11. Input devices¶
This week I worked on in reading data from RPLIDAR A1M8-R6 - 360 Degree Laser Scanner


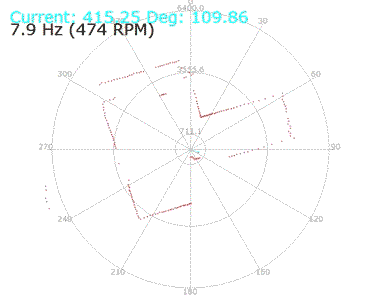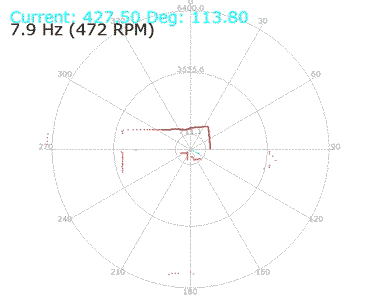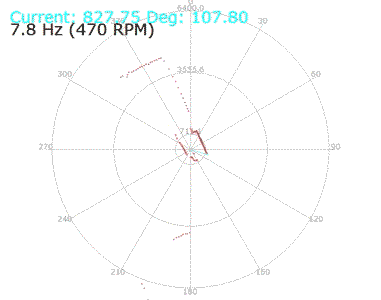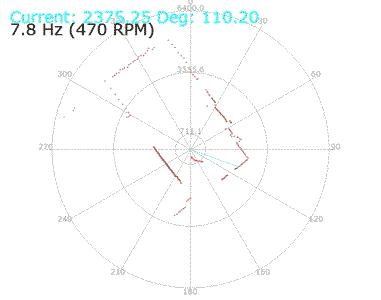
In the following video the LED will LED blink faster when the obstacle get closer to the sensor.
Wiring¶
- First I need to wire the RPLidar with my design board which I have made in Electronics Design Week
| My Board Pin | RPLidar |
|---|---|
| FTDI GND | GND |
| FTDI RX | RX |
| FTDI TX | TX |
| VCC | V5.0 |
| GND | GND |
| FTDI CTS | MOTOCTL |
| VCC | VMOTO |

- For programing I wire Arduino UNO board with ISP header of my board
| Arduino UNO Pin # | New Board ISP Port |
|---|---|
| 12 | 1-MISO |
| 5V | 2-VCC |
| 13 | 3-SCK |
| 11 | 4-MOSI |
| 10 | 5-RST |
| GND | 6-GND |

- Here is the full wiring

RPLIDAR library¶
-
First you’ll need to install the RPLIDAR library from GitHub by download the ZIP file

-
Export RPLidarDriver folder to Arduino libraries folder

Arduino Code¶
-
Open Arduino IDE and go to File >> Examples >> RPLidarDriver >> simple_connect

-
I modify the code by adding the following code
//perform data processing here...
if (angle >= 0.0 && angle <= 1.0) {
if ( distance <= 150 && distance > 100)
interval = 500;
else if ( distance <= 100 && distance > 50)
interval = 100;
else if ( distance <= 50 && distance >= 0)
interval = 0;
else
interval = 2000;
timeNow = millis();
if ( (timeNow - timeOld) >= interval) {
timeOld = timeNow;
if (LEDStatus == LOW)
LEDStatus = HIGH;
else
LEDStatus = LOW;
}
digitalWrite(pinLED, LEDStatus);
}
- Here is the full code
// This sketch code is based on the RPLIDAR driver library provided by RoboPeak
#include <RPLidar.h>
// You need to create an driver instance
RPLidar lidar;
#define RPLIDAR_MOTOR 2 // The PWM pin for control the speed of RPLIDAR's motor.
// This pin should connected with the RPLIDAR's MOTOCTRL signal
float distanceOld = 0;
unsigned long timeNow = millis();
unsigned long timeOld = millis();
unsigned long interval = 0;
int pinLED = 3;
byte LEDStatus = LOW;
void setup() {
// bind the RPLIDAR driver to the arduino hardware serial
lidar.begin(Serial);
// set pin modes
pinMode(RPLIDAR_MOTOR, OUTPUT);
pinMode(pinLED, OUTPUT); // initialize digital pin as an output.
digitalWrite(pinLED, HIGH);
}
void loop() {
if (IS_OK(lidar.waitPoint())) {
float distance = lidar.getCurrentPoint().distance; //distance value in mm unit
float angle = lidar.getCurrentPoint().angle; //anglue value in degree
bool startBit = lidar.getCurrentPoint().startBit; //whether this point is belong to a new scan
byte quality = lidar.getCurrentPoint().quality; //quality of the current measurement
//perform data processing here...
if (angle >= 0.0 && angle <= 1.0) {
if ( distance <= 150 && distance > 100)
interval = 500;
else if ( distance <= 100 && distance > 50)
interval = 100;
else if ( distance <= 50 && distance >= 0)
interval = 0;
else
interval = 2000;
timeNow = millis();
if ( (timeNow - timeOld) >= interval) {
timeOld = timeNow;
if (LEDStatus == LOW)
LEDStatus = HIGH;
else
LEDStatus = LOW;
}
digitalWrite(pinLED, LEDStatus);
}
} else {
analogWrite(RPLIDAR_MOTOR, 0); //stop the rplidar motor
// try to detect RPLIDAR...
rplidar_response_device_info_t info;
if (IS_OK(lidar.getDeviceInfo(info, 100))) {
// detected...
lidar.startScan();
// start motor rotating at max allowed speed
analogWrite(RPLIDAR_MOTOR, 255);
delay(1000);
}
}
}
Testing¶
In the following video the LED will LED blink faster when the obstacle get closer to the sensor.
ROS¶
Useful links¶
Last update: June 16, 2021