3D scanning and printing
Group Assignment
For the group assignment, we tested all the 3D printers of CIT-Fablab. Including: Makerbot replicator 2, replicator 2x, replicator +, Markforged and Nobel XYZ. We identified the optimal parameters, and solved the problems that we found. All the printers work with these files extension: .stl .obj, .thing. We will show the parameters that we found.
3D Printing
Makerbor Replicator 2
This is the makerbot’s printer of 4th generation, works with operation systems like: Windows 7/8+, Mac OS X 10.6+, Ubuntu Linux 10.10+. This printer use PLA filament. The maximum tilt angle without support is 25º. The minimum thickness that can generate with a perfect vertical extrusion is 2.5mm.
The raft of this printer is the hardest to remove, comparing with the other printers. The calibration takes a few minutes, but sometimes you have to repeat this process.

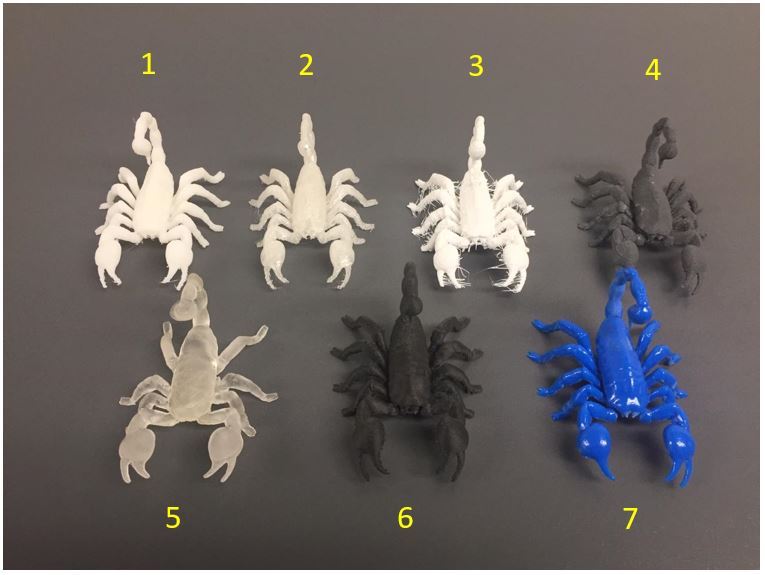
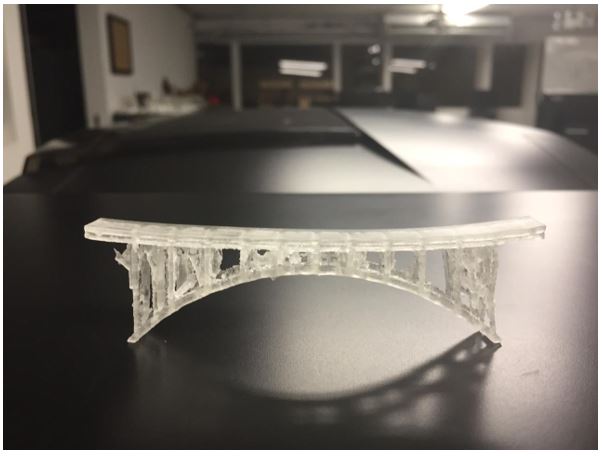
Here are some tests from this printer

Makerbot Replicator 2X
This 3D printer has two extruders, and is able to make complex designs with interior support using soluble materials. This printer works with ABS filament, for this reason the printer has a heat bed that needs 133º C to work without problems.
This printer also has a protector at the top, because need to conserve the heat of the bed. The maximum tilt angle without support is 25º. The vertical extrusion has failed when we tried to make designs with 2.5mm of thickness, broking in the top. Raft and support are easier to remove than replicator 2.
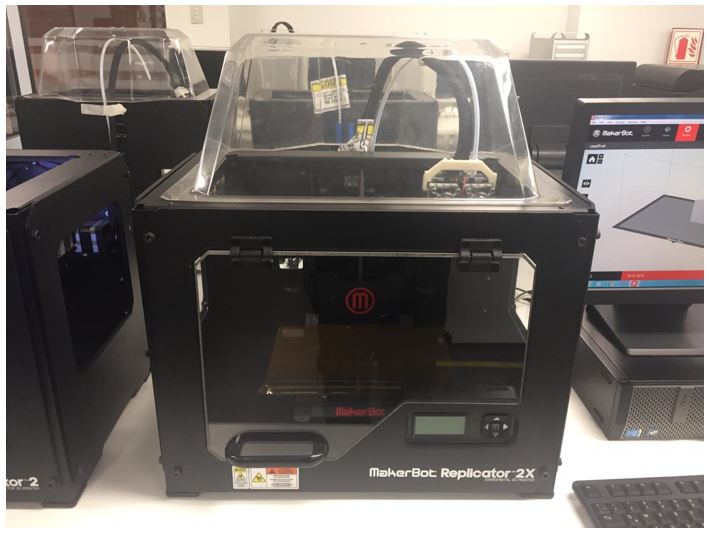
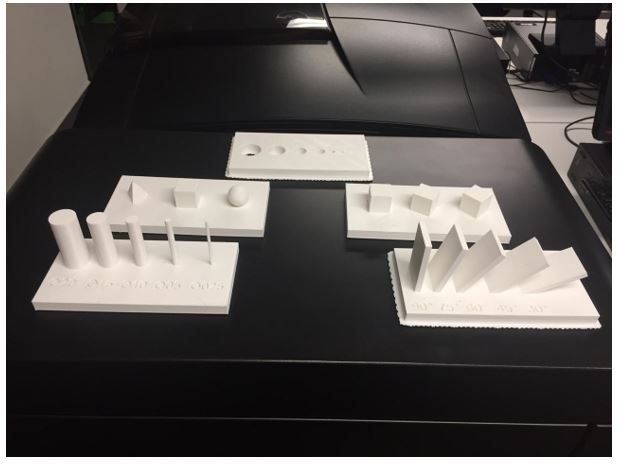
Here are some results
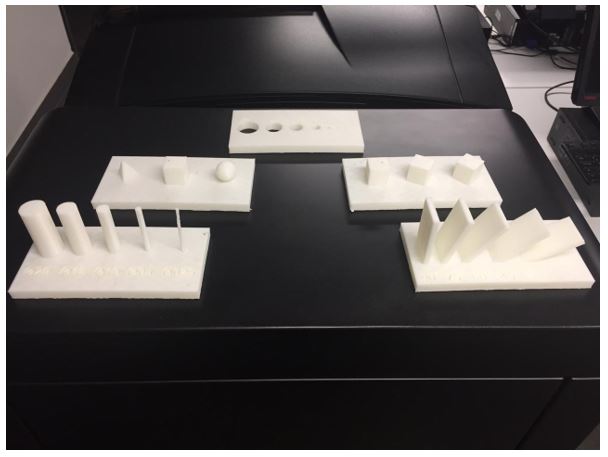
Makerbot Replicator+
Makerbot Replicator + prints 30% faster than his previous version and offers 25% more compilation volume. This model has a larger printing area and the calibration is easier than the others, just have to follow software’s instructions.
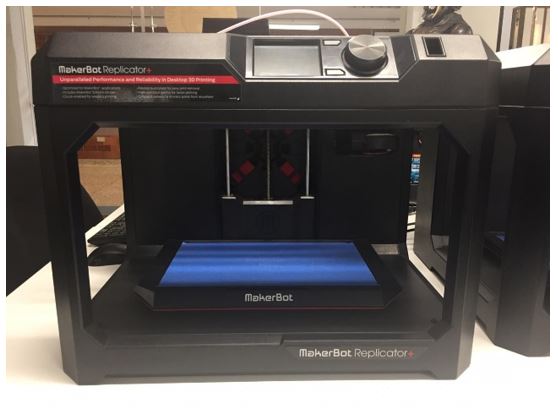
Below are some results
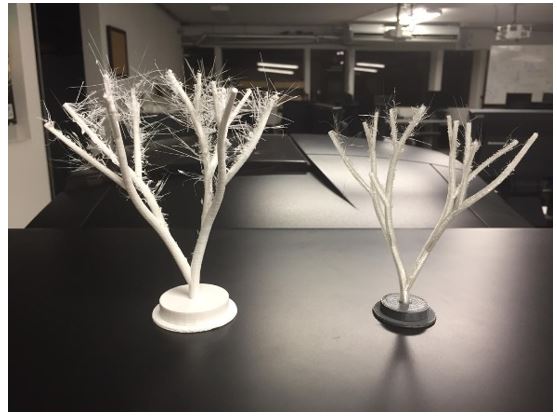

We test with some extruders like “tought” and “experimental”. Both with different materials of makerbot, both showed an increment of speed. Though has greater rigidity and works better in curvatures, Raft and support were hard to remove.

The experimental extruder allows to create flexible designs, the support has to be remove with precaution. Each material needs different parameters to work nice, in this case we use PLA filament for Tough extruder and Nylon filament for experimental extruder

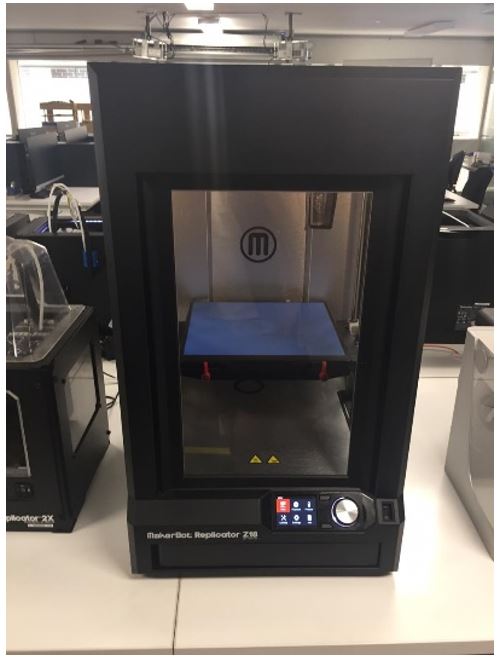
Makerbot Z18
Z18 printer creates large models and prototypes, thanks to the huge work dimension 30.0 L x 30.5W x45.7H CM. This printer works fine with system operations like Windows (7, 10) and Mac OS X (10.9+).

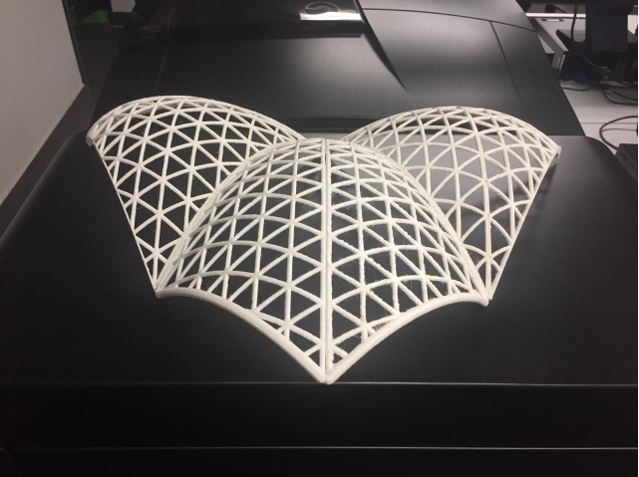
We made a triangulated coverage of 4 independent modules of 25x25cm and use another impression as support.

Markforged
Markforged can print nylon, carbon fiber, Kevlar, reinforced continuous fiber and metal.
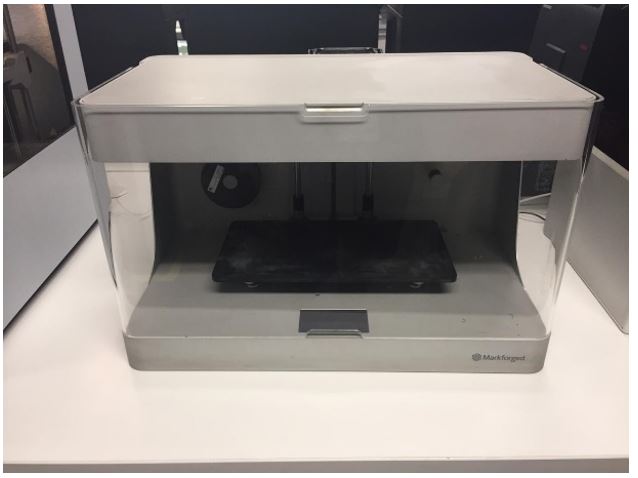

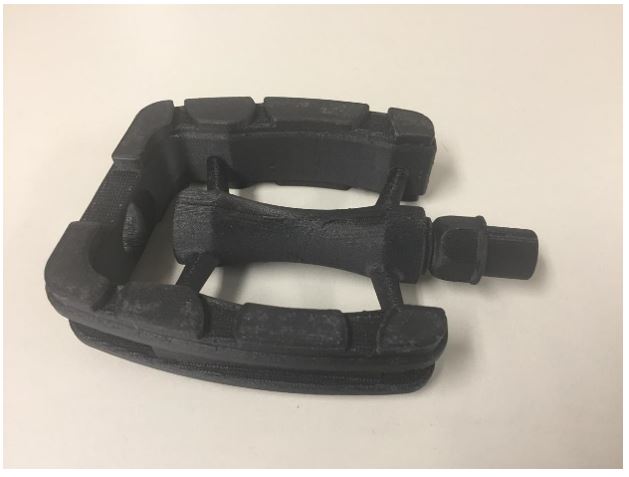
We have some resistant materials in our lab, so we decided to print a pedal using carbon fiber.

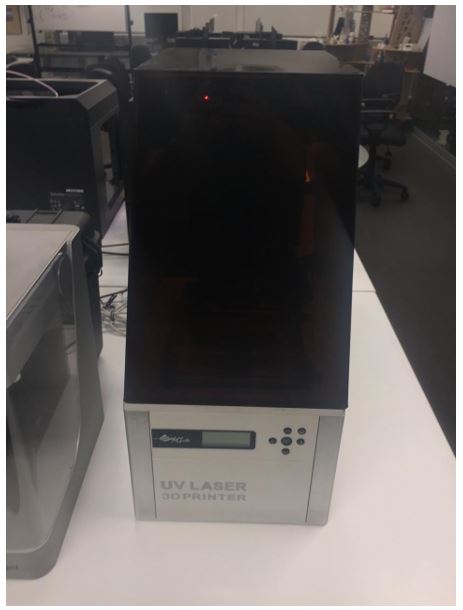
XYZ UV laser
Use resin as material allows to make models with high level of detail, this printer use a photopolymer in form of viscous fluid, like resin and a light source to solidify the resin.
We should consider the weight of the objet we want to make, because it will be printed from above.

If it doesn’t have acceptable support, the piece will break and will remain in the lower part of the work area.
Stratasys Object260 Connex3
PolyJet's signature precision plus soluble support allows you to be more versatile in your prototyping creation. It sharpens communication between your design and engineering teams, energizes collaboration between them and shortens your product development cycles.

Below are some results