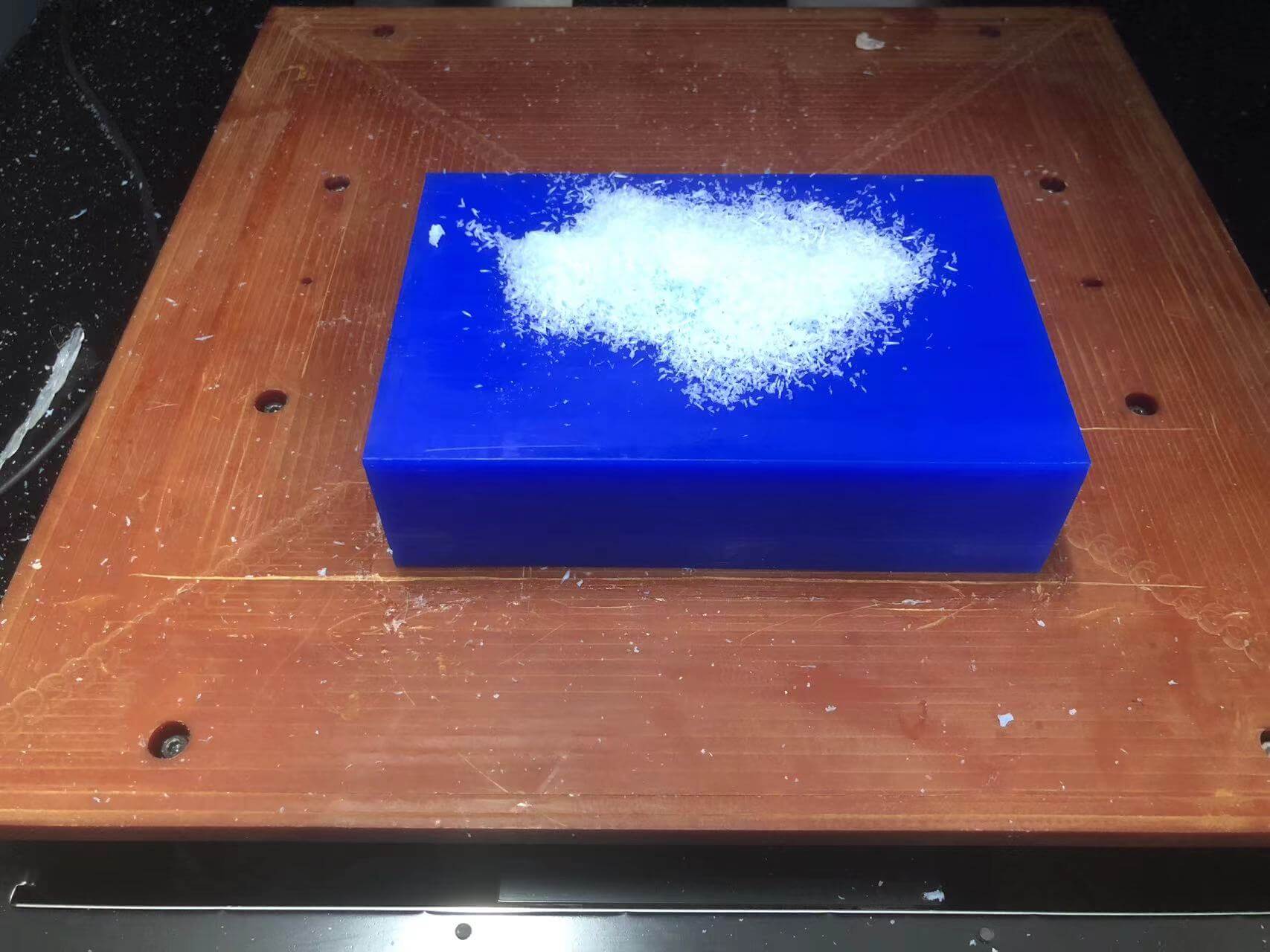


a. Watch out for sounds and debris.
4. Model casting
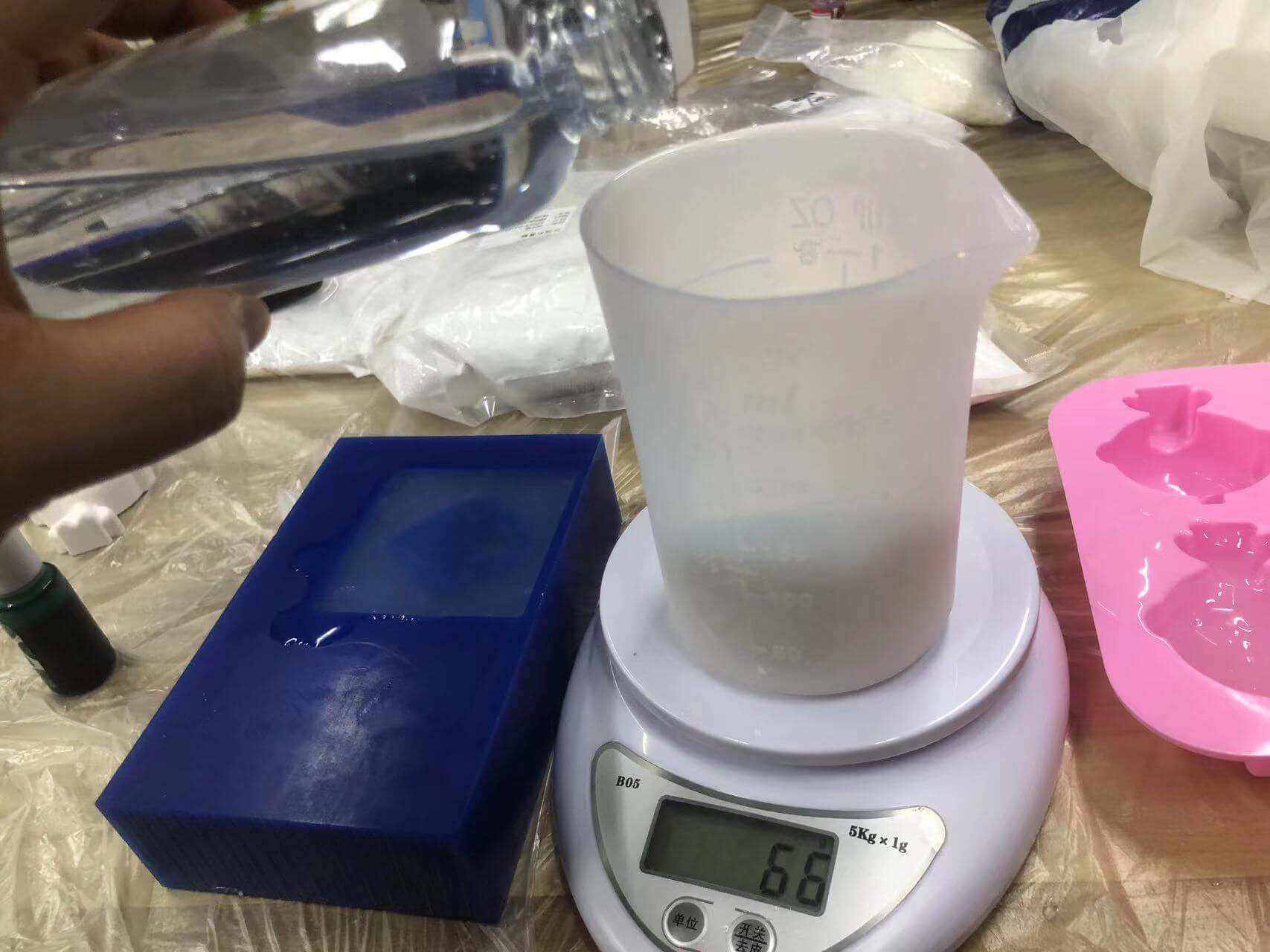
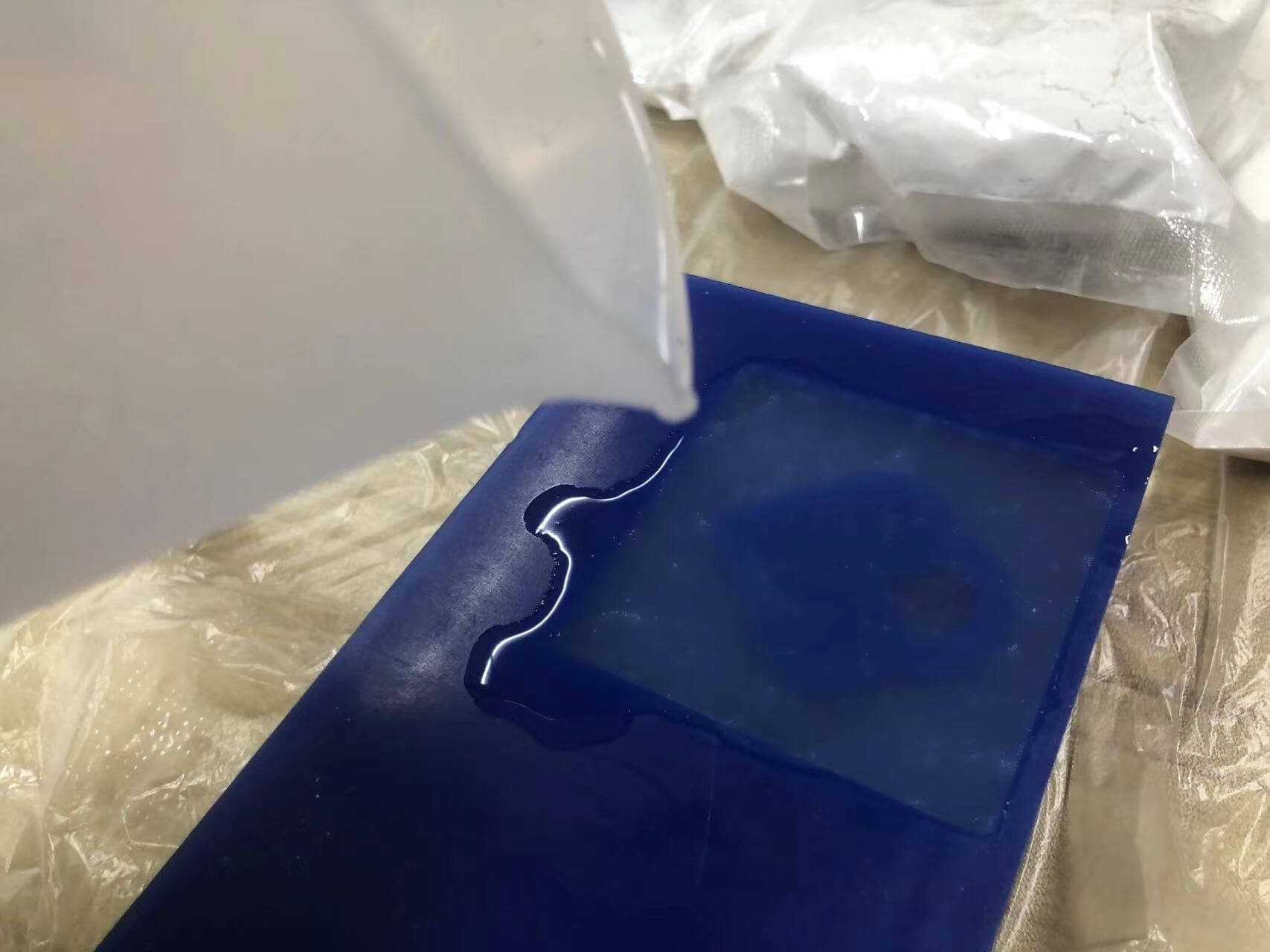



a. Mix glue A and glue B 1:1.
5.Forming
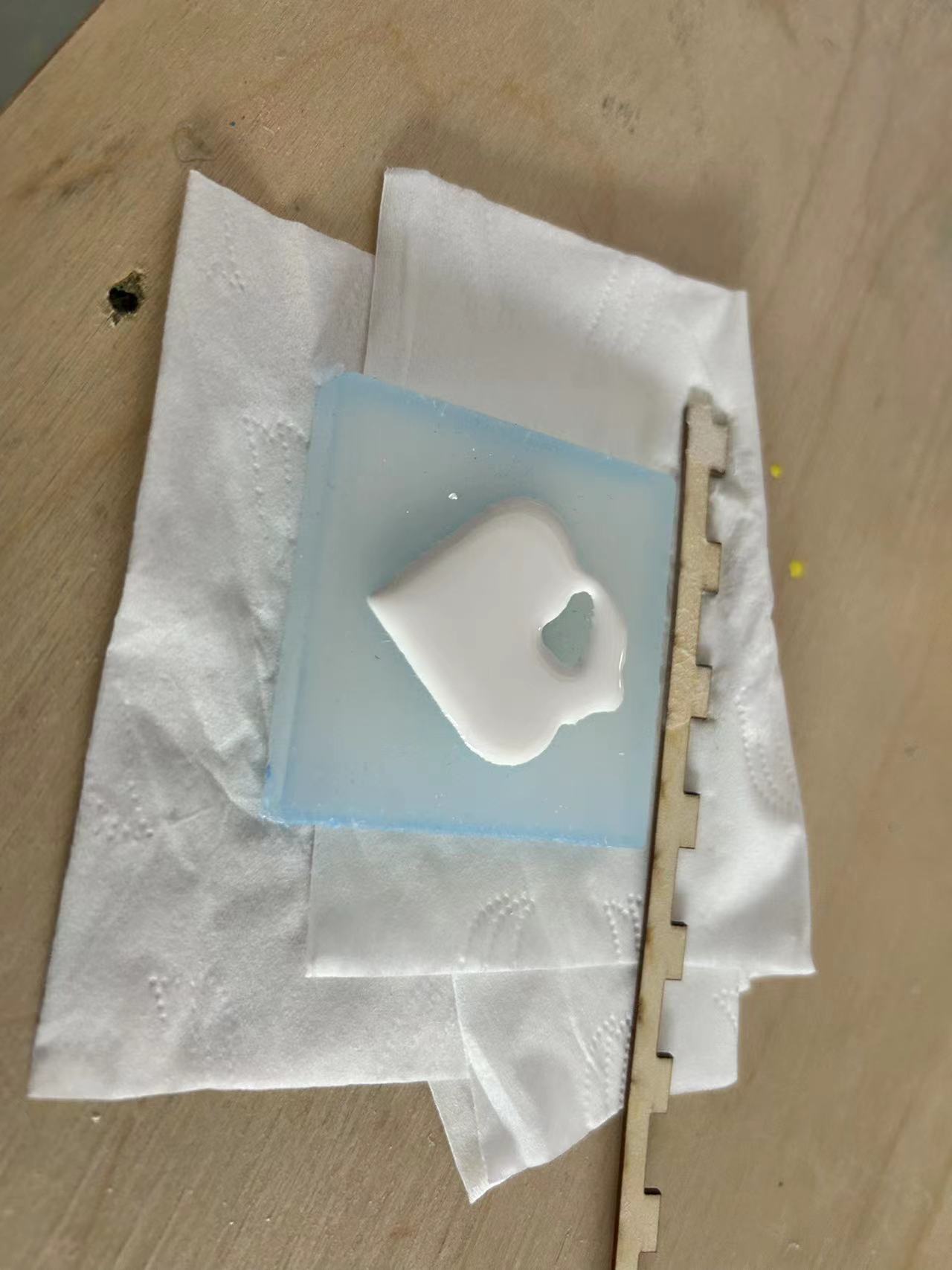
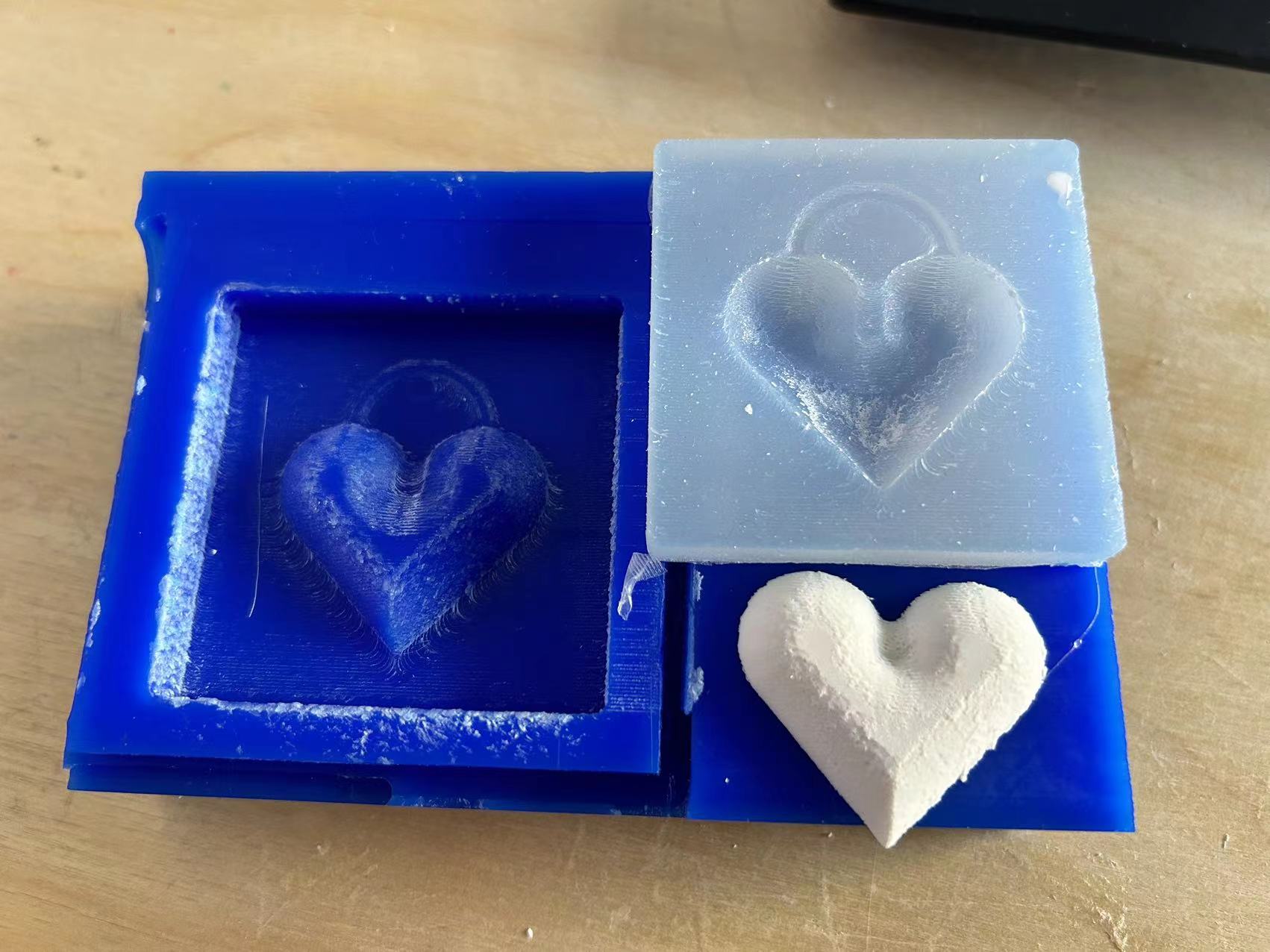


The mixing ratio:plaster 100g water 33g