3. Computer Aided design¶
jannuary 30
I did a sketch using paintbrush, a really simple 2D paint/drawing software. With this software you can edit also photos and change them, not only to reduce the canvas as well as to reduce file weights.
Openscad is a simple CAD software very reliable, parametric, easy to use for simple CAD structures. But you can do very complex functional shapes with high accuracy.
The drawbacks happens when the project start to be huge or you need to use simulations or calculations, or even measurements.
Project overview¶

Dimensions¶

Features¶

Security¶

Openscad¶
CGS, constructive solid geometry, where its possible to make a complex geometry using primitives with boolean operators.
If you want to start with Openscad, start here and here.
Openscad Rendering¶
MAC: fn+F5 (Preview) and fn+F6 (Rendering)
| Rendering step | meaning | comment |
|---|---|---|
| Compiling design (CSG Tree generation)… | Verify de code | |
| Rendering Polygon Mesh using CGAL… | CGAL is a software project | Acess to efficient and reliable geometric algorithms in the form of a C++ library |
| Geometries in cache: 55 | 55 primitives | |
| Geometry cache size in bytes: 9688424 | ~10MB | |
| CGAL Polyhedrons in cache: 10 | number of Polyhedrons | (examples bellow) |
| CGAL cache size in bytes: 75748224 | memory size | |
| Total rendering time: 0 hours, 0 minutes, 0 seconds | ||
| Top level object is a 3D object: | ||
| Simple: yes | ||
| Vertices: 13420 | number of vertices | |
| Halfedges: 67292 | see pic | It doubles the edges |
| Edges: 33646 | number odf edges | |
| Halffacets: 40448 | see pic | It doubles the facets |
| Facets: 20224 | number of facets | (see below) |
| Volumes: 2 | ||
| Rendering finished. |
In Solid modeling, two schemes are used: CSG and B-rep.
1In CSG, a solid is represented as a set-theoretic Boolean combination of primitive solid objects, such as blocks, prisms, cylinders, or toruses. The class of orientable 2-manifold objects is a popular and well understood class of surfaces commonly used for B-reps
Geometry basic names¶

Halfedges¶
(source: https://doc.cgal.org/latest/HalfedgeDS/index.html)
CGAL represent facets using 2 halffacets, the facet facing to the interior of the volume and the facet facing the exterior, and edges using halfedges, the halfedge facing into the interior of the facet, and the halfedge facing to the exterior of the facet.
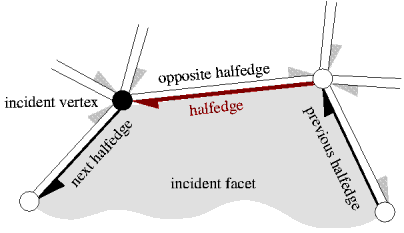
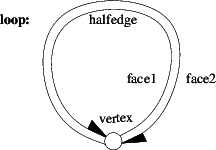
Polyhedrons¶
Polyhedral surfaces in three dimensions are composed of vertices, edges, facets and an incidence relationship on them.
The organization beneath is a halfedge data structure, which restricts the class of representable surfaces to orientable 2-manifolds - with and without boundary. If the surface is closed we call it a polyhedron:
Readings that help to understand the upper table:¶
https://doc.cgal.org/latest/Nef_3/index.html
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Manifold
Open halfspaces¶
Boat¶
$fn=128;
a=100; // altura do flutuador //hull height
r=200; //raio do cilindro //cylinder radius
b=1000;//boca do barco //boat width
c=600; //comprimento do flutuador //lenght
cep=250;//curvatura na popa //Stern curve
m=7;//scale
lmf=10;//scale
//flutuadores //Hulls
translate([b,0,0])mirror()difference(){
intersection(){
scale([1,m,m])cylinder(a,r,r);
translate([0,0,-5000])scale([lmf/2,8*m,8*m])sphere(a);
translate([0,0,5600])scale([lmf/2,8*m,8*m])sphere(a);
}
translate([150,0,400])scale([2,6,1])sphere(150,true);//abertura
translate([-150,0,400])scale([2,6,1])sphere(150,true);
}
difference(){
intersection(){
scale([1,m,m])cylinder(a,r,r);
translate([0,0,-5000])scale([lmf/2,8*m,8*m])sphere(a);
translate([0,0,5600])scale([lmf/2,8*m,8*m])sphere(a);
}//abertura
translate([150,0,400])scale([2,6,1])sphere(150,true);
translate([-150,0,400])scale([2,6,1])sphere(150,true);
}
//cobertura para os painéis solares //solar pannels
difference(){
translate([0,0,-4.7*lmf*a])rotate([0,90,0])cylinder(b,5.3*lmf*a,5.3*lmf*a);
translate([-10,0,-4.745*lmf*a])rotate([0,90,0])cylinder(b+20,5.3*lmf*a-10,5.3*lmf*a-10);
mirror([0,1,0])translate([c-100,-2.5*c,2*a])rotate([0,0,0])cylinder(4*a,c,c);//proa
translate([c-100,-2.5*c,2*a])rotate([0,0,0])cylinder(4*a,c,c);
translate([-15,-5.3*lmf*a,-5.15*lmf*a*2])cube([b+40,2*5.3*lmf*a,2*5.3*lmf*a]);//popa
}
Paintbrush¶

Photo source: (https://paintbrush.sourceforge.io)
Readings and Useful links¶
- sketchfab
- openscad cheat sheet
- paintbrush
- CSG
- More about CGAL
- CGAL
- Computational Geometry, introduction
- Mesh
- facets
- Geometry explained
NEXT: furher project 3D Models¶
I will use 3D Fusion360 for reasons related to calculations and simulation. I will share it at the my sketchfab site
Hull catamaran reference procedure with, Fusion360 forum work flow:
- 1. Create a number of planes which might be sufficient enough to represent the surface - 2. Create a sketch on every plane that woul represent a cut in this section of the boat - 3. Use the "Loft" feature in the "Sculpt" environment and select multiple sketches - 4. Delete the surfaces you would not need and mirror your design
But, I didn’t use it yet. My strategy, for this first Aqua Nostra design, was to use simple steps, like:
-
- Find the upper hull catamaran shape in the real market[1];
-
- Copy the contour and addapt it to the overall dimensions defined: 1200x1000x800mm;
-
- Use the extrude and fillet tools to shape the hull;
-
- Reinforce the structure wth aluminium bars (two), see reference [2];
-
- Include the engine;
-
- Mirror the hull, with the fusion 360 mirror tool;
-
- Draw the platform: error here, I did it based on a sketch that started in the hulls: if you change it, its a problem because all is linked;
-
- Assemble the boat: solar pannel;
-
- Rudder and motors.
-
- Cut transverse parts in Fusion360 to be cutted in a laser in order to reinforce the hulls.
[1] Reference from the market [2] Autonomous Surface Vessels
Simulation¶
Not totally completed.
- I just simulated it on FUSION360 using pressure.
- I want to use the Open Dynamics Engine and Modelica (don’t know how yet);
- I would like to use also BLENSER, UNITY or Unreal (don’t know how yet).
