Interface and application programming
The purpose of the week is to write an application that interfaces with an input and/or output device.
So decided to use the PiezoBoard I made during Input Device week.For the interface I will use Processing.
Tiny45 program :
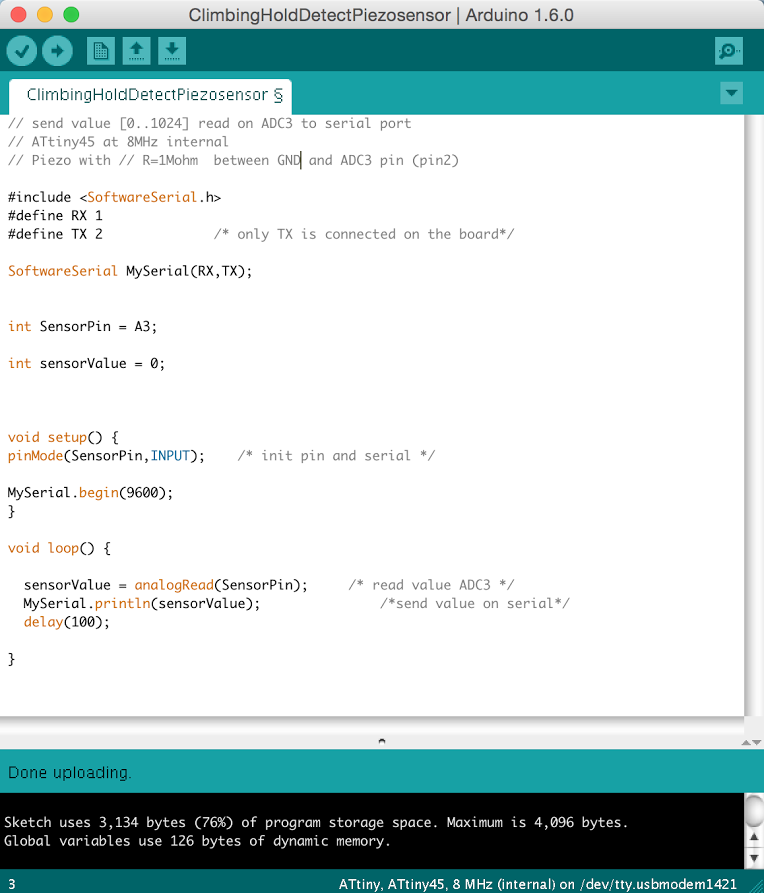
// send value [0..1024] read on ADC3 to serial port
// ATtiny45 at 8MHz internal
// Piezo with // R=1Mohm between GND and ADC3 pin (pin2)
#include
#define RX 1
#define TX 2 /* only TX is connected on the board*/
SoftwareSerial MySerial(RX,TX);
int SensorPin = A3;
int sensorValue = 0;
void setup() {
pinMode(SensorPin,INPUT); /* init pin and serial */
MySerial.begin(9600);
}
void loop() {
sensorValue = analogRead(SensorPin); /* read value ADC3 */
MySerial.println(sensorValue); /*send value on serial*/
delay(100);
}
Processing interface Program:
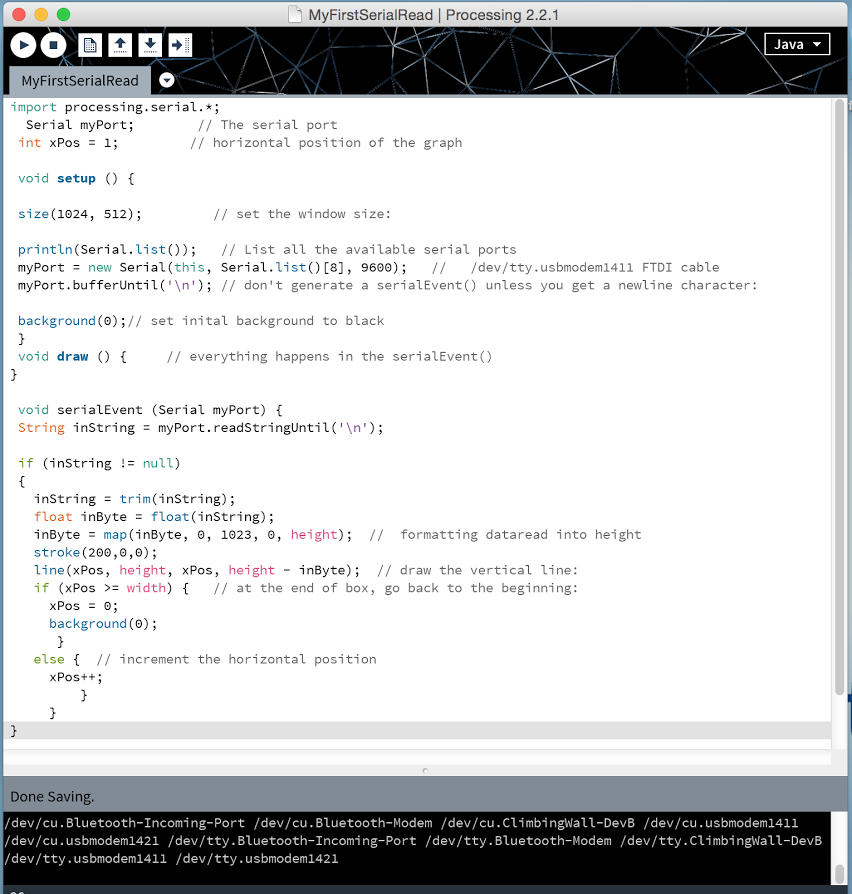
import processing.serial.*;
Serial myPort; // The serial port
int xPos = 1; // horizontal position of the graph
void setup () {
size(1024, 512); // set the window size:
println(Serial.list()); // List all the available serial ports
myPort = new Serial(this, Serial.list()[8], 9600); // /dev/tty.usbmodem1411 FTDI cable
myPort.bufferUntil('\n'); // don't generate a serialEvent() unless you get a newline character:
background(0);// set inital background to black
}
void draw () { // everything happens in the serialEvent()
}
void serialEvent (Serial myPort) {
String inString = myPort.readStringUntil('\n');
if (inString != null)
{
inString = trim(inString);
float inByte = float(inString);
inByte = map(inByte, 0, 1023, 0, height); // formatting dataread into height
stroke(200,0,0);
line(xPos, height, xPos, height - inByte); // draw the vertical line:
if (xPos >= width) { // at the end of box, go back to the beginning:
xPos = 0;
background(0);
}
else { // increment the horizontal position
xPos++;
}
}
}
the only difficulty was set the serial port name : on my mac my FTDI cable his: /dev/tty.usbmodem1411
Check the video:
Interface Programming from JM Durney on Vimeo.
you can find the code/sketch files on my
github repository :![]()