Redraw the echo hello-world board
Add (at least) a button and LED (with current-limiting resistor)
Check the design rules, and make it
Extra credit: simulate its operation
Use the test equipment in your lab to observe the operation of a microcontroller circuit board
Now I tried to draw a basic circuit with a microcontroller. In order to do so first I identified required components to glow LED with a button which runs by microcontroller program.
Required components are as below.
● Micro-controller (To perform required functionality by storing program)
● LED
● Resistor
● Button and Resistor (Initially I made mistake not to use resistor with button)
● ISP header (To connect PCB to programmer)
● Switch
● Resonator
● Autodesk Eagle is PCB design software with Electronic Design Automation (EDA) scripting. Eagle stands for Easily Applicable Graphical Layout Editor.
● It has two main work sections, 1) Schematic - Where one can load parts from component libraries and make connections between them. 2) Board layout - Where one can rout board connection (auto-rout with optimized flow, and manual as well) and design PCB for production
● Very good tutorial on Eagle by Sparkfun is here. Schematic tutorial and Board layout tutorial

● Component libraries we have to add in Eagle, there are some by default libraries available as well.
● I have downloaded the library package from internet
● Mostly I have used Fab libraries.
● In order to add library one has to go in Schematic -> Library -> Library manager -> Browse
● To add the components you will need the "fab" and the "supply" libraries. The "supply library'' is already standard on the Eagle software.
Eagle has two windows that you use simultaneously to design a board:
1) Schematic (.sch) - logical components
2) Board Layout (.brd) for the actual board that we mill
There is a schematic / board button ![]() so you can switch between the two as you can see in the image below.
so you can switch between the two as you can see in the image below.

NOTE: Never close layout and not schematic or vice versa. You need to keep both open all the time. Closing one view while the other view is open (and making edits) will break the link between the two.
There are 2 ways you can interact with Eagle one is though the Graphical Icons Toolbar (image below), and the odder ins, which, you can type a command at any point, then select the item in the schematic / board that you wish to interact with, see section on commands after the picture below.
![]()
• add = opens up the libraries so that you can add components in Schematic view
• move = moves an item
• net = makes a logical connection
• junction = adds a junction
• value = adds value to components (i.e. ohm rating)
• name = names a component
• label = displays the name of a component in schematic view
• copy = copies an existing component on the schematic.
• route = used in Layout view, this tells you if you need to add a connection (follow yellow lines)
• ERC = electronic rules check; this ensures your board will actually work (use in schematic view)
• DRC = design rules check (in board view) - keep all the default settings (16 mil is fine); it should display a "no error" message in the bottom
left hand corner of the screen
• group = groups components in Layout view together; if you right-click, then you can choose Move: Group to move the grouping
• rats = in board view, tells you if you have airwires
• rip = deletes connections in layout
• show = after typing this, select a component to see information about it displayed in the bottom left corner of the screen. Also, if you type
show + [name of component] you can see that component highlighted. You can use this to see all the ground traces, for example.
• text = allows you to add text to your board. You can also edit the exported .png file in The Gimp to give text and black and white line
images. I recommend adding text in The Gimp.)
• info = then click on text to get properties of the text
After all these steps you can start using Eagle.
Adding Components:
Add a component (either type "add" or select the "add icon from the toolbar". The add menu will open. You can either look through the listed libraries for a component to add or you can type it into the box above the "drop" button.
For example: Add ATTINY 44- SSU (in the fab.lbr library which is the same one I used)


There are two ways to connect components in a schematic:
1) First you can connect the components with a wire (also called a "net" in Eagle). This may make connections obvious at first, but can
get really messy quickly as nets cross over each other.
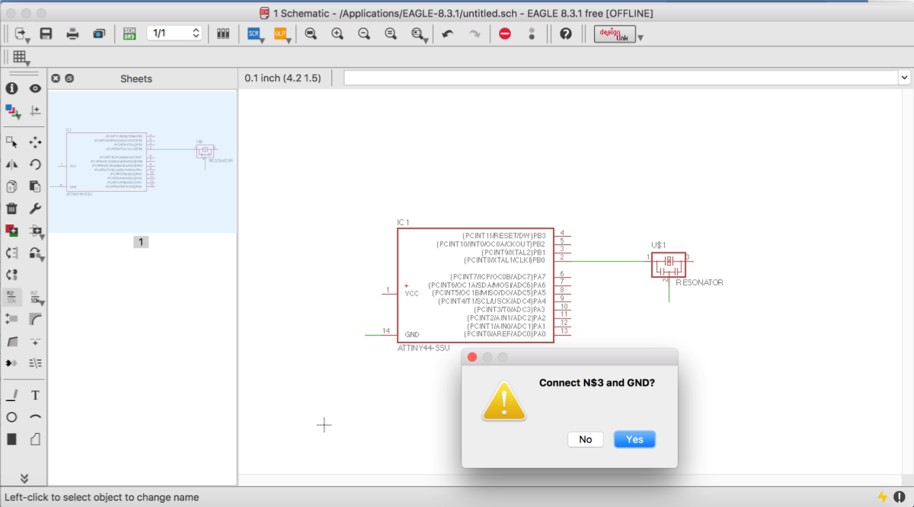
2) Or you can also name the nets attached to components that need to be connected by naming them with the same name. See example
schematic above. Eagle will ask you if you want them to be connected (type yes). After you name the component - label it so the name
appears in the diagram.
As you can see in the image below, I wanted to connect the pin 14 in the attiny with the pin 2 in the resonator, so I created a line in each one, and then I typed in name and enter, then I clicked on the green line (14) and I typed GND, I also did that to the line (2) and typed GND, then the Eagle asked if you want to connect both lines, now the lines are connected. You can also connect the pins with one line, as you can see in that I connect the pin (2) in the attiny with the pin (1) in the resonator.
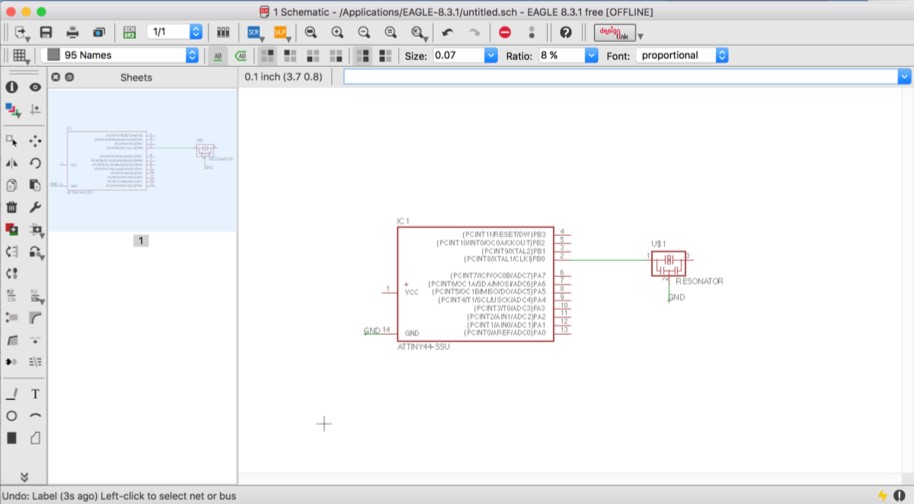
To show the names in the green lines you need to click on Label in the toolbar, then you click on the green line 14 for example and is going to show you the name you put already, you should also do it for the line 2 in the resonator. Now you know both are connected, even though you don’t see a line between them.

Now it was time to add a resistor and I wanted to connect the resistor with the VCC (pin 1) in the Attiny. I created a line between them. Now I needed to put the value in the resistor, by typing value> enter, then you click in the resistor, it will open a window for you to type the value.In this case my resistor had a 10K value, so I typed it. After that you press ok, then the resistor now has the value

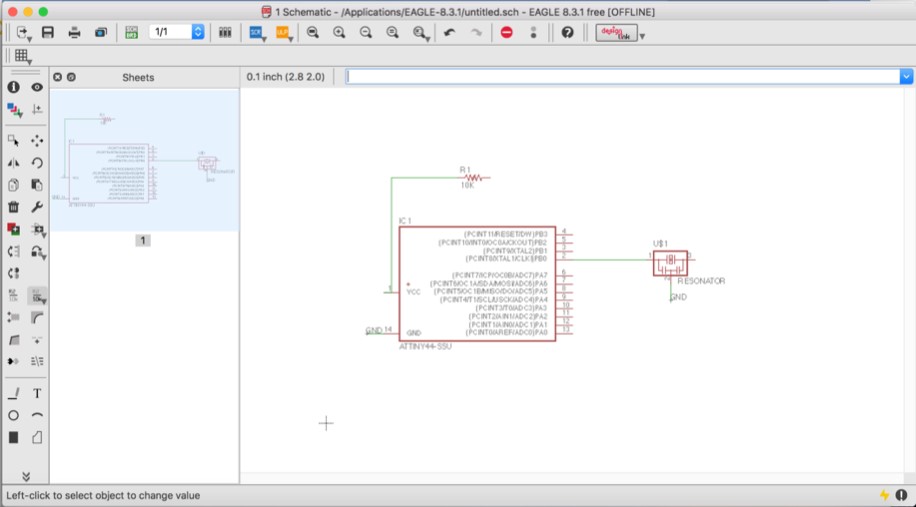
This is the schematic for "Hello Echo" that I drew:
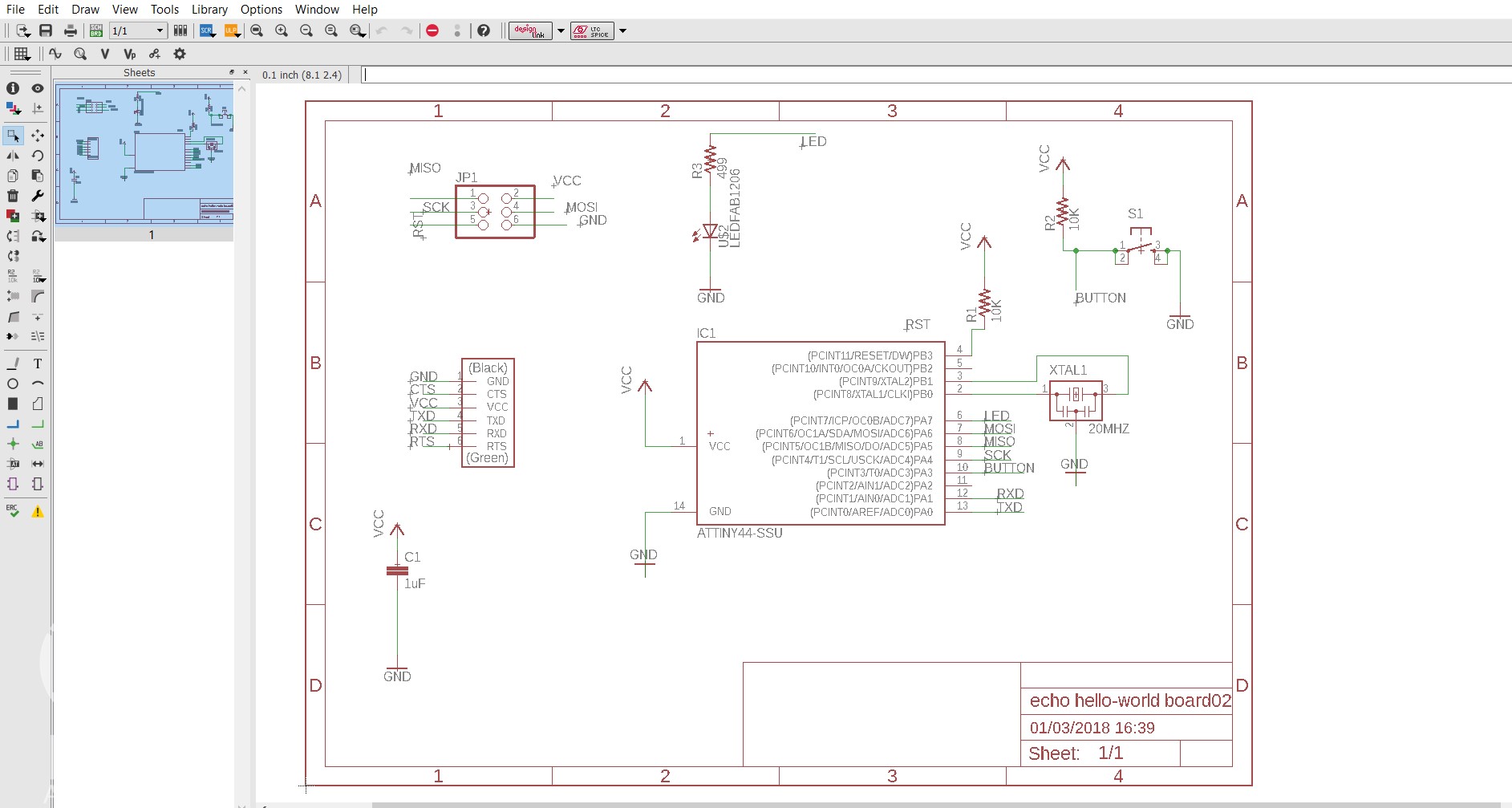
• Use "move" to move each individual component around.
• Use "route" to route each trace. The wire will turn red as you route it into place.
• After you route wires, you can use the "move" tool to move them around as lines.
• Route all the traces until it looks something like the diagram below.
• There is also an autorouter feature - it is good for making a general layout, but you will probably have to edit the traces manually. Especially on this
circuit.
• To use the autorouter go to: the "tools" menu in the top toolbar and select "auto".
• You can also type "auto"
• It doesn't have to look exactly the same, there is more than one way to route the traces. Just use this as a guide.
If you do not see it, go to "Layers" and select "Unrouted". Use the "Move" tool to position your components. After that try to route your connections using the tool "Route". You need to figure out how to connect them all without crossing paths to other connections.
Below you can see the routed board:
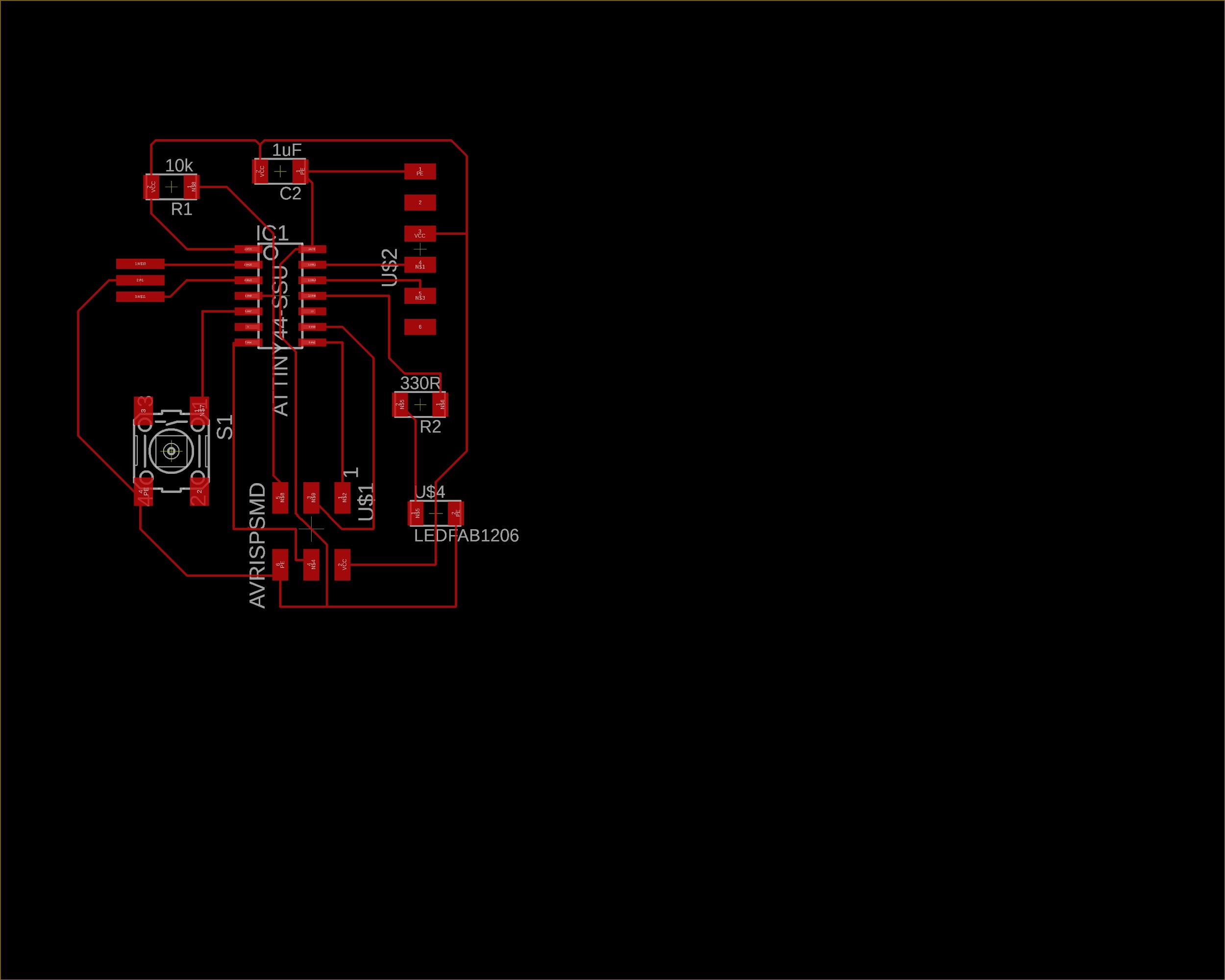
My first challenge was to put the routes in the positions that I wanted. I had a problem that the route was crossing in a wrong way, but after some tries I got it done. After you route your board you need to check the design rules.We need to check that the endmill we are using (1/64 usually) is able to go between all the traces so the machine is able to cut the board successfully. For this process we are going to use Design Rules Check (script) that will check that there is enough space everywhere.
In my lab we have MonoFab DGSHAPE SRM-20 for milling the circuit board. The detailed process of milling I have already explained in week-4 assignment.
First we have to design the trace of the board using 1/64 bit & cut it using 1/32 bit.
The below are the images for tracing & cutting the board
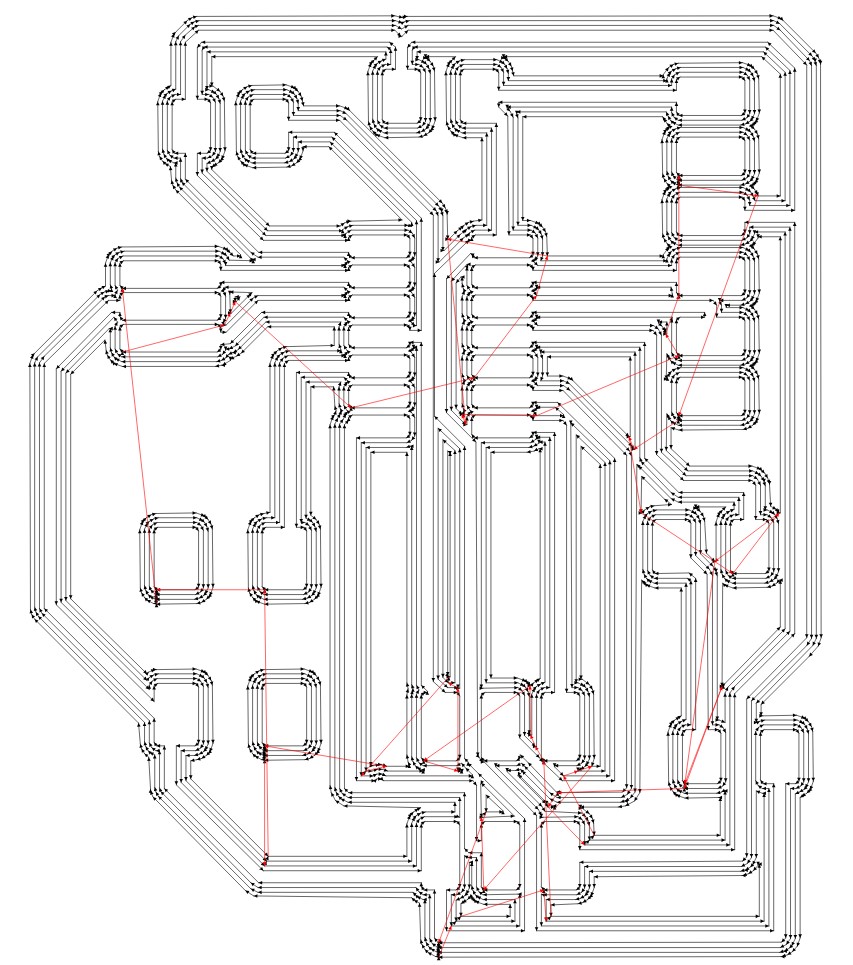
Then after tracing the circuit looks like this
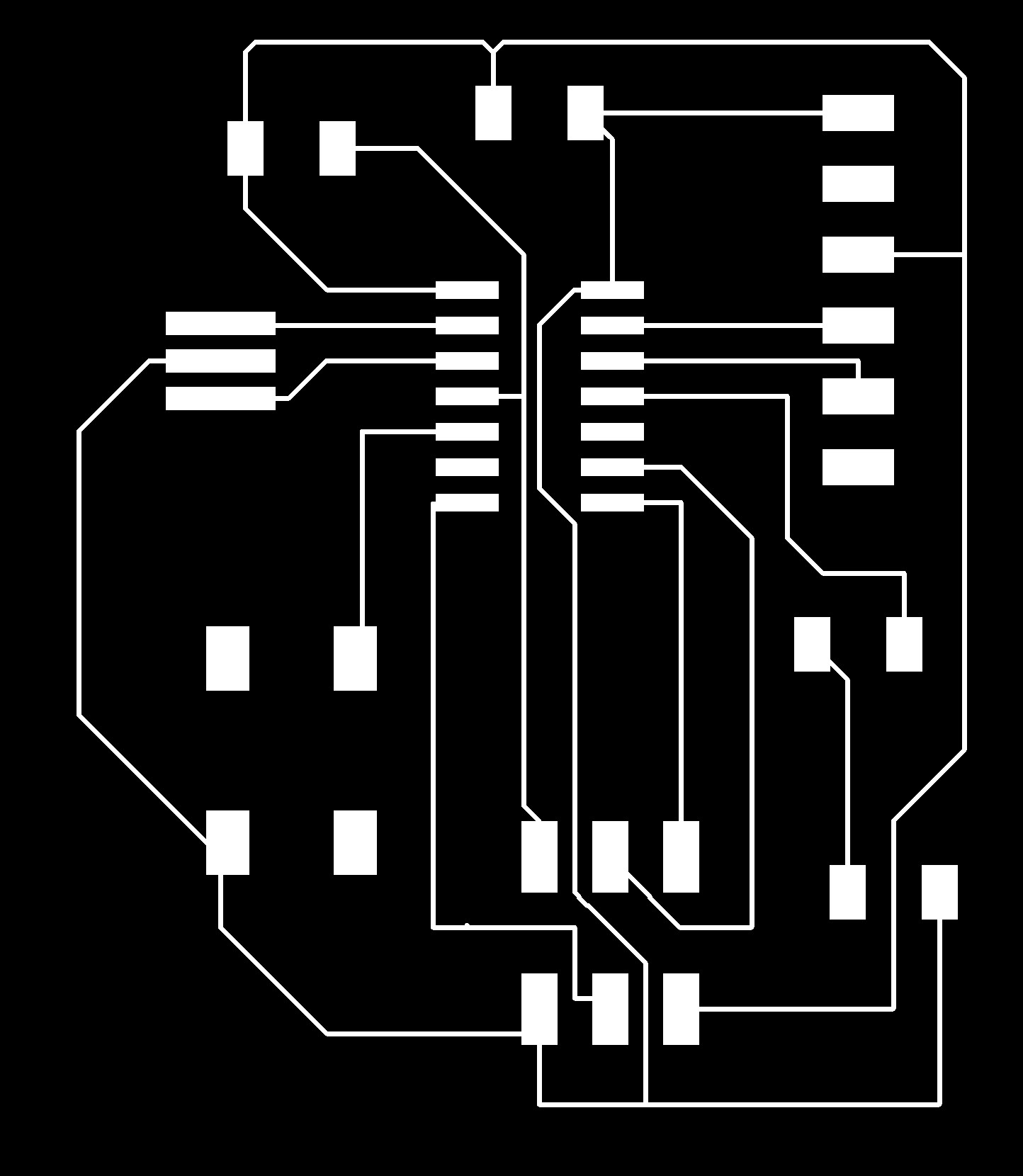
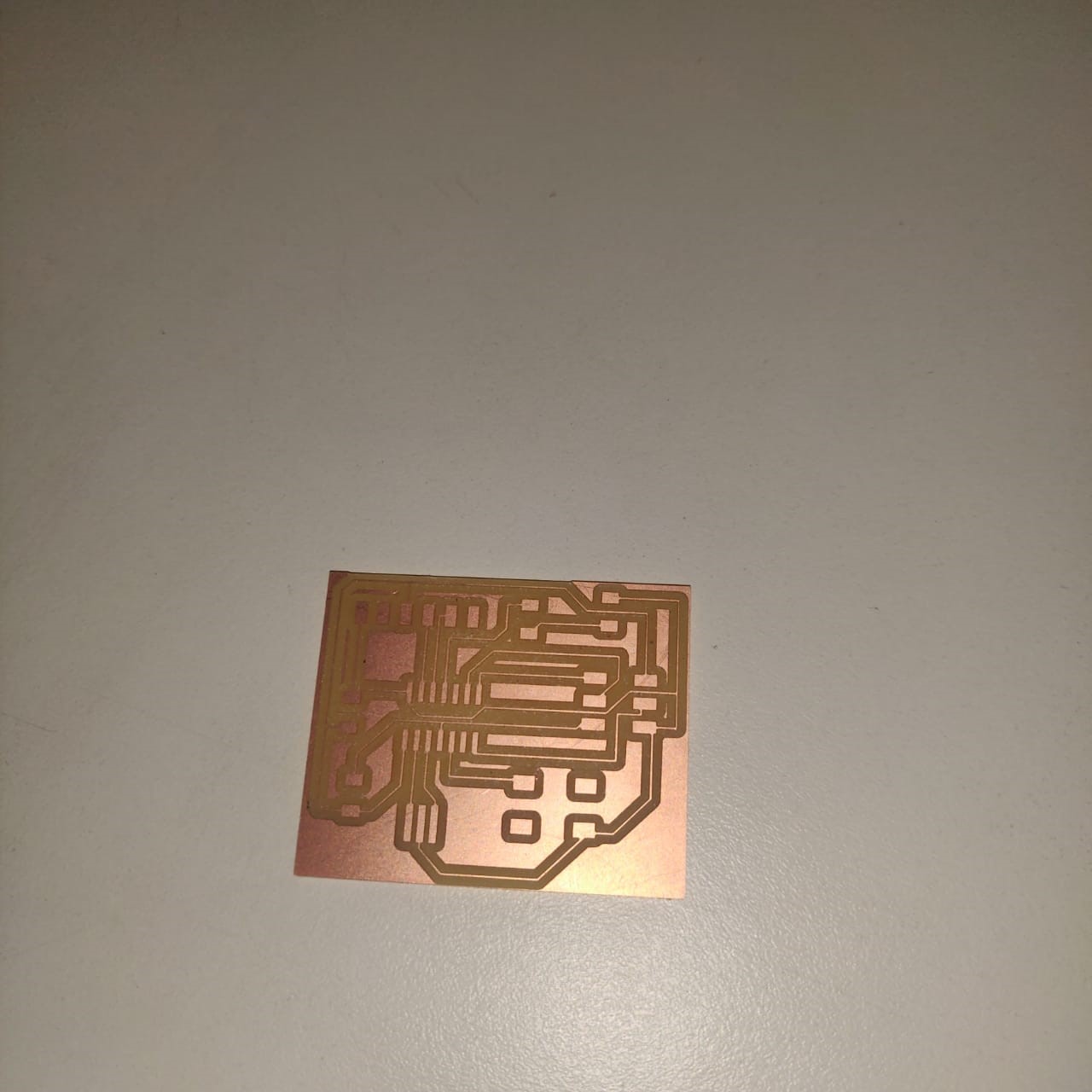
After I made all the routes as I wanted, I finally finished and exported the images to mill on the SRM-20. Here's how the first attempt looked like:

Finally after cutting the board the circuit looks like this

I then after milling it, cleaned it and started soldering the components onto the board.
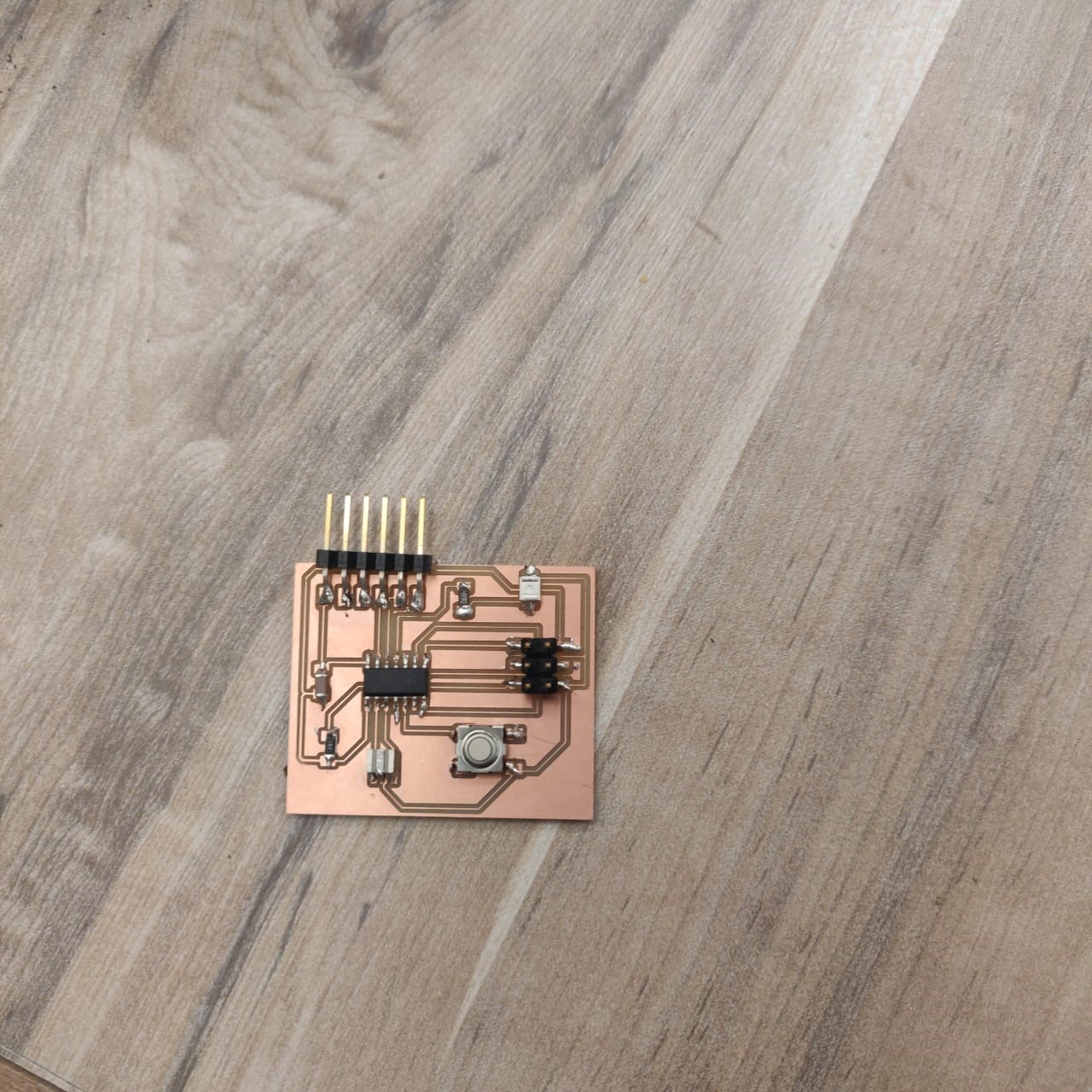
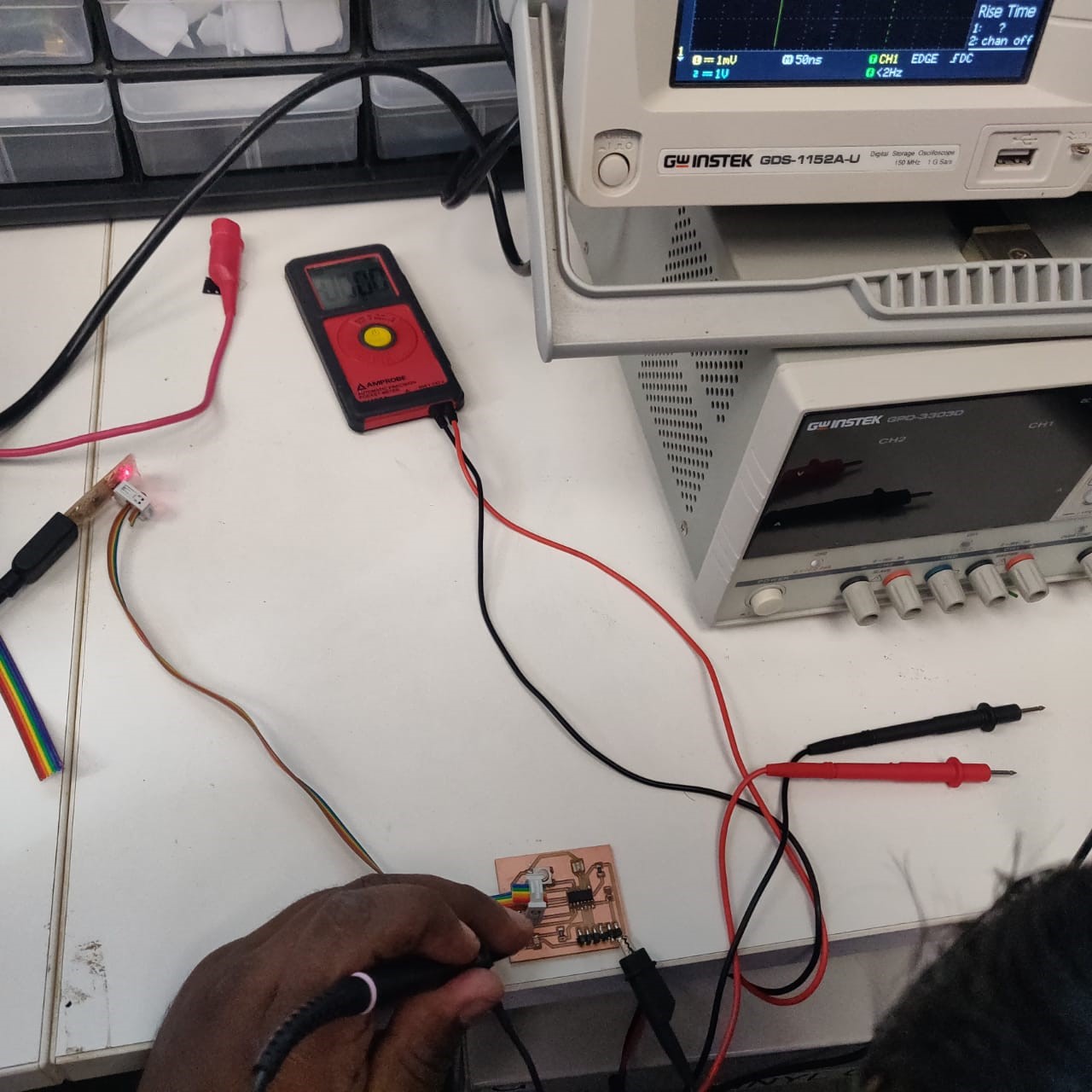
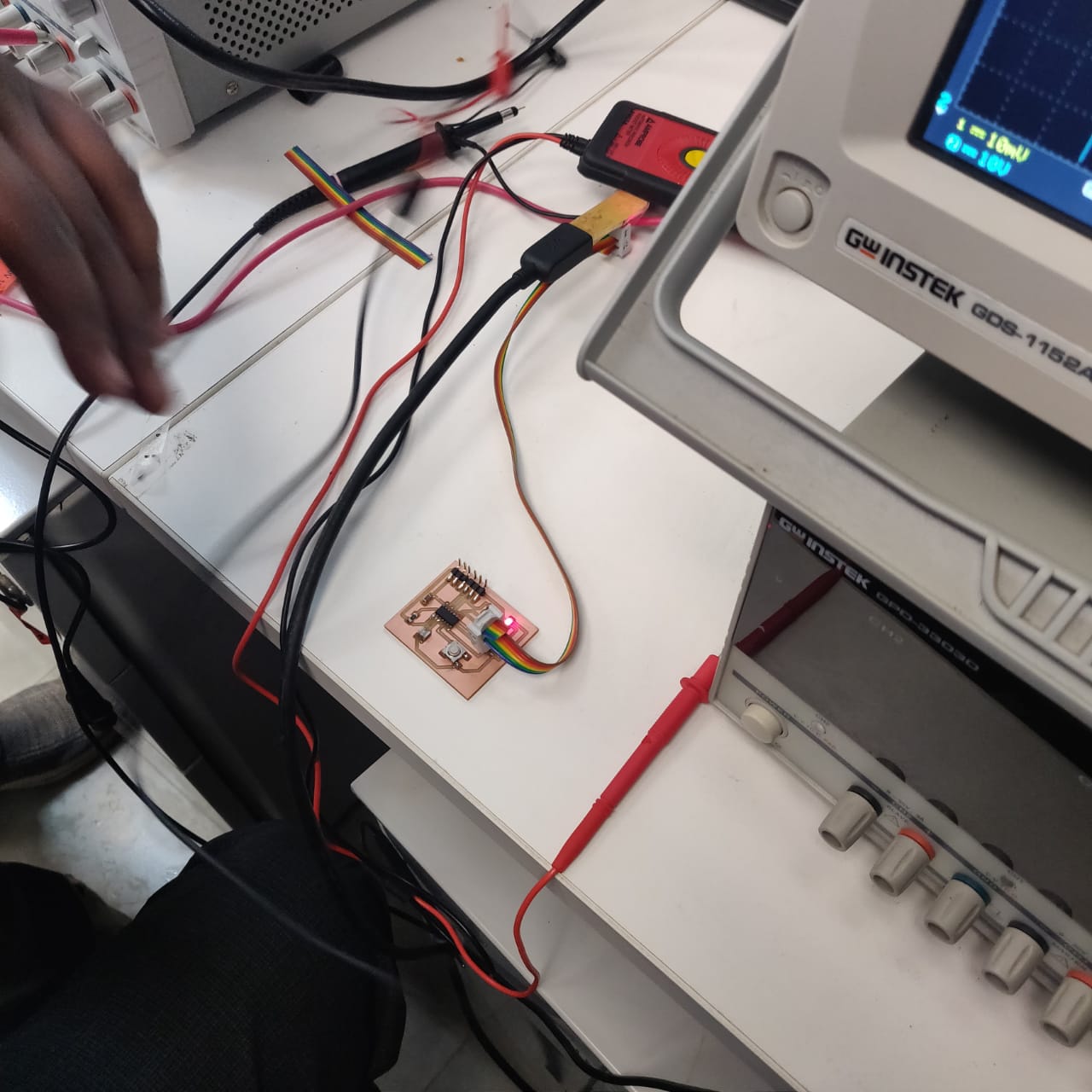
Use the test equipment in your lab to observe the operation of a microcontroller circuit board
The oscilloscope is a device for viewing oscillations, as of electrical voltage or current, by a display on the screen.
Here are two important controls:
Vertical position control: moves the whole displayed trace up and down. It is used to set the no-input trace exactly on the centerline of the graticule, but also permits offsetting vertically by a limited amount. With direct coupling, adjustment of this control can compensate for a limited DC component of an input.
The horizontal position control: moves the display sideways. It usually sets the left end of the trace at the left edge of the graticule, but it can displace the whole trace when desired. This control also moves the X-Y mode traces sidewise in some instruments, and can compensate for a limited DC component as for vertical position.

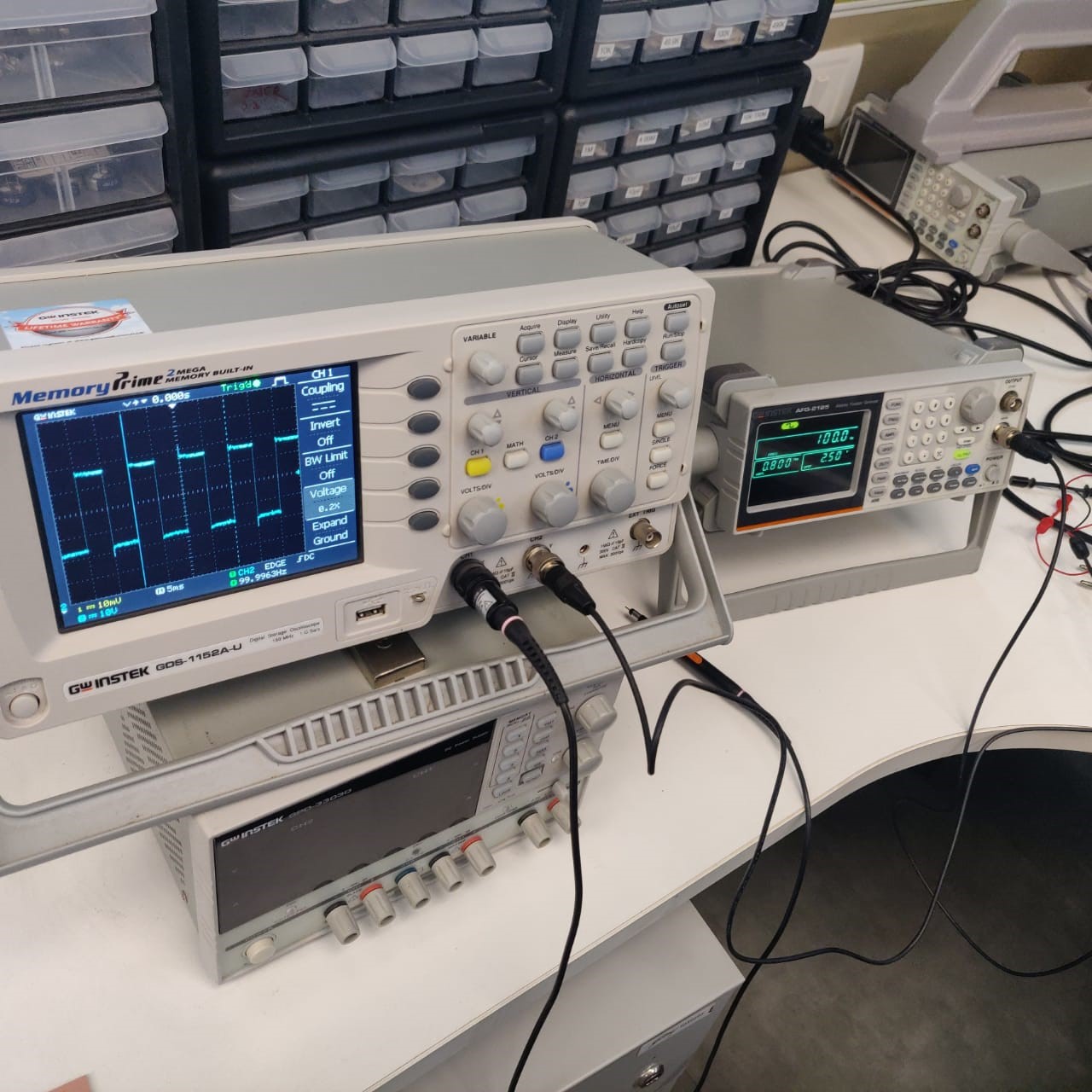
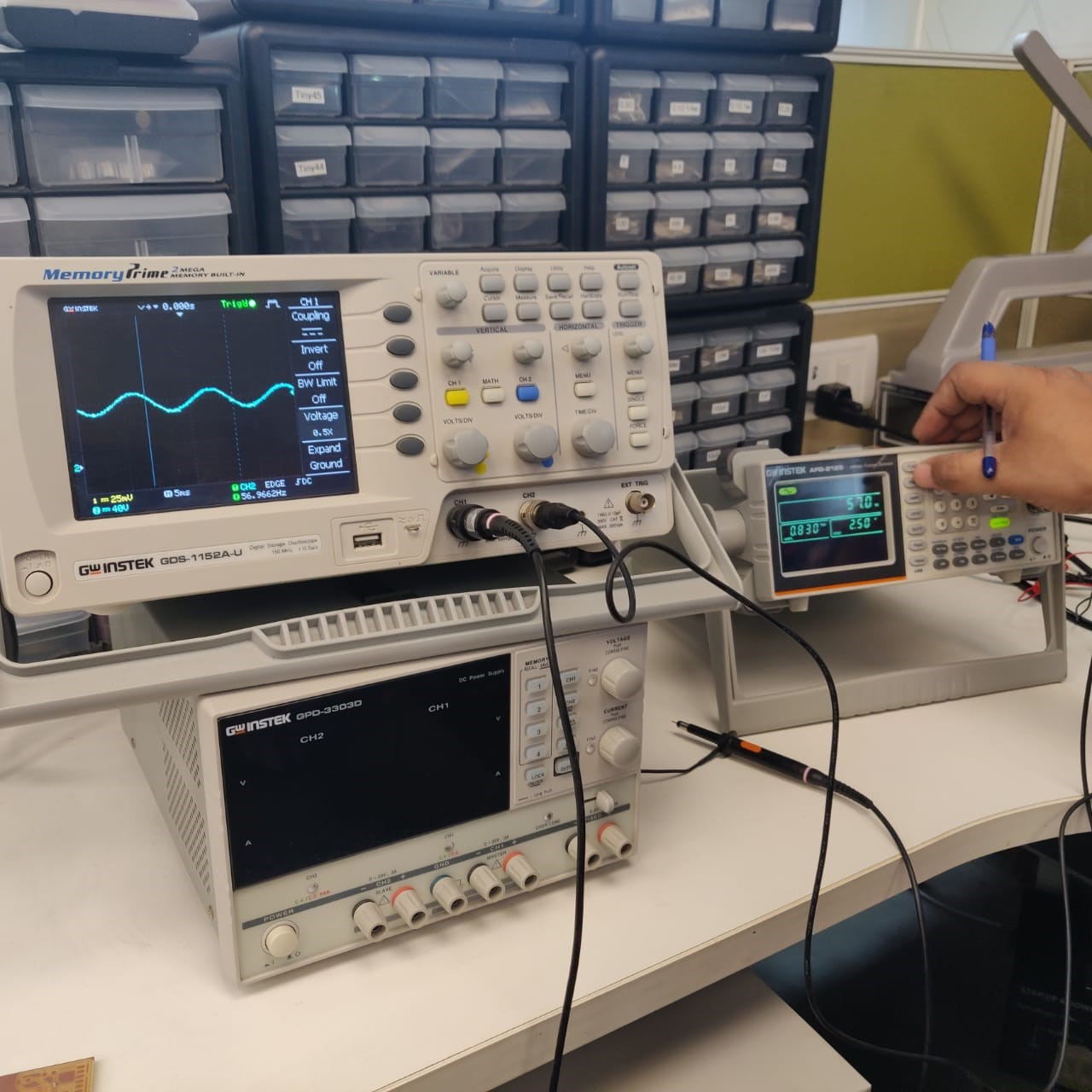
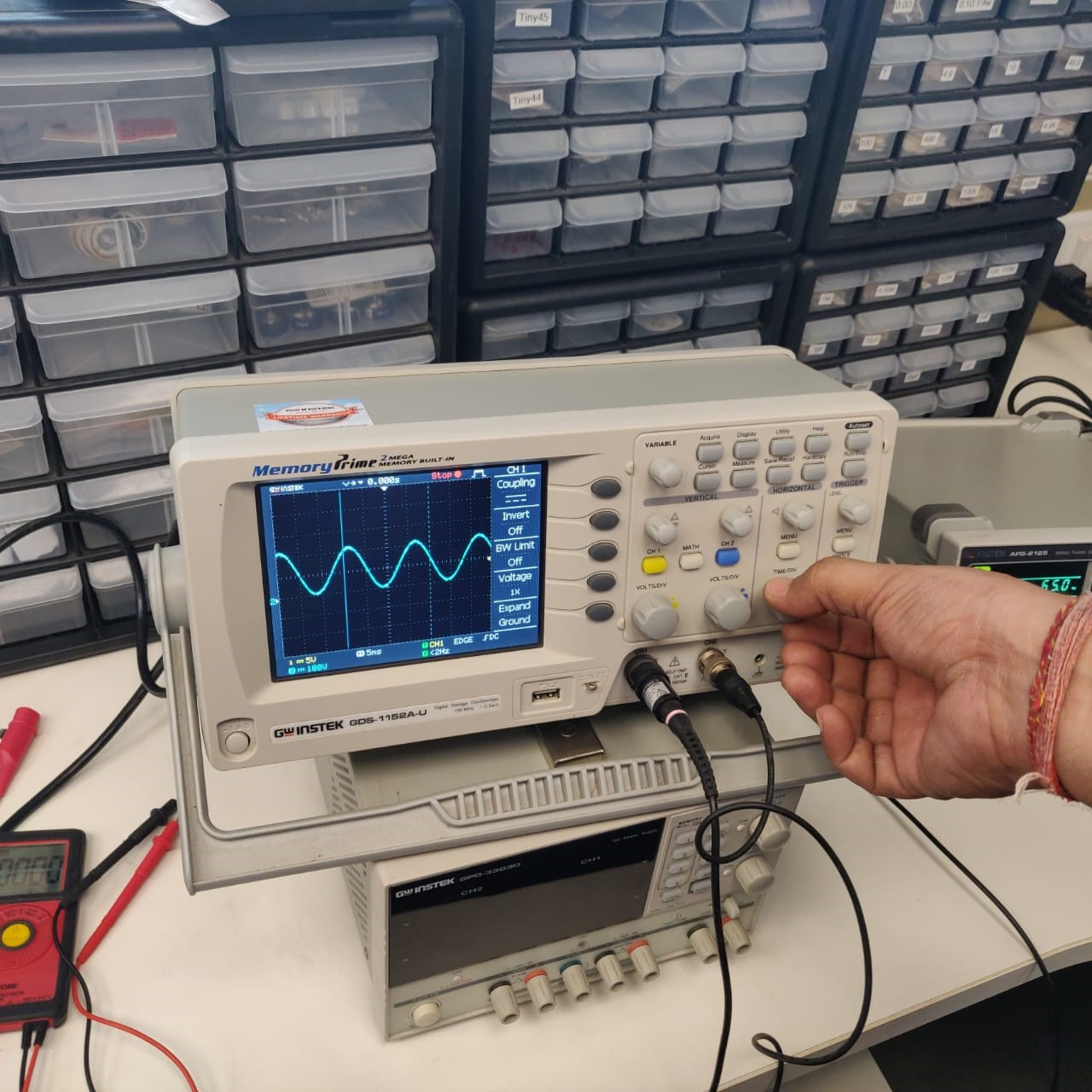
A multimeter is an electronic measuring instrument that combines several measurement functions in one unit. A typical multimeter can measure milliamps (mA) of current, voltage (V) and resistance (Ω).