Invention, Intellectual Property and Income:-
This week assignment was to
develop a plan for dissemination of your final project
prepare drafts of your summary slide (presentation.png, 1920x1080)
and video clip (presentation.mp4, 1080p HTML5, < ~minute, < ~10 MB)
and put them in your root directory
What exactly is intellectual property?
According to WIPO, Intellectual property (IP) refers to creations of the mind, such as inventions; literary and artistic works; designs; and symbols, names and images used in commerce. IP is protected in law by, for example, patents, copyright and trademarks, which enable people to earn recognition or financial benefit from what they invent or create. By striking the right balance between the interests of innovators and the wider public interest, the IP system aims to foster an environment in which creativity and innovation can flourish.\ Intellectual property is divided into two categories: Industrial Property includes patents for inventions, trademarks, industrial designs and geographical indications. There are also more specialized or derived varieties of sui generis exclusive rights, such as circuit design rights (called mask work rights in the US) and supplementary protection certificates for pharmaceutical products (after expiry of a patent protecting them) and database rights (in European law). Companies are diligent when it comes to identifying and protecting intellectual property because it holds such high value in today's increasingly knowledge-based economy. Also, producing value intellectual property requires heavy investments in brainpower and time of skilled labor. This translates into heavy investments by organizations and individuals that should not be accessed with no rights by others.
Extracting value from intellectual property and preventing others from deriving value from it is an important responsibility for any company. Intellectual property can take many forms. Although it's an intangible asset, intellectual property can be far more valuable than a company's physical assets. Intellectual property can represent a competitive advantage and as a result, is fiercely guarded and protected by the companies that own the property. The different types of intellectual property are:
Patents
A patent is a property right for an investor that's typically granted by a government agency such as the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office. The patent allows the inventor exclusive rights to the invention, which could be a design, process, an improvement, or physical invention such as a machine. Technology and software companies often have patents for their designs. For example, the patent for the personal computer was filed in 1980 by Steve Jobs and three other colleagues at Apple Inc.
Copyrights
Copyright provides authors and creators of original material the exclusive right to use, copy, or duplicate their material. Authors of books have their works copyrighted as do musical artists. A copyright also states that the original creators can grant anyone authorization through a licensing agreement to use the work.
Trademarks
A trademark is a symbol, phrase, or insignia that is recognizable and represents a product that legally separates it from other products. A trademark is exclusively assigned to a company, meaning the company owns the trademark so that no others may use or copy it. A trademark is often associated with a company's brand. For example, the logo and brand name of "Coca Cola," is owned by the Coca-Cola Company (KO).
Franchises
A franchise is a license that a company, individual, or party–called the franchisee–purchases allowing them to use a company's–the franchisor–name, trademark, proprietary knowledge, and processes.
Trade Secrets
A trade secret is a company's process or practice that is not public information, which provides an economic benefit or advantage to the company or holder of the trade secret. Trade secrets must be actively protected by the company and are typically the result of a company's research and development. Examples of trade secrets could be a design, pattern, recipe, formula, or proprietary process. Trade secrets are used to create a business model that differentiates the company's offerings to its customers by providing a competitive advantage.
Trade dress
Trade dress is a legal term of art that generally refers to characteristics of the visual and aesthetic appearance of a product or its packaging (or even the design of a building) that signify the source of the product to consumers.
Plant varieties
Plant breeders' rights or plant variety rights are the rights to commercially use a new variety of a plant. The variety must amongst others be novel and distinct and for registration the evaluation of propagating material of the variety is considered.
Open Source Intiative Licenses
Before joining fab academy, I never ever had an intention to make the projects that I had done free to use for everyone. I always beleived that the effort that I had put in must be protected and felicitated. Later I found that, during worst times, there is a need for opensource innovation compared to protected commertialization. Opensource designs of ventilators, oxygen concentrators, face shields etc. had already saved a lot of lives during the pandemic. I also found that opensourcing not only promotes innovation but also enhances accessibility of the product who are in need. From now onwards, I would always advocate opensource projects as our existance is not known for the number of patents that we own, but for the sheer number of opensource projects that we had contributed to the society. I am also proud to say that, the Superfablab Kochi also created an opensource 'Alternative Respiratory Assistance Equipment' to fight Covid 19 pandemic. Some of the open source licenses are:
Apache License 2.0
GNU General Public License (GPL)
MIT license
Mozilla Public License 2.0
Common Development and Distribution License
Creative Commons
Eclipse Public License
MIT License
It is the most liberal than most other licenses and anyone can use and modify the software when they speacify original file and creator's name . The only condition is that it be accombanied by license agreement.The MIT license declaration is given below.
The MIT License
Copyright
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy of this software and
associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal in the Software without restriction,
including without limitation the rights to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense,
and/or sell copies of the Software, and to permit personsf to whom the Software is furnished to do so,
subject to the following conditions:
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all copies or
substantial portions of the Software.
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT
NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT.
IN NO EVENT SHALL THE AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER LIABILITY,
WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM, OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE
SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE SOFTWARE.
GNU General Public License
The GNU General Public License (GNU GPL or GPL) is a widely used free software license, which guarantees end users the freedom to run, study, share and modify the software. There are currently three versions of license are available under GNU. The terms and conditions of the GPL must be made available to anybody receiving a copy of the work that has a GPL applied to it ("the licensee"). Any licensee who adheres to the terms and conditions is given permission to modify the work, as well as to copy and redistribute the work or any derivative version. Software under the GPL may be run for all purposes, including commercial purposes and even as a tool for creating proprietary softwares. The GPL is a copyleft license, which means that derivative work can only be distributed under the same license terms. This is in distinction to permissive free software licenses, of which the BSD licenses and the MIT License are widely used examples. GPL was the first copyleft license for general use.
I went through all the information which I mentioned and try to understand which one is useful for me.Finally I decided to go with creative commons open source license.
Creative Commons License:
All Creative Commons licenses have many important features in common.Every license helps creators — we call them licensors if they use our tools —retain copyright while allowing others to copy, distribute, and make some uses of their work — at least non-commercially. Every Creative Commons license also ensures licensors get the credit for their work they deserve.
Attribution(CC BY):
This license lets others distribute, remix, adapt, and build upon your work, even commercially, as long as they credit you for the original creation.This is the most accommodating of licenses offered. Recommended for maximum dissemination and use of licensed materials.
Attribution-ShareAlike(CC BY-SA):
This license lets others remix, adapt, and build upon your work even for commercial purposes, as long as they credit you and license their new creations under the identical terms. This license is often compared to “copyleft” free and open source software licenses. All new works based on yours will carry the same license, so any derivatives will also allow commercial use.
Attribution-NoDerivs(CC BY-ND):
This license lets others reuse the work for any purpose, including commercially; however, it cannot be shared with others in adapted form, and credit must be provided to you.
Attribution-NonCommercial(CC BY-NC):
This license lets others remix, adapt, and build upon your work non-commercially, and although their new works must also acknowledge you and be non-commercial,they don’t have to license their derivative works on the same terms.
Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike(CC BY-NC-SA):
This license lets others remix, adapt, and build upon your work non-commercially,
as long as they credit you and license their new creations under the identical terms.
I decide to create a license for my project using Creative Commons.
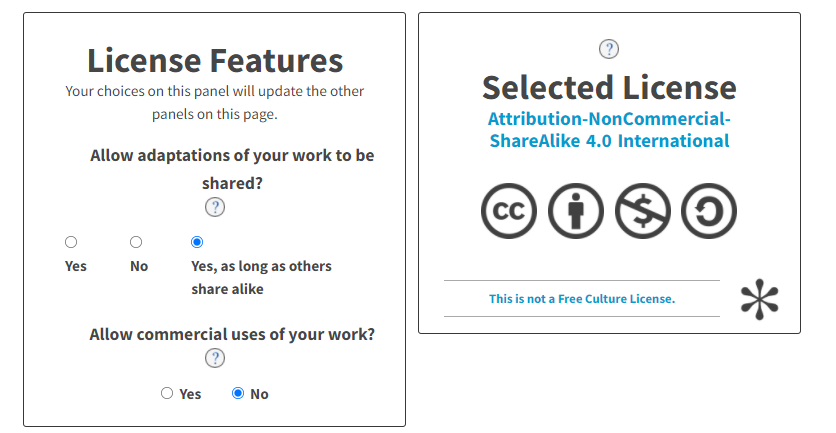

This is my Liscence

Smart Plant Monitoring System by https://fabacademy.org/2021/labs/bhubaneswar/students/deepak-chaudhry/ is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
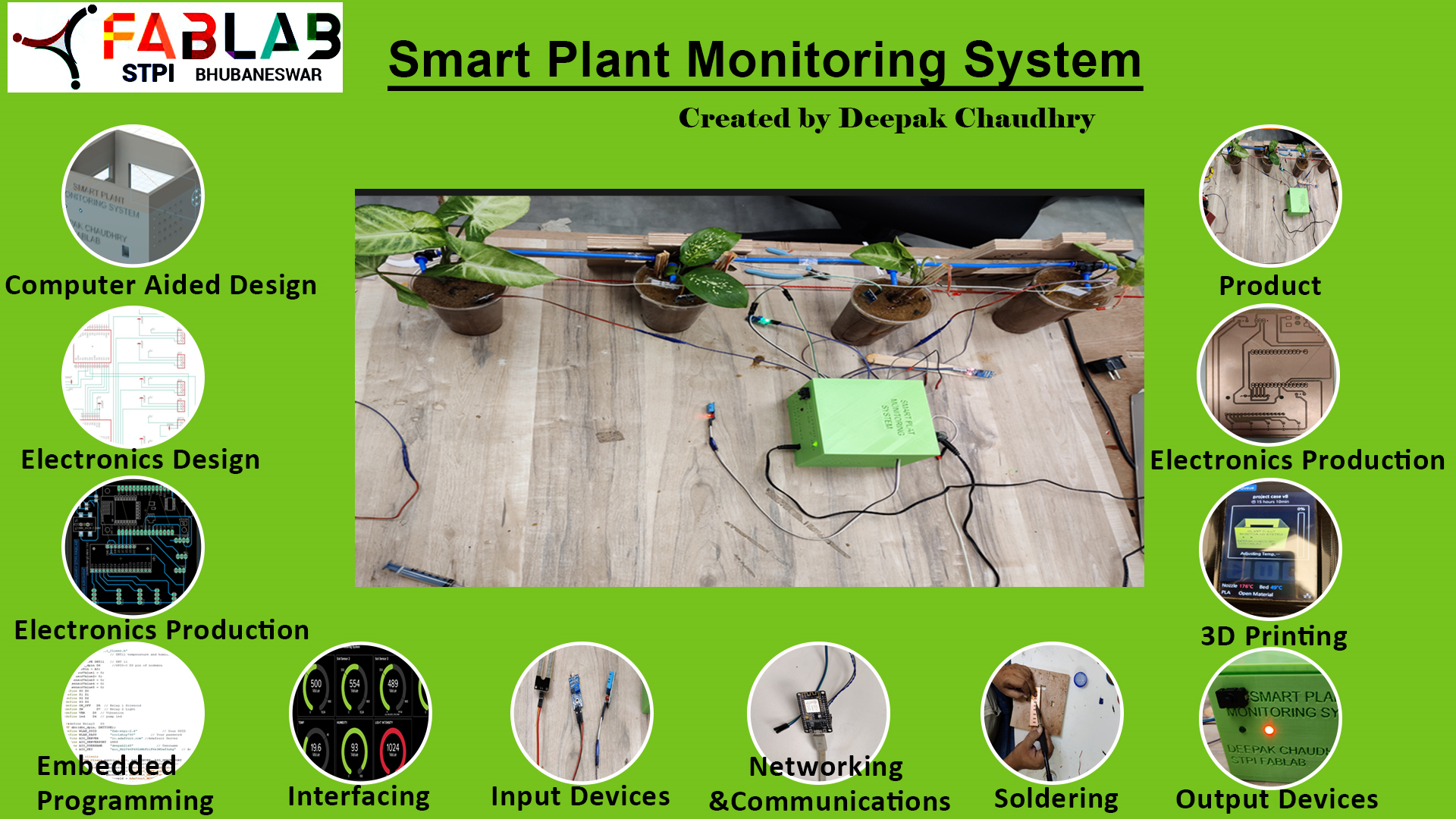
Project Slide