Group Assignment: Interface and Application Programming
Compare as many tool options as possible.
The objective of this week’s group work is to compare how the various interface tools work. We’ve selected three to highlight.
LabVIEW¶
National Instruments’ LabVIEW is specifically designed to interface with measurement devices. The program is essentially a graphical C++ compiler. There are two windows (panels in NI-speak): the left hand one below is the “front panel” (user interface), in grey to represent the old style 19” rack devices we used to use; the right hand one is the “wiring diagram” (coding environment).
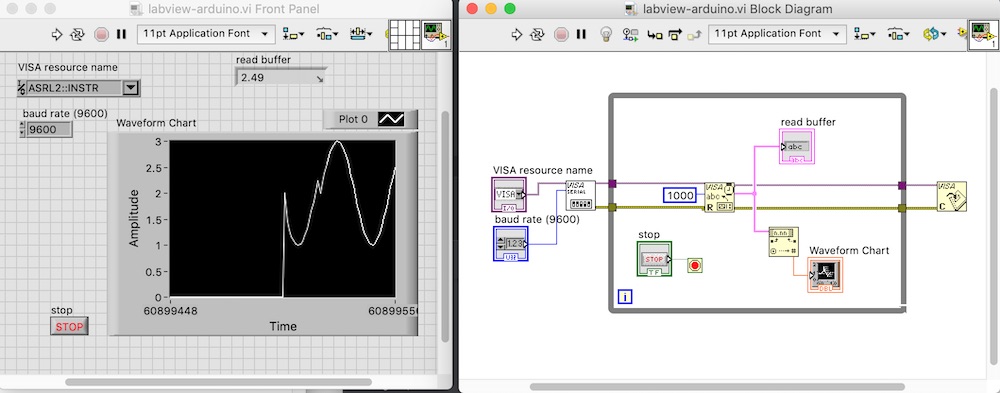
The design of our interface starts with a while loop (grey frame) and a stop button (in green). The main part of the serial interface to the Arduino is done through the three square icons (which represent functions/subroutines) in the centre of the wiring diagram. Outside the while loop, we start by initialising communications with the Arduino (VISA SERIAL). The next block is the command to read the serial buffer. This is converted to a floating point number and displayed on the front panel (Waveform Chart). Finally, again outside the loop, communications are closed with the Arduino after the stop button is pressed.
The connection to the Arduino is over the USB port.
The code is uploaded and run with the arrow at the top left of either panel.
Processing¶
The Processing 3 IDE is a text based programming environment which works well. It’s more work that the LabVIEW option, but can be used to provide a similar UI experience.
Processing works just like the Arduino IDE, in that there is an initial setup procedure that runs once, and then a draw procedure that repeats forever. All other procedures in the root part of the program also run in parallel, forever.
The code required is shown in the two screenshots below.
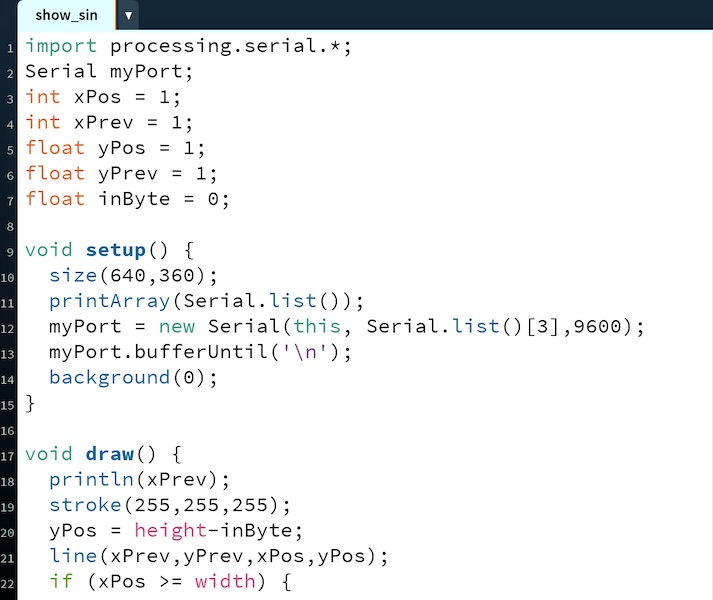

The first two lines create a serial object to use for communication with the Arduino. The next few lines are variable declarations.
The program starts with the setup subroutine, in which we define the serial port and create a connection to the Arduino.
The draw subroutine opens a new window and draws the data as a set of white lines on a black background. The code looks complicated, but it’s all just required to keep track of where the drawing cursor is from one update to the next. Trick is not to update any positional information until a new datum arrives over the serial port, which is the reason for the if (yPos != yPrev) condition.
The final subroutine reads the serial port and updates whenever there’s a new byte.
The output is shown in the screen shot below. The system isn’t quite the chart recorder of LabVIEW or Arudino - we’d have to keep track of the presented data more carefully in order to shift it along to the left. That would just require the use of an array.
JavaScript
JavaScript, often abbreviated as JS, is a high-level, interpreted programming language. It is a language which is also characterized as dynamic, weakly typed, prototype-based and multi-paradigm. Alongside HTML and CSS, JavaScript is one of the three core technologies of the World Wide Web. JavaScript enables interactive web pages and thus is an essential part of web applications. The vast majority of websites use it, and all major web browsers have a dedicated JavaScript engine to execute it.
It isn't a very difficult language, it was decidedly versatile and powerful. Being one of the most used languages for the web, has an almost infinite documentation: as a first approach you can take a look at
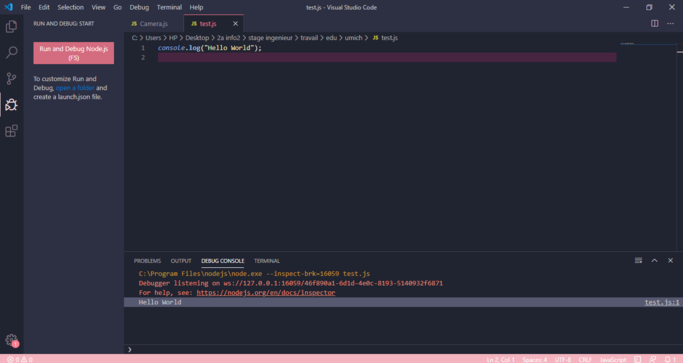
The basic "Hello World!" code in JS is:
Matlab
MATLAB (matrix laboratory) is a multi-paradigm numerical computing environment and proprietary programming language developed by MathWorks. MATLAB allows matrix manipulations, plotting of functions and data, implementation of algorithms, creation of user interfaces, and interfacing with programs written in other languages.
Although MATLAB is intended primarily for numerical computing, an optional toolbox uses the MuPAD symbolic engine allowing access to symbolic computing abilities. An additional package, Simulink, adds graphical multi-domain simulation and model-based design for dynamic and embedded systems.
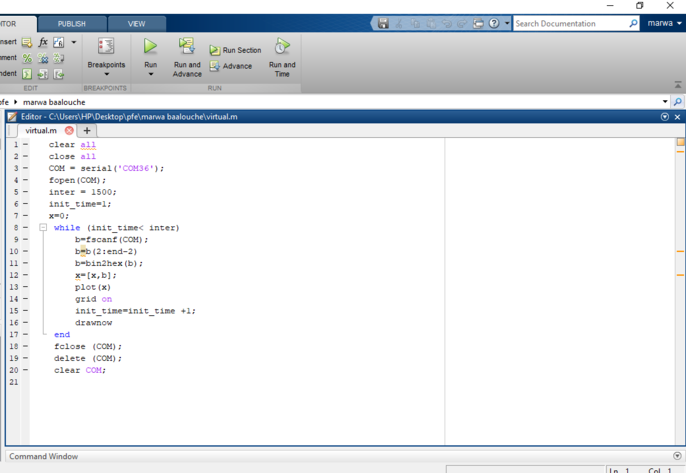
This code is wrotter to connect the arduino, sending data from it to matlab and show it in an interface;
Python
Python is an interpreted high-level programming language for general-purpose programming. Created by Guido van Rossum and first released in 1991, Python has a design philosophy that emphasizes code readability, notably using significant whitespace. It provides constructs that enable clear programming on both small and large scales. Python features a dynamic type system and automatic memory management. It supports multiple programming paradigms, including object-oriented, imperative, functional and procedural, and has a large and comprehensive standard library. Python interpreters are available for many operating systems. CPython, the reference implementation of Python, is open source software and has a community-based development model, as do nearly all of its variant implementations. CPython is managed by the non-profit Python Software Foundation.
As a first approach you can take a look at :
The basic "Hello World!" code in Python is:
Processing
Processing is an open-source computer programming language and integrated development environment (IDE) built for the electronic arts, new media art, and visual design communities with the purpose of teaching non-programmers the fundamentals of computer programming in a visual context. The Processing language builds on the Java language, but uses a simplified syntax and a graphics user interface.
This software is very simple to use (looks like arduino IDE) and on the web site of Processing there is a reference's page where you can find all the commands.
The basic "Hello World!" code in Processing is: println( "Hello world!" );
Unity
"Unity is a cross-platform game engine developed by Unity Technologies, which is primarily used to develop both three-dimensional and two-dimensional video games and simulations for computers, consoles, and mobile devices. First announced only for OS X at Apple's Worldwide Developers Conference in 2005, it has since been extended to target 27 platforms. Six major versions of Unity have been released."
I used Unity with a augmented reality project. Unity features a very unusual learning curve, meaning that since it has in itself many components (3d/2d editor, C# scripts, asset management, mechanim, audio editor, network manager and more) it can be easy to start to be proficient anyone of them, but still requires a lot of patience, practice and study to master the interconnection of all these topics in a single application.
The web is choke-full of tutorial regarding every facet of Unity, but personally I can state that one of the best starting and reference point is the official API documentation.