Assignment:
1. Develop a plan for dissemination of your final project
Artifacts for the commons
digiTalog is an experiment that will transcend into a singular artifact. One that is unique because it is embedded with the mistakes the author made while making it - while transposing his ideas into the physical object. Those mistakes are its originality and its most authentic value.
None of the processes or knowledge involved in this project can be considered an invention of mine. On the opposite I have build upon existing knowledge and informations therefore do not pretend to own any exclusive rights for it . If the fact that this object exists has had an effect on anyone's life or experience all I wish is to be mentioned, atributed and cited as its author.
The licence that I have chosen responds to this criteria.
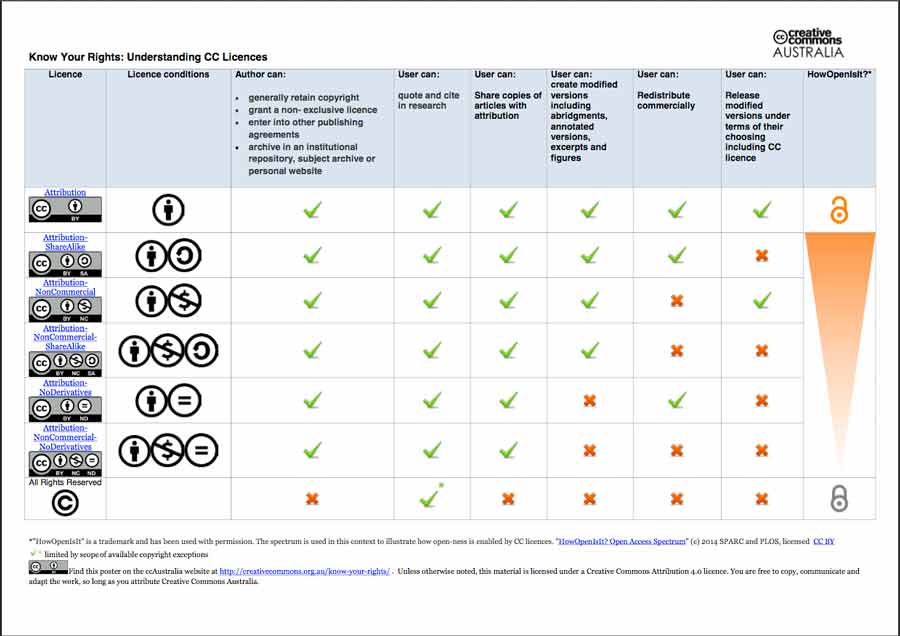
Creative commons Attribution 2.0 Generic (CC BY 2.0)
I have chosen the Creative commons Attribution 2.0 Generic (CC BY 2.0)
and registered at safecreative.org. The licence allows me to create an original work by building upon other peples work while limiting my legal responsability for other people to use it and comply with the licence terms. In other words:
to share — copy and redistribute the material in any medium or format
Adapt - remix, transform, and build upon the material for any purpose, even commercially.
While at the same time compromise me and/or any user of the licence to:
Attribute — must give appropriate credit, provide a link to the license, and indicate if changes were made. You may do so in any reasonable manner, but not in any way that suggests the licensor endorses the use.
And there is:
- No additional restrictions — may not apply legal terms or technological measures that legally restrict others from doing anything the license permits.
- No warranties are given- The license may not give all of the permissions necessary for some intended use. For example, other rights such as publicity, privacy, or moral rights may limit how you use the material.
Notes on patents, design register and licences.
Patents
A patent is a set of exclusive rights granted by a sovereign state or intergovernmental organization to an inventor or assignee for a limited period of time in exchange for detailed public disclosure of an invention. An invention is a solution to a specific technological problem and is a product or a process.
A patent is a very expensive operation and can only apply to inventions. Before one can patent it mnust prove authorship and that anyone has nort invented it before. And this requires a very secretiv creativ process which includes afgreement of confidenciality with all partners and colaborators involved in developping the project/invention, not to mention avoiding any public release of any information related to the project prior to filling for the patent.
Patents are also subject and limited to geographical territories which corresponds to Countries and continent. Patent costs are relative to each territories and are cumulative.
The delay to obtain a patent can be extensive and depends on the reserarch that needs to be executed in comfirming the existence or not of a similar (or identical) inventio in the suggested territory. Depending on the ourtcome one may be asked to make amandment, rectification or even support the provided informations with more pertinent proofs.
Patent process are fragile and precise legal operation which requires the service of a specialized professional to obtain, apply and defend the patents rights throughout the period of validity.
Utility model
A utility model is an intellectual property right to protect inventions. This right is available in a number of national statutes, as described below. It is very similar to the patent, but usually has a shorter term (often 6 to 15 years), shorter grant lag and less stringent patentability requirements.
A utility patent is a patent that covers the creation of a new or improved — and useful — product, process or machine. A utility patent, also known as a “patent for invention,” prohibits other individuals or companies from making, using or selling the invention without authorization.
Registered design (in Spain)
A design can be registered to protect the copy its external aspect which are the shape, materials, textures and colors used in the production of an object. Each alteration, changes or difference is subject to a new register.
While much cheaper and fast to obtain than a patents or utility model title, the register offers a limited legal copyrights and is ninded by national laws and treaties and limited by geographical territories.
Copyright/vs/copyleft
Making a piece of work private for one's benefit /vs/ sharing the work for the benefit of the society.
There is not one good licence. Only the right one for the right circumstances, type of work and pretention of the author.
While it seems that we should apply a licence to avoid others from copying our creation and make financial profit from it when you are small guy with fair ambitions, one of the main reason to apply a licence to this piece of work is to preserve the right to use the work freely. Because if you don't do it before you publish it someone else may do it for you and you may end up not even have the right to use the work that your-self have produced - even if there is no pretention to use it commercially.
Copyright is designed to help a creator redeem royalties from the use of its creation. Anyone is free to "copyright" a piece of work - but reinforcing a copyright is very expensive business that mostly benefits just a few.
Copyright had been for centuries and since the industrial revolution the only mean to legally protect original works from beeing stolen and copied without the authors agreement. But with time copyright got diverted into an indirect mean to monopolise and control knowledge in benefit of big Corporations who used it as a toll that restrict access to information, knowledge and cultural products.
At the end of the 1990's the Creative Commons licence emerged as an alternative to classical copyright by allowing to insert into licences the rights to copy and share the work - giving the authors a whole new set of choices when it came down to register one's creation. Thje Creative Commons are a direct response to a new movement of consciousness who tends to defend and preserve global access to knowledge and information by the general public. The commons is the cultural and natural resources accessible to all members of a society, including natural materials such as air, water, and a habitable earth.
As oppose to copyright which is limited to one exclusive licence, Creative Commons licences are very flexible and gives the authors liberty to choose from a wide range of licences that each established legal repsonsability between author and the user.
But just as any other copyright licence, Creative Commons licence must be registered, they are defenitive (cannot be changed), they are legally binding but are passive legal means - rights can be granted through legal monitorization.
How to register a work with a licence.
There start to be interesting Blockchain based project to register digital work and monitor its intelectual property atribution. See list here.
Another interesting solution is Safe Creative.org, a web site that allow to upload an original digital copy (PDF, jpg, etc) of a piece of work. The site generates a timestamp that autheticates the date of the upload. If case of legal pursuits this timestamp will act as legal proof of authorship.
The other and more bulky option is to register the work with your national institution but it is costly and do not offer any guarantee. If a big fish wants to sleal your work you won't be able to afford the layers to win the cese. To register your work allows you to legally place the licence logo on your work which may discourage many to steal it.
Income
I am not pretending to generate any direct income from the artifact created as final project. Neither through selling the original nor any reproduction of the product. My intention is merely to use it to acquire a series of skills that will help me develop a body of work and build a reputation amongst the community of artists, researchers, makers and profesionals from the Fablab ecosystem and beyond.
Dessimination
The work will be exhibited the window display of my art space in Barcelona during the 2nd half of June. During this period the public will be welcome to interact with the artifacts and we will recollect information about their experience in Curtidos , my art space blog.
Notes on licences of the Fab Academy web sites
I have applied a Creative Commons by-nc 4.0 licence for my Fab Aacdem,y web site. I have chosen this licence simply because there are design files and information that I used that were already regiustered with this licence. If anyone is interested in using any of the original files or information contained in my website they can do freely for non-commercial use while they attribute the work to the author of the wornk they are using. If some case me in some others people that created the original work I used, adapted or mixed. In case of wanting to use the work for commercial use they shall contact me and I will evaluate the possibility and, in the case, negotiate an agreement.
Conclusion
I did not go into the GNU and the most open licence but I am convinced that more open is the licence more benefits it gives. It leaves you with no obligation or responsability towards others so you can work from pure affinities and you have all the rights to benefit from what other make of your work. And the good thing about these licences is that they oblige to think about how one can make a living in a faire society, and it questions deeply granted assumptions.
