
Molding is a manufacturing process in which we are creating our own shapes using materials such as wood and wax ,
followled by casting with plastics, metals and even with rubber.
molding is usually preferred process for manufacturing plastic parts.
casting involves pouring liquid metal into a mold, which contains a hollow cavity of the desired shape,
and then allowing it to cool and solidify.
The solidified part is also known as a casting, which is ejected or broken out of the mold to complete the process.
Casting is most often used for making complex shapes that would be difficult or uneconomical to make by other methods
I decided to cast and mould a simple fab lab logo with my name on it
Design files were made in Inventor
review the safety data sheets for each of your molding and casting materials,
then make and compare test casts with each of them
I was in group with kioko derick and cedric
1.The Smooth-Cast™ 300 Series of liquid plastics are ultra-low viscosity casting resins that yield castings that are bright white and virtually bubble free. Vacuum degassing is not necessary.
They offer the convenience of a 1A:1B by volume or 100A:90B by weight mix ratio.
The differences between them are pot life and demold time.
2. Pot life 3 min, cure time 10 min.
3. Safety - Wear safety glasses, long sleeves and rubber gloves to minimize contamination risk. Use only in a well-ventilated area
4. Preparation - These products have a limited shelf life and should be used as soon as possible. Materials should be stored and used in a warm environment (23°C).
All liquid urethanes will react with moisture in the air, causing bubbles. Use in a low humidity environment (below 50% RH).
Mixing containers should have straight sides and a flat bottom. Mixing sticks should be flat and stiff with defined edges for scraping the sides and bottom of your mixing container.
Instructables LED and resistor Tutorial
1.Handling Precautions: Minimize breathing of vapors and avoid prolonged or repeated contact with skin. Wear proper protective equipment.
If ventilation is not sufficient, wear proper respiratory equipment. Avoid moisture contamination.
2. Respiratory Protection: Follow OSHA respirator regulations 29 CFR 1910.134 and European Standard EN 149; wear an MSHA/NIOSH or European Standard EN149 approved respirator.
3. Protective Clothing/Equipment: Wear chemically protective gloves. Wear protective eyeglasses per OSHA eye and face protection regulations
It is easy to use silicone rubber compounds that feature convenient one-to-one by volume mix ratios (no scale necessary).
Both have low viscosities for easy mixing and pouring, vacuum degassing is not necessary.It cures at room temperature with negligible shrinkage.
Silicones do not have great tear strength. They are good for making simple one- or two piece block molds.
It is suitable for a variety of art-related and industrial applications including making one and two-piece block molds for sculpture and
prototype reproduction, casting plaster, resins and wax.
Use in a properly ventilated area (“room size” ventilation). Wear safety glasses,
long sleeves and rubber gloves to minimize contamination risk. Wear vinyl gloves only.
Latex gloves will inhibit the cure of the rubber.
Store and use material at room temperature (73°F/23°C). Storing material at warmer temperatures will also reduce the usable shelf life of unused material.
These products have a limited shelf life and should be used as soon as possible. Premix Parts A and B thoroughly before using.
Allow to cure as prescribed (75 minutes for OOMOO® 25 ) at room temperature (73°F/23°C) before demolding.
Post curing the mold an additional 4 hours at 150°F (65°C) will eliminate any residual moisture and alcohol which is a by product of the condensation process and may inhibit some resins.
Allow mold to cool to room temperature before using. Do not cure rubber where temperature is less than 65°F/18°C.

The PMC®-121 Series urethane rubbers feature convenient one-to-one by volume mix ratios.
PMC®-121/30 Dry and PMC®-121/30 Wet are exceptionally strong and abrasion resistant for soft urethane mold rubbers.
The dry version does not exude oil and can be used for casting waxes, Smooth-On liquid plastics, gypsum plasters and other materials.
The wet version exudes oil that aids in demolding hard plasters and concrete.
Materials should be stored and used in at room (73°F/23°C). Humidity should be low.
These products have a limited shelf life and should be used as soon as possible. Wear safety glasses,
long sleeves and rubber gloves to minimize contamination risk. Good ventilation (room size) is necessary.
A release agent is necessary to facilitate demolding when casting into or over most surfaces.
Use a release agent made specifically for mold making (Universal® Mold Release available from Smooth-On).
A liberal coat of release agent should be applied onto all surfaces that will contact the rubber.
Allow rubber to cure overnight (at least 16 hours) at room temperature (73°F/23°C) before demolding.
Cure time can be reduced with mild heat or by adding Smooth-On “Kick-It®” Cure Accelerator. Do not cure rubber where temperature is less than 65°F/18°C.
a release agent should be applied to the mold before each casting. The type of release agent to use depends on the material being cast. The proper release agent for wax,
liquid rubber or thermosetting materials (i.e. Smooth-On liquid plastics) is a spray release made specifically for mold making (available from Smooth-On or your distributor.
Prior to casting gypsum plaster materials, sponge the mold with a soap solution for better plaster flow and easy release.

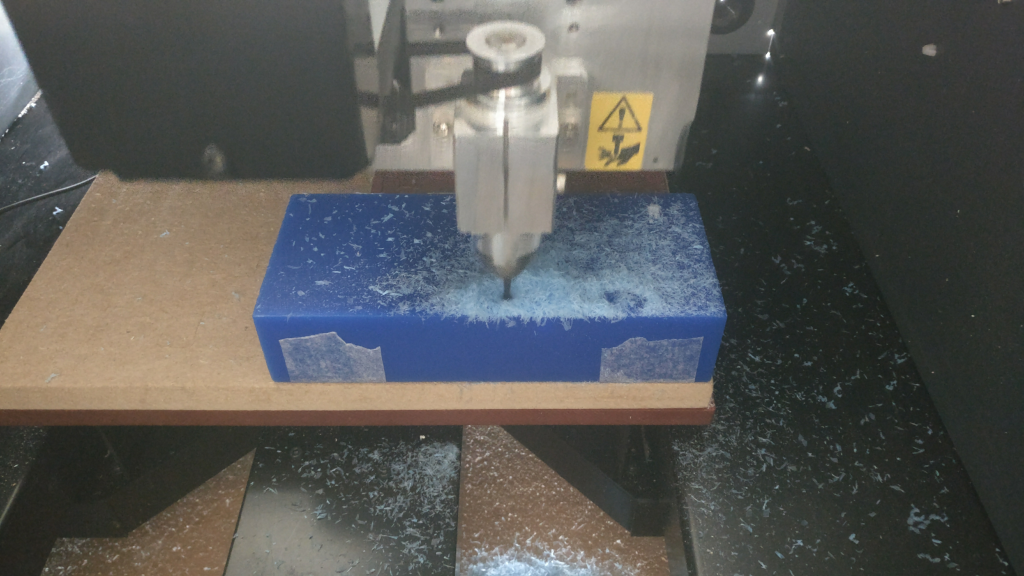
design a mold around the stock and tooling that you'll be using,
mill it (rough cut + (at least) three-axis finish cut),
and use it to cast parts
while designing i kept in mind that Casting is a manufacturing process in which a liquid material is poured into a mold,
which contains a hollow cavity of the desired shape, and then allowed to solidify.
Mold design is one of the most important steps in the process because the shape and attributes of the mold will directly affect the final product
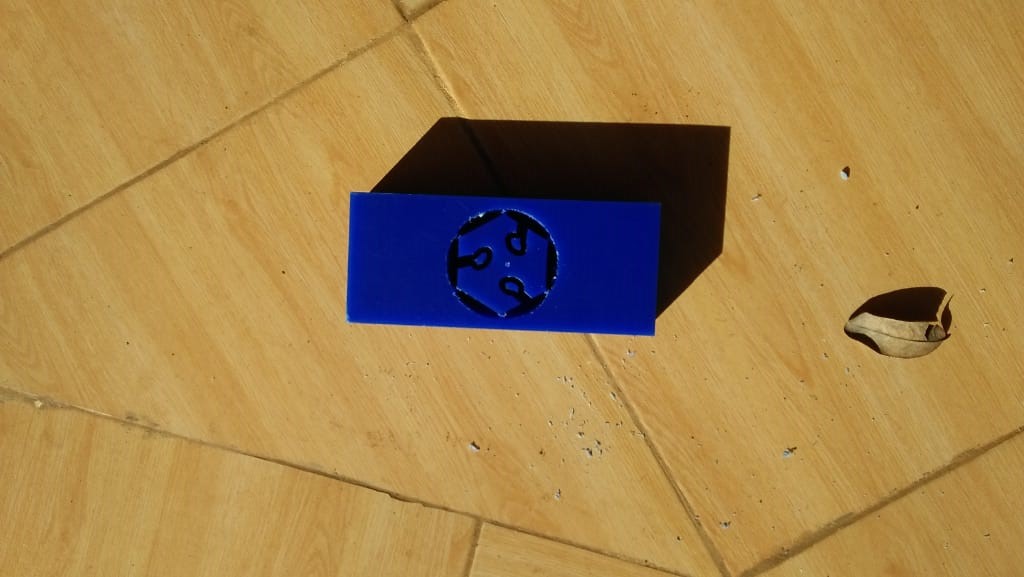
I designed the fab lab logo using inventor.
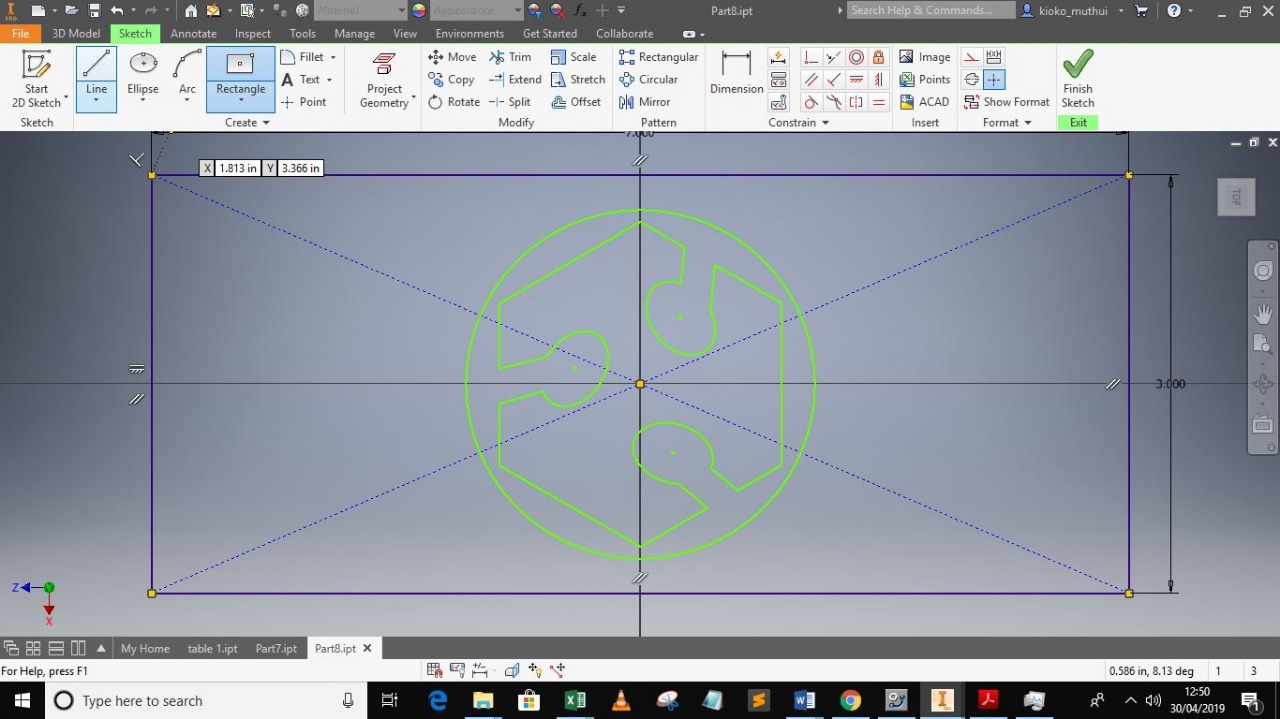
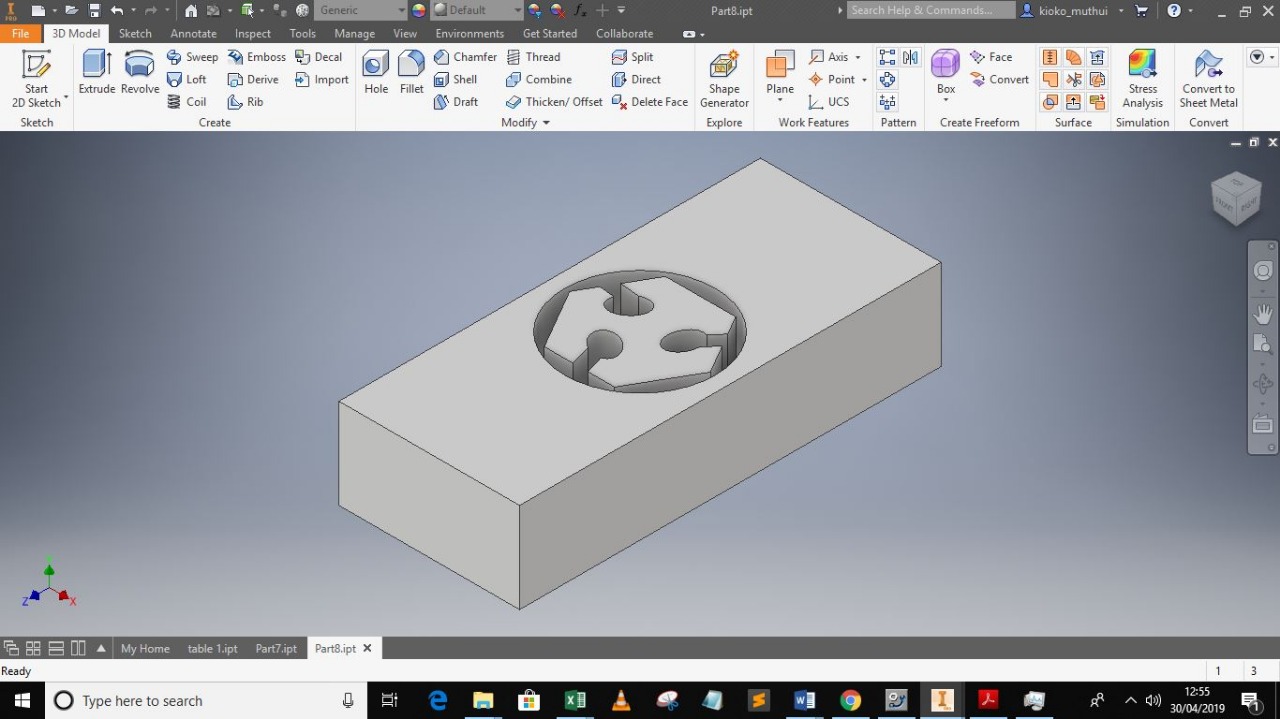
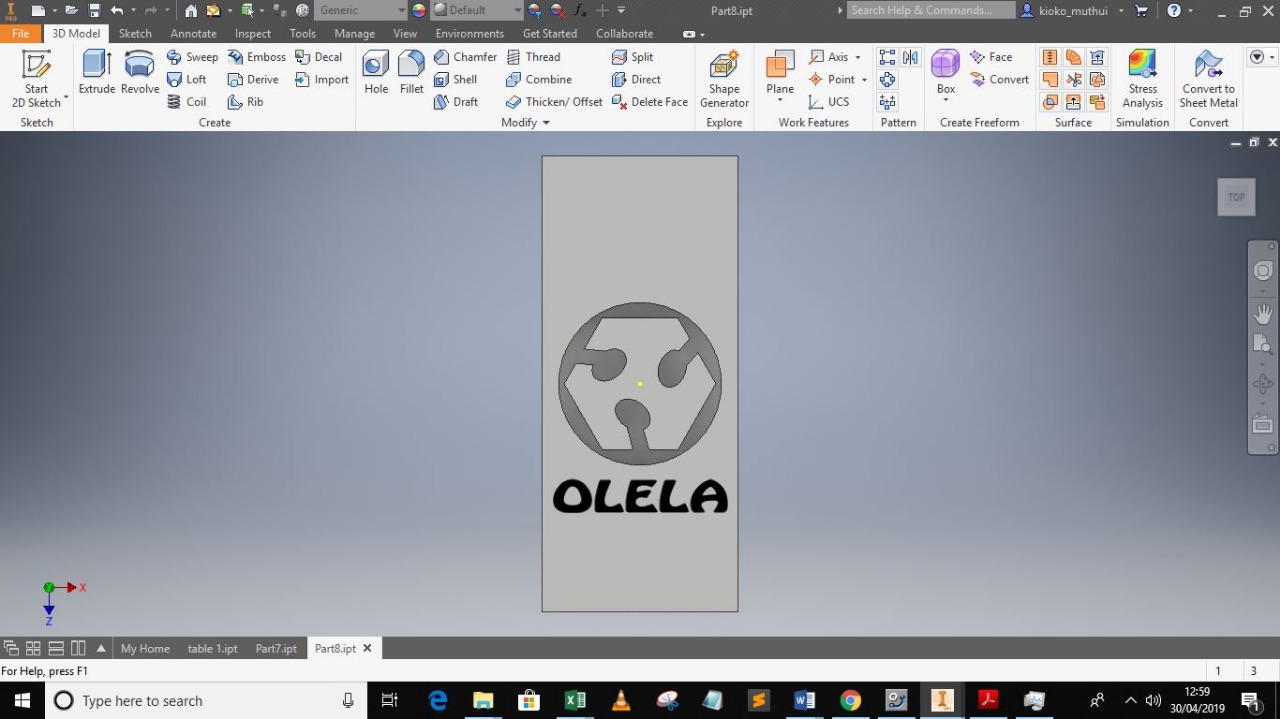
i desided to make my name part of the mould bt it was it was not extruding so i desided to print it without the name
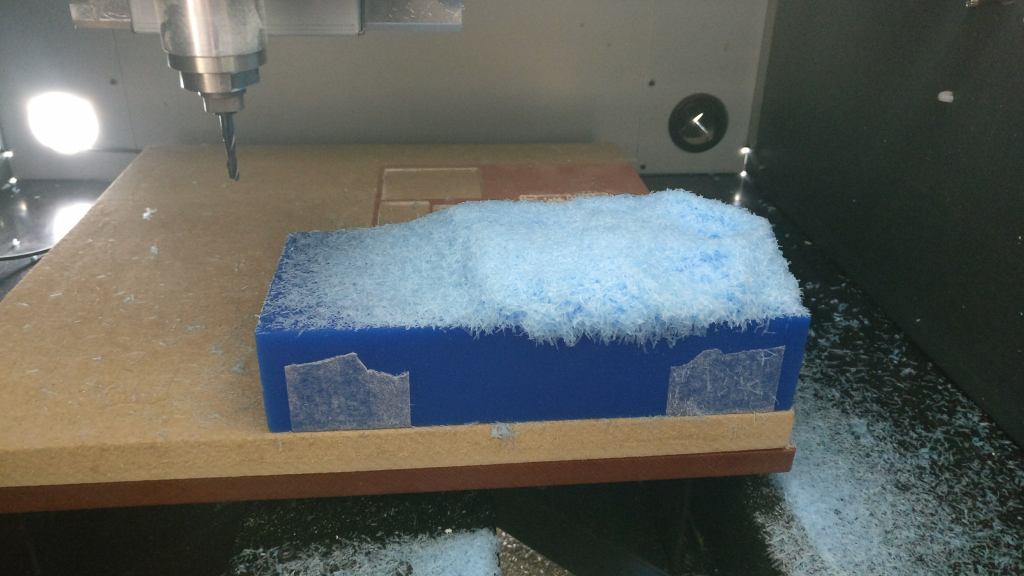
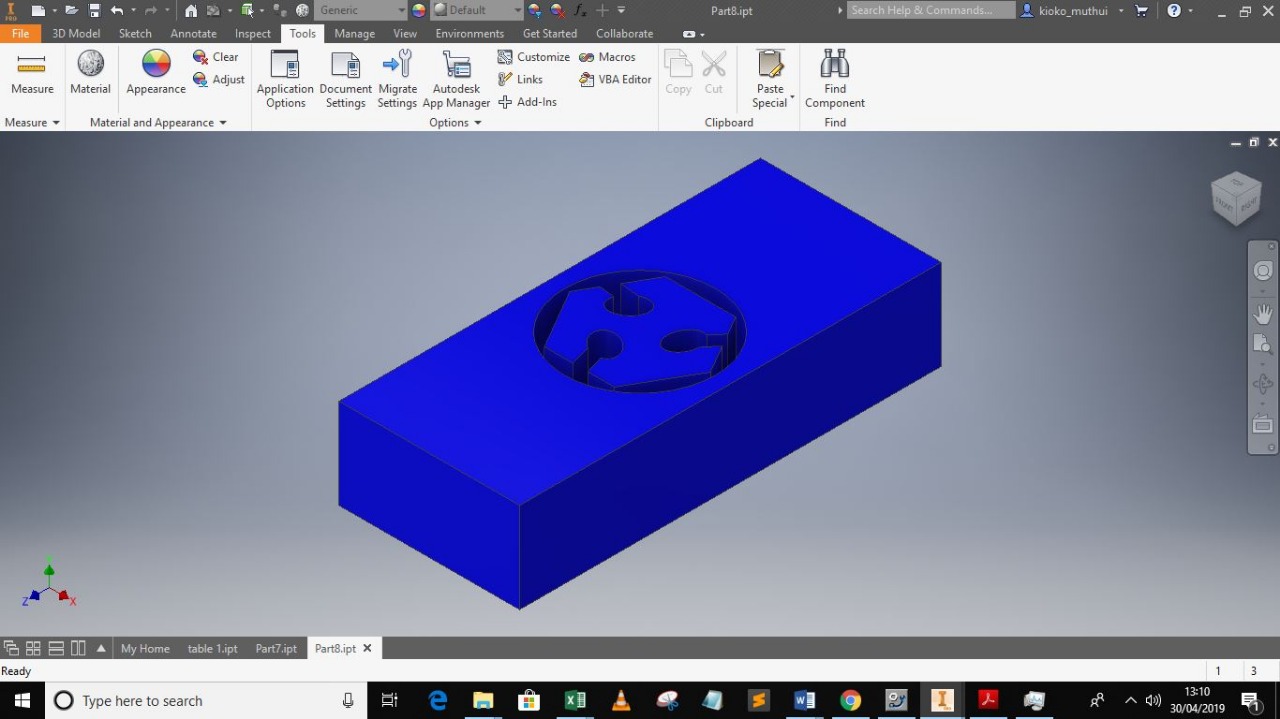
Machine run





Molding
For this practical I took two cups to measure the two parts of the molding liquids and a mixing container.
I set up in one of the tables in our labs as shown.
since I will be mixing the two ingredients I wore gloves.
Before mixing I made sure I had everything I needed set up on the table.
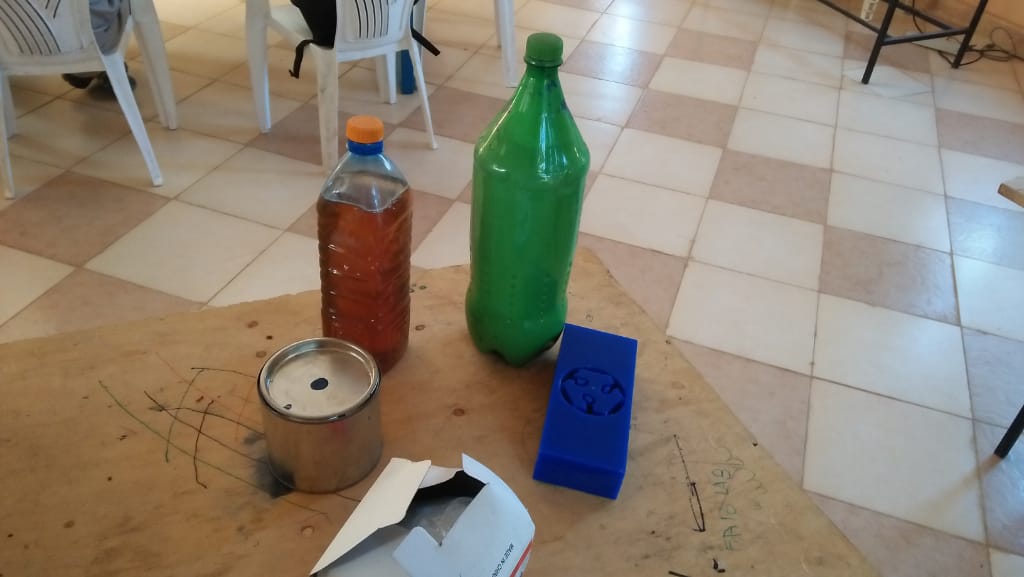
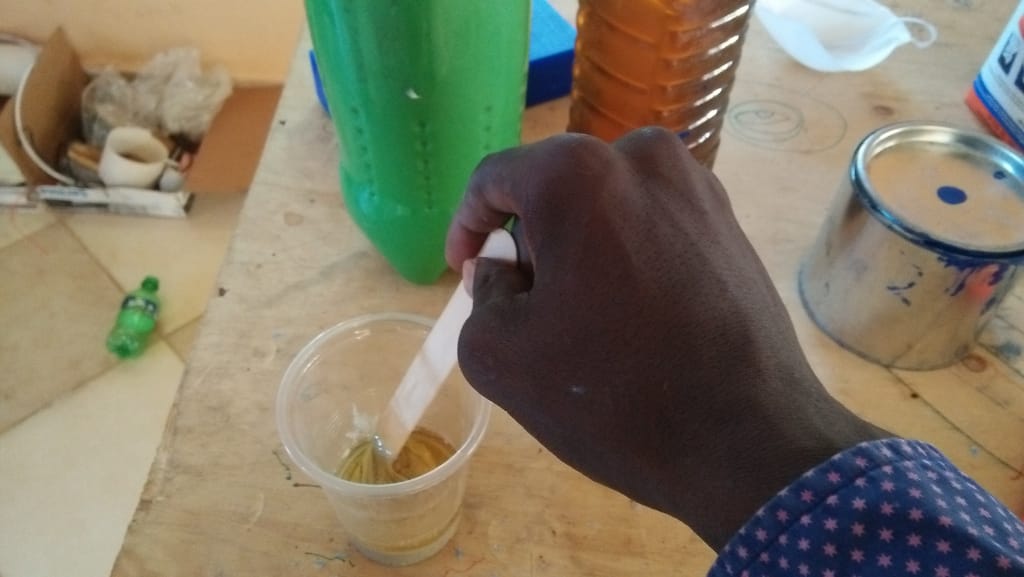


For casting I used epoxy, and it was delivered in measured quantities to the lab. The epoxy was to be mixed in the ratio of 2:1.
From the size of the bottles it is clear which bottle is for 2 and which one is for 1.
After one day, my mould was ready i then loosened the blocks and extracted them out.
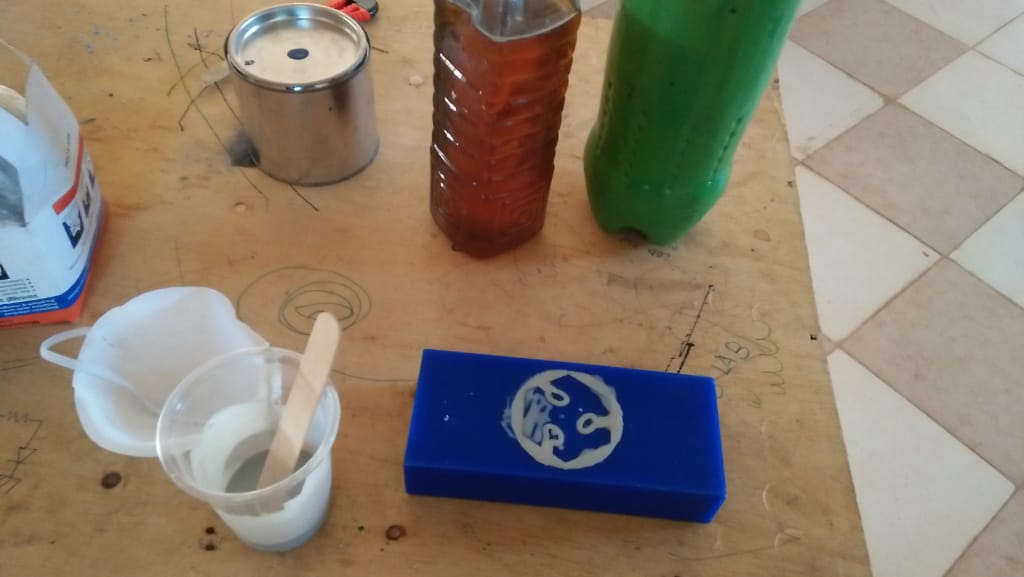
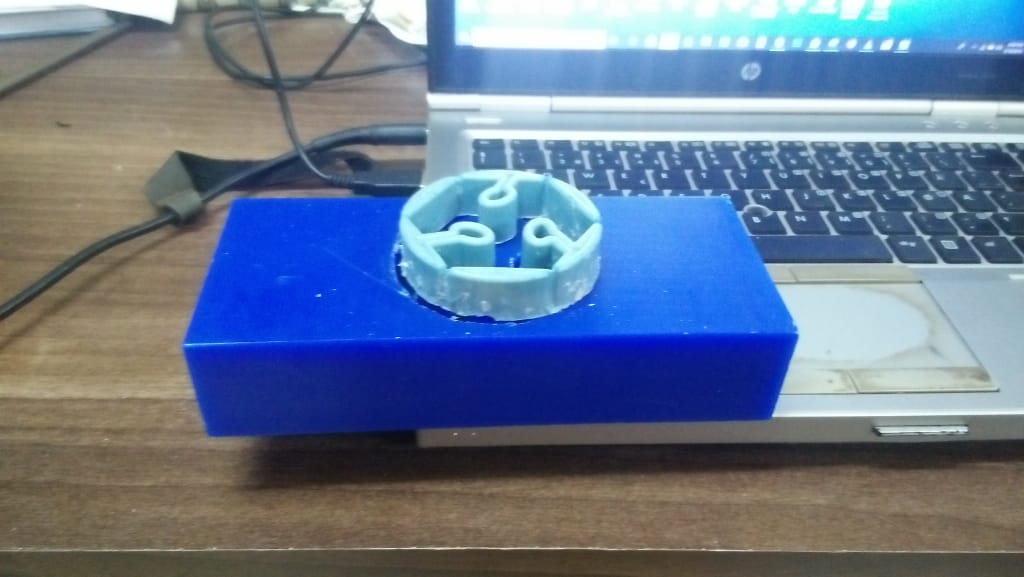
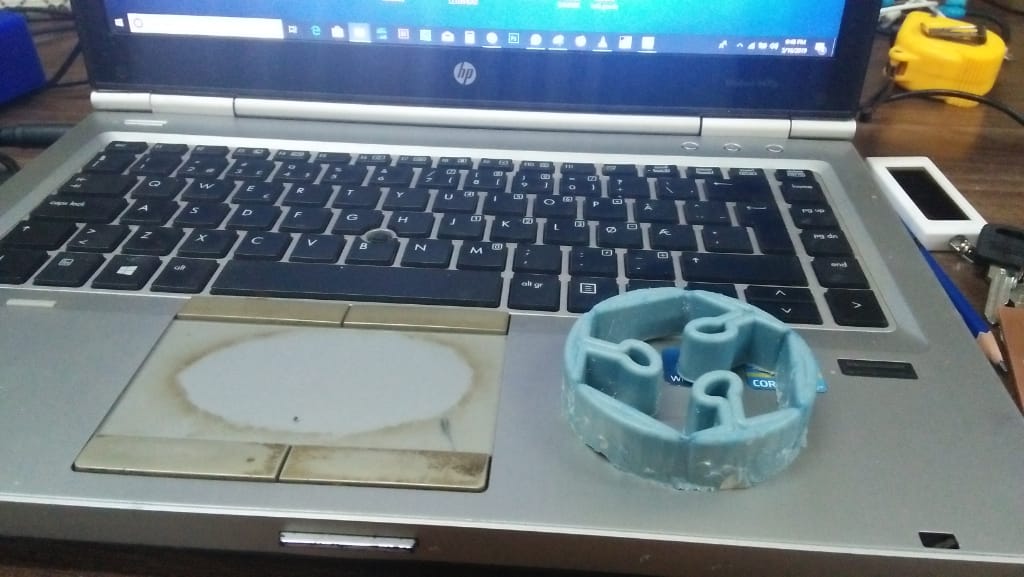
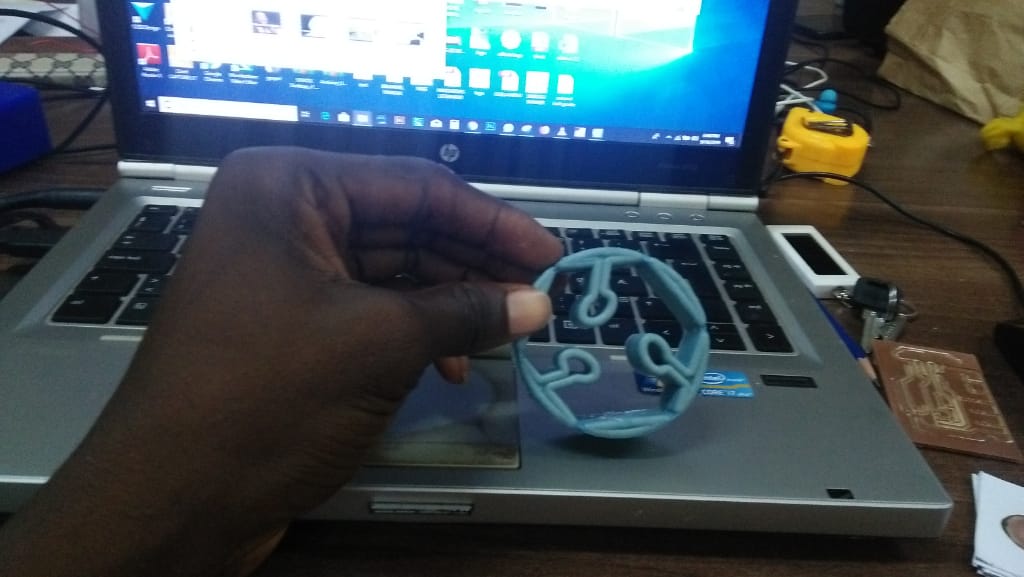




Finalybr>
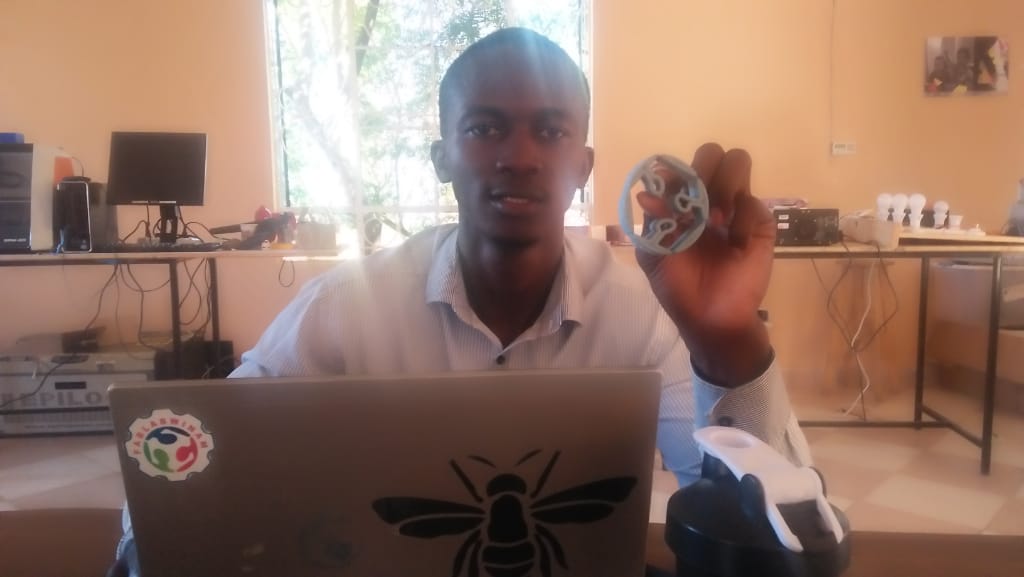

For custing i used Epoxy
For casting I desided to use cement as my material and below is the diagram of my process of casting
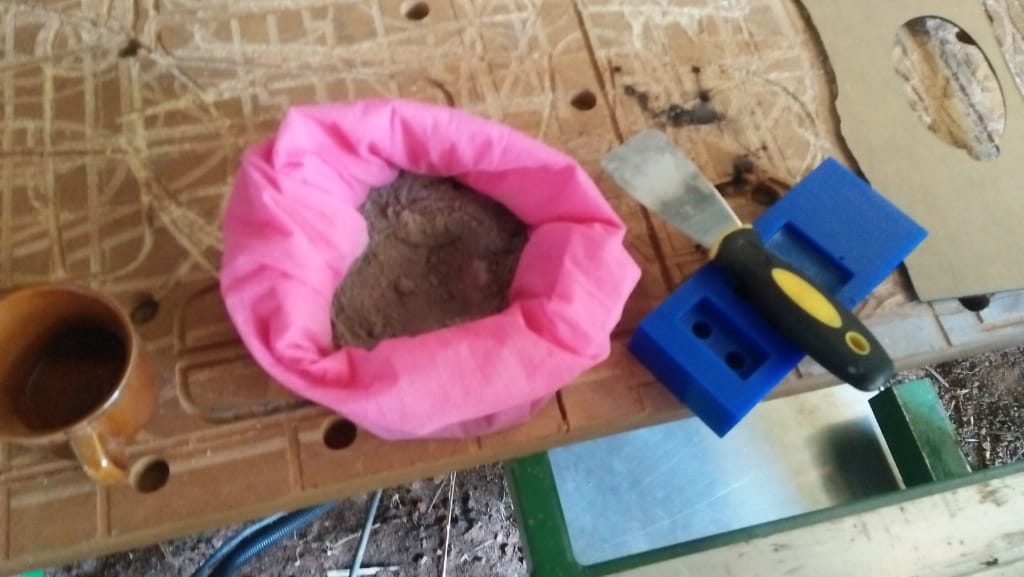
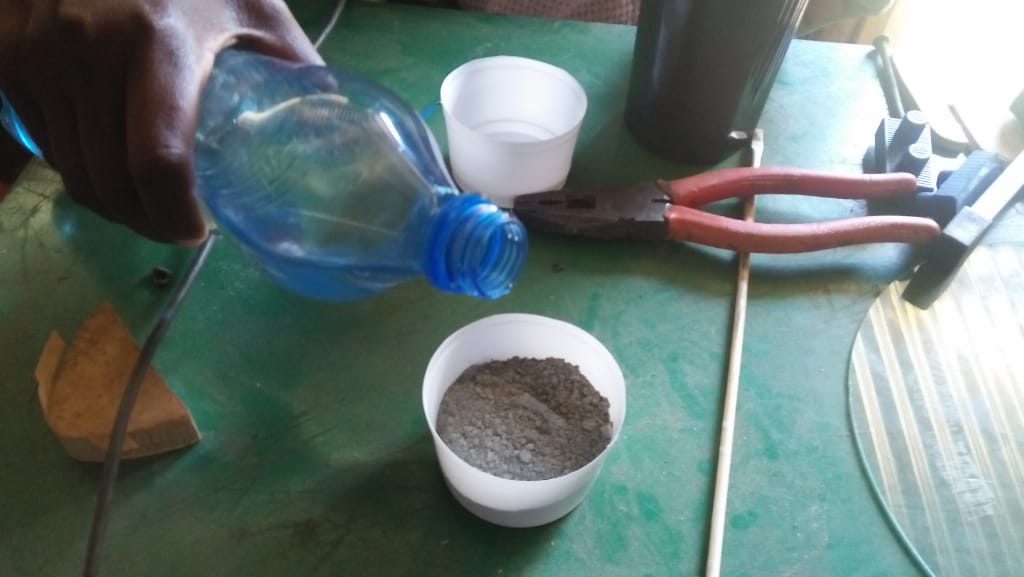
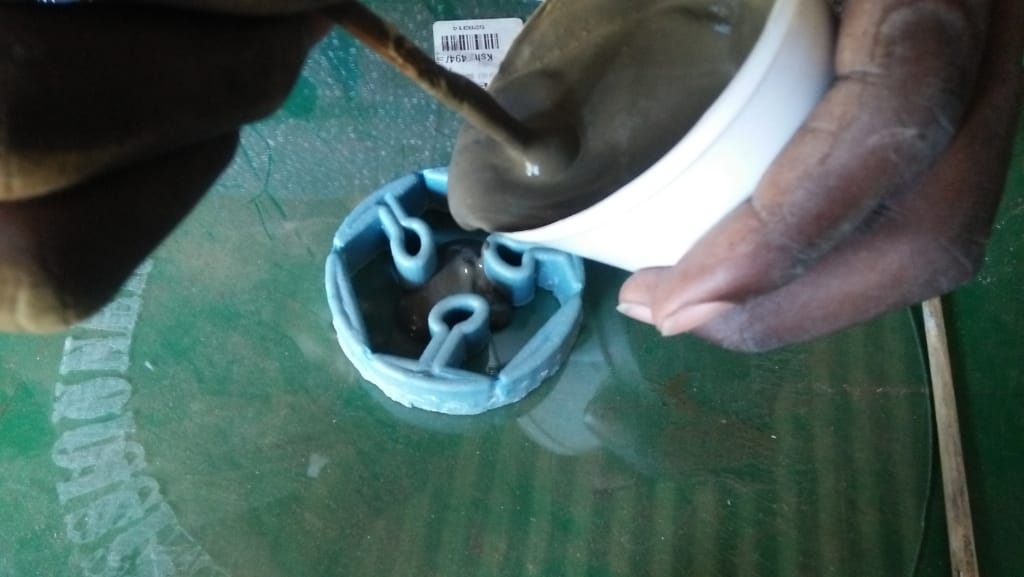
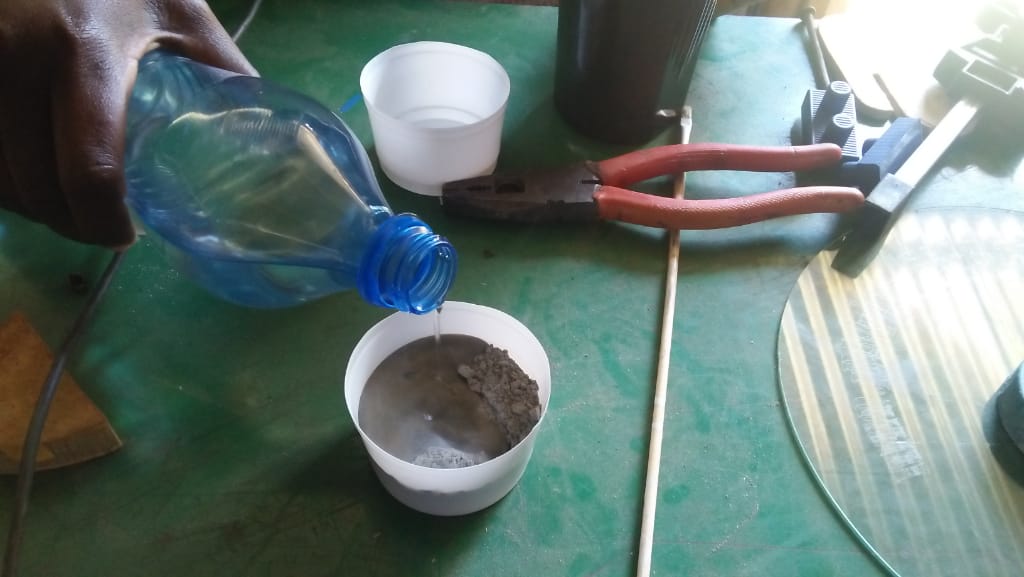
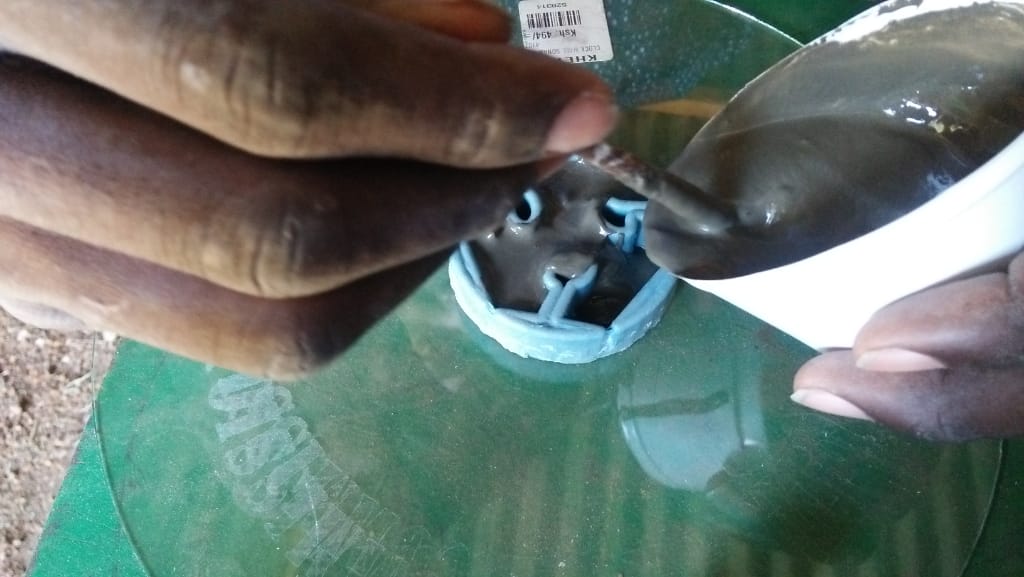
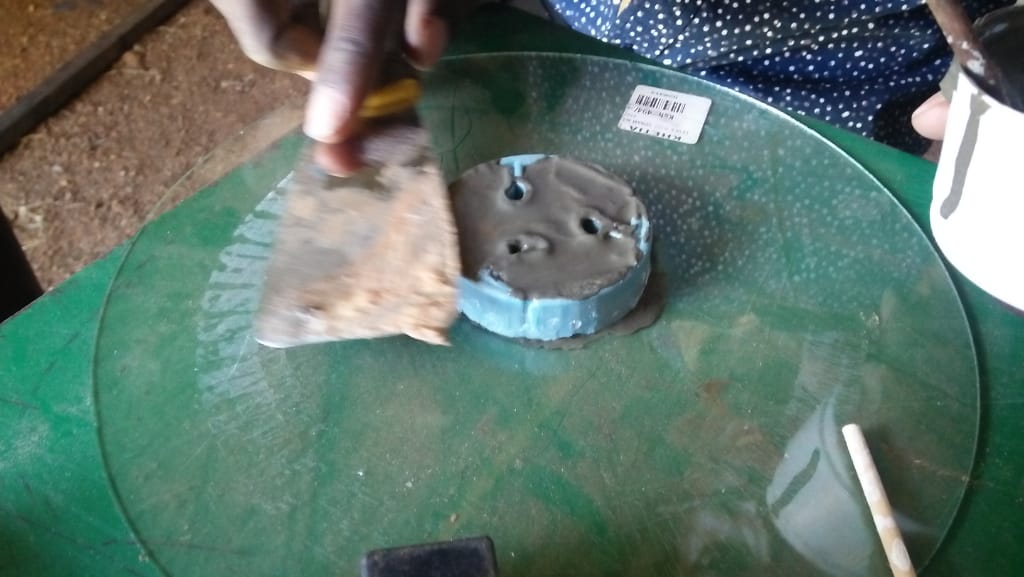






After several attempts i still dnt manage to produce my cast, in the second day after i had done my casting,
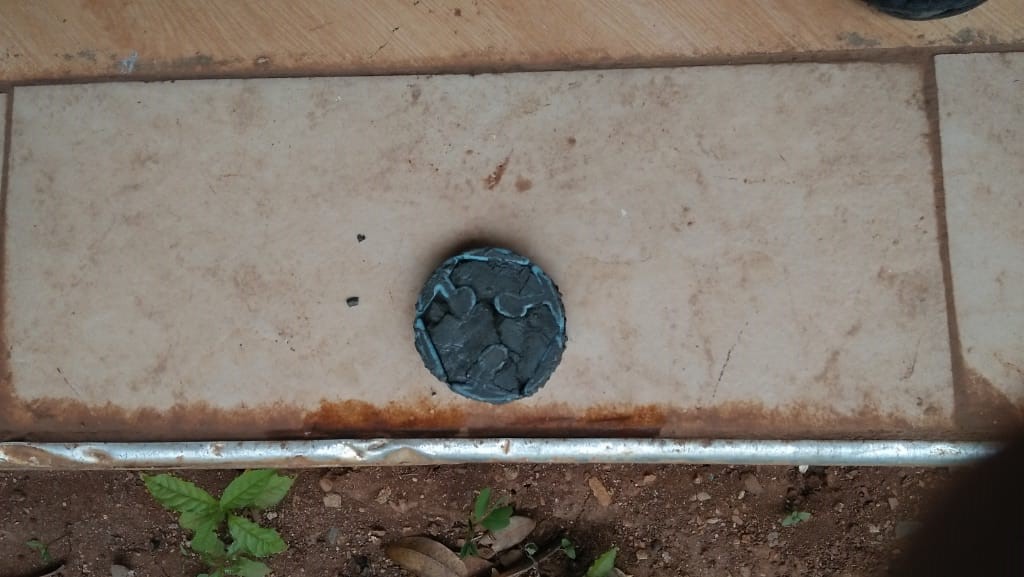
i dnt do curing since i used cement and i found it broken
I dint loose hope i tried another method here by i used soap as shown below

wile i was using soap
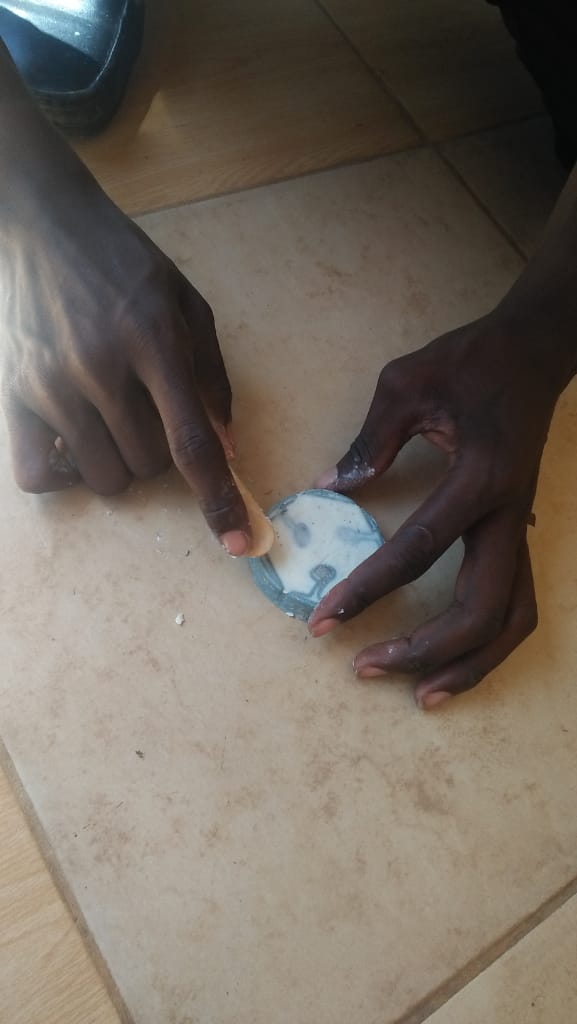
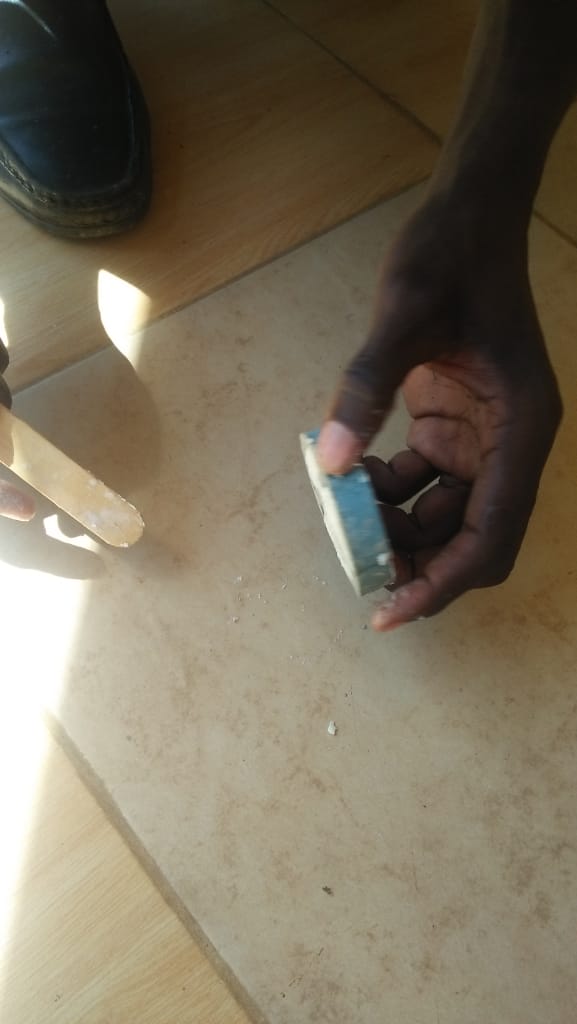


After all the strugle i had this is my final cast
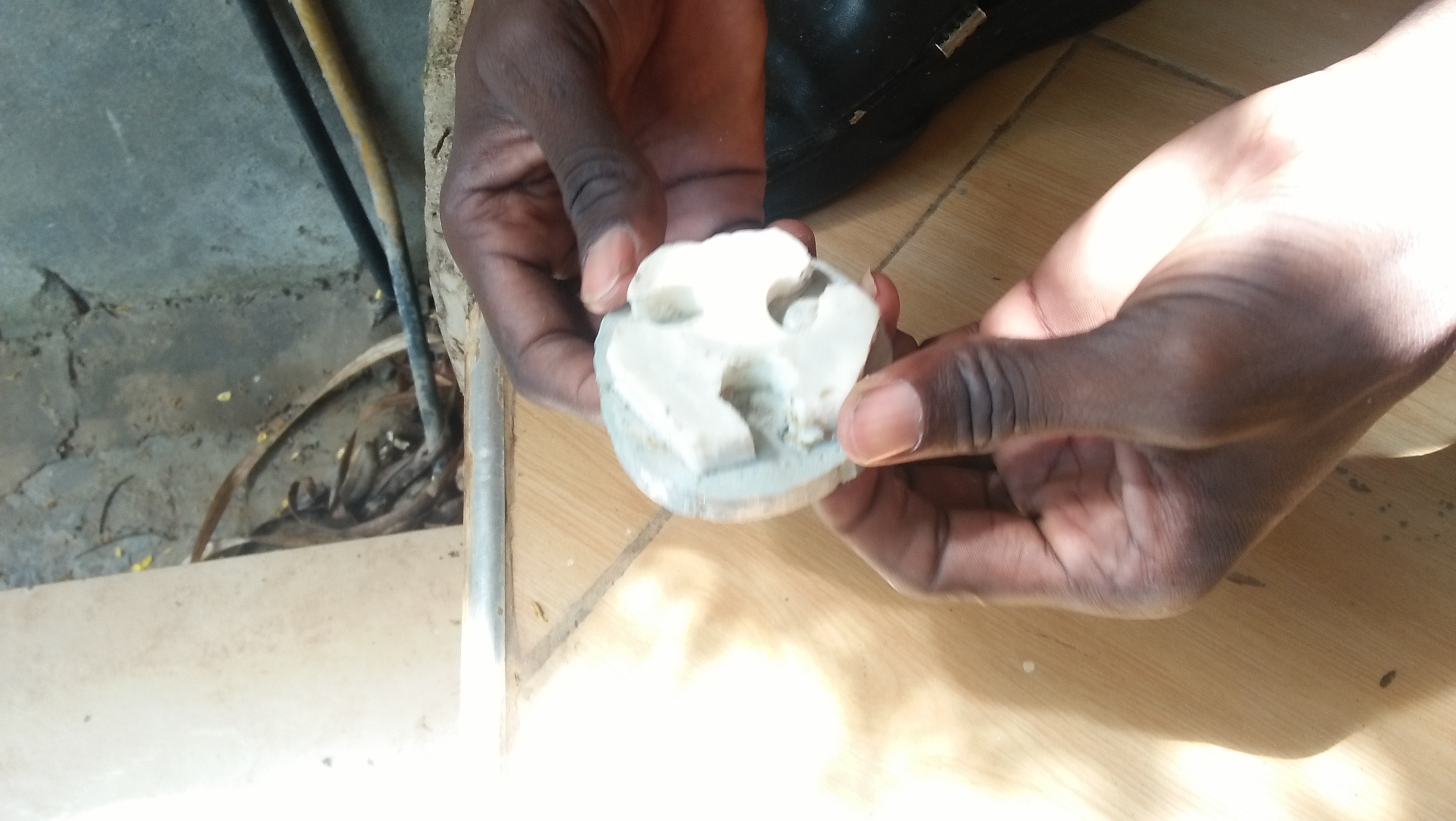
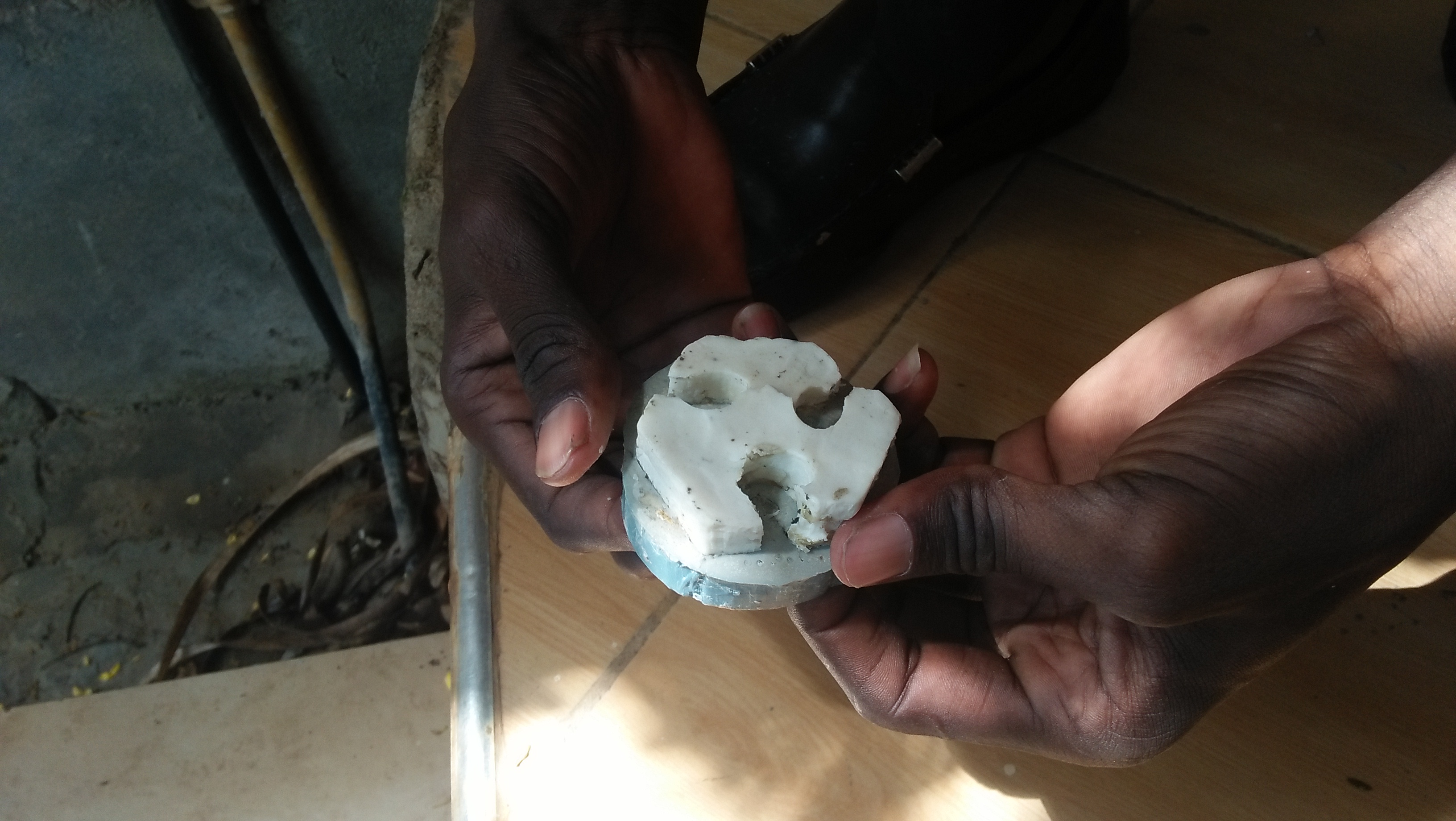
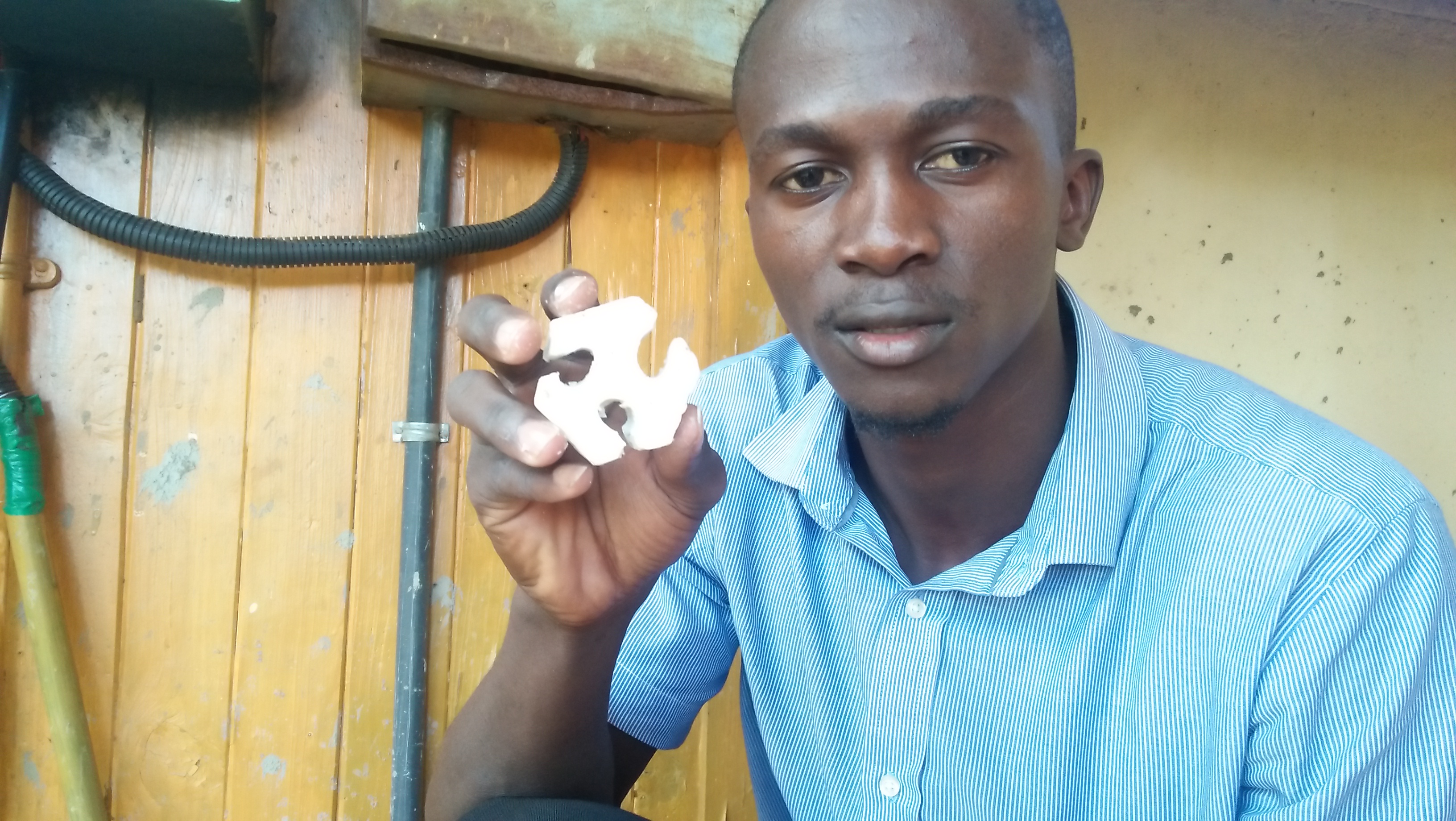



Download