Week seventeenth assignment is the Invention, Intellectual Property and Business Models.During this week we have learned about the definitions of inventions, patents and copyrights and their types. To detect under which category we want to classify our projects. our projects will not be an invention, so a patent is not necessary. I want my project to be an open source project but also I need a license to save my copyrights.
Assignment-17
Invention, Intellectual Property and Business Models
OBJECTIVES
Individual assignments
- Develop a plan for dissemination of your final project.
- Prepare drafts of your summary slide (presentation.png, 1920x1080) and video clip (presentation.mp4, 1080p HTML5,minute,~10 MB) and put them in your root directory
Individual assignment on Invention, Intellectual Property and Business Models.
What is Invention ?
An invention is a unique or novel device, method, composition or process. The invention process is a process within an overall engineering and product development process. It may be an improvement upon a machine or product or a new process for creating an object or a result. An invention that achieves a completely unique function or result may be a radical breakthrough. Such works are novel and not obvious to others skilled in the same field. An inventor may be taking a big step toward success or failure.Some inventions can be patented. The system of patents was established to encourage inventors by granting limited-term, limited monopoly on inventions determined to be sufficiently novel, non-obvious, and useful. A patent legally protects the intellectual property rights of the inventor and legally recognizes that a claimed invention is actually an invention. The rules and requirements for patenting an invention vary by country and the process of obtaining a patent is often expensive.(Wikipedia)
Types of Invention.
Inventions are of three kinds: scientific-technological (including medicine), sociopolitical (including economics and law), and humanistic, or cultural.
Scientific-technological inventions include railroads, aviation, vaccination, hybridization, antibiotics, astronautics, holography, the atomic bomb, computing, the Internet, and the smartphone.
Sociopolitical inventions comprise new laws, institutions, and procedures that change modes of social behavior and establish new forms of human interaction and organization. Examples include the British Parliament, the US Constitution, the Manchester (UK) General Union of Trades, the Boy Scouts, the Red Cross, the Olympic Games, the United Nations, the European Union, and the Universal Declaration of Human Rights, as well as movements such as socialism, Zionism, suffragism, feminism, and animal-rights veganism.
Humanistic inventions encompass culture in its entirety and are as transformative and important as any in the sciences, although people tend to take them for granted. In the domain of linguistics, for example, many alphabets have been inventions, as are all neologisms (Shakespeare invented about 1,700 words).(Wikipedia)
Intellectual Property.
Intellectual property (IP) is a category of property that includes intangible creations of the human intellect. There are many types of intellectual property, and some countries recognize more than others. The most well-known types are copyrights, patents, trademarks, and trade secrets. The modern concept of intellectual property developed in England in the 17th and 18th centuries. The term "intellectual property" began to be used in the 19th century, though it was not until the late 20th century that intellectual property became commonplace in the majority of the world's legal systems.
The main purpose of intellectual property law is to encourage the creation of a wide variety of intellectual goods To achieve this, the law gives people and businesses property rights to the information and intellectual goods they create, usually for a limited period of time. This gives economic incentive for their creation, because it allows people to benefit from the information and intellectual goods they create, and allows them to protect their ideas and prevent copying. These economic incentives are expected to stimulate innovation and contribute to the technological progress of countries, which depends on the extent of protection granted to innovators.(Wikipedia)
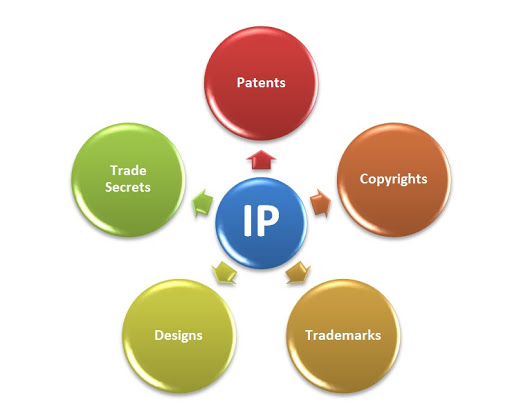
Types of Intellectual Property.
Patent.
A patent is a type of intellectual property that gives its owner the legal right to exclude others from making, using, or selling an invention for a limited period of years, in exchange for publishing an enabling public disclosure of the invention. In most countries, patent rights fall under private law and the patent holder must sue someone infringing the patent in order to enforce his or her rights. In some industries patents are an essential form of competitive advantage; in others they are irrelevant .
Copyright.
Copyright is a type of intellectual property that gives its owner the exclusive right to make copies of a creative work, usually for a limited time. The creative work may be in a literary, artistic, educational, or musical form. Copyright is intended to protect the original expression of an idea in the form of a creative work, but not the idea itself. A copyright is subject to limitations based on public interest considerations, such as the fair use doctrine in the United States.
Trademark.
A trademark (also written trade mark or trade-mark) is a type of intellectual property consisting of a recognizable sign, design, or expression which identifies products or services of a particular source from those of others, although trademarks used to identify services are usually called service marks. The trademark owner can be an individual, business organization, or any legal entity. A trademark may be located on a package, a label, a voucher, or on the product itself. For the sake of corporate identity, trademarks are often displayed on company buildings. It is legally recognized as a type of intellectual property.
Trade secrets.
Trade secrets are a type of intellectual property that comprise formulas, practices, processes, designs, instruments, patterns, or compilations of information that have inherent economic value because they are not generally known or readily ascertainable by others, and which the owner takes reasonable measures to keep secret. In some jurisdictions, such secrets are referred to as confidential information.
Right of publicity.
The right of publicity , sometimes referred to as personality rights, is the right of an individual to control the commercial use of one's identity, such as name, image, likeness, or other unequivocal identifiers. It is generally considered a property right as opposed to a personal right, and as such, the validity of the right of publicity can survive the death of the individual (to varying degrees depending on the jurisdiction).
Diffrent copyright licenses
Creative Commons (CC) license
A Creative Commons (CC) license is one of several public copyright licenses that enable the free distribution of an otherwise copyrighted "work".A CC license is used when an author wants to give other people the right to share, use, and build upon a work that the author has created. CC provides an author flexibility (for example, they might choose to allow only non-commercial uses of a given work) and protects the people who use or redistribute an author's work from concerns of copyright infringement as long as they abide by the conditions that are specified in the license by which the author distributes the work.
GNU General Public License
The GNU General Public License (GNU GPL or simply GPL) is a series of widely used free software licenses that guarantee end users the freedom to run, study, share, and modify the software. The licenses were originally written by Richard Stallman, founder of the Free Software Foundation (FSF), for the GNU Project, and grant the recipients of a computer program the rights of the Free Software Definition. The GPL series are all copyleft licenses, which means that any derivative work must be distributed under the same or equivalent license terms. This is in distinction to permissive software licenses, of which the BSD licenses and the MIT License are widely used, less restrictive examples. GPL was the first copyleft license for general use.
BSD license
BSD licenses are a family of permissive free software licenses, imposing minimal restrictions on the use and distribution of covered software. This is in contrast to copyleft licenses, which have share-alike requirements. The original BSD license was used for its namesake, the Berkeley Software Distribution (BSD), a Unix-like operating system. The original version has since been revised, and its descendants are referred to as modified BSD licenses.BSD is both a license and a class of license (generally referred to as BSD-like). The modified BSD license (in wide use today) is very similar to the license originally used for the BSD version of Unix. The BSD license is a simple license that merely requires that all code retain the BSD license notice if redistributed in source code format, or reproduce the notice if redistributed in binary format. The BSD license (unlike some other licenses e.g. GPL) does not require that source code be distributed at all.
MIT license
The MIT license gives users express permission to reuse code for any purpose, sometimes even if code is part of proprietary software. As long as users include the original copy of the MIT license in their distribution, they can make any changes or modifications to the code to suit their own needs.
It is one of the most simple open source license agreements. The intent was for the text to be understandable by average users and to avoid extensive litigation, which may arise from other similar Free and Open Source Software (FOSS) licenses.
Apache License
The Apache License is a permissive free software license written by the Apache Software Foundation (ASF).] It allows users to use the software for any purpose, to distribute it, to modify it, and to distribute modified versions of the software under the terms of the license, without concern for royalties. The ASF and its projects release their software products under the Apache License. The license is also used by many non-ASF projects.
going with Creative Commons (CC)
After read about different types of Licenses, I noticed that the Creative Commons license is the most appropriate type for me because it organizes the open-source copyrights with many options. Finally, i decided to go with creative commons open-source license .
Steps for creating license.
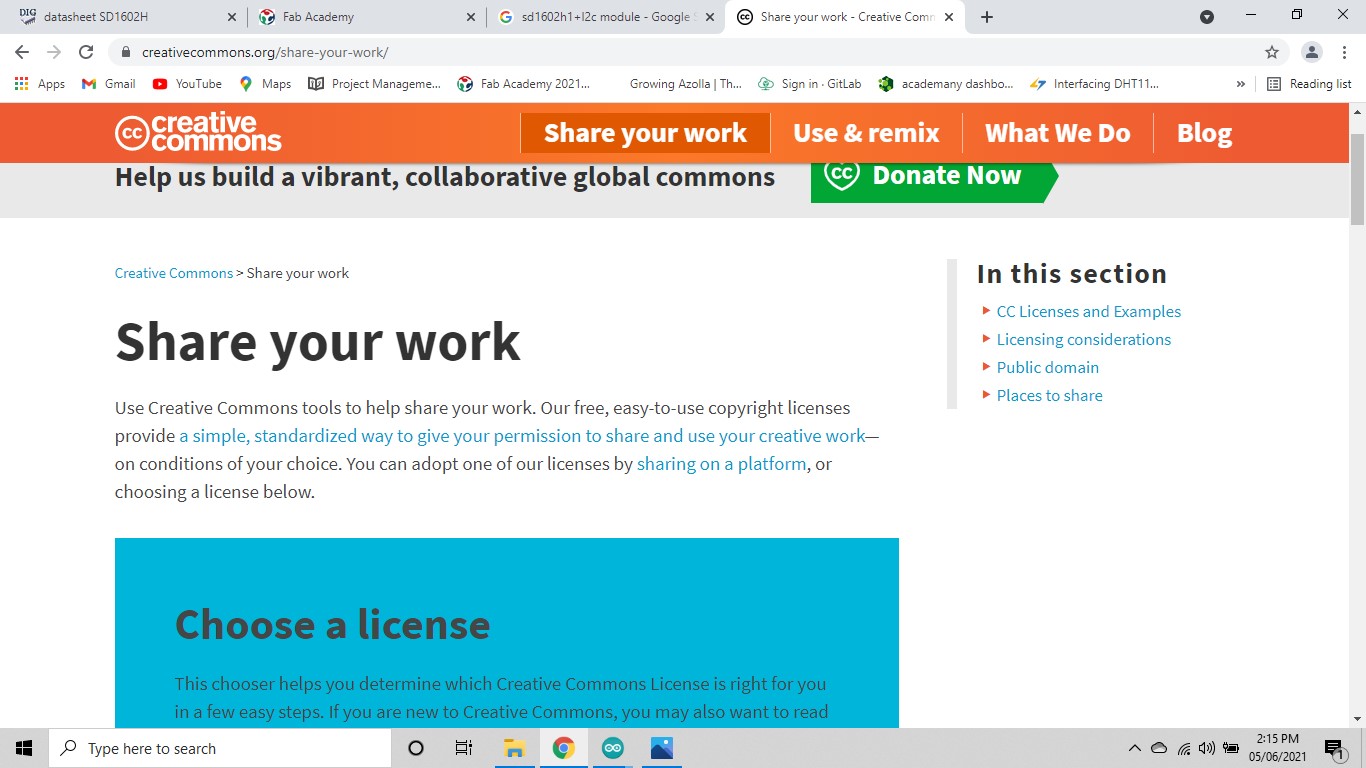
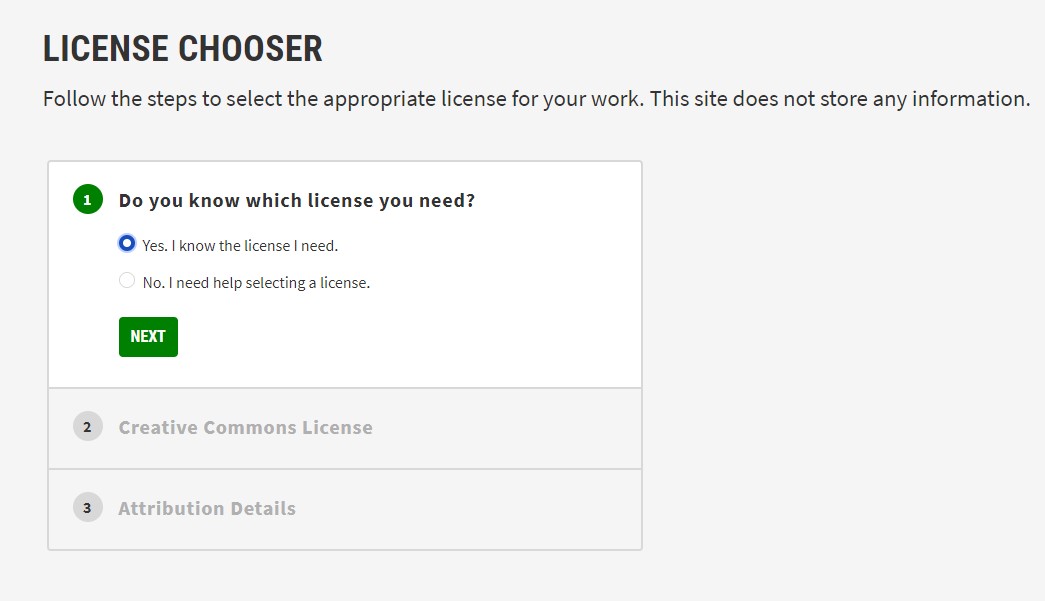
On web browser goto "Creativecommons.org" select "share your work".
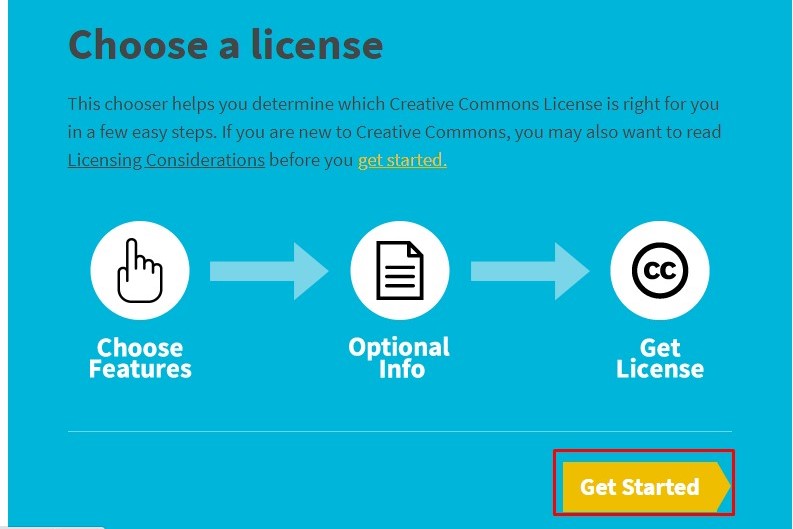
On choose License click on "get strated".
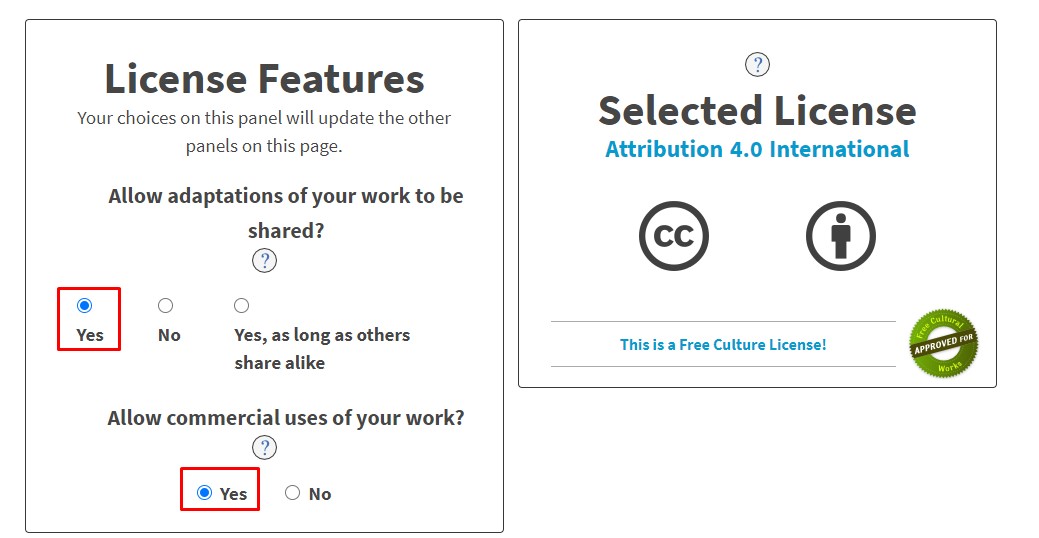
Go to license features.I allow adaptions of work to be shared also allow the commercial uses of my work.
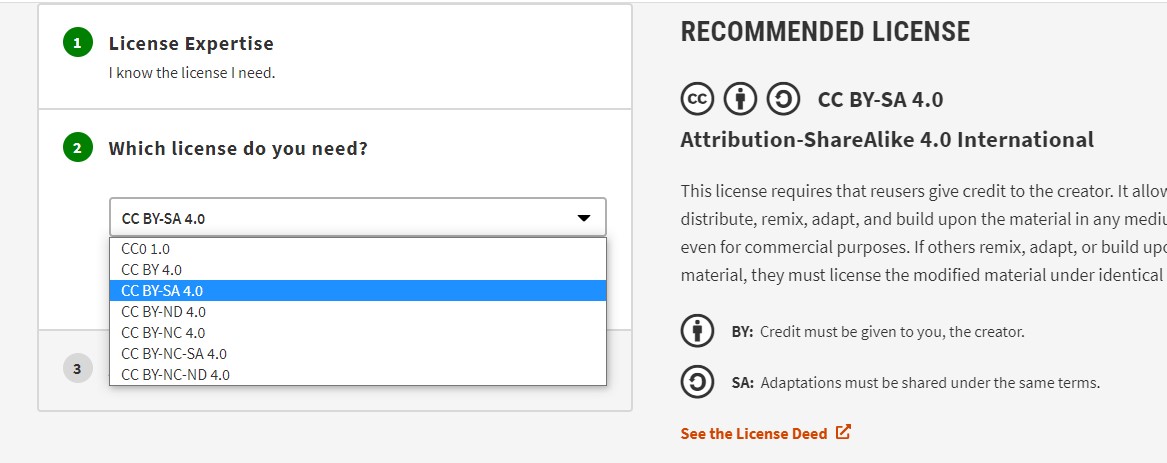
Go to chooser beta in the license chooser,follow the steps for appropriate license.
I have selected the "Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International".This license requires that reusers give credit to the creator. It allows reusers to distribute, remix, adapt, and build upon the material in any medium or format, even for commercial purposes. If others remix, adapt, or build upon the material, they must license the modified material under identical terms.
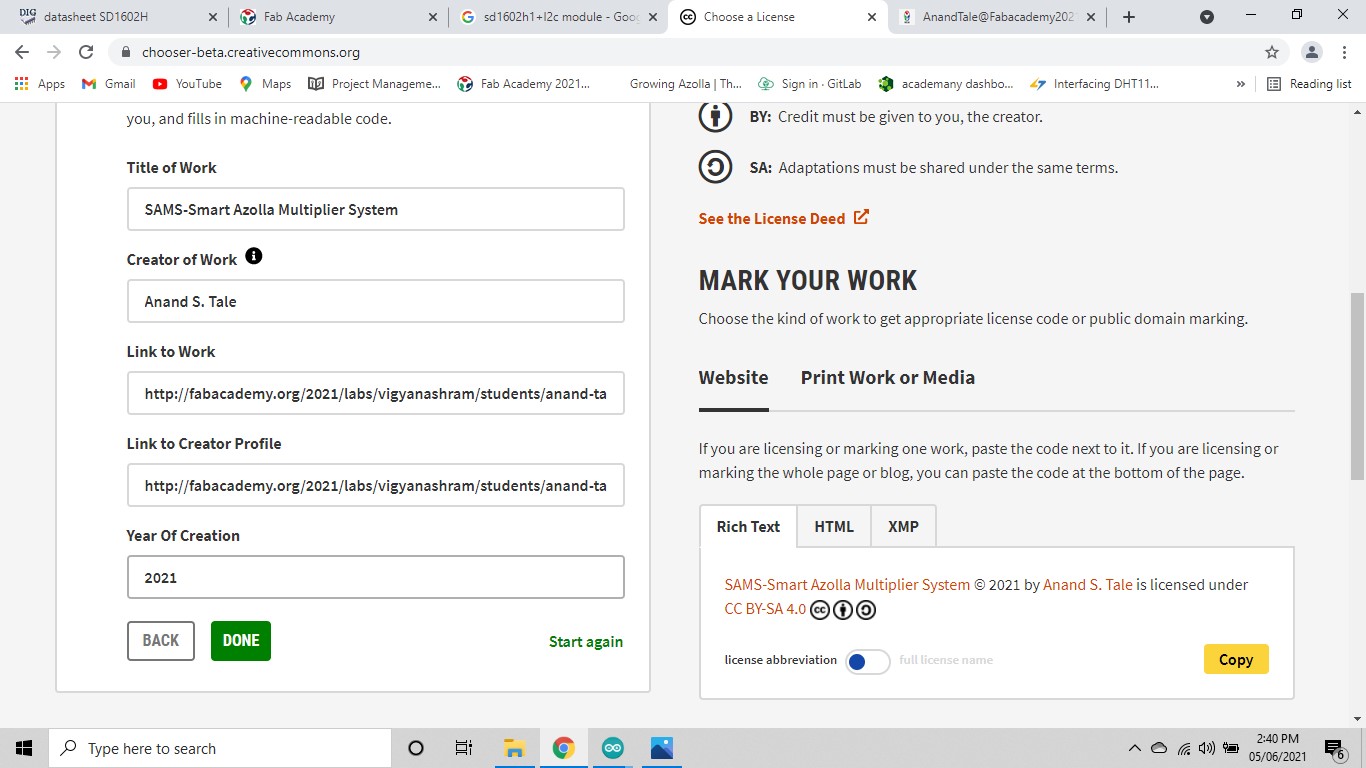
Fill the project work related informarion and done it. The HTML code for license would be appeared at the right done corner.
Planing and Possibilities for furture Development of Project
I am planning to make prototype of my project to control the parameter like humidity, temperature and light intensity for prior double the growth of azolla. I am going to make this project as an open source commercial project. I am going to develop the closed chamber model at our fab lab and test it performance in different control condition for increase the growth of azolla.
Where you would fabricate and assemble your devices?
I fabricated and assembled my project device at Fab lab Vigyan ashram.
How you would distribute the devices (you directly, resellers, through internet, under the shape of a kit, etc)
For distribution and deployment of this device in need of small survey. This device can be use in various laboratory for controlling different parameters. Researcher can use this device for research experiment. Farmers can use the device for the small-scale production not only azolla but any other plant that required the control condition.
Presentation Slide & video

SAMS-Smart Azolla Multiplier System by Anand S. Tale is licensed under CC BY-SA 4.0